June 12, 2020 Last revised: September 12, 2020 Oral diseases
A small percentage of Candida fungi are present in the oral cavity of most people. Under certain conditions, the fungus in the mouth begins to actively multiply. This is accompanied by pain, dry mouth, and swelling. In advanced cases, symptoms include general malaise and fever. Treatment in the early stages is quick and effective. Various lotions, ointments, and sprays are used. Traditional medicine and a special diet come to the rescue. All methods of treating fungus in the mouth in children and adults can be found in this article.
Fungus in the mouth - forms and stages of development
There are 82 species in the Candida family of fungi, but only a few of them are the most pathogenic to humans. They appear in the form of budding cells, whose diameter barely reaches 6 microns. They have good adhesive ability. This facilitates their penetration to the basement membrane of epithelial tissues, where they multiply. They are more often localized in an acidic environment and synthesize pathogenic substances that participate in the breakdown of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids in the body.
Microorganisms are found in 75% of all patients, but in an inactive stage of reproduction. They are excreted in urine, feces, sputum, vagina and superficial epidermis. Under the influence of certain factors (we will consider below) they begin to actively multiply, creating entire colonies, destroying tissue. In total, there are 4 stages of the disease:
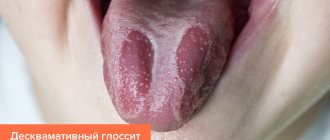
- Desquamative - areas of desquamation are found on the tongue, and the plaque itself is difficult to remove.
- Erythematous - the back of the tongue swells greatly, and the coating has a thick and foamy consistency.
- Infiltrative - the entire oral cavity is covered with plaque that is difficult to remove.
- Erosive - the plaque becomes loose and acquires a gray-milky color. Erosion forms underneath, which can be detected when the plaque is removed.
The disease candidiasis is divided into forms, each of which has its own clinical picture and is distinguished by its individual manifestation and course.
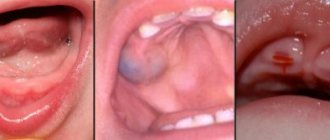
Pseudomembranous
The most common form of fungal infection of the oral cavity, which most often occurs in infants, as well as in patients using dentures. A white coating is found on the oral mucosa, rising on the mucous membrane. Its structure resembles cottage cheese or milk. Adults and older children complain of constant dryness. It responds well to treatment with antimycotic and antiseptic agents, which are available in the form of solutions for oral rinsing.
Chronic hyperplastic
This form develops due to the lack of proper therapy with a prolonged course of infection. It manifests itself as thickening of the hyperemic mucous membrane in the form of plaques and nodules of varying diameters. Most often, plaque is found on the palate and back of the tongue in older patients.
Important: Manifestations of hyperplastic candidiasis may indicate the presence of diabetes mellitus in the patient.
Acute atrophic
It manifests itself as a hyperemic state of the mucous membrane (overflowing with blood). The existing folds are filled with dense deposits, at the site of removal of which various bleeding cracks and erosions are found. The patient is concerned about: dryness, burning, soreness. Classical methods of treatment for this form of the disease are practically ineffective. The patient requires systemic therapy using strong antifungal medications.
Chronic atrophic
Most often, the disease develops as a result of improper prosthetics. This may be insufficient sanitation of the oral cavity during the procedure, or incorrect selection of structures in the form of removable mouth guards or implants. In this case, the mucosal area swells, fills with blood, and pain appears. Erosion begins to form in places with the greatest mechanical impact. Fungi penetrate into them, causing mycotic tissue damage.
General symptoms
At the beginning of the development of the disease, fungi begin to penetrate the cells of the mucosa. There they multiply intensively, resulting in the release of special enzymes that irritate the mucous membrane and destroy tissue. This causes swelling and redness, which is accompanied by a feeling of dryness and pain. When fungi actively multiply, pseudomycelium begins to form. A white coating with a cheesy consistency forms, rising above the upper layer of the mucosa. It contains bacteria, keratin, fibrin, as well as food debris and already destroyed cells.
In the first stages of the disease, plaque looks like white grains that are located on the inflamed surface of the tongue, cheeks or gums. As the infection spreads, these grains begin to increase in size and merge with each other. Plaques form, affecting more and more areas of the mucosa. The palate and tonsils become infected.
At the first manifestations of fungus, plaque can be easily eliminated. An inflamed surface remains in its place. But the activity of microorganisms continues. The enzymes they produce provoke allergic reactions, which are manifested by burning, itching and irritation. These painful sensations are especially intensified when eating sour, spicy or hot foods. Microorganisms affecting the tonsils and larynx cause difficulty swallowing.
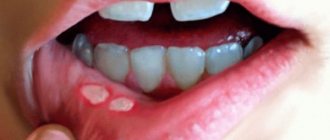
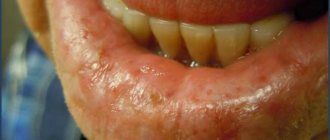
Fungus on the lips is manifested by inflammation of the skin, small cracks, white coating and scales. Found in the corners of the lips - a mycotic jam. The most common cause of candidiasis on the lips in adults is wearing prosthetic structures that were chosen incorrectly. As a result, the corners of the patient’s lips are in a lowered position and are regularly exposed to saliva, which becomes an excellent habitat for the fungus and its reproduction.
Important: The systemic activity of fungi leads to depletion of the immune system and intoxication of the entire body.
The resulting erosions easily become infected and begin to fester. This is accompanied by elevated temperature and deterioration in general well-being.
Symptoms of fungus in the mouth
Fungus in the mouth occurs under the influence of internal or external factors, and is also transmitted through close contact or household objects. The fungal spore, which was previously in an inactive state, quickly changes, divides and penetrates the mucous membrane. The fungus gradually destroys the body's cells, feeds on decay products and releases toxic substances. The latter disrupt local immunity and increase the vulnerability of the oral cavity to other bacteria, fungi and viruses.
Mycosis in the mouth is manifested by the following symptoms:
- increased sensitivity and pain when eating solid foods;
- swelling and redness;
- irritation when eating too hot or spicy food;
- feeling of dryness and rawness;
- burning, itching, tickling;
- temperature rise to average.
Seizures appear in the corners of the mouth - flaky redness. The listed symptoms of mycosis are accompanied by bad breath.
Features of candidiasis in children
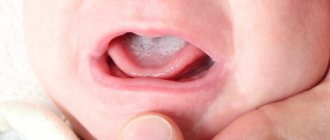
According to statistics, 20% of babies suffered from this disease before they were one year old. In 5%, thrush was discovered in the first days after birth. The baby is most often infected by his mother, but sometimes the source of infection can also be the maternity hospital staff. Why are children most susceptible to infection? The reason lies in the still immature mucous membrane, unstable microflora of the small organism, and the characteristics of the immune system. All this contributes to the active reproduction of the fungus that has entered the child’s mouth.
The most favorite places for fungus to localize in children are: pharynx, tongue, inner cheeks, tonsils and palate. The first days after infection, the diagnosis is difficult to establish. You can suspect thrush only by the reddened mucous membrane. The plaque itself is missing. After a few days, small white grains begin to appear (reminiscent of semolina). Further, the affected areas are covered with a milky film and take on the appearance of a curd substance. Such formations are easily removed, but blood may appear in their place and reddened areas remain.
In the advanced stage, plaques form, merging with each other and spreading over the entire surface of the oral cavity. The gums begin to bleed. The plaque becomes difficult to remove and changes color to brown. The baby begins to refuse the bottle or breast. Becomes moody and has trouble sleeping. This is explained by the painful condition of the mucous membrane and a burning sensation. With minor manifestations of the disease, the temperature may rise slightly. In the advanced stage, body temperature rises to 39°C.
Important: Untimely treatment provokes the rapid proliferation of microorganisms that can infect the baby’s genitals and digestive tract.
The fungus can also manifest itself in a child in the form of candidiasis. The cracks in the corners of the mouth become inflamed and covered with plaque. This jam can be caused by excessive pacifier or finger sucking in babies. For older children - excessive passion for chewing gum.
The main causes of fungus in the mouth
It has already been said above that yeast-like fungi are present in every organism. What is the reason for their active reproduction? Experts believe that the main reason is reduced human immunity, when the body’s protective functions are unable to cope with microorganisms. But for the development of fungus, accompanying factors are also needed. The main ones:
- receiving thermal or chemical burns in the oral cavity;
- carious deposits;
- mechanical injuries (usually wearing incorrectly selected prosthetic structures or implants);
- vitamin deficiency and iron deficiency anemia;
- the presence of hypothyroidism - a lack of thyroid hormones in the thyroid gland;
- immunodeficiency of primary or secondary form;
- taking antibiotics that were taken uncontrolled.
All these factors, combined with an immunodeficiency state, lead to intensive proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. The body's resistance to external aggressors is lost:
- if the patient has AIDS or HIV infection;
- damage to the skin or lungs by tuberculosis;
- the presence of tumors and metastases in the body;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract;
- insulin deficiency;
- severe endocrinopathies - various disorders in the functioning of the endocrine glands.
The cause of the development of candidiasis can be the use of cytostatic and corticosteroid drugs, which suppress the immune system, thereby provoking the proliferation of yeast-like microorganisms.
Candidiasis can also be transmitted through everyday contact through close contact with an already sick person.
Prevention
To prevent fungus from appearing in a child’s mouth, the following rules must be followed:
- Proper and regular personal hygiene. Teeth should be brushed morning and evening using dental floss, the brush should be changed regularly, and do not use mouthwash or mouth spray.
- Rinse your mouth with a saline solution (250 grams of warm water, half a teaspoon of salt).
- Take care of your health, strengthen your immune system after treatment with antibiotics.
- Avoid eating sweets.
- Have your child have dental checkups regularly.
The health of your child is in your hands. Take your child for walks in the fresh air often and monitor your immunity. Take a course of vitamins with your child every six months.
If you follow all these rules, your baby will grow up healthy and strong.
Drug treatment for fungus in the mouth
If a fungus is found in the mouth, treatment should only be prescribed by a specialist. At the first suspicion, you should contact a dentist or periodontist. Self-medication can cause the disease to spread to other organs. Then you will need the help of an infectiologist and mycologist.
Drug treatment is carried out using antiseptics, as well as local and systemic antimycotic agents.
Tables of drugs and their use
| Drugs | Admission rules | Duration |
| Antiseptics | ||
| Iodicirin, Lugol's solution. | Apply with a cotton swab up to five times a day. | About 16 days. |
| Chlorhexidine digluconate in the form of a solution. | Rinse the mouth for 5 minutes – 4 times a day. | 21 day. |
| Methylene blue, brilliant green Applications, Fukortsin solution. | Treatment 3 times/day. | 2 weeks. |
| 2% solutions: sodium bicarbonate, boric acid, borax solution. | Process up to four times/day. | 2 weeks. |
| Tantum Verde. | In the form of irrigation of the mucous membrane 4 times a day. | 2 weeks. |
| Antimycotic agents for local use | ||
| Kanesten. | 3–4 procedures per day. | 2 weeks. |
| Nystatin in the form of ointments and solutions. | The ointment is applied 4 times (daily) for 25 minutes. Solution – 15 ml with rinsing for 2 minutes. | 16 days. |
| Amphotericin. | Rinse 3 times/day. | 20 days. |
| Clotrimazole | Process up to 5 times/day. | 2 weeks |
| Antimycotic agents for systemic use | ||
| Fluconazole. | Dose per day 50–150 mg. | Day 15 |
| Ketoconazole. | Dose per day: 200–450 mg. | 10 days. |
| Nizoral. | Daily dose 200 mg. | 14 days. |
| Intraconazole. | Dose per day is 100–250 mg. | 7–12 days. |
| Diflucan. | Dose per day is 100–250 mg. | 16 days. |
During treatment, all prescribed drugs are used continuously and in strict dosages. Even the smallest break will lead to the need to start all treatment again. The risk of the disease becoming chronic also increases. In this case, the course of treatment will increase significantly.
Systemic treatment of oral fungus
It is impossible to destroy Candida fungi forever - a person remains a carrier of these microorganisms even after a full course of treatment. The goal of the therapeutic course is to reduce the number of fungi to the desired population.
When starting therapy, patients first think about how to treat fungus in the mouth . Getting rid of candidiasis is a long and complex process that includes taking systemic medications. Medicines in this group affect the entire body.
The active components of systemic drugs affect the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx and internal organs. The disadvantage of these drugs is the presence of contraindications and side effects. Antimycotics (anti-fungal tablets) are divided into imidazoles and polyene antimycotics. Below we consider drugs intended to treat this fungal disease:
- polyene antibiotics (Nystatin, Amphotericin B, Amphoglucamine, Levorin). Destroy the cell membrane of pathogenic microorganisms, help reduce ulcers and erosions;
- imidazoles. These include: Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Econazole. These are drugs that are actively used to combat fungus and stop their growth;
- remedies against microbes and parasites. Slows down the growth of fungi and other microorganisms. This group of medicines includes: Decamine caramel, Nizoral, Fluconazole, Diflucan;
- restoratives. Restore redox processes, increase immunity and activate the body's natural defenses. Doctors prescribe calcium gluconate, vitamin P, vitamins B2 and B6;
- antihistamines. Reduce the severity of allergic reactions. These include Suprastin, Diazolin, Diphenhydramine.
To prevent candidiasis, the patient is referred for vaccination or prescribed Methyluracil or Pentoxyl. These drugs stimulate the production of gamma globulins and leukocytes, which take part in the fight against infection.
Features of nutrition for candidiasis
In addition to taking medications, the patient will need to follow a strict diet. Some products can promote intensive growth of the fungus, while others suppress this process.
| Recommended for admission | Restrict or temporarily exclude |
| Various cereals and yeast-free baked goods. | All confectionery products and products containing yeast. |
| Liver, lean fish and lean meat. | Smoked meats, fatty fish and meat. |
| Dairy products. | Mushrooms. |
| Lots of greens and vegetables (preferably with garlic). | Coffee, teas and carbonated drinks. |
| Herbal teas and natural juices. | Sweet fruits. |
| Unsweetened fruits. | Spices (including mayonnaise and ketchup). |
| Nuts and seeds. | Alcohol. |
Do not forget that a special diet cannot get rid of the problem. It is only an auxiliary method for a speedy recovery.
Traditional medicine in the fight against fungus in the mouth
Traditional treatment is complemented by effective recipes from traditional medicine. These are mainly juices, compotes and decoctions for rinsing the mouth.
Which brands of toothpastes have you used?
- Colgate 32%, 29565 votes
29565 votes 32%29565 votes - 32% of all votes
- Splat 24%, 22195 votes
22195 votes 24%
22195 votes - 24% of all votes
- ROCS 16%, 15451 votes
15451 votes 16%
15451 votes - 16% of all votes
- Sensodyne 11%, 10446 votes
10446 votes 11%
10446 votes - 11% of all votes
- New pearls 11%, 10035 votes
10035 votes 11%
10035 votes - 11% of all votes
- President 6%, 5995 votes
5995 votes 6%
5995 votes - 6% of all votes
Total votes: 93687
Voted: 50514
17.01.2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
- Phytoncides of garlic, wormwood and onion can destroy microorganisms and help increase the body's protective functions. The oral cavity is treated with juices from these plants 3 times a day after the plaque has been removed. Improvement can be observed after 5 days, but the procedures should be repeated for about three weeks.
- Viburnum berries and cranberries contain a significant amount of natural antibiotics, as well as vitamins. The juice prepared from them can be rinsed in the mouth, and when drinking, linger in the mouth a little longer. Such juices are consumed throughout the month.
- Essential oils and natural antibiotics of calendula can destroy candida. This plant is used as tea and alcohol tincture. To prepare tea, you will need to pour boiling water over a spoonful of calendula flowers and leave, covered, for about an hour. Alcohol infusion is used to rinse the mouth. A teaspoon of infusion is diluted with a glass of water. The resulting solution should be used in 3 doses throughout the day.
- To strengthen the mucous membrane, you can rinse with carrot juice. Use it half a glass every 4 hours.
- It is also recommended to use honey in folk medicine. First, you will need to remove the existing plaque using a weak soda solution, and then give the child a spoonful of honey for resorption (it is better if the honey is already thickened). The regularity of this intake is up to three times a day and for a month.
Important: Independent and uncontrolled use of antibiotics can cause deterioration. These drugs can reduce the body's protective functions, which threatens to worsen the disease.
For the purpose of prevention, it is recommended to promptly seek qualified help from specialists at the first symptoms of any disease. Each of them can reduce the body’s protective functions, thereby provoking the growth of fungi. You should not ignore regular visits to the dentist for complete oral hygiene. Any antibiotics are taken only as prescribed by a specialist, and after taking them you should take care of restoring healthy microflora of the whole body.
Fungus in the mouth is considered one of the most common diseases. But if you seek help in time, it can be easily cured without any consequences for the human body.
Sources used:
- Thomas P. Habif (2009). Clinical Dermatology
. Elsevier Health Sciences. - Adaptive mechanisms of local immunity of the oral and pharynx mucosa / Maryam Gumerova, Liliya Aznabaeva and Nina Arefieva. - M.: LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, 2013.
- Diseases of the teeth and oral mucosa in children / I.O. Novik. — M.: Medicine
SIMILAR ARTICLES
Author of the article:
Lukanina Lyubov Valerievna (Author's page | All articles) is a dentist-therapist, periodontist. Specializes in the fields of: endodontics, aesthetic and functional restoration, professional hygiene and periodontology.
ethnoscience
To speed up recovery, you can supplement drug therapy with herbal remedies that suppress the activity of pathogenic microorganisms.
The following recipes are suitable for treating fungus in the mouth of a child or adult :
- It is necessary to lubricate the plaque-covered areas of the mucous membrane with the juice of wormwood, onion or garlic 3 times a day. Even if improvement occurs, therapy should be continued for at least 21 days.
- Viburnum and cranberries contain antibiotics of natural origin. You should rinse your mouth with juices squeezed from these berries for a month. If desired, the drink used for rinsing can be swallowed.
- A teaspoon of alcohol tincture of calendula flowers should be combined with a glass of water and used for rinsing 3 times a day.
- Plaque formed on the mucous membrane can be removed using a gauze swab dipped in a weak soda solution. After this, you need to take 1 tbsp into your mouth. l. candied honey and dissolve slowly. This procedure can be repeated 3 times a day for a month.