Benign tumors appear both on internal organs and on external mucous membranes. A cyst often forms on the palate or in the mouth. In this case, surgical intervention will definitely be required, since the consequences of an unattended neoplasm will be quite serious.
Benign tumors appear both on internal organs and on external mucous membranes.
What is an oral cyst?
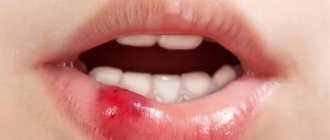
A cyst on the palate is a small lump in the shape of a white ball, round or oval. The internal contents are liquid and sometimes include patches of pus or blood. Inflammation develops for various reasons. It is promoted by diseases of the oral cavity, disruption of the passage of secretions through the ducts, and infections.
The seal is in the shape of a white ball, round or oval.
Both adults and children face pathology. An increase in size of the cyst leads to deformation of bone tissue, loss of teeth, and impaired diction. Due to the constant inflammatory process, immunity decreases and chronic diseases worsen.
Causes
Several main factors contribute to the appearance of oral cysts:
- poor oral hygiene, lack of regular teeth brushing;
- inflammation of the gums, including periodontitis. Voids form in the tissues, which are filled with pus and can degenerate into benign formations;
- caries or pulpitis, accompanied by the penetration of pus into the mouth;
Lack of dental and oral care.
- improper dental treatment, which leads to infection;
- complications after sinusitis, sinusitis and other sinus diseases, as well as weakened immunity;
- incorrect perforation of the canals, which causes an inflammatory process;
- poor-quality processing of instruments used in dental treatment, lack of sterilization;
- hereditary factor;
- mechanical injuries of the jaw;
- teething (eg wisdom teeth).
In some cases, a lump on the roof of the mouth is formed due to concomitant diseases of the ENT organs.
Classification
Cysts that occur in the oral cavity have their own classification. Due to their occurrence and location, these formations are divided into:
- Paradental, appearing in the area of the wisdom tooth.
- Cysts of the eye teeth that begin to form as a result of sinusitis.
- Follicular - most often formed in the area of teeth affected by caries.
- Eruption cysts are mainly detected in a newborn, a child or a schoolchild, when milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones (as a rule, they disappear on their own over time and do not require serious treatment).
- Radicular, which affects the root systems of the teeth.
- Congenital - found in a child’s mouth in the first 1 to 2 months of life and occurs due to abnormal development of tooth buds.
- Residual, which occurs after a surgical dental procedure at the site of an extracted tooth.
A cyst that occurs in the palate or on the cheek is most often retentional in nature. It is formed due to a violation of the outflow of secretions from the salivary glands. Various oral injuries lead to this.
Symptoms
At the initial stage, an oral cyst does not manifest itself in any way. The patient is not bothered by pain or deterioration in health. A person pays attention to the tumor when it increases in size. At this point, the growth can reach a centimeter in diameter and will feel like a dense ball that slightly changes position when the tongue touches it.
In the later stages of the cyst, the following symptoms appear:
There is bad breath, pain in the teeth and gums.
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth. It indicates the penetration of infection and the onset of purulent inflammation;
- you can feel the seal with your tongue, the boundaries of which are clearly defined;
- there is no pain syndrome. If pain appears, this indicates that the tumor will soon open spontaneously. In this case, liquid contents will flow out of the thickening, which contains pus and blood;
- general health worsens;
- there is pain in the teeth, discomfort when chewing food;
- with the development of the inflammatory process, body temperature increases, headaches, and nausea occur;
- The gums swell and become sore, which makes chewing food difficult.
How to cure a cyst in the mouth and why it might appear?
Cysts are benign neoplasms that have a dense capsule covered with mucous membranes and penetrated by small capillaries. They usually contain liquid exudate inside, which may contain impurities of pus or blood. Such tumors can form on the surface of any mucous membrane, including in the oral cavity. A cyst in the mouth causes a lot of inconvenience to a person, since its appearance negatively affects the quality of speech and chewing functions, which ultimately leads to serious digestive problems. Therefore, it is necessary to treat it immediately after detection.
Cysts can appear in both adults and children. And more often the cause is inflammatory processes, infections or blockage of the excretory ducts of the salivary glands. Such formations can occur in various parts of the oral cavity - on the cheek, on the palate, under the tongue, on the gums and even in the teeth.
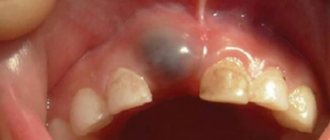
Externally, such cysts look like dense sacs containing liquid (usually purulent). They begin their development unnoticed by a person, that is, without causing him any discomfort. And only when the neoplasm reaches a large size (2 cm in diameter or more) do the first symptoms appear, but they will be discussed a little later.
At the initial stages of the development of this pathology, inflammatory processes occur in the soft tissues and a granuloma is formed. It is impossible to detect it with the naked eye. The only way to detect a cyst at this stage of development is to take an x-ray.
After the granuloma is fully formed, it marks its boundaries and then the cyst itself begins to appear. Over time, it grows, squeezing nearby tissues, causing depletion and gradually replacing them with itself. In this case, the bone tissue suffers. It is also subject to degenerative processes and sometimes cannot withstand the loads placed on it, which leads to a physiological fracture.
The presence of a cystic formation on the oral mucosa also negatively affects the entire body as a whole. The pathological fluid contained in it includes pathogenic bacteria, which gradually spread throughout the body, causing a decrease in immunity and exacerbation of chronic diseases.
Sometimes people experience discharge of the purulent contents of the cyst, which indicates its spontaneous opening and the formation of a fistula. As a rule, all these processes lead to a general deterioration in health, which is manifested by painful sensations and increased temperature.
Cysts that occur in the oral cavity have their own classification. Due to their occurrence and location, these formations are divided into:
- Paradental, appearing in the area of the wisdom tooth.
- Cysts of the eye teeth that begin to form as a result of sinusitis.
- Follicular - most often formed in the area of teeth affected by caries.
- Eruption cysts are mainly detected in a newborn, a child or a schoolchild, when milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones (as a rule, they disappear on their own over time and do not require serious treatment).
- Radicular, which affects the root systems of the teeth.
- Congenital - found in a child’s mouth in the first 1 to 2 months of life and occurs due to abnormal development of tooth buds.
- Residual, which occurs after a surgical dental procedure at the site of an extracted tooth.
A cyst that occurs in the palate or on the cheek is most often retentional in nature. It is formed due to a violation of the outflow of secretions from the salivary glands. Various oral injuries lead to this.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of a cyst:
- Improper oral care.
- Dental diseases of an inflammatory and infectious nature (caries, stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontal disease, etc.).
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Injuries to the oral cavity.
- Inflammatory processes resulting from the eruption of wisdom teeth.
- Congenital dental defects.
- Inflammatory and purulent processes in the nasopharynx (sinusitis, sinusitis, etc.).
- Weakened immunity, which is unable to independently fight pathogenic microorganisms.
The most common cause of cysts in the oral cavity is the negligence of dentists who perform their work poorly. Infection of the mucous membranes and further formation of cystic formation on them can provoke:
- Excessive tissue trauma during the procedure.
- Poor cleaning of dental canals and their filling.
- Using poorly sterilized instruments.
Read also: Cheek hurts inside the mouth in the corner
But it should be noted that for these reasons, a cyst of the tooth or gum appears more often. A teratoma on the palate, on the cheek or on the inside of the lip most often occurs as a result of blockage of the minor salivary glands.
You can determine the presence of this formation in the oral cavity yourself, knowing what a cyst looks like (this was discussed earlier). However, the appearance of external signs is typical already in the later stages of the disease.
At the very beginning of its formation, the cyst does not show any signs. It does not cause pain or discomfort. The only thing a person can notice during this period is the redness of a small area of the mucous membranes and their swelling, as well as the presence of bad breath, which indicates the beginning of purulent processes in the oral cavity.
However, after some time, a small bump appears on the surface of the mucous membranes. It is dense to the touch and has clear boundaries. There is no pain when pressed. They appear only when the cyst becomes inflamed and is close to spontaneous breakthrough.
At the same time, the person begins to experience discomfort. The cyst greatly interferes with chewing food and speaking, especially when it is located under the tongue. If you press hard on the tumor, exudate will begin to come out of it. Depending on the nature of the cyst, it can be purulent, transparent, jelly-like, etc. After this, the formation decreases in size, allowing the person to relax a little, but after some time it grows back.
The cyst must be treated immediately and preferably immediately after its discovery. In itself, it does not pose any threat to human life, but if removed untimely, it can cause severe harm to health.
For example, cysts of the gums or teeth lead to suppuration of the bone structures, which can lead to tooth loss, and neoplasms located in the cheeks, under the tongue or covering the palate can cause malocclusion and speech defects.
In addition, the presence of infection in the oral cavity can provoke an exacerbation of chronic diseases and the development of new pathologies that require immediate treatment. Often, the spontaneous opening of such formations and the release of purulent contents out leads to blood poisoning and the development of sepsis or an abscess.
Considering that cystic formations in the oral cavity can lead to serious health problems, it is simply necessary to treat them as early as possible. Unfortunately, it is impossible to get rid of the tumor with the help of creams and ointments. In this case, they will not give any result. The only way to solve this problem is surgery.
There is no need to be afraid, as it is performed very quickly and using local anesthesia, which makes it completely painless for the patient. How exactly the surgical intervention will take place is decided only by the doctor. For example, if a tumor appears on the palate, in the lower lip or cheek, then it is excised along with the affected tissues, without affecting healthy mucous membranes. If a cyst appears in the submandibular salivary gland or in the sublingual region, not only the formation itself is removed, but also the gland, which helps prevent relapse of the disease.
After surgery, the wound is sutured with special threads and a bandage is applied over it. The sutures are removed only after the wound has completely healed, which is observed after 2 to 3 weeks.
Important! Such surgical interventions should be carried out only by qualified specialists, since any incorrect action during the operation can lead to damage to the facial nerves, which ultimately results in paralysis of the facial muscles for the patient.
Surgical intervention to remove the cyst does not require hospitalization of the patient. The patient can go home as soon as it ends. But he will need to carry out further treatment on his own. As a rule, it includes treating the wound with regenerating and anti-inflammatory ointments and gels, as well as rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions after each meal.
In the postoperative period, many experts advise resorting to alternative medicine. To speed up the wound healing process and prevent the development of complications, you can use decoctions and infusions prepared from medicinal herbs. In this case, the most effective are:
Decoctions and infusions of these herbs should be used at least 5 times a day. At the same time, you need to rinse your mouth with them after each meal and at night.
If you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, the process of restoring the oral mucosa after surgery will go very quickly and without complications. Well, if in the postoperative period there is severe bleeding or suppuration of the wound, then you should consult a doctor again, since these symptoms may indicate the development of complications that need to be eliminated immediately.
Diagnostics
In the early stages, the internal cyst remains undetected. If the compaction is small in size, its detection occurs by chance. During a routine examination or during dental treatment, an x-ray is taken and the development of pathology is detected.
To determine the exact boundaries of the pathology, x-rays are prescribed.
In cases where the patient feels unwell, the thickening is already palpable, diagnosing a cyst in the mouth is not difficult. At this point, the symptoms clearly indicate the development of pathology, however, to clarify the diagnosis and determine the exact boundaries of the tumor, x-rays are prescribed.
Treatment
To prevent a retention cyst from leading to the development of complications, it must be diagnosed before it reaches a large size. If you suspect a growth, consult a doctor. At an earlier stage, the surgical intervention will be practically painless, and the recovery period will not last long.
If you suspect a growth, consult a doctor.
In the presence of large tumors, there is a risk of complications. In most cases, regardless of the size of the benign tumor, surgery is prescribed to remove it. Drug treatment is also available, but most often it turns out to be ineffective and can only slow down the growth of the cyst.
Drug treatment
Even if pathology is detected at an early stage, drugs are ineffective. Only surgery can completely get rid of a cyst in the mouth. However, drug treatment is necessary during the recovery period after surgery. In this case, the following remedies are prescribed:
Antiseptic solutions are used to treat the oral cavity.
- antibiotics to prevent the development of the inflammatory process. They must be used if the cyst has festered or spontaneously opened;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- antiseptic solutions used to treat the oral cavity during the rehabilitation period;
- restoratives, immunomodulators, vitamins, etc.
Surgical removal
To completely rid the patient of a benign formation, the cyst on the cheek is surgically removed. The operation is simple and is performed under local anesthesia. In half an hour, the doctor removes the capsule along with its contents, cleans the cavity of pus or blood clots, then sutures it. It resolves within a week.
If a tumor appears in the mouth due to improper functioning of the salivary gland, it is also removed to prevent relapses. In other cases, they are limited to getting rid of the capsule.
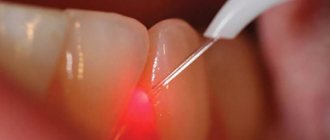
The laser virtually eliminates bleeding, injury to mucous membranes or glands.
The operation is performed using a classic surgical method, in which the doctor cuts out the cyst with a scalpel or using a laser. This is a more modern method of intervention, in which the risk of complications is minimized. The laser virtually eliminates bleeding, injury to mucous membranes or glands. The advantage of this method is that it is painless for the patient. Tissue restoration is faster than after classical surgery.
Appearance and symptoms of a cyst in the mouth
A cyst is one of the diseases of the oral mucosa. It is a round, mobile formation ranging in size from 0.5 mm to 3 cm and is filled with liquid with purulent contents. The inside of the growth is lined with stratified epithelium, and the outer shell consists of connective tissue.
The inside of the cyst is lined with multilayered epithelium.
A formation appears due to blockage of the minor salivary glands. Most often it is localized on the inside of the lower lips, less often on the tongue or under it (in this case they speak of ranula), on the cheeks, gums or on the roof of the mouth.
As a result of blockage of the salivary gland duct, the outflow of secretions becomes difficult. It gradually accumulates and penetrates the walls of the capillaries. This leads to the formation of a cyst. Education is growing slowly. Sometimes for several years. This disease of oral mucosa is complicated by the absence or mildness of symptoms.
Important! It is necessary to distinguish between salivary gland cysts and dental cysts that develop at the apex of the roots. The latter are a consequence of complications of dental diseases: pulpitis, periodontitis, poorly treated canals.
The main signs of a cyst include:
- discomfort while eating and talking;
- heaviness in the gum area;
- sensation of a foreign object in the mouth;
- as growth progresses, discomfort develops into painful sensations that intensify with chewing;
- difficulty moving the jaw;
- increased fatigue;
- low-grade body temperature;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Sometimes salivary gland cysts are congenital.
Often, a cyst of the mucous membrane opens on its own during eating, talking, or hygiene procedures. The liquid filling it drains away and the formation decreases. But since the full functioning of the salivary glands is not restored, after a while the growth is again filled with secretion and increases in size.
Possible consequences and complications
If there is no treatment, the cyst in the mouth continues to progress and increase in size. In this regard, the following complications arise:
The bite is disrupted and problems with diction begin.
- the patient is constantly faced with diseases of the gums and teeth, as an acute inflammatory process develops;
- complete loss of teeth is possible, since bone tissue is destroyed;
- the bite is disrupted, problems with diction begin;
- the patient has difficulty chewing and swallowing food;
- if the growth spontaneously ruptures, pus gets inside, causing an inflammatory process to develop, including in the internal organs. Chronic diseases are getting worse;
- in some cases, angioma develops into a malignant tumor. Up to 2% of the total number of victims experience cancer.
Unpleasant consequences can occur if the cyst is removed incorrectly and the surgeon acts incorrectly. However, complications also appear in cases where the doctor did everything correctly. Some patients have a fever (most often slightly), general weakness, and swelling of the mucous membranes in the mouth.
There are also more serious complications after surgery:
- the facial nerve is damaged, which provokes temporary paralysis of the muscles responsible for facial expressions;
- the capsule with its contents was not completely removed, as a result of which the cyst re-formed;
- divergence of sutures at the border between the soft and hard palate.
Prevention
To minimize the risk of developing a cyst in the mouth, follow these recommendations:
Brush your teeth twice a day.
- eat right. Limit the consumption of spicy, fatty foods, confectionery products;
- give up bad habits, alcohol and smoking;
- Maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth twice a day, rinse your mouth with special solutions;
- If dental pathologies are identified, eliminate them in a timely manner. This applies to problems with teeth and gums;
- Visit your dentist every few months and monitor for any unpleasant symptoms.
A tumor on the palate forms for various reasons. Risk factors include inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, poor hygiene, and general weakening of the immune system. There is only one way to permanently eliminate the seal - surgical removal. Medications are ineffective and can only be used in complex treatment and during the recovery period after surgery.
Preventing the recurrence of cysts in the mouth
If you consult a dentist in a timely manner, there is a high probability that the removed cyst will no longer bother you. However, it is worth remembering the preventive measures that should be taken:
- hygiene is paramount (it is important to regularly change toothbrushes and use only the highest quality ones from the range available in stores);
- absence of situations where there is a risk of mechanical damage to teeth;
- treatment only from qualified dentists with a good reputation;
- quitting smoking and drinking alcohol, eating healthy;
- strengthening the immune system (by creating protective barriers, a person protects his body from infections and viruses).