Types and reasons
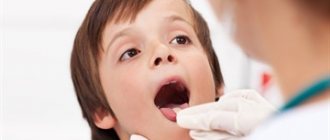
Throat diseases (photo below) can be caused by a variety of factors. However, they have one thing in common - their location. They are accompanied by pain. When feeling discomfort, people most often take cough drops with mint or menthol. This helps, but only at the very early stage of an infectious disease. There is a wide range of reasons that cause pain.
If a person does not receive proper treatment at an early stage of the disease, it becomes advanced. In this case, it becomes much more difficult to fight him. It is worth considering that a number of diseases cause serious complications. Treatment in this case may be lengthy and less effective. Chronic illnesses are especially difficult to deal with.
There are several classes of diseases that can develop in the throat area. These include:
- Infections. The provoking factor is viruses or bacteria.
- Fungus. This group of diseases is rare. However, they cannot be excluded.
- Benign neoplasms. They are caused by neoplastic processes that occur in the larynx or nasopharynx.
- Malignant neoplasms.
- Other pathologies.
Infectious diseases most often affect the throat. However, we should not exclude the possibility of other diseases. The causes of throat diseases are also quite varied. Most often, this condition is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. They constantly live in our body. However, they begin to multiply on mucous membranes under favorable conditions. This happens when immunity decreases.
The pathological process can be triggered by hypothermia, severe strain on the throat (screaming), stress, hormonal disorders, throat injuries, as well as increased sugar levels. Bad habits, especially smoking, negatively affect the condition of the entire body, including the throat.
Viruses
When studying throat diseases and symptoms (photos of an infectious disease can be viewed below), you should start with the most common cause of the development of the disease - infectious diseases. They are caused by bacteria and viruses. For treatment to be effective, the type of pathogen must be determined. Some drugs are used for viruses, and others for bacteria.
This group of diseases is common in both adults and children. Viral diseases include ARVI and influenza. Also less common infections in this group are chickenpox and measles. The inflammatory process that develops in the throat under the influence of pathogens spreads throughout the throat. At the same time, the patient feels soreness and pain.
One of the common diseases (when you have a sore throat, you shouldn’t write it off) is mononucleosis. Mononucleosis develops due to herpes type 4. This is an insidious disease. Its complications can be serious. With mononucleosis, the inflammatory process spreads over time to the spleen and liver. Lymph nodes enlarge.
Almost all viral diseases are characterized by the appearance of characteristic symptoms. A person feels a loss of strength, general weakness. Headaches may occur. The temperature rises, but only slightly. The disease is accompanied by a severe runny nose and cough. If the cause of the disease lies in the spread of the measles or chickenpox virus, a characteristic rash appears on the skin. In some cases, the temperature may rise significantly.
Almost all of these diseases enter the body through airborne droplets or household contact (through dishes). Therefore, during an epidemic, it is better not to go outside unless necessary, and to avoid public places. Anyone can become infected with such viruses if their immunity is weakened. The consequences of some diseases can be sad. Viruses constantly mutate, so symptoms may vary from person to person. Only laboratory tests will help determine the cause of the disease.
Bacteria and fungus
Throat diseases (photo below), which are caused by bacteria, are the most common. This category of ailments includes pharyngitis, laryngitis and sore throat. The causative agents of such diseases can be different. Most often these are staphylococci and streptococci. Atypical pathogens of such diseases are chlamydia, gonococci, tubercle bacilli, and mycoplasma. They act in this area less often, but such a phenomenon is still possible.
Less commonly, people suffer from infectious diseases caused by bacteria, such as diphtheria and scarlet fever. They are also accompanied by a sore throat. An even rarer disease is epiglottitis. Therefore, when considering options for the name of the throat disease that manifested itself in him, a person may not guess what exactly caused the disease. It is worth noting that small children under 4 years of age are more susceptible to epiglottitis. The disease is very dangerous. It can cause deterioration or complete absence of air passage through the respiratory tract. If certain symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Common symptoms that accompany bacterial infections are weakness, sore or sore throat, and swelling of soft tissues (tonsils, larynx). The temperature also rises quite significantly. Sometimes it reaches 40 ºС.
Yeast-like or mold fungus can cause various throat ailments. This class of diseases can also lead to the development of sore throat, pharyngitis and laryngitis. If the cause of the disease is mycosis, a characteristic white or curdled coating appears on the mucous membranes. The sore throat becomes very severe. However, the body temperature does not increase.
Mycoses are caused by decreased immunity. Especially often, such ailments occur during periods of vitamin deficiency, as well as after taking antibiotics or hormonal therapy. Also, such ailments cause disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
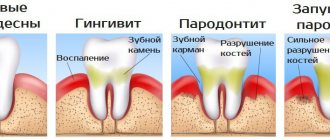
Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the throat: symptoms
Lymphatic tissue is part of the immune system. It acts as a “barrier” to the infectious pathogen. Based on which lymph nodes are inflamed, the primary lesion can be detected.
In acute tonsillitis, the submandibular lymph nodes are often affected. They enlarge and become painful to the touch. Proper treatment of tonsillitis leads to the disappearance of signs of lymphadenitis.
An adenovirus infection can be indicated by damage to the cervical, submandibular, and anterior auricular lymph nodes. The tonsils of the oropharynx are usually significantly enlarged.
Adenovirus infection is characterized by a combination of lymphadenitis and conjunctivitis against the background of moderate intoxication.
A significant increase in cervical nodes, as well as nodes in other areas accessible to palpation, requires the exclusion of infectious mononucleosis.
The disease is accompanied by severe sore throat and fever. Mononucleosis is characterized by an enlarged liver and spleen.
Changing the size of several groups of lymph nodes at once requires consulting a doctor. The same applies to situations with long-term persistence of lymphadenopathy.
Angina
Sore throat (photo) is a throat disease, the symptoms of which are familiar to almost everyone. Few people know its second (official) name – acute tonsillitis.
Sore throat is an inflammatory disease that develops in the pharynx, as well as on the tonsils. The reasons that cause such an illness can be very diverse. Sore throat occurs due to injury to the pharynx. This can, for example, occur during treatment procedures or diagnostics. The infection also enters the body through contaminated food.
There are several types of sore throat. However, their symptoms are very similar. The sore throat becomes very severe. It is especially felt when swallowing or breathing. It also becomes difficult to speak. Purulent plugs appear. They are localized in gaps and look like small yellow sacs. When pressed, their contents may leak out.
Purulent exudation also develops. A lot of pus is released from the lacunae. This is caused by an infection. The pharynx becomes swollen and hyperemic. Even with an independent examination of the pharynx, this is visible. The structure of the soft tissues becomes loose, and the body temperature rises greatly.
The tonsils are also inflamed. They are covered with a white coating. This condition is often accompanied by joint pain and migraine. In this case, you cannot do without antibiotics for a sore throat. They are prescribed in combination with drugs that support intestinal microflora and liver function.
Sore throat can cause serious complications. This especially affects the functioning of the heart, lungs and kidneys. Therefore, it must be treated promptly and correctly. Folk remedies are not enough here. The doctor will definitely prescribe analgesics, anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, antiseptics for local treatment of the throat, as well as antipyretics.
Inflammatory diseases
Most often, such pathologies are of infectious origin - bacterial, fungal, viral. The infectious factor comes from the external environment or from foci within the body itself. In this case, it could be carious teeth or chronic sinusitis. If the protective capacity of the mucous membrane is insufficient, an inflammatory process develops in any part of the throat. The following factors can reduce the protective properties:
- decreased local and general immunity;
- bad habits;
- drinking cold food and drinks;
- poor nutrition.
As a result of a combination of causative and predisposing factors, the following diseases develop:
- pharyngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- angina;
- laryngitis
The symptoms of these pathologies are quite similar. Treatment is also carried out according to general principles.
Symptoms
The clinical picture of diseases of the pharynx and larynx is presented in the comparative table:
| Disease and localization | Symptoms | What does it look like |
| Pharyngitis - damage to the pharynx | It manifests itself as a sore throat and discomfort when swallowing. On examination, the mucous membrane of the pharynx is red and slightly swollen | |
| Tonsillitis is an inflammatory process in the tonsils | A person is bothered by a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing. On examination, the tonsils are red and swollen | |
| Tonsillitis is an inflammatory process in the tonsils | A person is bothered by a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing. On examination, the tonsils are red and swollen | |
| Sore throat - acute damage to the tonsils, exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis | A person is bothered by a severe sore throat, the inability to talk and eat food, even liquid food in case of severe sore throat. Upon examination, the tonsils are swollen, red, white plaques are visible - spotty or widespread | |
| Laryngitis - inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa | A person complains of pain when swallowing, hoarseness of voice. During a routine examination, it is impossible to notice inflammation, since the vocal folds are affected. | |
| Laryngitis - inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa | A person complains of pain when swallowing, hoarseness of voice. During a routine examination, it is impossible to notice inflammation, since the vocal folds are affected. |
Laryngitis can also be non-infectious. This disease often occurs in people who are forced to talk a lot - teachers, actors.
There are also several specific forms of the disease that have characteristic symptoms presented in the following table:
| View | Causes | Symptoms | Photo |
| Candidal pharyngitis | This inflammation is common in HIV infection. Caused by candida fungi | Characterized by pain and burning in the throat. The mucous membrane of the pharynx is swollen, covered with a curdled white coating | |
| Diphtheria sore throat | The disease is caused by diphtheria bacillus | A person complains of severe sore throat, malaise, and high fever. The tonsils are swollen, covered with a dirty gray coating; when removed, the mucous membrane bleeds | |
| Diphtheria sore throat | The disease is caused by diphtheria bacillus | A person complains of severe sore throat, malaise, and high fever. The tonsils are swollen, covered with a dirty gray coating; when removed, the mucous membrane bleeds | |
| Herpangina | This disease is caused by the herpes virus | Characterized by a burning sensation in the throat. Small blisters appear on the mucous membrane, which quickly burst and form ulcers. |
General symptoms of pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis are mild. With angina, there is a rise in temperature, general malaise, and headache.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of an inflammatory process in the pharynx or larynx is not difficult to make.
The doctor determines the pathology based on the person’s complaints and characteristic symptoms during examination. To determine the pathogen, a smear is taken from the mucous membrane and a bacteriological examination is carried out.
Treatment
Treatment of infectious diseases is carried out using medicinal and non-medicinal methods. Depending on the type of pathogen, antibacterial or antiviral therapy is prescribed. For any pathology, local anti-inflammatory and painkillers are used. To increase the protective properties of the body, vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed.
Table. Medicines for inflammatory diseases of the throat
| Group of drugs | Examples | Therapeutic effect | Mode of application |
| Antibacterial | Ceftriaxone, Levofloxacin | Suppress microbial flora | Use as prescribed by the doctor - orally or intramuscularly, course 7-10 days |
| Anti-inflammatory and painkillers | Hexoral, Tantum Verde | Eliminate inflammation, relieve pain | Irrigate the mucous membrane of the pharynx 3-4 times a day until symptoms disappear |
| Rinses | Miramistin, Chlorhexidine | Have an antiseptic and cleansing effect | Used to rinse the throat 5-6 times a day |
Folk remedies are also used in treatment:
- chamomile or sage decoction for rinsing;
- carrot and beet juice to lubricate the mucous membrane;
- onion juice compress.
The use of folk remedies should be symptomatic only, after consultation with your doctor.
Pharyngitis
There are a wide variety of throat diseases and symptoms. Pharyngitis is a common disease in both children and adults. Inflammation affects the oropharynx. It occurs due to hypothermia, a sharp contrast in temperature, for example due to drinking cold water on a hot day, as well as taking deep breaths of air in the cold.
Long-term use of drops that constrict blood vessels can also lead to such consequences. Pharyngitis can be a consequence of chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract, such as sinusitis, etc. It can be triggered by throat injuries, thermal or chemical burns.
The symptoms of this disease can be easily confused with other diseases. The sore throat becomes intense. There is a sensation of tickling and tingling. Discomfort is concentrated in the tissue of the soft palate. It may intensify when swallowing or talking.
With pharyngitis, an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. This is explained by the development of pathogenic flora. The voice may change somewhat and become rougher. Sometimes it becomes very difficult to speak. The temperature is rising. The patient's condition is accompanied by headache and general weakness. The cough is usually dry, but a small amount of sputum may be produced.
Treatment for this type of throat disease is also quite specific. It is prescribed by a doctor. He prescribes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs as well as steroids (glucocorticoids). It is also necessary to use broad-spectrum antiseptics. Antibiotics are prescribed only after testing the flora for sensitivity to drugs. If timely, comprehensive treatment is not completed, various complications may appear, and the disease will become chronic.
Pharyngitis: classification
Pharyngitis is one of the most common diseases of the pharynx, manifested in inflammation of the mucous membranes of the pharynx and its lymphatic tissues. Patients often confuse the manifestations of a sore throat with pharyngitis and begin to treat a completely different ailment. However, you should know that with angina, the inflammatory process spreads to the tonsils, and pharyngitis affects the mucous membrane .
Despite the fact that the pathology has only two forms of development, there are quite a lot of varieties of this disease. In most cases, the disease develops along with other diseases, so the causes of its occurrence must be identified among them: injuries, colds, caries, sinusitis, rhinitis, etc.
Classification of pharyngitis
There are two forms of pharyngitis: acute and chronic . The acute type develops as an independent pathology, however, sometimes it can be accompanied by an infectious disease (chickenpox, measles, etc.) or ARVI. This type of pharyngitis occurs after eating spicy or hot food, hypothermia, and also as a result of the fact that a person has inhaled dust or vapors. The classification of acute pharyngitis is determined by the type of pathogen.
There are the following types of illness:
- allergic;
- traumatic;
- viral;
- bacterial;
- vesicular;
- provoked by exposure to irritating factors;
- fungal.
The course of chronic pharyngitis is less acute; there are no signs such as a feeling of weakness, fatigue, or fever. Mucus formed in the larynx interferes with normal coughing, resulting in a person constantly coughing.
If chronic pharyngitis is not treated for a long time, the disease develops into one of three forms: catarrhal, atrophic or hypertrophic.
Catarrhal form is the most common type of pharyngitis. Its appearance is caused by the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and viruses into the pharynx.
The main cause of pharyngitis, both acute and chronic, is infection. According to statistics, in 70% of cases the main pathogens are viruses. A pathogenic virus, as a rule, is associated not only with the respiratory system. In fact, the source of infection may be in the stomach, intestines and other organs. For example, in adults the infection is often localized in the genitourinary system. Therefore, among the causative agents of pharyngitis there are gonorrheal, chlamydial and candidal types of harmful microorganisms. The initially emerging viral factor subsequently provokes the development of bacterial damage.
The hypertrophic form is caused by a secondary growth of the mucous membrane on old areas, as a result of which the doctor identifies granules or ridges on the back wall of the pharynx.
In the atrophic form, areas of the mucous membrane atrophy, and the whole process is accompanied by a feeling of soreness and dryness in the throat. With timely treatment, the symptoms of the disease intensify.
Causes of the disease
Typically, pharyngitis develops as a result of exposure to the following factors:
- development of inflammatory and cold processes;
- excessive consumption of ice cream;
- hypothermia;
- viral or fungal infection;
- hormonal imbalances;
- decreased immunity;
- endocrine disorders.
Chronic pharyngitis, as a rule, affects people employed in hazardous work, as well as heavy smokers.
In addition, the development of the disease can be triggered by the following factors:
- caries;
- regular consumption of spicy, salty and spicy foods;
- chronic stomach diseases, causing belching, heartburn;
- absence of tonsils or their inflammation;
- inflammatory processes of a purulent nature in the sinuses;
- prolonged use of vasoconstrictor drugs.
All of the above reasons for the development of pharyngitis are typical mainly for the adult population. Children from 0 to 5 years old have very weak immune defenses, so the main culprits in the development of the disease in them are viruses and bacterial infections. In addition, a child may develop pharyngitis against the background of an advanced form of tonsillitis, rhinitis, laryngitis and other chronic diseases of the nasopharynx .
Laryngitis
When considering the symptoms of throat diseases, you should pay attention to another common ailment - laryngitis. It is characterized by inflammatory processes in the larynx. This is a common disease that a large number of people have experienced.
There may be several main causes of laryngitis. One of them is a laryngeal injury. The larynx can be damaged when diagnosing the throat area. Laryngoscopy is especially dangerous in this case.
Also, inhalation of various toxic, pathogenic substances (dust, fumes, pollen, etc.) can lead to similar consequences. The disease can be caused by allergens. Allergic laryngitis develops rapidly and leads to inflammation and swelling of the laryngeal mucosa.
Also, mechanical damage and burns of the larynx can lead to this phenomenon. Strong screaming, hypothermia, decreased immunity also contribute to the development of the disease.
This throat disease has quite specific symptoms - pain in the area not only of the throat, but also of the neck. It is almost impossible to determine where the location of unpleasant sensations is concentrated. Sometimes it’s even difficult to formulate your complaints because of their vagueness. A cough also appears. It is intense and bark-like. This is a characteristic sign of laryngitis. No sputum is produced.
During treatment, drugs are used that suppress cough. They act on the reflexes of the central nervous system. Peripheral antitussive drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or glucocorticoid drugs are also prescribed.
When treating laryngitis, mucolytic agents are not required. In this case, they are not only useless, but can also be quite dangerous.
Inflammation of the back of the throat
We are talking about pharyngitis. In 9 out of 10 cases, acute mucosal irritation is caused by a viral infection. In the absence of bacterial complications, there is no point in treating such pathology with antibiotics.
A patient who has an inflamed back wall of the pharynx may experience pain when eating, soreness, scratching, and the desire to cough. Viral pharyngitis is not characterized by the formation of films on the mucous membrane.
Intense pain and hyperthermia up to 40°C are a concern with an abscess of the retropharyngeal space. On the inflamed wall of the pharynx, an area of protrusion is found (a place where pus accumulates).
The disease can only be eliminated surgically, by opening the abscess followed by antibiotic therapy.
Red spots in the throat
This symptom requires the exclusion of a number of highly contagious infectious diseases. The main ones:
- Measles;
- Rubella;
- Scarlet fever;
- Meningitis;
- Mononucleosis;
- Herpetic lesion.
To understand the genesis of the rash on the mucous membrane, you should pay attention to the main symptoms. For example, rubella and scarlet fever are characterized by damage to the skin.
what does a sore throat look like photo
With meningitis, signs of pathology of the central nervous system are observed: severe headache, photophobia.
It's not always about infection. Small red spots on the mucous membrane can also occur due to allergies.
What to do? The appearance of any rash requires contacting a specialist. Complete differential diagnosis is possible only in a medical facility.
ARVI
One of the most common viral diseases is ARVI. This disease also causes a sore throat. The disease belongs to the viral category. A feeling of dryness and soreness appears in the throat. Pain may occur. The disease is also accompanied by hoarseness and runny nose. The temperature is high, but rarely rises above 38 ºС.
You can become infected with this disease in different ways. But the main route is airborne (inhalation of the aerosol generated by coughing or sneezing). Therefore, it is important to avoid crowded places during the epidemic. The second common route of transmission of ARVI is oral. For example, with kissing, a normal handshake, or touching a contaminated surface (plates, common hygiene items, etc.) with subsequent spread into the mouth. Much less often, the infection is transmitted from one person to another through household items, linen, toys, etc.
When an infection enters the body by airborne droplets, it can travel from the nasopharynx or further from the throat. The viruses that cause the disease travel through the blood and lymph fluid.
In older people and children, throat diseases are often more severe and more difficult to tolerate. The treatment process is also especially difficult for adults who have reduced immune function. Antibiotics are contraindicated in this case. Not only do they have no effect on the virus, but they will also significantly worsen the already weakened protective functions of the body.
In this case, the doctor prescribes antiviral drugs. Immunomodulators and vitamin complexes are also extremely necessary. The throat should be gargled with anti-inflammatory drugs. You also need to drink more warm tea. In this case, herbal decoctions of linden, rose hips, currants and raspberries are best suited. You can also eat honey. It needs to be gradually dissolved in small portions. However, honey does not need to be added to hot drinks.
Causes of laryngeal disease
There are many factors that can trigger the development of laryngeal diseases.
The nasopharynx and organs of the respiratory system are the most vulnerable parts of the human body. This is largely due to their specific functions, as well as the fact that the throat area consists of a large amount of soft, muscle and cartilage tissue.
Despite the active protection of the entire respiratory tract by the tonsils, the risk of disease is always high in any case. The anatomy of the nasopharynx makes the larynx one of the organs most susceptible to illness. Diseases occurring in the laryngeal region in most cases represent an acute inflammatory process.
This phenomenon does not just happen; the main reasons for the onset of inflammation and other ailments of the larynx can be:
- activation of pathogenic viruses, fungi, infections and other microorganisms that adversely affect the tissues of the nasopharynx
- physical damage, expressed by injury to the throat area
- thyroid disease
- excessive load on the muscular-ligamentous apparatus of the throat caused by the specifics of the work (speaker, teacher, singer, etc.)
- adverse effects of external factors (low/high air humidity, temperature, etc.)
- allergic reaction to dust, smoke, etc.
- bad habits
- poor nutrition
Usually, all unfavorable factors act in a complex manner during a weakening of the body’s protective functions caused by a decrease in immunity or vitamin deficiency. It is extremely important to treat the potential occurrence of the disease with due seriousness, and try in every possible way to reduce the risk of the onset of the disease.
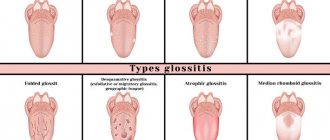
Types of diseases
There are several types of larynx diseases, each of which has its own symptoms
Most diseases of the larynx are infectious. The process of development of any disease is very simple: it all begins with the settling of pathogenic microorganisms on the tonsils, when the body is no longer able to protect itself from their adverse effects, an inflammatory process begins, occurring first in the nearby areas of the nasopharynx, but later making its way into the laryngeal region.
There are a lot of diseases of the larynx and throat, but a number of main ones can be identified:
- laryngitis
- all types of tonsillitis (tonsillitis)
- pharyngitis
In addition, the laryngeal area may become “sick” due to swelling not caused by inflammation, the development of adenoiditis or tumors. All types of illnesses are quite dangerous and can cause complications, so it is simply impossible to delay their treatment. Only a specialist can accurately determine a particular disease, but you can make the initial diagnosis yourself if you know the specifics of the diseases. Let's look at each ailment in more detail.
Tonsillitis or tonsillitis is characterized by inflammation of the lymphadenoid tissue of the tonsils, which develops in nearby areas of the nasopharynx, including the larynx. There are three types of disease:
- Primary, caused by fungi and coccus viruses, is transmitted through household or airborne routes. The provocateurs of the disease are a general weakening of the immune system or hypothermia.
- Secondary is the result of the development of some other diseases, sometimes chronic. As a rule, it occurs in a more severe form than the previous type.
- Specific tonsillitis is a fairly rare disease that occurs due to the impact of rare types of infections on the human body.
Pharyngitis is also an infectious disease, but manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx. The disease does not often occur separately from other diseases of the human respiratory tract, and therefore is often not independent. Pharyngitis is treated quite simply, but in the absence of therapy or its incorrectness it can become chronic.
More information about pharyngitis can be found in the video:
It hurts to swallow on the left side, what is the reason and how to treat
Laryngitis is characterized by damage to the mucous membrane of the vocal cords, affecting other parts of the nasopharynx. The disease manifests itself as an inflammatory process and occurs as an addition to other ENT diseases. This disease can be distinguished from others due to its characteristic feature - changes in the timbre of the voice or its complete loss.
Adenoiditis is a disease that is characteristic in the vast majority of cases in children. The disease is a chronic inflammation of the tonsils and peri-almond area, sometimes life-threatening for the child. Adenoiditis occurs due to poor treatment of various ENT diseases.
Laryngeal edema can be either infectious or non-infectious. May appear due to:
- long-term progression of any ENT disease
- pathologies in the larynx (tumor, disorders in the lymph nodes, thyroid gland, etc.)
- adverse effects of allergens
Swelling of the larynx requires immediate treatment, as it can cause suffocation.
Symptoms
Sore throat, sore throat, loss of voice, high temperature and weakness in the body are signs of diseases of the larynx
The signs of the development of all diseases of the larynx are very similar, although some types have their own specific symptoms. The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the variety of possible ailments.
Not every specialist will always be able to determine what exactly is tormenting his patient. In this regard, in addition to examining the respiratory tract and talking with a doctor, additional tests and diagnostic measures are often prescribed. In any case, there are quite a few common symptoms of laryngeal diseases:
- spontaneous rise in temperature
- sore throat, sore throat, redness
- general poor health, increased drowsiness and aches throughout the body
- worsening cough
- excessive nasal discharge
- systematic occurrence of headaches and dizziness
- hoarseness, loss of voice
- difficulty breathing
- enlargement and redness of the tonsils
Even knowing the full etiological picture of each disease of the larynx, it is extremely problematic to determine just by symptoms what is tormenting you. Therefore, it is not advisable to postpone going to the clinic to see professionals, because the development of the disease and the appearance of complications can occur quickly.
Adenoids
Symptoms and treatment for throat problems can vary greatly. The pain may be significant or absent altogether. The second option is often characteristic of tumors. Often they do not show themselves at all. Their presence is felt only after the tumor becomes large enough.
Benign tumors do not tend to metastasize. However, due to their growth, breathing may be impaired and some discomfort may appear. Sometimes they grow so large that it becomes life-threatening and suffocation can occur.
One type of neoplasm that does not even belong to the category of benign or malignant tumors is adenoiditis. It appears as a result of the inflammatory process of the adenoids. In this case, the palatine tonsil grows.
Adenoiditis is most often diagnosed in children. Adults are practically immune to this disease. Only in some exceptional cases can the disease appear after 15 years of age.
The disease manifests itself with a number of symptoms. Nasal breathing is impaired. This process becomes difficult. Enlarged adenoids cover the vomer and choanae. This causes discomfort. The child has to breathe through his mouth. This also leads to frequent inflammatory throat diseases.
With adenoiditis, body temperature may rise slightly. In this case, symptoms of general intoxication of the body may be observed. In most cases, this throat disease is treated with surgery. In this case, the adenoids are removed. This is a radical solution to the problem.
Tumors
When considering the symptoms of throat diseases, it should be noted that benign and malignant neoplasms may not manifest themselves for a long time. These include many ailments. When the tumor develops to a significant size, there is difficulty breathing, a sore throat, the ears may become blocked, and it becomes difficult to swallow. Sometimes bloody mucus comes out of the nose.
Unexplained toothache may develop over time. The voice may change and become rougher. Infections in the ears and nasopharynx may occur. Hearing and breathing noticeably deteriorate, and headaches appear. Self-medication and folk remedies will not help in this case. Treatment must be correct and fast. Otherwise, the tumor can lead to disability and death.
Benign neoplasms include polyps, cysts, papillomas, lipomas, angiomas, and fibromas. Malignant tumors include sarcoma, squamous cell carcinoma and chondrosarcoma. The earlier the disease is detected, the more effective the treatment will be, and the consequences will be less dangerous.
Prevention
Throat diseases are entirely preventable. You need to lead a healthy lifestyle, quit smoking, diversify your menu, adding fruits, vegetables and protein. You need to add foods rich in vitamin C to your diet.
You also need to humidify the air in the room if it is very dry. You need to follow the rules of hygiene, wash your hands before eating. Regular visits to the doctor will also help avoid the occurrence of ailments that are asymptomatic. You need to dress according to the weather.
Having examined the most common throat diseases, we can conclude that without proper diagnosis it is impossible to accurately establish the cause of the disease. Treatment in this case may be ineffective. Therefore, if pain and characteristic symptoms appear in the throat, you should consult a doctor.