What causes the symptom of a loose throat in children and how to avoid harmful consequences
Pharyngitis and sore throat are the most common diseases that cause a red and sore throat in a child.
The causative agents of illnesses vary, but if symptoms are identified in time and treatment is started, then unpleasant consequences can be avoided. The throat becomes painful and loose with colds.
In this case, systemic and symptomatic treatment is necessary. The younger the child, the more carefully the drug is selected.
Provoking factors
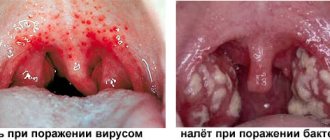
The nasopharynx is the first to encounter infections from the outside. This is why the throat gets sick more often than other organs. Loose tonsils may indicate a viral infection in the body. It is ARVI that most often causes throat diseases in children. Less commonly, the disease is bacterial or fungal in nature. Additional symptoms help determine the true cause of the disorder.
The situation can be aggravated by:
- weakened immunity and frequent colds;
- hypothermia or overheating;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- chronic diseases of the ENT organs;
- thermal or mechanical damage to the mucosa.
Pain and sore throat are the first symptoms of scarlet fever. Enlargement and soreness of the tonsils may indicate the penetration of a coccal infection. In the presence of a chronic focus of inflammation, enlargement and hyperemia of the throat mucosa often occur, which means that the process has reached a critical point.
Clinical picture
Loosening of the mucous membrane is not the only symptom in the presence of infectious processes in the body. If the cause lies in pharyngitis, then the clinical picture includes:
- persistent swelling of the throat in a child;
- pain radiating to the ears;
- coughing, tickling, hoarseness;
- headache;
- increase in body temperature.
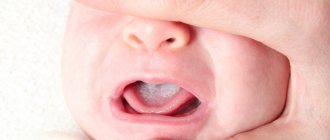
If a child has tonsillitis, then the body temperature can exceed 38.5 ᵒC, and a fever develops, the baby becomes delirious, and becomes covered in sticky sweat. Congestion in a child's throat is a typical manifestation of a sore throat. At the same time, the submandibular lymph nodes enlarge, the tonsils are bright red and covered with plaque.
The symptoms of tonsillitis vary depending on the form of the disease. Ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis is extremely difficult and requires shock therapy. Lacunar tonsillitis is easier to treat, but in the absence of timely medical intervention it can become chronic.
Among throat diseases, allergic diseases deserve special attention. They are becoming more common and are not always accurately diagnosed. Allergies are characterized by swelling that turns into suffocation. Watery eyes and a runny nose may bother you, but your body temperature is normal. Some children experience an allergic cough, nasal sound, and changes in voice timbre.
An allergy in the throat can occur as an independent disease, but in some cases it accompanies infectious diseases. Allergy to medications for acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections is one of the causes of throat irritation.
If the throat loosens due to inflamed adenoids, then the symptoms expand due to problems with nasal breathing, nasal sound, and hearing impairment. A child with adenoids constantly breathes through his mouth, which increases the risk of hypothermia and secondary infection.
Therapeutic measures
Medicines for sore throat for children are selected individually. If the child’s condition is stable and does not cause concern, light therapy or preventive methods are used.
Chronic foci of inflammation are the most difficult to treat. Recurrent ENT diseases require medical intervention and the use of medications.
With a mild form of sore throat or pharyngitis without fever, it is possible to cope with the disease by rinsing and warming procedures.
Conservative therapy
Gargling is indispensable for inflammation of the mucous membrane. The optimal antiseptic for the throat for children is furatsilin. This is a budget product that has pronounced antimicrobial activity. If you gargle with furatsilin solution for 2-3 days, not only looseness and redness will disappear, but also pain when swallowing, soreness and hoarseness.
If you are worried about severe pain, then sprays with an anesthetic effect will help. They can only be used from 2 years of age. The list of effective drugs for children includes:
- "Stopangin" - has antiseptic properties, is active against bacterial, viral and fungal infections;
- "Tantum Verde Forte" - used in childhood only with the consent of a doctor. The drug has an analgesic and antiseptic effect;
- "Ingalipt" is a combined agent with antimicrobial activity. Removes inflammation and redness.
What to give a child for a sore throat if the baby cannot tolerate sprays and does not know how to gargle? Throat syrups are recommended for young children. They help with ARVI and sore throat.
Syrups often contain plant components that have a high level of allergenicity.
Therefore, before carrying out therapy, it is necessary to ensure that there are no allergic reactions to the components of the syrup.
An otolaryngologist will tell you how to treat a red, sore throat in a child over 3 years old. At this age, you can already use lozenges. They have anesthetic properties, relieve symptoms and eliminate swelling. Septolete lozenges have proven themselves well. They contain benzalkonium chloride, which anesthetizes and exhibits antiseptic properties.
Source: https://ZdorovyeDetei.ru/uxo-gorlo-nos/gorlo/ryxloe-gorlo-u-rebenka.html
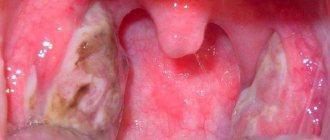
Complications of scarlet fever
During the illness, purulent complications may occur - retropharyngeal abscess, cervical lymphadenitis. After recovery - rheumatic complications: acute rheumatic fever with or without carditis, post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Scarlet fever is contagious. Infection occurs from patients when coughing, sneezing, talking, as well as through dishes, toys, and underwear. In Soviet times, those who had recovered from scarlet fever were allowed to be sent to a children's institution 22 days after the onset of the disease. Currently - 2-3 days after a course of antibiotics.
To determine the diagnosis, read Fever and rash.
Take care of yourself, Your Diagnosticer !
Tags: sore throat, scarlet fever, rash
Loose throat in a child: causes, methods of treatment and prevention
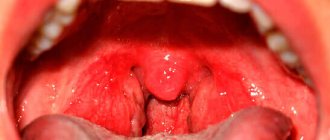
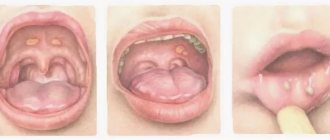
Sometimes, when examining a child’s throat, you can find that the tonsils and pharynx have an uneven mucous membrane with a bumpy surface.
Such changes are characterized by enlarged tonsils with a large number of depressions.
The tubercles themselves are pink-yellow or pink in color. This phenomenon is called a child's sore throat. This is not a medical term, but a “folk” one.
Main reasons
Often, with a loose throat, there are no signs of inflammation, such as high fever, pain, plaque on the tonsils and drowsiness. In this case, there is no particular cause for concern. But if the baby’s tonsils are loose, you should find out what exactly provoked this condition.
Often in the first years of life in children, the mucous membrane of the throat reacts to the environment and is a reaction of the immune system.
It is worth noting that every person's pharynx contains lymphatic tissue, and its concentration forms the follicles that dot the back wall.
When various kinds of microbes enter through the nasopharynx, the process of their rapid reproduction begins, which is the cause of the appearance of a loose throat.
During the inflammatory process, the body produces lymphocytes, which are immune cells. In the process of their production, redness of the tonsils is observed, they increase in size, and the mucous membrane becomes uneven. In appearance, loose tonsils resemble a sponge.
Due to the fact that the child’s body constantly encounters and gets acquainted with new microorganisms that surround us, this symptom often appears in children. In medicine, this condition is considered normal in the vast majority of cases and does not require treatment. In addition, the tonsils can be enlarged after an infectious disease.
Signs
A loose throat is visually determined by parents or a doctor when examining a child. However, signs of the disease itself can manifest themselves in different ways.
- Foul smell. Due to the fact that the tonsils have an uneven surface, food can be retained in them. As a result, bacteria begin to spread, which leads to an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Painful sensations. The development of infection leads to a sore throat, which is especially acute when swallowing.
- Headache. Due to swelling of the pharyngeal mucosa, breathing becomes difficult, which is accompanied by general weakness and headaches.
- Temperature increase.
- Lethargy. The active development of infection in the body leads to its weakening. The child cannot breathe fully during sleep, so he quickly gets tired and looks lethargic.
In what cases should you seek help?
A red, loose throat in children does not require therapy if there are no accompanying symptoms of the disease. In certain cases, this condition may signal the initial stage of infection.
Loose tonsils may be associated with the following diseases:
- colds, ARVI;
- tonsillitis;
- sore throat;
- pharyngitis.
Treatment with traditional remedies is required only in certain cases, so at the first signs of illness you should contact a medical facility. Therapy at home is acceptable for colds or ARVI. They are accompanied by symptoms such as runny nose, pain when swallowing, and a slight increase in temperature.
It is imperative to consult a doctor if the loose surface of the child’s throat is combined with the following manifestations:
- severe redness of the mucous membrane;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- soreness in the throat;
- the presence of plaque and plugs of pus on the tonsils;
- an increase in the size of the lymph nodes under the neck;
- high temperature;
- the presence of a film on the walls of the throat.
In such cases, a series of studies are prescribed to determine the type of infection and the optimal treatment tactics are selected.
Antibiotic therapy is often required.
Parents should be wary if the baby gets tired quickly, is lethargic, or feels unwell for a long period, and there are no apparent reasons for this.
This behavior requires immediate consultation with a doctor, since such symptoms may be the cause of chronic tonsillitis.
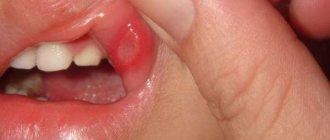
When diagnosing this disease, a soft palate, swelling of the tonsils, accumulation of pus and yellowish-white plaque are observed.
A sore throat can also mean a chronic sore throat. This disease is quite specific and often causes problems that are caused by disruption of other organs. Chronic sore throat must be treated. Pharyngoscopy is used as a diagnosis.
Treatment methods
With such a phenomenon as loose tonsils in a child, treatment requires an individual approach. Tactics are determined after a complete diagnosis with all necessary tests. A throat swab must be taken to determine the nature of the disease and the resistance of bacteria to certain medications.
Mild and moderate degrees of pathology do not require hospitalization and can be easily managed at home. To do this, it is enough to take care of a moderate regime and drink plenty of fluids. The doctor may also recommend rinsing, which removes plugs of pus from the tonsils and reduces their swelling. As a rule, such a procedure is carried out as a medical precaution.
You can rinse with herbal solutions at home. The most effective option is calendula-based products. To prepare it you will need one spoon of tincture and a glass of warm boiled water. To relieve swelling of the tonsils, it is recommended to gradually reduce the temperature of the rinsing water. Thus, the effect of hardening the child’s throat is achieved.
If the throat is not red and the baby does not complain of pain when swallowing, then you should not use antiseptic drugs. In such a situation, it is better to rinse the affected area with a salt solution.
This product relieves inflammation well and removes plaque. To prepare it, you need to dilute one large spoon of sea salt in a glass of water. If the disease worsens, rinse every 30 minutes.
For loose tonsils, tonsil cleaning is also prescribed. It can be done in the hospital using ultrasound or at home using a small spoon. Before the procedure, it is necessary to treat the throat with an antiseptic to prevent the spread of infection.
More severe forms of the disease require the use of ultraviolet light, laser or ultrasound. The last method is the most effective. In most cases, a positive result of treatment is obtained by removing pus from the lacunae of the tonsils. All procedures of this kind are aimed at complete recovery and prevention of surgical intervention.
Sometimes, with frequent and severe inflammation of the tonsils, their removal is required. But this is a last resort. The fact is that the tonsils perform a protective function. This way they prevent pathogenic microbes from entering our body. Their removal contributes to the development of various infectious diseases. That is why it is important to determine the cause of a loose throat and eliminate it in time with conservative treatment.
Preventive measures
If a child has a predisposition to these types of diseases, it is important to prevent their development. The main goal is to increase immunity and reduce the possibility of developing a throat infection. To do this, you need to maintain oral hygiene, because pathogenic microorganisms often multiply on the teeth and tongue.
It is also necessary to periodically visit an otolaryngologist, who will carry out preventive washing of the palatal lacunae. If for some reason it is not possible to see a doctor, then you can rinse the tonsils yourself with a solution of furatsilin. It has a detrimental effect on streptococcal and staphylococcal infections, which can cause the development of an inflammatory process in the tissues of the nasopharynx.
It is acceptable to alternate medical solutions with herbal decoctions. To prepare them, it is recommended to use chamomile, sage or calendula. It is necessary to rinse for four weeks, then take a break for the same amount of time.
It is important to ensure an optimal indoor microclimate so that the child’s body can quickly cope with pathogens. Dry mucous membrane is a favorable environment for the development of bacteria in it, so it is necessary:
- drink often;
- provide daily walks;
- organize wet cleaning in the child’s room more often and ventilate regularly;
- Monitor the humidity level in the room where the baby is.
All children, regardless of whether they have a loose throat or not, are recommended to undergo hardening in various ways in order to strengthen local immunity.
Source: https://DeteyLechenie.ru/lor-zabolevaniya/ryhloe-gorlo-u-rebenka.html
When is a doctor needed?
You should seek help from a doctor if your child has the following symptoms:
- difficulty breathing, wheezing;
- severe pain in the throat;
- significantly increased body temperature;
- the presence of mucus or pus on the surface of the tonsils;
- fever accompanied by pain in the limbs.
A symptom such as a red throat in a child can be associated with many reasons. Many of them do not pose a threat to the baby’s health, but some can cause serious consequences. In order to prevent the development of complications, it is recommended to promptly seek help from a doctor, who will conduct diagnostic procedures and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Loose throat in a child: symptoms, treatment, prevention
A sore throat is medically associated with chronic tonsillitis. The use of the term is appropriate when, upon examination, a large amount of lymphoid tissue is found in the child’s throat. The tonsils, which are located on the back wall of the pharynx, are covered with lymphoid follicles, as a result of which they become loose.
A sore throat develops if a child often has a sore throat. When this diagnosis is made, the doctor prescribes an appropriate course of treatment.
Features of the disease
The tonsils are a kind of barrier. It is part of the immune system that fights pathogens.
Tonsils consist of lymphoid tissue, which performs the function of hematopoiesis. Lymphocytes are directly related to immunity. The infection enters the body through airborne droplets. When this happens, white blood cells become activated. They begin to fight bacteria, destroy them, as a result of which the tonsils become inflamed.
If a child often suffers from tonsillitis, the structure of the tonsils begins to deteriorate and a loose throat develops. The situation is aggravated by the presence of carious teeth in the oral cavity, poor personal hygiene, chronic inflammation of the nose and pharynx, and frequent colds.
The disease is accompanied by pain when swallowing, frequent fatigue, and headaches. A child may often have a temperature of up to 37.5 degrees. When the process worsens, disturbances in the functioning of the excretory, cardiovascular, and nervous systems are observed.
With chronic tonsillitis, the danger to the child’s health is that the tonsils are no longer a barrier that protects the body. They themselves represent the source of infection.
The child’s immune system weakens; complications can develop at any time, which affect other systems of the body.
Symptoms
A loose throat in children with chronic tonsillitis is often found. Usually the cause is incorrect or untimely treatment of a child with sore throat. The acute form of the disease is easier to treat with antibiotics.
If the disease has become chronic and the child has a loose throat, then treatment often ends with surgery.
With chronic tonsillitis, the clinical picture is typical.
For specialists, the symptoms do not cause diagnostic difficulties:
- sore throat;
- body temperature can rise sharply from subfebrile to hyperthermic;
- headache;
- general weakness;
- an increase in the size of the tonsillar lymph nodes.
For diagnostic purposes, pharyngoscopy may be prescribed. With tonsillitis, the picture is typical:
- soft sky;
- hyperthermia and swelling of the tonsils;
- the presence of pus in the lacunae of the tonsils;
- the presence of a white-yellow coating.
Treatment is prescribed only after a microbiological examination of a smear. This allows you to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to antibiotics that multiply on the tonsils.
Treatment
The traditional method of therapy is used more often. For inflammation of the tonsils, treatment is provided with antibacterial drugs. Usually the doctor prescribes aminopenicillins with clavulanic acid.
Beta-hemolytic streptococcus belongs to a group of pathogenic microorganisms that cause acute inflammation of the tonsils. In this case, synthetic penicillins have their role.
Treatment is also carried out with cephalosporin antibiotics. These drugs are cefadroxil, cefaclor, axetil.
Antiseptics are used along with antibiotics. They cause analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. Treatment is carried out using stopangin, hexoral, tantum verde.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Be sure to read: how to strengthen a child’s throat
Physiotherapeutic procedures that are appropriate in the treatment of tonsillitis include exposure to ultraviolet light.
Ultrasound and laser exposure to inflamed areas of the tonsils are also considered effective procedures. The most common methods are vacuuming and exposure to low-frequency ultrasound. The effectiveness of treatment in some cases sometimes reaches 90%.
The essence of vacuuming is that with the help of this physiotherapeutic procedure, pus is sucked out of the tonsillar lymph nodes. After the procedure, rinse with an antiseptic solution with an antibiotic.
After a course of this physiotherapeutic technique, low-frequency phonophoresis is sometimes prescribed. The entire course of treatment lasts 7-15 weeks.
Physiotherapeutic techniques are considered an alternative to surgery. To perform a tonsillotomy, the doctor's indications must be significant. Removal of the tonsils is carried out when other body systems begin to suffer from the disease, but no other method of therapy is effective.
Rinsing
A saline solution is used for rinsing.
You can prepare it at home. To do this, take one teaspoon of table salt and dilute it in a glass of water. Then add a small amount of soda or iodine. Salt has a bactericidal effect. Iodine or soda helps remove pus from the tonsils.
- : how to teach a child to gargle
Calendula has an astringent and antibacterial effect. To prepare the solution, you need to dilute one tablespoon of calendula in a glass of water.
Rinsing can be done up to 10 times a day, depending on the severity of the disease.
Prevention
If a child is susceptible to diseases of the ENT organs, prevention should be an integral part of his lifestyle. The goal of prevention is to prevent immunity from decreasing to a level where the risk of developing infection is high.
- Be sure to read: how to harden a child’s throat
It is necessary to maintain personal oral hygiene. Pathogenic bacteria can multiply on teeth and tongue. You can carry out preventive rinses with antiseptic solutions.
Sometimes experts recommend regular visits to an otolaryngologist for the purpose of preventive rinsing of palatal lacunae. If it is not possible to visit a doctor, you can rinse at home. To do this, use a solution of furatsilin. It has a detrimental effect on streptococci and staphylococci - microorganisms that cause the development of inflammation of the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils.
Medication solutions can be alternated with herbal decoctions. For rinsing, you can use a decoction of chamomile, sage, and calendula. It is recommended to carry out rinsing procedures for a month. Then you can take a break for the same period of time.
▼We RECOMMEND YOU TO STUDY▼
Source: https://LechenieDetej.ru/uxo-gorlo-nos/ryxloe-gorlo.html
Treatment of scarlet fever
Patients with scarlet fever are treated at home. Hospitalization is only necessary in severe cases. A course of antibiotics is 5-7 days. Penicillin or ampicillin intramuscularly, amoxicillin orally 50 mg/kg per day (Flemoxin Solutab). For allergies to penicillins, azithromycin, Rulide, Duracef, and sulfonamides are used. It is important not to miss taking your medication and complete the full course of treatment!
On days 5-7, scarlet fever ends in recovery even without an antibiotic. The antibiotic protects against purulent and rheumatic complications.
A child's sore throat: what does it mean and how to treat this pathology?
Such a symptom in children as “loose throat” is familiar to many parents. The previously pink and smooth mucous membrane looks hyperemic and lumpy.
What diseases are these changes associated with and how to eliminate them? Can a “loose throat” in a child be absolutely normal? Let's consider these questions, and also find out the structural features of the tonsils in children and their reaction to various pathogenic bacteria.
What does the term “loose throat” mean?
A loose and congested throat in a child: what does this mean? Before defining this term, it is necessary to consider the anatomy of the mucous membrane of the throat and tonsils. Under normal conditions, the throat is lined with pale pink mucous.
It is smooth in appearance and has no deep folds or rashes. There is no colored coating on its surface. In addition to glandular cells, the mucous membrane contains lymphoid cells, which have a protective function.
These cells are the first to respond to pathogens entering the body through the respiratory tract.
The set of changes in the throat during acute respiratory viral infection and other respiratory diseases is popularly called “loose throat.” There is no such term in medicine, but doctors still use it. This makes it easier to convey the clinical picture of the disease to parents. The concept of “loose throat” in children includes the following local changes in the throat (pictured below):
- redness of the arches of the soft palate;
- tubercles on the back of the pharynx;
- enlargement of the tonsils (appearance of lymphoid growths);
- formation of ulcers.
A baby's sore throat occurs against the background of immune defense disorders, which are provoked by the following internal and external agents:
- dust;
- industrial hazards;
- hypothermia of the body;
- increased content of toxic elements in the air;
- allergy;
- taking certain medications.
What diseases does it occur with?
Red and swollen tonsils, the formation of mucus and films on them, pain when swallowing are typical signs of an acute inflammatory reaction of the respiratory tract. If it occurs no more than 1-2 times a year, it does not cause irreversible processes in the tissues of the pharynx. The course of the pathology is complicated by concomitant diseases: tuberculosis, oncology, heart and gastrointestinal problems.
For ARVI
Infection with viruses or bacteria occurs during communication with a sick person. The disease appears a couple of days after infection. Chronic inflammation in the tonsils can cause the development of neuritis and sepsis. The following signs are characteristic of ARVI:
- coughing attacks;
- thick sputum;
- joint pain;
- loss of appetite;
- accumulation of plaque on the tonsils.
Sore throat with pharyngitis
Pharyngitis means inflammation of the pharyngeal mucosa. The guys complain about a lump and sore throat; The feeling of dry mouth causes discomfort. There are several forms of pharyngitis:
- Catarrhal. Simultaneously with hyperemia and proliferation of the mucous membrane of the tonsils, a lot of mucus is produced.
- Hypertrophic. Lymphoid tissue is constantly growing. Its structure becomes even looser.
- Atrophic. The mucous membrane gradually becomes thinner. Its distinctive features are dryness and the formation of crusts.
Loose throat due to tonsillitis
The inflammatory process is localized in the pharyngeal tonsils. The tonsils become red and covered with plaque. If a child gets sick more than 3 times a year, this means that the disease becomes chronic. During pharyngoscopy, the ENT doctor notes the loose structure of the tonsils. Changes in lymphoid tissues occur against the background of constant entry of streptococci into the respiratory tract.
Signs of tonsillitis depend on the characteristics of its course:
- Remission of the disease is characterized by low-grade fever, loss of strength and drowsiness.
- Relapse of the disease is accompanied by nasal congestion. It appears against a background of hypothermia and severe stress.
- In severe cases, pain in the joints and behind the sternum occurs, and kidney function is impaired. Rheumatism and sepsis develop.
Loose throat as a physiological feature
Sometimes a loose throat is normal. This is indicated by the absence of complaints of sore throat and other signs of illness. The reason why a loose throat in a baby will be normal is considered to be a restructuring of the immune system. A growing organism is regularly in contact with new exogenous factors:
- viruses and bacteria;
- food products that can cause allergies;
- aggressive components of air and water.
The tonsils remain red during the period of “acquaintance” with these factors or for some time after recovery. The famous doctor Komarovsky assures that in this case, parents should not worry, because the child’s red tonsils are a local immune response to changes in the environment.