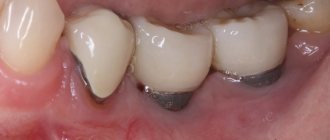
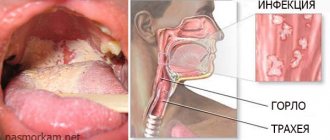
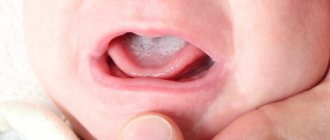
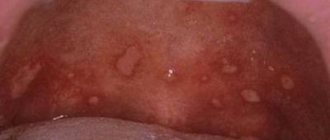
What to do if your throat is swollen? See a doctor, undergo a series of examinations and begin treatment. A swollen throat is a sign of pathological processes occurring in the human body and can lead to serious complications. This symptom is a consequence of an existing disease in the body, manifested by a feeling of tightness, difficulty swallowing and breathing. There are many reasons that cause swelling of the throat in adults and children. Emergency medical care helps prevent tragic consequences. To get rid of a problem, you need to find out its cause and determine the most effective way to eliminate it.
The respiratory tract is the entry point for infection. Foreign substances that enter the body with inhaled air settle on the mucous membrane of the throat. The larynx does not have protective barriers in the form of cilia of the ciliated epithelium. It is most affected by infectious diseases. Bacteria that grow in the throat or larynx cause swelling in the throat. It swells with allergies, infectious inflammation, diphtheria, injuries and tumors. In response to a pathological process that develops due to damage or external irritation, the throat swells. The airways narrow, which prevents the normal flow of air into the lungs and the access of oxygen. The first clinical signs of the disorder are: pain, soreness, scratching and tickling in the throat, hoarseness and change in voice timbre, cough, suffocating attacks.
Swelling of the throat can be limited and diffuse. In the first case, swelling is associated with local tissue damage. Timely and adequate therapy provides a quick and lasting therapeutic effect. Pathological changes are eliminated without any problems. Patients complain of discomfort and pain in the throat, slight coughing, hoarseness, and respiratory problems. Patients have difficulty speaking and painful swallowing due to a narrowing of the glottis. Diffuse swelling of the throat - maximum narrowing of the entire larynx. The disorder is manifested by a feeling of a foreign object inside, a sore throat, a dry paroxysmal cough, and loss of sonority of the voice. In severe cases, intoxication symptoms are added to the manifestations of the disorder - fever, chills, tachycardia, hyperhidrosis, pale skin, acrocyanosis, suffocation.
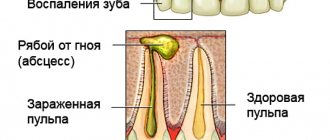
The throat swells when inflammation of the paratonsillar tissue of the pharynx or loose submucosal tissue of the larynx develops in the body. In response to the penetration of infection, tissue swelling and serous impregnation are formed. When the body's defenses are weakened and a highly virulent infection is present, a pronounced infiltration of fiber by formed blood elements develops. As a result of these pathological changes, the tissues of the larynx swell and narrowing occurs.
If the throat is swollen due to simple inflammation, the prognosis for recovery is considered favorable. Sore throat, false croup, diphtheria and laryngeal cancer are very severe and are manifested by severe swelling of the soft tissues. These deadly pathologies require emergency medical care and long-term and persistent therapy. If the problem is ignored, a swollen throat can lead to suffocation and death.
Treatment
Allergic manifestations of edema suggest the use of vasoconstrictors, mainly antihistamines.
In case of pronounced asphyxia, the lungs are saturated with pure oxygen. All these measures are resuscitation and are carried out by a specialist first.
If injection therapy and oxygen inhalation are ineffective, they resort to the last resort for curing stenosis - tracheotomy of the respiratory tract.
Its essence lies in excision of throat tissue just below the swollen area using a surgical method.
Reference! A special device in the form of a tube (cannula) is inserted into the resulting incision, which ensures a complete supply of oxygen to the patient’s lungs.
Inflammatory swelling of the throat should be eliminated with antibiotics that suppress the proliferation of pathogens, namely:
- Bioparox. The spray contains the active substance fusafungin, which relieves inflammation of the throat and normalizes its functions. The product is quite expensive, but at the same time quite effective.
- Amoxiclav. Sold in the form of tablets or powder for injection. The symptoms of inflammation are relieved due to the amoxicillin and clavulanic acid contained in the drug.
- Cephogram. Powder for injection based on ceftriaxone fights the inflammatory process and relieves swelling in just a few hours.
- Inhalipt. The spray contains sodium sulfonamide, which relieves swelling in a fairly short period of time.
- Theraflu. The drug in the form of tablets or powder contains a significant dose of paracetamol, which significantly improves the patient’s well-being. Theraflu is the cheapest medicine and can be prescribed even to children.
In order to cope with sputum, expectorants such as Mucaltin, Herbion, Prospan or Gedelix are prescribed.
In case of severe fever, antipyretics such as Ibuprafen or simple Paracetamol will come to the rescue.
To reduce discomfort in the throat, it should be lubricated.
Remember ! Inflammation should be relieved with antipyretic medications only when the patient’s temperature rises to 39 degrees.
The body's natural resistance can be helped by restorative drugs and various vitamin complexes.
For swelling of the throat due to laryngitis, folk remedies can help only in the first stage of the disease.
These include rinsing with soda, salt, juice or herbal solution.
For acute or chronic laryngitis, only antibiotics can help. But at the same time, folk methods are a good help on the path to recovery.
Complex therapy for inflammatory forms of throat swelling consists of alternating gargling and inhalation procedures.
Inhalation is effectively carried out through a special drug sold in a pharmacy - a nebulizer.
Note! Severe inflammation can be treated with alkaline inhalations based on mineral water, carried out at least three times a day.
How to relieve swelling of the throat with a sore throat at home?
It must be remembered that during a sore throat, the tonsils are a breeding ground for germs. Therefore, you should constantly gargle after eating.
Swelling of the tonsils can be treated with a decoction of chamomile or sage.
Hard foods are contraindicated for people prone to edema.
To relieve swelling of the throat, it is useful to gargle only with warm water. Do not use cold water as this may aggravate the situation. When rinsing, you need to tilt your head back and put as much medicine into your mouth as possible, and pronounce the sound “aaaa”. It is also important to rinse the nose, this will increase the activity of pathogens during local treatment.
Former fellow with the Without Borders program at the University of Kentucky in the United States. Won three awards for best blog on health, culture and education. It's not just celiac disease that causes some people to move away from wheat-based foods and products. The proteins in this grain can also cause allergies, which, although it has some symptoms similar to those of celiac disease, should be treated differently because its more severe attack can be fatal.
This allergy is more common in infants and young children, who are still developing their immune and digestive systems. It tends to go away as they grow, but adults can also develop the disease. Some of its symptoms are similar to those of celiac disease, such as stomach cramps or diarrhea. “The difference is that the allergy does not cause intestinal damage, as does celiac disease,” says Barbuti. While celiac disease gradually damages the intestines, wheat allergies have almost immediate symptoms.
Beet juice works well to relieve swelling of the tonsils.
Known in the treatment of edema for its antiseptic properties, calendula is also known. To relieve swelling of the throat, you need to dilute one teaspoon in 1/2 glass of water, and gargle with this solution, if necessary, five times a day.
Salt and iodine are effective against swelling. They should be dissolved in hot water along with salt, take ½ teaspoon of salt, soda, and the same amount of iodine up to four drops, mix, and apply this solution.
When an allergy sufferer eats food containing this cereal, he will soon experience itching of the skin, irritation or swelling in the mouth or throat, or headache. It is also common for your nose to start leaking and start sneezing. In more severe cases - and rarely - this allergy can lead to glottis closure and anaphylaxis, which can be fatal. In such cases, a person feels swelling or tightening of the throat, chest pain, heavy breathing and swallowing, tachycardia and dizziness.
The diagnosis of wheat allergy is usually made through an allergy test performed on the skin. You may also need to do blood tests or take a definitive test by eating foods that contain grains. Treatment is similar to that for celiac disease: allergy sufferers should stop eating wheat, although they can freely consume rye and barley. In some cases, they may even return to eating wheat.
Carrot juice will help relieve throat swelling. Dilute carrot juice with half a glass of boiling water. Treatment of swelling of the tonsils with this rinse is used five times a day.
Horseradish juice is used when a patient has swelling of the tonsils. Dilute the grated horseradish with water and rinse, you can also separate the pulp from the juice.
The antiseptic properties of chamomile are known; it helps with severe sore throat. The recipe is as follows: 20 g of vegetable oil per half liter of water, and add a decoction of dried chamomile flowers.
There are situations where desensitization can be done, in which the allergist is exposed to a small amount of food containing wheat and then gradually increases the amount consumed, explains Jaime Zaladek Gil, a clinical gastroenterologist at the Israeli Albert Einstein Hospital. The body gets used to the contact, and the allergic picture disappears. This does not work for celiac disease.
Allergy patients should read food labels carefully, as wheat may be hidden in products such as soy sauce, ketchup and ice cream. Stopping wheat consumption isn't just stopping pasta. Allergy patients should read food labels carefully because wheat may be hidden in products made with hydrolyzed vegetable protein, soy sauce, condiments such as ketchup, ice cream and even modeling clay.
Apple cider vinegar is also effective in relieving throat swelling.
The pharmaceutical drug Chlorophyllipt fights staphylococcal infections and relieves swelling of the tonsils. This pharmaceutical preparation, in the form of a one percent alcohol solution, can be gargled three times a day. Today, the pharmaceutical drug Chlorophyllipt is produced in the form of aerosols. This is for those who cannot sit at home even when they have a sore throat. Treatment of swelling of the tonsils with Chlorophyllipt is carried out for at least five days. It is important to know that Chlorophyllipt may cause allergies in some people, so you should be very careful when using this drug.
Some foods that suffer from allergies should be avoided. When you open your mouth and look in the mirror, you will notice it as a bright structure of what hangs from the soft palate. The main purpose of the uvula is to produce various sounds with the help of air that enters through the roof of the mouth and throat. It also helps to minimize throat infection and direct entry into the digestive tract. Consists of muscle fibers and connective tissues.
A swollen uvula is a commonly reported problem. What causes swollen uvulas? Inflamed uvula, or uvulitis, is not a disease, but the swelling of this mass is caused by other health problems. Any disease that focuses on the throat area can cause the uvula to swell. A persistent dry throat is one of the main causes of abnormal swelling of the uvula. Those who have a habit of breathing through their mouth while sleeping are more prone to this uvula condition than other people. Possible reasons for the appearance of tongues during swelling - many of them are listed below.
How to prevent throat swelling with sore throat
To prevent swelling:
Strengthen your immunity.
Temper yourself, play sports, do the legendary morning exercises.
To prevent throat swelling, eat more vitamins, in particular fresh fruits and vegetables, and establish a nutritious diet.
Take care of the hygiene of both the oral cavity and tonsils.
The most noticeable symptom accompanying uvulitis is pain in the throat. The intensity of the pain is most important when swallowing food, talking, and enjoying any activity that involves moving the swollen area. In general, patients experience increased redness and itching, as well as swelling of the uvula. Such symptoms are signs of bacterial or viral infections and require medications to treat.
Treatment of swollen uvulas. Effective tips on how to cure a swollen uvula are decided according to the causes. Therefore, identifying the factors responsible for the swelling of this fleshy mass is a prerequisite before proceeding with the treatment of swollen uvulas. For example, if swelling is due to a dry throat, then avoid shouting by breathing through your mouth and avoid processed foods that contain salt. Some of the effective home remedies for swollen uvulas that you can practice are mentioned below.
Remember that healthy sleep is just as important as proper wakefulness; lack of sleep can be the main reason for weakening the immune system, since the body is being restored during sleep. The consequence of lack of sleep is increased irritability, and an increased amount of stress has a detrimental effect on our health, up to the appearance of such a phenomenon as swelling of the throat.
3694
Currently, many diseases localized in the throat are accompanied by such a phenomenon as swelling of the entire mucous membrane and uvula. The causes of these conditions can be very different, accompanied by soreness, a feeling of lack of air or severe pain. What kind of pathological processes in the throat area cause swelling, and what treatment is necessary for this symptom?
Non-infectious factors
Most often we are talking about allergies of varying severity. Including extreme forms of anaphylactic shock or Quincke's edema.
The essence of the process is as follows:
- During the course of the pathology, an allergen substance penetrates into the patient’s body. This could be a harmless object, such as a particle of pollen, house dust, animal dander, fur, pigment contained in food, etc. Within the framework of the described system, an allergen is called an antigen.
- The body initiates a powerful immune response in response to the penetration of pathogenic structures into the body. Specific immunoglobulins are produced that combine with antigens, forming a single antigen-antibody complex.
- These formed structures settle on the tissues of the larynx and other anatomical structures and destroy basophilic mast cells. The result is the release of a large amount of a toxic substance, histamine. It is also a mediator of inflammation and initiates swelling at the local level.
- Histamine destroys tissue, provokes inflammation and sudden severe swelling.
Allergies of this kind can be relieved only with first-generation antihistamines in large dosages.
Another common cause of throat swelling is the entry of a foreign body into the anatomical structures of the lower respiratory tract.
In such a situation, it is necessary to remove the object to normalize breathing.
Then anti-inflammatory therapy and the use of antihistamines are carried out to stop secondary processes. This is mainly observed in preschool children.
Symptoms of laryngeal edema
The first sign is the appearance of pain and sore throat, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body. As the vocal cords begin to swell, the timbre of the voice also changes, becoming hoarse, dull and lower.
With further increase in swelling, the lumen of the larynx begins to decrease, which leads to the development of stridor - noisy breathing caused by difficult passage of air through the upper respiratory tract. In severe cases, suffocation develops.
Against the background of increasing hypoxia of the body, patients develop irritability and anxiety. These symptoms are more pronounced in children than in adults.
Considering that laryngeal edema can be caused by various pathologies, the clinical picture of this condition may vary. The main differences are presented in the table
| Diseases | Viral laryngotracheitis | Allergic edema | Epiglottitis | Foreign body | Laryngospasm |
| Etiology | Influenza viruses, parainfluenza, RS infection | Presence of allergic diseases | Streptococci, staphylococci | — | Reflex irritations (rough intubation, inhalation of polluted air), hypocalcemia |
| Premorbid background | Not complicated | Exudative diathesis, neurodermatitis, various allergic reactions | Not complicated | Not complicated | Spasmophilia, congenital stridor |
| Recurrence of attacks | Rarely, always against the background of ARVI. Usually seen in children aged 3 to 7 years | Often, usually in spring and summer | Not typical | No | If the provoking factor is not eliminated, the attacks may recur many times. |
| Onset of the disease | The increase in symptoms occurs quite slowly (2-5 days) | Fast (several hours) | Acute, with increased body temperature (8-10 hours) | Sudden | Sudden |
| Intoxication | Moderately expressed, fever up to 38-39 ° C | No | Hyperthermia up to 40 °C and above | No | No |
| Voice, cough | Hoarseness, wet cough | Unchanged, cough dry, rough, barking | Not changed | Unchanged, cough dry, intrusive | "Cock crow", no cough |
| Dysphagia | No | No | Swallowing any food is difficult and sharply painful | No, vomiting due to a coughing fit | No |
| Other signs | Symptoms of rhinitis, nasopharyngitis | Positive dynamics from taking antihistamines | When examining the pharynx - swelling of the epiglottis, the root of the tongue is cherry-red in color | When breathing, a popping sound is sometimes heard, associated with the movement of a foreign body by air current | Signs of calcium metabolism disorders |
Nature of pathology
Swelling of the throat occurs when an inflammatory process develops in the soft tissues of the pharyngeal cavity. The syndrome can signal many diseases, for example, tuberculosis, laryngotracheitis, pharyngitis, influenza, or a burn of the mucous membrane after an X-ray examination, which is carried out in patients with tumor processes in the neck.
Laryngeal edema in a child can develop due to infectious diseases that occur in the acute stage - for example, tonsillitis. If the syndrome occurs outside of inflammation, it may indicate pathologies of the kidneys, liver and heart.
The swelling may also be of an allergic nature. This manifestation should always be taken seriously, without ignoring the symptoms of swelling. If first aid is not provided to the patient in time, he may simply suffocate and die from asphyxia.
The cause of edema is often untreated, which is indicated by pronounced symptoms.
The inflammatory process can be of several types - edematous, catarrhal, fibrinous-necrotic and infiltrative. Edematous and catarrhal stenosis often occurs against the background of a viral infection or allergy. If therapy is started on time, then the symptoms of allergic laryngeal edema can be easily eliminated and the patient’s life is not in danger.
With fibrinous-necrotic and infiltrative edema, a bacterial infection often occurs. The mucous membranes begin to produce copious amounts of thick and viscous secretion, which further aggravates the situation. Stenosis of this kind can be complicated by the formation of a hemorrhagic cortical layer on the mucous tissue, the appearance of pus and necrotic deposits.
Diagnosis of laryngeal stenosis
If the above symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. This could be a general practitioner, pediatrician, or otolaryngologist.
If there is severe stenosis of the larynx, it is recommended to call an ambulance.
When examining a patient with a sore throat and swelling of the throat, the following is discovered:
- [enlarged tonsils];
- purulent plaque on the tonsils;
- enlarged submandibular, parotid, cervical lymph nodes;
- laryngoscopy reveals swelling and hyperemia of the vocal cords;
- [the degree of stenosis is visible];
Important to know: Quincke's edema of the larynx - symptoms and treatment
In a general blood test, there are signs characteristic of [bacterial inflammation]: an increase in [the number of leukocytes] and an increase in the sedimentation rate [erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)].
Symptoms and treatment
Many people cannot always recognize laryngeal edema, the symptoms of which are not so varied.
Such ignorance is very dangerous, so you should remember that the main signs of such an illness are considered to be hoarseness of voice, dry cough, and blueness of the face.
All this is accompanied by heavy breathing, developing into suffocation.
Only if all the symptoms are correctly analyzed, laryngeal edema can be quickly and effectively treated.
Swelling of the throat will most likely be accompanied by swelling of the soft palate, tonsils and uvula. With this syndrome, the patient hears a characteristic chest whistle while breathing.
Quincke's swelling may be accompanied by additional swelling of the hands, face, lips, fingers and other parts of the body.
If laryngeal edema is suspected, treatment should begin by calling an ambulance. This should be done as soon as possible, before the patient begins to experience suffocation.
There are medical recommendations on what to do if your throat is swollen before the medical team arrives. It is necessary to take a number of actions that can alleviate the patient’s condition rather than treat it.
First aid for swelling of the larynx consists of unbuttoning the sick person’s clothes, removing his scarf, tie or any other item that can interfere with the flow of air.
If the condition is caused by an allergic reaction, then it is urgent to stop the entry of the allergen into the patient’s body.
Allergies can be easily distinguished from other causes, since they rarely occur without a runny nose, redness of the eyes or mucous membranes.
The person should be revived, then placed in a hot bath, or at least with their limbs submerged in a container of warm water.
If you can’t count on a quick arrival of doctors, and the patient’s throat is already quite swollen, you can try to relieve or at least alleviate its manifestations by rinsing the mouth with adrenaline hydrochloride.
A strong nasal spray will also help in this situation. Sometimes there may be nothing left but to relieve swelling in the nasopharynx by intramuscular injection of an antihistamine (like suprastin or diphenhydramine).
Non-inflammatory swelling
In the presence of an allergic reaction, exposure to a number of substances, irritation of the larynx of a mechanical or thermal nature, swelling also develops. Mostly, this condition is associated with a risk to human life, therefore, in case of such violations, you should immediately go to the hospital for examination and immediate assistance.
Before the doctor arrives, the only thing that can help in this case is applying a cold compress directly to the neck, and as a distracting procedure, steaming the legs, or mustard plasters on the calf area. Swelling in the area of the larynx, trachea, palate, tonsils and uvula is not a separate disease. This is just a symptom that may indicate a number of pathological conditions of various natures. Sometimes treatment is needed immediately, especially when symptoms begin suddenly and progress quickly.
Symptoms
Allergens can enter the body in different ways, penetrating through the skin, mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and nasopharyngeal organs. Typically, the first symptoms of throat constriction occur immediately after the penetration of the allergen. The more pronounced the symptoms, the faster the process of narrowing the lumen in the larynx occurs.
Signs of swelling vary depending on the stage of the disease. Thus, in the early stages of an allergic reaction, swelling of the larynx can be confused with a common cold, because the pathology is accompanied by rhinitis, sneezing, the sensation of a foreign object in the throat, soreness, and pain when swallowing. However, apart from these reasons, there are no other manifestations of a viral infection, such as body aches, chills, or general weakness.
In later stages, swelling is manifested by hoarseness, shortness of breath, dry cough, and difficulty breathing. The patient has a desire to inhale more air, but deep breathing causes pain. Due to lack of oxygen, the skin turns pale, and the patient experiences a panicky fear of suffocating.
Important! The most dangerous stage of the disease is the state when breathing becomes shallow, the skin turns pale, the pupils dilate, and the patient is in a pre-fainting state. . Allergic laryngeal edema can be divided into several main types, depending on the location, causes and symptoms of the disease:
Allergic laryngeal edema can be divided into several main types, depending on the location, causes and symptoms of the disease:
- allergic pharyngitis;
- allergic laryngitis;
- Quincke's edema;
- anaphylactic shock.
With allergic pharyngitis, the nasopharyngeal mucosa becomes inflamed. The disease is accompanied by swelling of the uvula and mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the larynx, dryness in the nasopharynx, the feeling of a foreign object, hoarseness, and sharp painful sensations when swallowing. Most often, allergic pharyngitis occurs against the background of inhalation of strong chemical odors.
With allergic laryngitis, swelling of the entire surface of the larynx occurs. In this case, the patient experiences difficulty breathing. Also, this type of allergy is characterized by symptoms such as a dry cough, similar to barking, numbness of the lips and in the area of the nasolabial fold. There are many causes of allergic rhinitis:
- infectious diseases;
- Food;
- dust;
- medications.
Quincke's edema occurs unexpectedly, affecting the nasopharyngeal mucosa. In this situation, the eyelids, lips, oral mucosa, and respiratory tract swell.
If timely assistance is not provided for Quincke's edema, oxygen starvation (asphyxia) often develops. The patient experiences difficulty breathing, the tongue becomes blue, and the person can speak only in a whisper.
Anaphylactic shock develops immediately after the body comes into contact with an allergen. Most often, this condition occurs after consuming medications to which a person has an individual intolerance. More than a quarter of all cases of anaphylactic shock result in death due to suffocation.
After a dangerous substance enters the body, an allergic reaction begins to develop: pronounced edema, swelling appears, the site of injection of the medicine or bite turns red and begins to itch. As symptoms progress, which occurs in a period from a few minutes to several hours, itching spreads throughout the body, the patient’s blood pressure decreases, swelling of the throat develops, and as a result, hypoxia. The skin becomes pale and the limbs become bluish.
If anaphylactic shock develops against the background of a food allergy, then in this case pain occurs in the stomach, nausea, vomiting, indigestion, and swelling of the nasopharyngeal mucosa.
Causes of laryngeal edema
The development of mucosal edema can be triggered by various diseases of the larynx and traumatic injuries in the neck area. The most common causes of this condition are:
- allergic reactions to house dust, pollen, animal hair, food and medications;
- traumatic damage to the larynx by a foreign body, various chemical and physical factors;
- acute infectious diseases (influenza, scarlet fever, laryngeal tonsillitis, measles, diphtheria);
- inflammatory diseases of the larynx (infiltrative or phlegmonous laryngitis in adults, subglottic laryngitis in children);
- benign and malignant laryngeal tumors;
- injuries and diseases of tissues and organs located near the larynx (abscesses and cellulitis of the neck, tumors of the mediastinum and thyroid gland).
Depending on the rate of increase in clinical symptoms, swelling occurs:
- fulminant - develops against the background of injuries and allergies, for example, Quincke's edema;
- acute – its occurrence is caused by infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- chronic – caused by oncological pathology.
Otolaryngologists include factors that increase the risk of developing pathology:
- hypovitaminosis conditions;
- decompensated course of diabetes mellitus type I and II;
- general exhaustion;
- chronic liver and kidney failure.
Swelling usually occurs in the area of the arytenoid cartilages and folds, subglottic space, epiglottis and vestibular folds. This is explained by the presence of well-developed loose connective tissue in these anatomical zones. The consequence is a narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, which provokes the development of stenosis.
Treatment with modern methods
When treating swelling inside the throat, it is recommended to exercise and vocalize as little as possible. Doctors limit the patient from taking fluids. Drug treatment involves the use of antihistamines, glucocorticoids, and dehydration agents.
In cases of severely weakened immunity, oral administration of vitamin C and glucose is prescribed. In the absence of positive dynamics of treatment or with a general deterioration of the patient’s condition, intravenous infusions are additionally used for treatment.
Treatment for swelling in the throat involves complete rest and silence for several days. A special diet is prescribed, consisting of liquid or semi-liquid food, which does not irritate the throat mucosa as much as solid food. The food consumed should be at room temperature and of plant origin. It is forbidden to eat food seasoned with spices, vinegar or hot seasonings.
Traditional methods only complement the main therapy and are used after consultation with the doctor. To relieve inflammatory processes and reduce swelling, special rinses using a soda solution are used. To prepare, you need to take about 250 milliliters of warm water and add 1⁄2 tsp to it. soda You can supplement the soda solution by adding a little salt or a few drops of iodine.
A decoction made from ginger has worked well: you need to finely chop the root of the plant and then boil it in water for about 10 -15 minutes. This decoction has good anti-inflammatory properties and accelerates the healing process of damaged laryngeal tissue.
Cold compresses are great for eliminating inflammation. You can use a rag soaked in cold water or pieces of dry ice well wrapped in a thin cloth. Some people use a very ordinary heating pad filled with cold water.
Carrot juice mixed with a small amount of honey eliminates swelling well. It is recommended to use this composition at least 3 times a day. One dose of such a solution should not exceed a dose of 100 milliliters.
In order to eliminate excess fluid from the entire body and reduce the size of edema, you should use decoctions made from a plant such as rose hips. It is known that it has a pronounced diuretic effect, due to which excess fluid is quickly eliminated. For cooking you need to take 1 tbsp. berries of this plant and boil them well in one liter of water. The solution should infuse for at least 3-4 hours in a dark place. It is recommended to consume it in an amount of 100 milliliters throughout the day.
Preventive measures to prevent swelling and sore throat include undergoing regular medical examinations. It is also recommended to avoid getting foreign objects into the throat.
Relieving throat swelling with folk remedies
If the swelling of the pharynx is not extensive, does not cause discomfort, or does not interfere with breathing, then you can use traditional medicine to eliminate it.
- The best home remedy to relieve swelling is to gargle with a baking soda solution. To prepare the solution, dissolve a teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of warm water. You can drop a little eucalyptus oil into the medicinal liquid. Rinsing is carried out daily until the discomfort in the throat disappears.
- In addition to soda, to prepare medicinal solutions for rinsing, you can use decoctions of plants: chamomile, calendula.
- Natural carrot juice with honey helps relieve inflammation and swelling of the mucous membranes of the pharynx. The medication is taken three times a day, 100 ml. It is recommended to drink the juice immediately after preparation.
- To reduce swelling caused by infection, you can apply a cold compress to your neck: a towel soaked in cold water, ice cubes in a gauze envelope.
Rosehip decoction helps relieve swelling. The drink has a strong diuretic effect and quickly removes excess fluid from the body. A tablespoon of berries is boiled in a liter of water and left for several hours. The finished decoction is taken half a glass during the day.
Suitability0
Types and symptoms
Laryngeal edema can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory. In each of these cases, the symptoms of the disease will be different. Let's take a closer look at these two types of disease.
Inflammatory
In this case, the swelling occurs due to an infectious process leading to inflammation in the larynx. This swelling is most often caused by colds, infectious diseases, as well as measles and diphtheria.
This is what laryngeal swelling looks like
This type of edema is characterized by both rapid and slow development. Sometimes it takes two to three days for the presence of swelling to become obvious, and in some cases it forms quickly. The slow course of the disease is characteristic of laryngitis of a tuberculous or syphilitic nature, radiation sickness of the throat: quite rare diseases. In all other cases, the attack develops quickly.
Symptoms
If inflammatory edema occurs, the patient’s general condition will be quite unimportant: the severity depends on the person’s immunity, the type of infection, and its toxicity. And how pronounced the swelling will be depends more on its location.
Most often, this type of edema is perceived by a person as a lump in the throat, a foreign body. It seems to the patient that he will not have enough air now: such thoughts lead to panic horror. Sometimes panic overcomes a person to such an extent that he can even harm himself. Therefore, in such a state you cannot do without the help of others and doctors.
Inflammatory edema develops, most often, acutely: a high temperature may rise, chills, and general weakness may occur. Often, at the initial stage of the disease, a hysterical, dry cough occurs. When swallowing, pain is felt, and when trying to talk, too.
If the inflammatory edema is aggravated by a purulent infection, the patient’s condition becomes worse. The following symptoms appear:
- Increasing pain, “shooting” in the ear.
- Changing the timbre of the voice to a more hoarse, hoarse voice. Then the voice may disappear altogether until it is completely impossible to speak except in a whisper.
- Even at rest, the patient has shortness of breath.
- Laryngeal stenosis becomes more pronounced and may be accompanied by cardiac and respiratory failure.
The most pronounced signs of laryngeal edema of an inflammatory nature can be seen with existing or past colds. Various respiratory infections, flu, sore throats largely contribute to the appearance of this symptom.
Video of laryngeal edema:
Non-inflammatory
In this case, swelling occurs due to changes in the laryngeal mucosa due to any non-inflammatory diseases or metabolic disorders. Possible causes of this swelling include the following:
- allergy;
- hypothyroidism;
- cervical tumor;
- heart failure;
- goiter, both benign and malignant, and other diseases.
These pathologies cause disruptions in the water-salt balance and also contribute to the accumulation of fluid in soft tissues. As a result of such influences, swelling of the larynx of a non-inflammatory nature occurs. By the way, the well-known and dangerous Quincke's edema, sometimes even leading to death, is a non-inflammatory type.
Symptoms
In this case, the mucous membrane of the throat turns pale and becomes looser in structure.
Swallowing is difficult. A person experiences a sensation of a lump in the throat, feels that there is a foreign body in the larynx that interferes with breathing.
The voice becomes more hoarse and hoarse. A cough is likely.
This type of disease develops at a slower pace than the previous one. On average, it takes three to five days for the swelling to fully manifest itself. But with existing uremia, non-inflammatory edema can develop critically quickly - literally in 1-2 hours.
What is Quincke's edema
The German physician Heinrich Irenaeus Quincke first gave a complete description of the disease and suggested the causes of its occurrence in 1882, for which angioedema was named after him.
Quincke's edema, or angioedema, is an acute inflammatory reaction of the body that occurs locally in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The mechanism of appearance is similar to urticaria, the only difference is in deeper tissue damage.
Allergic reactions are one of the immune system's response to foreign proteins. They involve mast cells - one of the types of leukocytes that are able to combine with immunoglobulin proteins Ig E. This leads to a cascade release of biologically active substances - mediators of inflammation. These include histamine, prostaglandins, bradykinin and many others. These substances increase the permeability of blood vessels, reduce their tone, and change the water-salt balance.
The peculiarity of mast cells is that they are not constantly in the blood, like other leukocytes, but are localized in tissues:
- in the skin;
- subcutaneous tissue;
- on mucous membranes;
- in the membranes of internal organs.
Therefore, Quincke's edema has specific manifestations and is observed only on the skin and in places with the most pronounced fiber.
The increased permeability of blood vessels caused by these substances leads to the release of the liquid part of the blood from the vessels. It permeates the local area, which is externally manifested by swelling of the soft tissues. Fluid losses can be significant; blood volume in the vascular bed decreases. As a result, heart function suffers and rhythm disturbances appear. In adults with a predisposition to heart disease, the consequences can be fatal.
Drug treatment
In order to decide how to treat swelling of the throat, the doctor needs to know the causes of the disease, and based on this, this method can be medicinal or surgical. Therapy for laryngeal stenosis should be aimed at restoring a person’s unobstructed breathing.
When the throat is swollen, drug treatment is carried out using the following drugs: broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs, antiallergic (antihistamines), diuretics and corticosteroids. The doctor chooses medications based on the diagnosis. In case of edema of infectious origin, antibiotics are used, and in case of allergic edema, antihistamines are used.
If after taking medications the swelling does not decrease, then surgery is performed. To do this, a tracheotomy is performed - at the beginning of asphyxia, the larynx is dissected and a cannula is inserted into the operated area. This allows you to restore the respiratory process.
You need to know that with throat stenosis, doctors advise limiting fluid intake, not talking loudly and refraining from heavy physical activity.
Why does the throat swell: reasons
Since swelling of the throat itself is a secondary pathology, its treatment depends on the causes that provoked it.
The sensation of a swollen throat occurs with traumatic injuries, as well as with diseases of the larynx and pharynx of various origins.
1 Allergy
The throat becomes swollen due to allergies due to the body's reaction to the effects of biological and chemical substances that are allergic in nature. These include:
- pollen;
- animal hair;
- food;
- medicines;
- insect poison;
- olfactory stimulus;
- cosmetical tools.
This condition is acute and unpredictable and can cause life-threatening angioedema, which causes difficulty breathing, hoarseness, barking cough, and hypercapnic coma.
2 For sore throat
A red, swollen throat on one or both sides may be evidence of the development of a sore throat, which is always acute and is a consequence of a viral or bacterial infection. This disease is manifested by:
- the tonsils increase in size and become covered with a mucopurulent film;
- it becomes impossible to swallow;
- severe pain in the throat radiating to the ear;
- the temperature rises to 38°C and above.
In the cold season, the disease occurs more often, which is due to weakened immunity, which cannot cope with pathogenic microorganisms.
3 In case of injury
Any injury to the throat is dangerous and can lead to swelling. The most commonly diagnosed injuries are:
- mechanical - as a result of a foreign object, bruises of the larynx, attempted suicide (hanging);
- thermal and chemical burns, which were the result of swallowing hot and caustic liquids, as well as exhaling toxic fumes.
Invasive interventions during surgery or intubation can also cause swelling and secondary infection.
It has been established that the inside of the throat swells during prolonged singing, attacks of dry cough, and forced screaming.
4 Pregnancy
Due to hormonal changes in the body, expectant mothers may experience a narrowing of the larynx area, causing pain when swallowing. This condition is usually aggravated by the presence of inflammatory processes in the body caused by viruses and bacteria.
5 Alcohol abuse
After drinking alcohol, many people experience a sore throat, which is caused by a malfunction of the circulatory and excretory systems.
In tissues, due to an imbalance in the acid-salt level and ionic equilibrium, fluid accumulates and stagnates. The body's reaction is manifested not only by a feeling that something is swollen in the throat, but also by swelling of the face, arms and legs.
6 Neoplasms
Tumor formations that are localized on the pharyngeal mucosa can cause swelling. They have different origins:
- benign – angiomas, cylindromas, cysts, fibromas, etc.;
- malignant - in which the tumor spreads to the tissue around the site of the lesion and metastasizes to the lymph nodes and tonsils.
Source: nasmorkam.net
Characteristic symptoms
Symptoms of laryngeal edema are quite extensive, its pathological manifestations are as follows:
- a significant increase in temperature to +38-+40C, which is life-threatening;
- against the background of general intoxication, headache, drowsiness, and lethargy appear;
- increased pain during the swallowing reflex, up to refusal to eat;
- sharp pain in the neck or ear when opening the mouth;
- extensive swelling, due to which the relief of the neck changes;
- putrid odor from the mouth due to the development of microflora on the mucous membrane;
- spasm of the masticatory muscles and excessive salivation.
Sometimes hoarseness and a feeling of a foreign body in the throat develop. In adults, the symptoms of laryngeal edema are not as pronounced; children are much more seriously ill. The condition is alleviated if the abscess opens spontaneously.
Allergic edema
Acute damage to the larynx with edema occurs under the influence of allergens. It could be dust, animal hair, a new food product, or medicine. Irritating particles enter the mucous membrane and cause allergic swelling.
It is characterized by:
- rapid development and unexpected manifestation;
- lack of voice;
- the occurrence of suffocation.
On examination, a light pink, translucent or gelatinous mucous membrane of the larynx is observed. This pathology is especially dangerous because it occurs quickly, causing swelling and asphyxia. The disease develops against the background of a weak immune response and poor environmental conditions.
In the worst case scenario, angioedema occurs, in which the tongue, neck, lower part of the face, and sometimes the genitals swell. This is also allergic swelling, which does not happen so often. Its development is associated with the consumption of new foods, medications, and insect bites.
It is necessary to use antihistamines and corticosteroids as soon as possible, and contact an ambulance. In this condition, laryngeal stenosis occurs when the lumen of the walls of the larynx quickly narrows, causing swelling and blocking the access of air to the tissues.
Important! With Quincke's edema, pain in the throat is not felt. Swelling and suffocation develop quickly and the patient begins to panic, which aggravates the situation.
Infectious swelling of the throat
With chronic tonsillitis or laryngitis of a bacterial nature, infectious edema develops. This is possible if throat diseases remain untreated and colonies of microbes remain on the mucous membrane of the larynx. Follicular and necrotic tonsillitis are especially dangerous.
In case of characteristic symptoms, treatment of laryngeal edema is supervised by a doctor. Manifest:
- sore throat;
- breathing problems;
- hoarse voice;
- difficulty eating.
The main role is played by infectious factors due to which swelling turns into asphyxia. To prevent the process, it is necessary to treat the sore throat that preceded it. Self-medication for inflammatory throat diseases is strictly prohibited.
Swollen throat: what first aid is required
In most diseases, the throat swells on the inside, but there are cases when it swells on the outside as well.
From time to time, most people have to deal with throat swelling, the etiology of which can be either inflammatory or non-inflammatory.
Therefore, if your throat is swollen, it would be a good idea to visit the hospital, because swelling of the throat can cause more serious symptoms - paroxysmal coughing and difficulty breathing.
It is extremely important that the treatment of edema is not only symptomatic, but involves identifying the cause and, if possible, its absolute elimination.
In this article we will talk about why the throat swells, what diseases can cause it to swell, and how to help a person if the throat is very swollen.
Why might my throat become swollen?
To determine the reason why your throat is very swollen, you must remember that swelling is not an independent disease, but just a symptom. The localization of edema, its extent and the presence of pain depends on various factors, including the individual structure of the subcutaneous fat and mucous membranes.
The most common reasons are:
- foreign bodies of the respiratory system;
- inflammatory diseases of the throat of infectious or viral etiology;
- burns of the mucous membrane;
- allergic reactions;
- exposure to radiotherapy or x-rays;
- infectious diseases.
In order to determine the cause of the swelling, you need to consult a doctor. The instructions that the specialist follows for conducting diagnostic studies include pharyngoscopy and laryngoscopy - procedures necessary to examine the throat and assess the degree of swelling.
Clinical manifestations
Any reason why your throat hurts and is swollen has its own characteristic symptoms. In order to understand what was the impetus for the appearance of this symptom, you need to take a more specific look at all possible situations.
So:
- Throat burns are dangerous injuries that damage the mucous membrane of the throat. A burn can occur under the influence of hot food or drinks, chemicals, and is often accompanied by a burn not only of the throat, but also of the mouth and esophagus. Most often, burns occur at home, during suicide attempts, in production, and during self-medication. It is not uncommon for young children to find household chemicals, for example, for clearing clogs or ordinary vinegar, and drink it.
Burns are accompanied by increased salivation, nausea and vomiting, increased body temperature, and a burning sensation in the throat. In addition, with a burn, the throat hurts and is swollen; with chemical burns, there is a specific odor from the mouth; in severe cases, it can lead to a state of shock.
Depending on the degree of the burn, bubbles may form on the mucous membrane, covered with grayish films, which, when bursting, leave behind scars; or the tissue affected by the burn dies, with the formation of scabs and ulcers. After these elements heal, scars remain in their place, interfering with the normal functioning of the larynx, pharynx and esophagus.
- Foreign bodies quite often pose a serious threat to human life. Most often they occur in young children; due to their age, children can swallow small objects or toys, which can cause complete or partial obstruction of the airways.
The origin of the foreign body plays an important role in the manifestation of symptoms, for example, if it is a bone, needle, or other object with sharp protrusions, it can penetrate the mucous membranes, as a result of which during diagnosis it will be noticeable that the throat is swollen inside, and a reflex cough, occurring in such cases, can aggravate the condition by moving the foreign object deeper into the tissue.
In addition, shortness of breath, hoarseness or aphonia (loss of sonority), pain, panic and fear may occur, and in severe cases, cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes in the area of the nasolabial triangle and laryngeal stenosis.
Important! Laryngeal stenosis is an extremely serious condition that requires immediate attention without delay, otherwise it can lead to asphyxia, loss of consciousness and death.
- Angioedema (Quincke's edema) is one of the most severe reactions of the body to the action of allergens. An allergic reaction can occur to pollen, lint, dust or wool, chemicals and cosmetics, household hygiene products or food. This condition develops acutely and unpredictably, causing swelling of the skin, mucous membranes and subcutaneous tissue.
With Quincke's edema, you may notice that the throat is swollen outside and inside, and occasionally the arms and legs swell. Pallor of the skin appears in the area of swollen tissues, it becomes difficult to breathe, hoarseness is noticeable in the voice, dark red spots are visualized on the body, causing itching and merging with each other.
In addition, there is a rough and barking cough, anxiety increases, and in severe cases of edema, narrowing of the lumen of the pharynx, loss of consciousness and suffocation are possible.
Important! In case of angioedema, it is extremely important to react quickly by calling a specialized team and providing the victim with all possible assistance.
- If the throat is swollen on one side, you can judge a sore throat . The disease develops acutely, under the influence of viruses or bacteria. One or both tonsils may be involved in the pathological process. A sore throat is accompanied by high body temperature, sudden chills and fever, weakness, and you may notice that your throat is swollen and sore, especially when swallowing. Depending on the form of the disease, purulent films, small whitish dots or plugs may form on the tonsils. If the sore throat is viral in nature, then a sore throat is accompanied by a runny nose, cough, and in some cases conjunctivitis.
- Laryngitis is an inflammatory process concentrated in the larynx. The disease occurs when the ligaments are overstrained, hypothermia, or against the background of viral and infectious diseases.
If laryngitis occurs in a diffuse form, the mucous membrane is sharply hyperemic, swelling is more pronounced in the folds of the vestibule, and the inflamed vessels bleed. In isolated form, the process is concentrated in one place, for example, it can be noted that the throat is swollen on the left side and in this place it is hyperemic.
Laryngitis is accompanied by a slight rise in temperature, or proceeds without it at all; changes in voice, headache, and dry cough are noted, which over time turns into a wet one. In addition, with laryngitis, spasm or swelling of the throat is possible, which causes difficulty breathing and sometimes suffocation (see Conditions in which choking is observed in the throat and their classification).
- Diphtheria is an acute infectious disease that causes an inflammatory process in the area where the pathogen has settled. Previously, it was believed that only children were affected by this disease, but recently an increase in diphtheria has been noticed in people under 40 years of age. Diphtheria can be complicated or uncomplicated and occur in the following forms:
- non-toxic (in vaccinated patients);
- subtoxic (with moderate intoxication);
- toxic (severe intoxication and swelling of the neck);
- hemorrhagic (severe intoxication, bleeding, death);
- hypertoxic (fulminant intoxication, death after 2-3 days).
The disease is accompanied by sore throat and difficulty swallowing, sore throat, coughing, redness and sore throat. A couple of days after the onset of the disease, grayish fibrinous films are visualized at the site of entry of the pathogen, which are difficult to separate, and when trying to remove them, they cause bleeding.
The throat is swollen; in more severe cases of the disease, you may notice that the outside of the throat is swollen, so much so that in some cases the swelling can reach the collarbone. In addition, with diphtheria there is a feeling of weakness and general malaise, body temperature rises to 40 ° C, drowsiness, headache, pallor and tachycardia are present.
- Scarlet fever was also previously considered an exclusively childhood infectious disease, but very often adults also suffer from it. The causative agent of scarlet fever is beta-hemolytic streptococcus, which belongs to group A. Scarlet fever can be contracted through nutrition, household or airborne transmission. The disease occurs in one of the possible forms:
- erased;
- toxic-septic;
- extrabuccal.
In more than half of the cases in adults, the disease is diagnosed in an erased or toxic-septic form. With scarlet fever, there are bright red rashes on the body, a sore throat, you can also notice that the inside of the throat is swollen and it becomes painful to swallow.
Blood pressure decreases, extremities become cold, patients feel weak and are in a pre-fainting state.
Note! The toxic-septic form of scarlet fever can lead to complications such as myocarditis or endocarditis, pneumonia, arthritis, otitis media or pyelonephritis.
If your throat is swollen on one side, this may be a manifestation of a sore throat or an allergic reaction.
Causes of a swollen throat
In case of symptomatic recurrence of edema, it is necessary to carry out a detailed diagnosis of the patient’s condition and keep at hand methods for quickly eliminating the pathology.
Among the main causes of impairment in adults are the following:
- oral diseases;
- purulent sore throat;
- phlegmous laryngitis;
- epiglottis abscess;
- purulent inflammation of the root of the uvula;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- kidney and liver diseases, including cirrhosis;
- allergic reactions;
- problems with blood circulation in the larynx area;
- pathological proliferation of lymphatic tissue;
- injuries to the throat, back wall and surrounding areas;
- cancerous tumors;
- postoperative period, especially in cases where a tube was inserted;
- infectious diseases;
- severe hypothermia of the patient;
- poisoning with toxic substances.
In a child, the cause of laryngeal edema can be the same factors as in adult patients. But in children, such conditions are much more acute, complex and dangerous.
If swelling begins, you should immediately call emergency help.
Due to the characteristics of the respiratory system, children have weakness in the muscles of the respiratory organs, their passage is very narrow, and the mucous membrane is sensitive to the slightest irritants.
With a slight swelling of 1 mm, the clearance in the larynx is reduced by half, which can lead to shortness of breath and the inability to breathe at all.
There may be several reasons for this disorder, including infections, ingestion of hot foods, injuries, allergies, and angioedema.
Painful swallowing and sore throat - infections
painful to swallow, chickenpox
During infections, the throat hurts and the temperature rises.
Listed below are typical diseases with these symptoms.
1. Acute pharyngitis.
Accompanied by malaise, weakness, swelling, dryness. Enlarged lymph nodes. When they are palpated, pain is felt. The acute form of the disease is accompanied by swelling. It forms in the area of the posterior wall of the larynx.
2. Sore throat.
A typical cause is an advanced cold. It is characterized by severe intoxication of the body. In the vast majority of cases, the patient's tonsils are covered with plaque. There is also a high temperature and general weakness. Headaches and muscle pains significantly complicate the well-being of a sick person.
3. Diphtheria.
The causative agent is Loeffler's bacillus. There is a noticeable enlargement of the tonsils and the appearance of a gray coating on them. During the disease, the tonsils become smooth and dense. Removing plaque leads to pinpoint bleeding.
4. Chickenpox.
A typical symptom is blisters on the mucous membrane. With this disease, the temperature may rise sharply. There will be severe pain even when swallowing saliva. Accompanied by hoarseness, cough, itching of the skin.
5. Other cases.
In addition to the listed common diseases, a sore throat can be a kind of warning from the body about problems with the digestive tract, the development of oncology, pathological changes in the thyroid gland (compression of the trachea), sexually transmitted diseases
Allergic edema
Allergic swelling of the larynx is caused by a number of factors to which the human body reacts negatively. This could be certain food products, household chemicals, street or house dust, medicines, and others.
The provoking factor that caused the development of allergic laryngeal edema can be identified during examination of the patient. If the irritant enters the body through the respiratory system, stenosis will affect the area of the larynx and epiglottic cartilage. If the esophagus has become the conductive path, then the swelling is localized among the arytenoid cartilages.
How dangerous the manifestations of stenosis will be depends on whether the airway lumen is severely narrowed. At the first stage, the beginning symptoms of allergic edema are noticeable - it is difficult for the patient to inhale and exhale, the time interval between these phases is significantly reduced, breathing becomes deeper, with elements of shortness of breath, pulse and heart rate decrease. Upon examination, swelling of the tonsils, uvula and soft palate is recorded.
Symptoms of throat diseases
If first aid measures are not taken at the initial stage of allergic stenosis, subsequent symptoms will manifest themselves much more intensely:
- pain when swallowing saliva;
- hoarseness of voice;
- lack of oxygen;
- suffocation;
- feeling as if a foreign object is stuck in the throat;
- barking, rough cough;
- pale skin, which becomes bluish as stenosis progresses;
- sweating and chills, possibly a slight increase in temperature;
- anxiety.
First aid for this type of stenosis should include intravenous administration of Atropine and magnesium sulfate. More qualified assistance will be provided by the arriving medical team, which must be called immediately when symptoms of stenosis appear. However, before the ambulance arrives, it is necessary to limit the patient’s contact with the irritant and try to restore his respiratory function.
Often allergic stenosis of the throat leads to the development of severe swelling, called Quincke's edema.
The allergic form of stenosis is very dangerous, especially in children, since the swelling grows quickly, one might say instantly, and such a condition threatens the health and life of the patient.
First aid for allergic stenosis
Every person prone to allergic reactions, as well as his loved ones, should be aware of the urgent measures that need to be taken in case of stenosis. First aid for swelling of the larynx includes, firstly, immediately calling an ambulance.
Secondly, the patient needs to rinse the stomach if there is a suspicion that the throat is swollen after eating any irritating food. After this, it is recommended to give the patient Smecta, activated carbon or another similar drug.
If stenosis occurs as a result of an insect bite, you need to remove the sting from the skin or suck out the poison. The patient should be placed on a hard surface, with his feet above head level. Ice is applied to the victim’s head and neck, clothing is unfastened and cool air is provided into the room.
Antiallergic tablets that can be given to the patient are Tavegil, Suprastin, Zyrtec. The patient is also provided with plenty of fluids; if the condition is satisfactory, a warm foot bath can be taken without any additives. If the condition is critical, then the patient can be given an injection of Dexamethasone or Prednisolone - glucocorticosteroid drugs.
It’s clear what to do before the doctors arrive. Severe manifestations of allergic stenosis should be treated in a hospital, where the patient will be shown the following medications:
- calcium gluconate in the form of a solution for infusion;
- ascorbic acid and glucose intravenously;
- Veroshpiron;
- Furosemide;
- Bumetanide.
If there is no effect of drug therapy, the patient is intubated and then tracheotomy. The throat is cut at the site of swelling, and a cannula is inserted through which the respiratory function is carried out.
How to treat laryngitis
To prevent the development of laryngospasm caused by severe edema, laryngitis must be treated as soon as the first symptoms appear. A doctor should prescribe therapy after conducting a complete diagnosis.
Pharmacy products
Treatment of laryngitis is carried out comprehensively, including the following groups of drugs:
- Antibiotics. They are used strictly according to indications, for laboratory-confirmed bacterial infection (Ceftriaxone, Augmentin, Ampicillin).
- Antihistamines. They relieve swelling and prevent its further development (Eden, Zodak, Suprastin).
- Anti-inflammatory. Reduce the activity of the inflammatory process, improve the regeneration of damaged tissues (Erespal, Inspiron).
- Antipyretic. They lower body temperature and improve overall well-being (Paracetamol, Eferalgan, Nurofen).
- Mucolytics. They thin sputum and improve drainage function (Ambroxol, Lazolvan).
In addition to these means, it is effective to carry out inhalations with a nebulizer with saline solution and mineral waters. With the permission of the doctor, if there is a tendency to laryngospasms, the hormonal drug Ventolin is administered by inhalation.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies in the fight against laryngitis are used only as adjuvant therapy to medications.
Good rinses for laryngitis. The following solutions are used for this procedure:
- soda-salt solution with added iodine;
- herbal decoctions;
- juices and tinctures of plants;
- apiproducts.
Drinking plenty of warm drinks with the addition of honey, lemon, and raspberries also helps in the treatment of laryngitis.
Steam inhalations will also be effective. To carry them out, decoctions of medicinal herbs, essential oils, and decoctions of root vegetables are used.
The easiest way for inhalation at home: boil the potatoes, cool slightly, add a spoonful of soda, cover with a towel, breathe in the steam for 10 minutes. This procedure for swelling of the larynx can only be performed with the permission of a doctor, so as not to harm the body.
Herbal decoctions.