Every person who is about to undergo surgery under general anesthesia experiences natural anxiety and curiosity. These worries are understandable, since even today’s advanced advances in medicine do not make it possible to predict 100% the consequences of both the operation itself and general anesthesia. People have individual tolerance to anesthesia, which affects everyone differently, so it is impossible to predict exactly what sensations the patient will experience after anesthesia.
How general anesthesia can affect the body, and what the recovery from it will be, depends on a number of factors:
- age;
- hormonal status;
- presence of chronic diseases;
- proper preparation for surgery;
- presence of bad habits;
- allergic reactions.
Each person handles general anesthesia differently.
A large degree of responsibility falls on the shoulders of the anesthesiologist, who must carefully study the patient’s medical record and make the right choice regarding anesthetic drugs and the method of their administration. The anesthesiologist is obliged to conduct a conversation with the patient about the proper preparation of the body for the upcoming surgical intervention. The doctor should give the most complete answer to the patient’s questions about how long and exactly how he will recover from general anesthesia, without hiding the likelihood of complications.
It is important to remember that going into medicated sleep under general anesthesia is a justifiable risk. However, it has been experimentally proven that if the patient properly prepares his own body for surgery, anesthesia works reliably and recovery from it is not accompanied by severe symptoms.
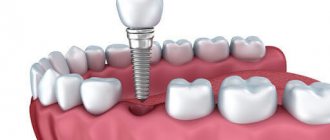
Classification of anesthesia in dentistry
Anesthesia, or anesthesia, in dentistry has a certain classification. Various drugs and their types are used in individual cases, depending on the time required by the doctor for the operation, the patient’s condition, and the presence of severe fear or phobia. First of all, anesthesia is divided into two types:
- general anesthesia, or anesthesia;
- local anesthesia.
Anesthesia is usually used only in isolated cases of necessity, if the operation is expected to be very long. So, general anesthesia can last about six hours. Moreover, it has a number of advantages relative to local anesthesia:
- you can remove several teeth or perform several procedures in one go;
- Treatment under general anesthesia is completely painless;
- During anesthesia, the secretion of saliva is blocked, which is very beneficial to the doctor.
However, in most cases there is simply no need for anesthesia, so local anesthesia is used, which is often popularly called tooth freezing.
How to quickly recover after anesthesia?
The anesthesia procedure always raises a lot of questions among patients. Common stories and unpleasant memories of feeling unwell after anesthesia make you worry about your condition after surgery. To reduce the likelihood of developing unwanted symptoms after general anesthesia, it is recommended to find out in advance how to remove anesthesia from the body and whether it is possible to speed up this process.
Woman after surgery under anesthesia
How do you wake up after anesthesia?
The stage of recovery from general anesthesia after surgery is considered very important and requires the anesthesiologist to fully focus on the patient’s condition. Recovery from anesthesia begins the moment the anesthetic supply stops.
Consciousness and sensitivity begin to return to the patient: first, muscle tone and reflex muscle reactions return, and the nervous system is excited, which can manifest itself as incoherent speech and motor restlessness.
After this, consciousness slowly returns and the patient wakes up - in the first minutes he is disoriented in space, lethargic, inhibited, speech and expression of emotions are difficult.
At the awakening stage, the anesthesiologist performs a series of tests that allow you to correctly assess the restoration of respiratory function. Only after a positive result is the patient extubated and given permission to be transported to the ward.
In most cases, after surgery, the patient is transported to the ward of his department, where he was before surgery. The exception is those situations when the patient is in serious condition - in this case he is transferred to the intensive care unit.
Transporting the patient after surgery
Folk remedies for recovery after anesthesia
In combination with drug support, the patient can use folk remedies. Arnica officinalis extract helps the patient recover faster and improves cerebral circulation after major surgery.
Passionflower (passion flower) and chamomile have a relaxing and calming effect.
It is better to buy the necessary herbs at the pharmacy - they come in the form of filter bags, convenient for use; you just need to pour boiling water over them and leave for a few minutes.
Source: https://NarkoZzz.ru/rekomendatsii/kak-otojti-i-vyvesti-narkoz-iz-organizma-posle-operacii.html
Features of local anesthesia
Local anesthesia is simple and in most cases can satisfy the need for pain relief, which is why it is especially popular among dentists. In turn, tooth freezing is divided into the following types:
Application anesthesia
It is carried out using gels or sprays that are applied to the gum or cheek. The effect can be observed approximately five minutes after application. However, topical anesthesia is used only in cases where it is necessary to get rid of tartar, remove a falling out or loose tooth, treat gums, or carry out another practically painless procedure, because the spray or gel freezes only the surface of the mucous membrane.
Moreover, topical anesthesia cannot be used for children under five years of age, as well as people with lung diseases.
Infiltration anesthesia, or injection
This type of anesthesia is performed by injecting an anesthetic into the soft tissue located near the diseased tooth to freeze it. It affects the deep layers of tissue. The injection is administered near the location of the entrance of the nerve trunks leading to half of the jaw or its separate part. Usually, not only the cheek and the necessary gums are frozen, but also other organs of the oral cavity, since the exits of all nerves are located close to each other.
It is also important to understand that freezing the upper and lower jaws are somewhat different in their methodology and action due to differences in the structure of the skeleton. Considering that the lower jaw usually has greater loads relative to the upper jaw, evolutionarily it has developed that it has a more dense structure and its muscles are more developed.
Therefore, when injecting an anesthetic into the lower jaw, the needle is inserted deeper, which also affects the duration of the anesthetic.
Duration of action of the anesthetic
A huge number of patients are usually interested in how quickly tooth frost will go away, but it is necessary to understand that the duration of action of the anesthetic depends not only on the type of anesthesia, the area of its application, dosage, the person’s age, metabolic rate and other individual parameters, but also on the painkiller used facilities. Thus, dental anesthetics can be divided into three groups according to the duration of their effect:
- short-acting (Novocaine) – up to twenty minutes;
- medium-acting (Prilocaine, Articaine, Trimecaine, Lidocaine) - from half an hour to an hour;
- long-acting (Bupivacaine) - the effect in some cases can last up to six hours, but usually a sensitivity-blocking dosage is used for two hours.
However, as mentioned above, there are a number of factors that influence the duration of action of the painkiller:
- the presence of inflammation at the site of drug administration;
- the presence of vasoconstrictors in the composition of the anesthetic - substances that narrow blood vessels;
- injection depth;
- site of drug administration;
- chronic diseases of the urinary system;
- individual parameters of the human body.
But in most cases, drugs when injected into the upper jaw last for the next two hours, and when injected into the lower jaw - up to four. However, again, this all depends on the freezing method and many other factors, so if the anesthesia persists for a longer period of time, there is no cause for concern.
Only if freezing remains relevant even after 24 hours should you consult your doctor.
What affects the duration
The effectiveness and duration of anesthesia depends on the choice of agent and is based on the patient's profile. On average, when combined with adrenaline, you can expect it to go away within 2-4 hours. For patients with heart disease, high blood pressure, or an allergy to adrenaline, the local anesthetic lasts for at least an hour.
Vasoconstrictors increase the rate of absorption of the anesthetic into the bloodstream, reduce the risk of systemic toxicity, and increase the duration of action and hemostasis. When administering local anesthesia, vasoconstrictors are used unless there is a compelling reason or an absolute contraindication describing circumstances in which the drug should not be administered under any circumstances.
A relative contraindication refers to conditions where it is used cautiously after careful analysis of risks and benefits and there is no other safe alternative.
Method for reducing the effect of anesthesia
Usually, even after an operation or a procedure requiring anesthesia, the painkiller continues to make itself felt: the lips remain numb, it is not possible to eat normally, the smile becomes distorted. Therefore, people are looking for a way to help the anesthetic stop working as quickly as possible.
In this case, dentists usually recommend applying warm compresses to the cheek. This will help dilate the blood vessels, which will ultimately increase the metabolic rate and remove the anesthetic from the body. However, this is contraindicated after tooth extraction or if inflammation remains. Thus, it is strictly forbidden to heat a tooth or cheek during gumboil. Therefore, it is highly recommended that you consult your dentist initially.
Anesthesia during pregnancy
Typically, dentists recommend treating teeth and gums while planning pregnancy, because anesthetics can indirectly affect the intrauterine development of the fetus. However, if necessary, it is better to go to the doctor in the second trimester of pregnancy, but if there is an urgent need for treatment, then it can be performed at any stage.
The most modern painkillers, which do not contain adrenaline, are used for pregnant women to avoid the possibility of increased blood pressure and contractions of the uterus. Usually, drugs with minimal toxic effects on the body are also used.
In some cases, pregnant women are transferred to a hospital for treatment.
Thus, all necessary procedures can be carried out under the strict supervision of the attending physician to avoid any complications.
Coming out of anesthesia
Anesthesia is an unconscious state of a person caused artificially in order to disable currently undesirable body functions.
But the unconscious state is only one part of the effects of anesthesia. Its other task is to prevent the body from automatically reacting to pain.
The autonomic nervous system is responsible for them, and it cannot be controlled by consciousness and works even in its absence.
And the final goal of anesthesia is to relax muscle tissue in order to provide full access to the problem area and create favorable conditions for the surgeon to work.
Managing anesthesia is a difficult job, since the doctor can never predict what the reaction of a particular organism will be to certain substances. But recovery from general anesthesia is an equally important moment.
It poses many dangers to the health and sometimes the life of the patient.
Please note that the term “anesthesia” assumes that the patient is in an unconscious state, therefore it is referred to only as general anesthesia. If pain relief is achieved in a specific area of the body, while the patient retains the ability to perceive the outside world, then it is incorrect to use the term “local anesthesia” here, since this is local anesthesia.
What kind of anesthesia is there?
Anesthesia is characterized by many parameters: by the potent substance used and the method of its entry into the body, by duration and depth, and by the purpose of use. Each of these groups has its own tasks, its own characteristics and advantages, as well as its own dangers, so:
Local anesthesia is intended to turn off sensitivity in specific areas of the body. And it is achieved through medicinal effects on certain areas of the nerves, which ensures loss of sensitivity of the tissues innervated by them. At the same time, the patient retains clear consciousness, as well as respiratory activity.
This type of pain relief is used for patients with severe concomitant pathologies or in cases where the patient must be conscious. It does not have a general effect on the body, so removal from it is difficult and its consequences are minimal.
The main disadvantage of this anesthesia is that the technique for performing it is quite complex and requires experienced specialists to perform it.
Inhalation anesthesia is achieved by inhaling anesthetic drugs using a special mask. It uses special “volatile” liquid substances, which include inhalational anesthetics and gas-like narcotic substances. Among them are nitrous oxide, fluorothane, methoxyflurane, and cyclopropane.
In its pure form, this method is used only in pediatrics, and for adult patients, mainly as one of the components of complex anesthesia. It is quite easy to use, has no serious side effects, is inactivated in the liver and is easily excreted from the body. That is why it is preferred in pediatric practice.
A very significant point is that the surgeon has the opportunity to freely control the anesthesia during the operation. This is especially important when the patient has concomitant pathology of the circulatory system and respiratory system.
Non-inhalation anesthesia - involves the administration of anesthetic drugs using one of the parenteral routes (intramuscular, intravenous, rectal). Its advantages are that it is technically simple, passes without a period of excitement, has a good relaxing effect, and its effect occurs quickly.
The disadvantage of this method of pain relief is that its effect is short-lived, which makes it impossible to use it during long-term operations. Its area of application is many diagnostic procedures or minor surgical interventions.
Recovery from this type of anesthesia is simple and lasts no more than one to two hours.
Combined anesthesia is a single type of anesthesia that can be administered in various ways, sequentially or simultaneously.
Its most popular type is neuroleptanalgesia, when a mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen, fentanyl, droperidol and muscle relaxants are used simultaneously.
In this case, medications are administered intravenously, and to prolong their effect, the patient receives an inhalation mask. This method is characterized by the greatest safety, with a minimum number of deaths in the operating room due to anesthesia.
Combined anesthesia, in contrast to combined, is characterized by the use of different types of anesthesia (general + local). It is also widely used in today's surgery, especially in cases where a complex intervention is planned, and there is a risk that the effect of local anesthesia will be insufficient.
Endotracheal anesthesia is performed by inserting a special tube into the patient’s trachea, which will carry a narcotic substance.
This method allows you to keep the patient’s airways open even in an unconscious state, which makes it possible to reduce the risk of possible complications, as well as, if necessary, remove blood and vomit from the lumen of the respiratory system.
Staged action of general anesthesia
Once in the human body, narcotic substances affect the functioning of all systems and organs. At each of the four stages of anesthesia, these changes vary.
- Analgesia – when anesthetic substances enter the body
- Excitement – characterized by short-term activation of all systems, followed by long-term relaxation.
- Surgical intervention is the time of the operation when the functioning of the internal organs is maintained at the required stable level.
- Awakening is when consciousness returns and sensitivity is restored.
How does a person recover from general anesthesia?
The moment of removing the patient from the state of general anesthesia should be considered the most crucial, when the anesthesiologist should focus on the patient and his condition. How long does it last? From the moment the anesthetic is stopped, the patient begins to recover from anesthesia. How long it will last depends on several factors:
- Duration of surgery (the longer the operation took, the longer it will take to recover from anesthesia)
- The dose of the anesthetic received (in addition to the duration of the operation, it is affected by the patient’s weight and his sensitivity to the drug)
- Health status. People exhausted by the disease with many concomitant pathologies have a harder time recovering.
- Patient's age. At a young age, general anesthesia is tolerated more easily than at an older age.
At this point, the patient gradually returns to sensitivity and consciousness.
At the first stage, muscle tone and their reflex reactions are restored, later the nervous system comes into an excited state, this is noticeable by incoherent speech and the presence of motor restlessness.
Only after this consciousness fully returns, then the patient awakens. At first, he is lethargic and inhibited, cannot navigate in space, has difficulty speaking and expressing emotions.
At this point, the anesthesiologist performs a series of tests to give a correct assessment of the degree of breathing restoration. Only after ensuring a stable positive result is the patient allowed to be extubated and transported to the ward.
What a person may feel when coming out of general anesthesia
Until the narcotic drugs are completely removed from the patient’s body, he will feel their effects. On average, this process takes about four hours.
When anesthetics are removed from the body, sensitivity to pain returns, so the first day after the operation, or even two (depending on the degree of complexity of the surgical intervention), the patient is administered strong painkillers, sometimes tranquilizers, according to the schedule, this makes the patient lethargic and lethargic. Typically, the infusion of medications continues at this time.
For the first hours after the end of the operation, the patient is prohibited from drinking; you can only wet your lips or rinse your mouth. After 3-6-10 hours, water is allowed to be drunk, starting with a few sips, gradually this dose increases and after a day or two reaches the usual volume.
On the first day the patient may complain:
- For dizziness and headache. It is associated with the effect of anesthetic drugs on the central nervous system. In addition, medications used to suppress pain can lower blood pressure, which is manifested by dizziness of varying degrees of intensity. Another cause of headache is the use of epidural anesthesia, but it goes away after a few hours.
- For painful sensations in the throat when swallowing and breathing. These phenomena may be caused by injury to the pharyngeal mucosa during intubation. As a rule, it takes two to three days to recover.
- For nausea and vomiting. These are the most common complaints upon recovery from anesthesia; they directly depend on the type of drug used. To prevent this condition, you need to take your time to drink water, and if this happens, then there are medications that can cope with this problem. You just need to ask the nurse to give you an injection.
- For chills. Very often, after regaining consciousness, patients complain of trembling; this is a consequence of a thermoregulation disorder. To normalize the condition, it is enough to cover the patient warmly and cover him with warm heating pads.
Tooth freezing while breastfeeding
Some mothers are afraid to visit dentists while breastfeeding, thinking that anesthetics through milk can have a negative effect on their children. However, there is practically no reason for this.
Neither the anesthetic itself nor the accompanying possible toxic substances are reflected in the milk, because they act only on a certain area of the jaw and are not introduced into the blood.
But in order to further reduce the likelihood of negative effects of drugs on babies, dentists recommend feeding them before visiting the doctor, and also preparing in advance the required amount of milk for the next feeding of the baby. Thus, the toxic substance will not have the opportunity to enter the child’s body.
Category Miscellaneous Published by Mister dentist