Author of the article
Dmitry Savelyev
Practicing dermatovenerologist, graduated from the Russian National Research Medical University named after N.I. Pirogov.
Articles written
60
Neoplasms on the skin and mucous membranes are not a rare occurrence. Many of them go unnoticed for a long time because they are located in hard-to-reach places for examination. The primary cause of their appearance is infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). The first signs of the disease may appear several months after infection.
Types of oral papillomas
The oral cavity and tongue can be affected by the following types of papillomas:
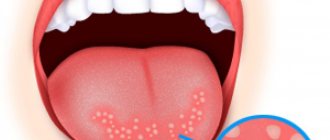
- Flat. They are formed in the form of compacted papules, round in shape with clear boundaries. Often, they are brightly colored and form on the sides or back of the tongue.
- Thread-like. They have a small width, but can protrude up to 5 mm above the surface. Rarely appear alone.
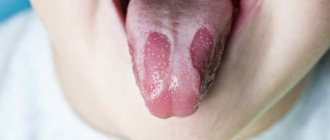
- Pointed. Mainly formed under the tongue. They look like papillae with a sharp ending. They often succumb to injury, which causes them to grow and increase in size. Most of them have the appearance of a cockscomb.
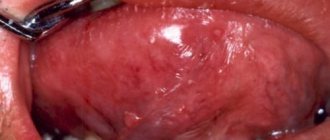
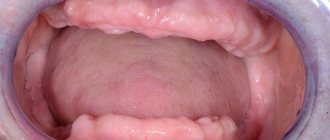
External manifestations
External (pictured) neoplasms look different depending on the specific form. The table presents general manifestations, regardless of the specific origin of the pathology (viral, traumatic, neoplastic) due to the extreme similarity between them.
| View | Manifestations |
| Pointed | · Protrude significantly above the surface of the skin; · often multiple; · have a bumpy surface; · are on a thin stalk, hanging over the surface of the tongue; · the color does not differ from the surrounding tissues (rarely it can be lighter or darker depending on the concentration of blood vessels); · localized, as a rule, along the edge or at the tip of the tongue (they have the greatest risk of injury); · soft-elastic and painless on palpation. |
| Flat | · Have a wide base and protrude slightly above the skin (a type of wart); · diameter up to 2 cm; · more often multiple, although single ones are also found; · whitish with a smooth surface (less often they will have an intense color); · sharply demarcated from surrounding tissues; · spherical or oval shape. On palpation, soft-elastic, painless. |
There are also divisions into non-keratinizing (pale pink color and soft consistency) and keratinizing papillomas (white color and denser consistency). Often there is a weak rim of inflammation around the formation.
Both types of formations grow slowly, however, there are a number of alarming symptoms indicating possible degeneration:
- discomfort when eating food;
- bleeding (directly into the formation itself with a change in its color or into the oral cavity);
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- ulceration;
- rapid growth and color change;
- the disappearance of clear boundaries and the tendency to merge;
- strengthening of the keratinization process and, as a result, compaction of the formation.
If the presented symptoms occur, a thorough diagnosis should be carried out with a number of oncological diseases, which externally in the initial stages appear almost the same as typical papillomas.
Photo
[Show slideshow]
Reasons for appearance
There are several dozen provoking factors for the appearance of growths on the tongue. The impetus for their spread is the presence of human papillomavirus in the body.
It is impossible to determine the carrier of the virus the first time. The infection process is not noticeable; the spread of the virus throughout the body can last for months. In addition, it can be in a “sleeping” state for a long time.
Reasons that cause the virus to become active:
- Constant depression, stressful conditions.
- Unprotected sexual intercourse with a carrier of the virus.
- Microtraumas or scratches of the tongue.
- Violation of hygiene rules, eating low-quality, poorly washed and unprocessed foods.
- Unbalanced diet, weakened immune system.
The last three factors can cause papillomas to appear in children. Therefore, in order to prevent complications, you should not neglect preventive recommendations.
Prevention of papillomas on the tongue
Photo 3. Healthy food filled with vitamins is the main guarantee of good immunity that can resist the papilloma virus.
Source: Flickr (Stephen Yamada) Preventive measures are mainly related to increasing immune defense. A healthy lifestyle , good nutrition, giving up bad habits , periodic medical examinations - these measures will help prevent infection with the papilloma virus. Strong immunity blocks the development of the virus.
If you notice growths or warts on your tongue or other organs, you should immediately visit a dermatologist.
Diagnosis of the disease
You can detect most papillomas on your own, since they cause significant discomfort. When contacting a doctor for advice, a visual examination of the tongue and oral cavity will be performed. Its etiology will definitely be determined.
Diagnosing growths in the mouth in children is much faster, since they can grow over the entire surface of the tongue, sometimes including the tonsils.
In adults, it is necessary to conduct more frequent examinations, since the risk of the growth degenerating into a malignant formation is much higher.
Treatment
Papillomas on the tongue often bring discomfort to the patient, which prompts him to seek treatment and removal methods. Modern treatment of papillomas occurs in a complex:
- Taking antiviral drugs.
- Removal of papillomas.
- Taking a complex of immunomodulators.
Drug treatment
Before giving preference to this method, you need to consult a specialist.
- If surgical removal of the growth is not planned, a course of therapy with vitamin A can be used.
- The use of interferons, which will reduce the number of viral particles in the growth.
- Alpha interferons will also be a good and effective treatment alternative. But their use is possible only if the growths do not provoke an exacerbation.
- The use of immunostimulants as a way to increase the body's defenses. This will put the virus into a dormant state.
Unfortunately, modern medicine cannot offer a single remedy that would completely destroy the human papillomavirus.
Folk remedies
The use of traditional methods to eliminate papillomas has conflicting opinions. They can be used as an adjuvant therapy and applied carefully and carefully. In addition, many traditional medicine methods are prohibited from being used to treat the oral cavity.
The most effective traditional medicine recipes:
- Juice from potato tubers, which should be used to treat papillomas, will help to quickly overcome growths.
- Potato tincture with vodka. It is best to use it if there is pain.
Conditions for the formation of growths
Papillomas form for various reasons. The primary factor that triggers this mechanism is the human papillomavirus. Infection with the virus occurs through sexual contact, this is the most common cause.
A child develops a viral infection due to a genetic predisposition. If the mother had HPV, it could be passed on to the child. And also due to poor hygiene, many objects that a child puts in his mouth can become infected.
Papillomas under the tongue interfere with a full life; they have different symptoms. Causes of infection in adults:
- Sexual contact with an HPV carrier.
- Transmission of the virus through the use of household items on which it is located.
Finding out who is carrying the virus is very difficult. Warts may not appear for decades. The main factors causing papillomas on the tongue:
- stressful situations;
- decreased immunity;
- poor nutrition;
- microtraumas in the oral cavity;
- unbalanced food;
- lack of vitamins in food.
Important! Individuals who drink alcohol, smokers, or abuse medications are not protected from the virus.
Removal of papillomas
[Show slideshow]
Removal of papilloma is carried out if drug therapy does not give the desired result. Surgeons offer several removal methods. Which one will be preferable is influenced by the location of the papilloma and the individual characteristics of each organism.
Methods for removing papilloma on the tongue:
- Laser removal. One of the most effective and painless methods. The number of complications and relapses after its use is minimal. The method is safe because infection during the procedure is almost impossible; the process itself occurs very quickly. The only disadvantage of this method can be its high price.
- Removal with liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction). The papilloma is affected by deep cold, due to which it dies and disappears. This happens throughout the week.
- Electrocoagulation. The procedure is affordable, but it may cause pain and a long recovery period. Electrocoagulation is difficult to use to remove papillomas on the root of the tongue or areas close to the pharynx. Cauterization with electric current does not leave scars, mucous areas heal very quickly.
- Radio wave method. Unlike the previous method, there is no high degree of pain, a short rehabilitation period, and rapid healing.
- Surgical method. Used to remove single papillomas (or if there are no more than three). For this, a special loop or scalpel is used. Mini-sutures are placed on the damaged part of the tongue.
Prevention
To prevent the body from becoming infected with the human papillomavirus or its activation, doctors recommend adhering to a number of preventive measures:
- Carry out hygiene procedures for the body and oral cavity in a timely manner. A mandatory condition is washing your hands after visiting the street, toilet, or contact with animals.
- Use only personal hygiene products. Do not allow strangers to use them.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: switch to a balanced diet, exercise, and take a course of vitamins and minerals if necessary. It is necessary to carry out activities that are aimed at strengthening the body's defenses.
- Avoid unprotected sex.
- If possible, get vaccinated against human papillomavirus.
- Avoid stressful situations; women undergo timely preventive examinations by a gynecologist and dentist.
Papillomas on the body require timely diagnosis and treatment (removal), since there is a risk of their degeneration into malignant formations.
Modern medicine offers vaccinations that will help protect the body from HPV. However, the opinions of doctors are not clear. A vaccine is a substance that does not provoke infection, but only promotes the formation of cells that will block the penetration of the virus into the body.
The most popular vaccines are Cervarix and Gardasil. They can be used to prevent the penetration of the virus, but not for the treatment of papillomas. Vaccine manufacturers claim that 1 injection can protect the body from the virus for 8 years. The maximum effect can be obtained only if the procedure is done before the start of sexual activity. The maximum allowable age is 26 years. Slight pain in the area, swelling and redness, and a slight increase in temperature after vaccination is normal.
Papillomas on the tongue are not the safest disease, and their treatment and removal require a particularly careful approach. It is on the mucous membrane that many irritants influence the growths.
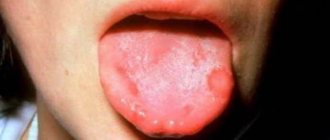
Clinical picture
White growths on the tongue may not cause discomfort if they are small. After some time, they increase in size and new lesions appear. The patient reports itching and burning in the organ, especially when eating or drinking drinks. Sensitivity increases when exposed to heat on tumors. Hot and cold dishes, tea and coffee provoke deterioration of the condition.
With an increase in the number of papillomas or warts, pain is present when talking and even at rest. The tongue becomes swollen, a white coating and cracks appear. If the growths are constantly damaged, pathogenic microorganisms enter the wounds and an inflammatory process develops. Sometimes a purulent focus forms in the area of damage.
In the absence of therapy, neoplasms spread to the inner surface of the cheeks, pharynx and larynx, which significantly worsens the course of the pathology. The patient refuses food to avoid pain. There is an unpleasant odor from the mouth, the mucous membrane is very sensitive.
As the pathology progresses, general symptoms appear: weakness, irritability, indigestion, headache, drowsiness, fatigue and decreased performance. When several papillomas form in different parts of the tongue and throat, doctors talk about the development of papillomatosis. The long course of the disease leads to nervous and physical exhaustion of the patient and the development of complications.
The most common consequence is stomatitis, caused by the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity. Quite often, glossitis develops - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the tongue. One of the dangerous complications will be the degeneration of a wart or papilloma into a malignant neoplasm.