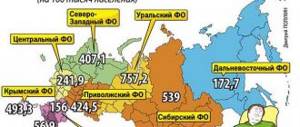
According to the World Health Organization, almost a third of the population suffers from a fungal infection. Moreover, about 40% of this pathology is caused by fungi of the genus Candida (Candida). According to doctors, 50% of women over 20 years of age have already been diagnosed with vulvovaginal candidiasis at least once in their lives. To treat such conditions, a large number of antifungal drugs are available, both local and systemic. The instructions for use of Flucostat indicate that this is one of the systemic drugs.
Candida fungi are widespread in the environment and are part of the normal microflora of the human body. Upon microscopic examination, they can often be found on the skin, mucous membranes that come into contact with the external environment, and on the fingers. In pathology, the type of fungus that most often multiplies is Candida albicans; it is this fungus that is detected in candidiasis of the genital organs, oral cavity, and skin.
When does the disease develop?
So far, experts do not know for sure why and how the intensive proliferation of the fungus begins on the surface of the skin or mucous membranes. Experts point to some exogenous and endogenous causes that provoke the occurrence of the disease.
Exogenous causes include:
- taking antibacterial medications (when taking antibiotics);
- hormonal contraceptives;
- taking cytostatics, hormones;
- chronic stress;
- physical fatigue;
- wearing tight synthetic underwear.
Among the endogenous causes, the following are of great importance:
- diabetes;
- intoxication with drugs, alcohol;
- anemia;
- lack of vitamins in the diet;
- dysbacteriosis;
- previous bacterial infection (sore throat, bronchitis, etc.);
- pregnancy.
Candida fungus can affect any organs and systems of the human body. However, in most cases localized candidiasis is detected:
- on the skin;
- in the genital area;
- oral cavity;
- urethra.
In women of reproductive age, urogenital candidiasis is especially often diagnosed. It manifests itself as redness and itching in the vaginal area and external genitalia. The second characteristic sign of the disease is the presence of cheesy discharge with a sour odor. Symptoms of candidiasis intensify a few days before the onset of menstruation.
Does Fluconazole help with thrush?
Have you been fighting thrush for many years without success?
Head of the Institute: “You will be amazed at how easy it is to cure thrush by taking it every day.
Candidiasis or thrush is a dangerous fungal disease that affects the mucous membranes of the mouth, genitals, and gastrointestinal tract in women, men and children. If specific clinical signs are detected, you must immediately contact a specialist to begin therapy. Thrush goes away on its own only if the cause of its occurrence is dysbacteriosis, which appears due to the use of antibacterial drugs.
How to get rid of fungus
Treatment of candidiasis, including the genital organs, is carried out with the help of antimycotic pharmaceuticals. They can be both local and systemic. When using systemic medications, pregnancy or breastfeeding is a limitation, so if your period is late, you should refrain from taking antifungals.
Among systemic antimycotic drugs, fluconazole (Flucostat) occupies a special place. This drug has been used in medical practice for many years and during this time its effectiveness and safety have been proven. The medicine has a number of advantages: Flucostat can be taken during menstruation, it quickly suppresses the growth of fungus and has few side effects.
What is the drug
The main active ingredient of Flucostat, fluconazole, acts on most types of Candida fungi, and therefore is effective against candidiasis of any localization. In addition, the medicine is used for infections by other fungi: microsporia, trichophytosis, cryptococcosis.
The mechanism of action of this drug is due to its ability to disrupt the synthesis of fungal cell membrane structures. This stops the proliferation of the fungal infection, and when administered in large doses, leads to its death.
An important feature of this pharmaceutical is its ability to penetrate well into any liquid environment of the human body. Quite high concentrations of it are determined in saliva, urine, and sputum. The drug is eliminated through the urinary system.
Release forms
Flucostat is available in capsule form. The content of the main active ingredient in them can be 0.5 or 0.15 g. In addition, the composition contains additional components:
- starch;
- lactose;
- magnesium and silicon salts.
You can also purchase Flucostat in the form of a solution in pharmacies. It is administered intravenously in hospitals to treat severe forms of fungal infections.
The use of Flucostat suppositories is not practiced by gynecologists, since there is no such release form. However, the doctor can create a treatment regimen with the simultaneous use of other topical antifungal and antibacterial drugs. This is especially true in cases where candidiasis is combined with other infections (for example, caused by ureaplasma, chlamydia).
For what diseases is it prescribed?
The main indications for the use of Flucostat are the following pathologies:
- vaginal candidiasis (vaginitis, vulvovaginitis, cervicitis);
- damage to the mucous membranes of the respiratory system;
- candidiasis of the urinary system (cystitis, urethritis);
- fungal infection of the gastrointestinal tract;
- candidal stomatitis, pharyngitis;
- generalized candidiasis;
- candidiasis of the skin, otomycosis, onychomycosis, pityriasis versicolor.
The drug is also effective for cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, paracoccidioidomycosis, sporotrichosis. In addition, Flucostat can be used to prevent candidiasis in patients with weakened immunity and receiving cytostatics, chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Sometimes on the forms you can find messages about the use of Flucostat for psoriasis. However, medicine does not provide clinical recommendations on this matter, so you should be skeptical about such advice.
Instructions for use of "Flucostat"
Take Flucostat capsules only orally. After entering the gastrointestinal tract, the main component of the drug is quickly absorbed and almost completely enters the systemic circulation. The drug begins to act within an hour and a half, and quite high concentrations are detected in the blood. Since food does not affect the absorption of fluconazole, it can be taken at any time of the day. Depending on the diagnosis, dosage regimens differ.
- For acute vaginal candidiasis. "Flucostat" is taken one capsule (0.15 g) once. At the same time, already on the first or second day after taking Flucostat, discharge and signs of the disease decrease.
- For chronic vaginal candidiasis. The dose is also 0.15 g. However, the drug must be taken monthly a few days before the onset of menstruation. Reviews of Flucostat for thrush indicate its fairly high effectiveness, it prevents the occurrence of relapses of the disease.
- For oral candidiasis. The dose of Flucostat is 0.1 g. It is taken once a day. If you take Flucostat correctly, the symptoms of oral thrush will go away after one week of treatment.
- Treatment of the urinary tract. For urethral candidiasis, the recommended dosage of Flucostat capsules is 0.05-0.2 g per day. The duration of therapy ranges from seven days to four weeks.
Flucostat can also be taken to prevent candidiasis during antibiotic therapy. In this case, the dosage regimen is as follows: 0.15 or 0.3 g once. The amount of medicine depends on the degree of risk of candidiasis. A high degree is determined based on the duration of antibiotic use (a week or more) and the presence of a history of candidiasis.
Side effects
According to reviews from doctors and patients, Flucostat is well tolerated. Very rarely, the following side effects may occur when using it:
- dyspepsia in the form of nausea, vomiting, stool thinning;
- epigastric pain;
- impaired liver function (increased transaminases);
- hepatitis, jaundice;
- vestibular disorders;
- hair loss;
- kidney dysfunction;
- allergic manifestations (urticaria, Quincke's edema).
Very rarely, when taking large doses of Flucostat, signs of an overdose may appear:
- psychomotor agitation;
- hallucinations.
In case of overdose, gastric lavage is performed and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. Hemodialysis is also effective in this case.
When the drug is contraindicated
The following pathologies are contraindications for the use of Flucostat:
- individual intolerance to the drug;
- renal failure;
- liver failure;
- severe heart disease with rhythm disturbances;
- alcoholism.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing Flucostat simultaneously with drugs that prolong the QT interval on the cardiogram. This is also true for drugs whose metabolism occurs with the participation of the liver cytochrome P450 system. It is not recommended to combine Flucostat tablets and alcohol.
Acquisition and analogues
You can buy Flucostat at any pharmacy without a doctor's prescription. The cost of one package ranges from 200 to 380 rubles and depends on the dosage, number of tablets, and trade markup (data as of October 2020).
In addition, pharmacy chains offer many analogues of Flucostat:
- "Fluconazole";
- "Diflazon";
- "Mikosist";
- "Diflucan";
- "Mikomax".
These drugs also contain fluconazole as the main active ingredient. Their indications and dosages are similar to Flucostat, so these medications can be purchased if the latter is not available in the pharmacy.
Thus, Flucostat is an effective antifungal agent with systemic action. It can be used to treat candidiasis of the mucous membranes and skin, including generalized forms of the disease. However, in each specific case, it is necessary to consult a doctor who will suggest the correct treatment regimen and dosage of the medication.
Treatment of oral candidiasis, how to treat oral thrush in adults
Treatment of oral candidiasis includes general and local methods of therapy. Before drawing up a treatment regimen, doctors prescribe to patients a set of laboratory tests that allow them to determine the type of pathogen and select the appropriate medicine to which it will be unstable.
Therapy for the disorder differs for each patient depending on his age, symptoms of candidiasis and individual reactions to certain components of the drugs.
To eliminate signs of the problem, therapeutic measures are usually prescribed in combination. They include local treatment of damaged mucous membranes, strengthening the immune system, the use of traditional medicine and diet.
Let's take a closer look at each method of combating oral candidiasis.
Without an accurate examination, it is impossible to accurately determine the cause of the fungal disease. Even with obvious signs of candidal stomatitis, the doctor will prescribe a series of tests for the patient.
The main study, the results of which must be taken into account when drawing up a treatment regimen, is a biochemical blood test. The pathological process is indicated by a high number of leukocytes in the biological fluid and a decrease in hemoglobin.
Experts also pay attention to blood sugar levels to rule out diabetes mellitus as a possible cause of the development of oral thrush. To obtain a reliable result, you must take the test 12 hours after your last meal. The blood sugar level of a healthy adult is between 5 and 6.1 units.
Another important analysis for determining the type of pathogen is scraping from the mucous membranes for further PCR diagnostics. DNA fragments of pathological cells are compared with the existing database.
Microscopic analysis allows you to determine the sensitivity of the drug to drugs. The letter “U” or “P” denotes the resistance of pathological particles to a certain group of medications.
The abbreviation “DZ” means the weak effectiveness of the antimycotic agent relative to the identified type of pathogen. The letter "H" is used to indicate effective remedies against fungus in the mouth.
Oral candidiasis - what is it, symptoms
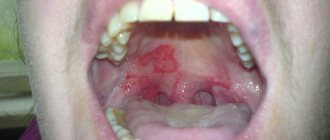
Oral candidiasis (also known as oral mycosis) is a disease in which the fungus C. albicans is diagnosed on the mucous membranes of the mouth. This organism can occur normally, but when it grows it causes characteristic symptoms.
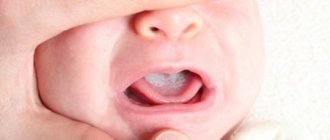
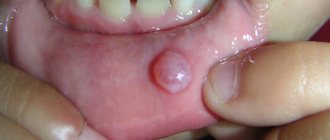
Candidiasis causes white, curd-like lesions on the tongue and inside the cheeks, and can sometimes spread to the roof of the mouth, gums, tonsils, or throat.
Children and the elderly are most susceptible to infection due to weakened immune systems, people with diseases that affect the immune system, and those taking certain medications.
Normally, the immune system gets rid of harmful microorganisms such as viruses, bacteria and fungi, maintaining a balance between “good” and “bad” microbes in the body. However, when defense mechanisms are disrupted, the number of Candida fungi can increase, ultimately leading to candidiasis.
www.mayoclinic.org
Causes of fungal infection
More often the disease affects women. In men it occurs when they abuse bad habits, especially smoking.
Yeast-like fungi are found on all mucous membranes of the human body in the form of saprophytes. The inflammatory process is provoked mainly by Candida albicans. An acidic environment is ideal for them.
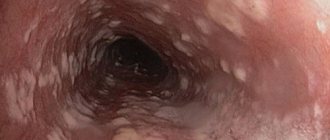
The photo shows a fungal infection of the oral mucosa
Fungal infection of the oral cavity occurs for the following reasons:
- weakened immune system;
- severe general infections (tuberculosis, HIV infection);
- endocrine system disease;
- long-term and improper use of cytostatics and corticosteroids;
- pregnancy;
- allergic reaction to components of the material from which the denture is made;
- oral contraceptives;
- long-term antibacterial therapy;
- lack of vitamins B, C, PP;
- diseases of the digestive system;
- systematic use of antiseptic solutions for rinsing the mouth;
- chronic mechanical trauma of the oral mucosa;
- alcohol abuse.
It happens that infection occurs during a kiss or unprotected sex. The infection can be transmitted to infants by the mother during childbirth.
Treatment of oral candidiasis in adults
In case of uncomplicated course of the disease, for the treatment of oral candidiasis in adults, clotrimazole in tablets 10 mg 5 times a day or miconazole 50 mg is used, on the inner surface of the cheek for 7-14 days.
As an alternative, you can use nystatin suspension (100,000 units/ml) 4-6 ml, 4 times a day, or 1-2 lozenges (200,000 units) 4 times a day, 7-14 days. For moderate cases of the disease, oral fluconazole 100-200 mg per day is recommended for 7-14 days.
Source: https://osp-sakhalin.ru/rotovaya-polost/flukonazol-pri-kandidoze-polosti-rta.html