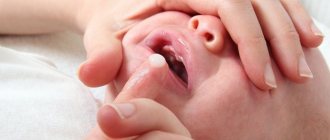
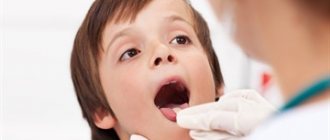
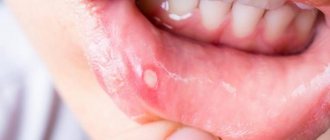
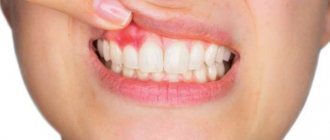
Fungus in the throat belongs to a number of infectious and inflammatory processes that occur like a sore throat. The pathology has similar symptoms to bacterial infection of the tonsils, and is also accompanied by pain in the larynx, fever and the formation of plaque on the mucous membrane.
The problem occurs not only in adults, but also in children, and fungal infections in the oropharynx have become increasingly common in recent years.
In order to effectively cure fungus in the throat and respiratory tract, timely diagnosis is necessary to differentiate pharyngomycosis from similar diseases (bacterial tonsillitis of the lacunar and ulcerative-necrotic type, diphtheria).
Fungal throat disease - causes
What infections can be in a person's throat? Viral, bacterial and fungal are the main etiologies of damage to the laryngeal mucosa.
What does it look like
This particular fungal throat infection is caused by the yeast-like pathogen Candida albicans in 93% of cases. In the remaining 5-7%, the development of pharyngomycosis is facilitated by mold mycotic pathogens.
It has been established that yeast-like fungi live in the oral cavity of every person, but for the time being do not cause the development of inflammation. The main reason for the activation of a pathogenic pathogen is considered to be a decrease in the body’s immune defense as a result of a number of negative factors:
- after antibiotics (as a result of their long-term uncontrolled use), the use of glucocorticosteroids, or undergoing a course of chemotherapy;
- in the presence of concomitant diseases - diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, malignant neoplasms, thyroid dysfunction, obesity, pathologies of the hematopoietic system;
- injuries of the laryngeal mucosa;
- constant wearing of dentures and poor quality care for them.
When several factors are combined, such an infection recurs up to 10 times during the year, especially if the patient does not follow medical recommendations or completely ignores the signs of pharyngomycosis.
Candidiasis of the oral mucosa and pharynx
Candidiasis is a fungal disease of the skin, mucous membranes of the mouth, pharynx and internal organs, caused by a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida albicans. The development of candidiasis is promoted by hypoparathyroidism, dysfunction of the liver, pancreas, carbohydrate metabolism, as well as intestinal dysbiosis, which occurs most often during long-term treatment with antibiotics and corticosteroids. Often the disease occurs due to traumatic damage to the mucous membrane and atmospheric occupational hazards.
Candidiasis (yeast stomatitis, or thrush) most often develops in infants and the elderly, especially those weakened by chronic, severe diseases. First, dryness of the oral mucosa appears, then multiple pinpoint whitish plaques on the palate, tongue, and cheeks. When they merge, large whitish-gray films are formed, which are later easily separated; beneath them, superficial opalescent-looking (“dry”) erosions are found. There are several forms of candidiasis of the oral cavity and pharynx.
Acute form
- acute pseudomembranous candidiasis (thrush, soormycosis), the most common form of this disease. It manifests itself in the formation of white or bluish-white spots on the oral mucosa.
Chronic hyperplastic candidiasis
characterized by the appearance of tightly fused plaques on the hyperemic mucous membrane of the oral cavity and pharynx. Often the plaque is located on the back of the tongue in an area typical of rhomboid glossitis. Patients feel dryness in the oral cavity, a constant desire to moisten the mouth, and hyposalivation is also noted, aggravating the dryness of the oral cavity.
Chronic atrophic candidiasis
characterized by atrophy of the papillae on the back of the tongue or manifests itself in the form of atrophic rhomboid glossitis.
Candidal tonsillitis
characterized by the appearance of white shiny “plugs” in the depths of the follicles of the palatine tonsils. The tonsils are hyperemic and painless. This form of candidiasis usually has a long course, body temperature does not rise, and there is no pain when swallowing.
Chronic generalized (granulomatous) candidiasis
usually occurs in children with an immunodeficiency state and insufficiency of the parathyroid glands.
It manifests itself, as a rule, in early childhood in the form of thrush, candidal cheilitis, as well as damage to the larynx, trachea, bronchi, small focal pneumonia, and sometimes cavities
.
Treatment
consists in prescribing antifungal agents (nystatin, levorin, nizoral, etc.). For chronic candidiasis, immunotherapy is performed. Patients receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics and corticosteroids for a long time are recommended to take nystatin to prevent candidiasis. Locally, lubrication of the affected areas with a solution of mycostatin on glycerin is prescribed.
Forecast
, as a rule, favorable. Relapses are possible.
Symptoms
Almost all infections of the throat and larynx occur with severe pain, but they require different treatments. It is necessary to focus not only on the accompanying symptoms, but also to identify the specific causative agent of the disease in order to prevent relapse and remove the fungus from the mucous membrane.
Pharyngomycosis, or fungal tonsillitis, is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- irritation and dryness in the affected area, a tearing unproductive cough;
- severe pain - it is aggravated by eating food, especially salty and spicy dishes (the discomfort can be so strong that it radiates to the jaw and neck);
- enlargement of neighboring lymph nodes, their pain during palpation;
- an increase in temperature to 37-37.5 ° C against the background of headaches, weakness, aches in muscles and joints;
- damage to the corners of the mouth with the formation of painful cracks, the development of glossitis and cheilitis - the edges of the lips are covered with fungal plaque, the person cannot open his mouth wide;
- candidiasis on the tonsils, which spreads to neighboring areas - tongue, cheeks, trachea and esophagus.
1
Candida Albicans is a yeast fungus, which is why the coating on the mucous membrane is cheesy in nature. It is easily removed from the surface of the tonsils, and inflamed and swollen tissue is visible below.
2
The affected areas may ulcerate and bleed slightly. If the inflammation is caused by mold, you will not be able to remove the plaque from the mucous membrane on your own. It has a yellowish tint and is similar in texture to diphtheria.
3
Acute fungal infection is localized on the tonsils, but can spread to neighboring areas, causing maximum discomfort with pain and hyperthermia. But chronic fungi do not cause obvious symptoms, being limited to the location of a small amount of plaque on the posterior laryngeal wall.
Symptoms and signs
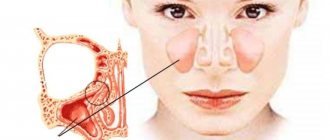
If a fungus appears in the nose, then the following symptoms are distinguished:
- severe itching. It irritates the nasal mucosa and causes swelling. Itching intensifies when the patient is in a dry room, as well as when taking vasoconstrictor drops;
- sneezing that doesn't stop for three weeks. The reason for this is a large amount of accumulated mucus in the sinuses;
- nasal discharge of different shades and thickness. Unlike a viral infection, the discharge does not stop, but only increases and produces an unpleasant, pungent odor;
- nasal congestion and swelling. Nasal drops and sprays only temporarily relieve painful symptoms. Swelling of the nasopharynx threatens a lack of oxygen. The patient becomes irritable;
- headache.
There are several types of fungus in the nasal cavity and each has its own symptoms:
- Staphylococcus aureus. The disease begins with a common runny nose. Nasal discharge takes on a greenish-yellow hue with the presence of pus. Ulcers appear in the nasal passage, and the patient ceases to smell. The voice becomes hoarse. The patient finds it difficult to breathe, so he often inhales oxygen through his mouth. The body temperature rises sharply, which leads to complications: an inflammatory process of the larynx or bronchitis begins.
- Rhinosporidiosis. The infection is caused by fungi that live in water and air. The patient complains of headaches and mucus discharge from the nose. Bleeding from the nasopharynx is possible. As a result, polyps grow inside the cavity, which interfere with normal breathing.
- Candidiasis. Discharge from the nose resembles a curd mass with an unpleasant odor. The patient experiences discomfort due to severe itching and burning in his cavity. Infection occurs through airborne droplets, as well as due to non-compliance with the usual rules of personal hygiene.
- Histoplasmosis. Characteristic signs: runny nose and itching inside the nose; the appearance of wounds and ulcers that constantly ooze.
- Aspergillosis. The disease occurs in people who work in dusty areas. The disease is manifested by congestion in one sinus, where a fungal pea appears, which may not bother you for a long time. Symptoms: dizziness, feeling of suffocation, nosebleeds, mucous discharge.
Fungi in a child's throat
If a fungus appears on a child’s tonsils, parents may not immediately notice the problem. Symptoms depend on the severity of the infectious process, and they can easily be confused with signs of another disease, such as ARVI.
The child has
A yeast-like fungus that causes a non-productive cough initially resembles bronchitis or laryngitis. If the baby can speak, then he complains of dryness and soreness in the larynx, pain while eating and drinking.
If an adult looks into a child’s throat, he will see swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. And with advanced inflammation, the entire back wall, including the tonsils, will be covered with a cheesy coating.
There may be no temperature, and the baby’s general condition depends on the degree of pain.
The reasons that cause fungi in the throat in the form of inflammation in children, in addition to those that provoke pharyngomycosis in adults:
- unbalanced diet with a lack of vitamins and nutrients;
- violation of hygiene rules - in infants the fungus enters the mouth through dirty nipples during feeding, in older children through shared household items with a family member already affected by the Candida microbe;
- decreased immunity as a result of birth trauma, prematurity, and the presence of congenital defects;
- diseases of the endocrine system and severe, long-term infections.
If parents do not pay attention to the child’s complaints for a long time or do not properly treat him at home, mycotic organisms affect the respiratory tract and internal organs.
What other fungal infections can affect the throat?
Not only candida can affect the mucous membrane of the oropharynx. There are many other fungal infections that can invade the tissues of the upper respiratory tract. At the same time, so-called “non-candidiasis” fungal infections are very rare, but they are much more dangerous than candidiasis. Let's look at some of them:
- Aspergillosis
There are more than 160 species of Aspergillus fungus, and 10 of them have been proven to be pathogenic to humans. Aspergillus is found in large quantities in the environment - soil, fallen leaves, rotting plants. The spores of these fungi are volatile, and people quite often inhale them while relaxing in nature. However, humanity has never encountered an epidemic of aspergillosis, and this proves that mycoses are opportunistic diseases that develop only in people with weakened immune systems. However, the prevalence of aspergillosis is increasing every year. Currently, aspergillosis ranks 2nd in the world in terms of prevalence among fungal infections (candidiasis ranks 1st).
Inhalation of Aspergillus spores can cause the fungus to grow in any part of the upper respiratory tract, from the mouth and sinuses to the trachea.
The disease is often confused with other acute respiratory infections - bacterial sinusitis, laryngitis, etc. In this case, the patient’s body temperature is slightly increased, and the sputum released during a runny nose or coughing has a green or black color and an unpleasant odor.
- Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is a systemic fungal disease that affects the skin and mucous membrane of the oropharynx, and then the lymphatic tissue and internal organs. As with aspergilosis, infection occurs by inhalation of spores in the soil. Blastomycosis of the larynx can occur in isolation or simultaneously with skin lesions. On the skin, blastomycosis appears as a red, papular rash over the entire body. The papules merge with each other and become covered with purulent crusts. If there is a rash on the skin, diagnosis is greatly simplified. The isolated form of blastomycosis of the larynx is often mistaken for other diseases - bacterial or viral laryngitis, etc.
- Cryptococcosis
Spores of the Cryptococcus fungus have been found in soil, rotting vegetables, the excrement of pigeons, canaries, budgerigars and other birds, and less commonly in the feces of cats, horses, and dogs (the animals do not get sick). Their inhalation leads to cryptococcosis, which can affect the mucous membranes of the upper and lower respiratory tract, as well as organs of the nervous system - the brain or spinal cord.
Cryptococcosis is an insidious infection; For a long time it can be asymptomatic. The disease begins to manifest itself gradually. Nodules, ulcers, and papillomas appear on the mucous membrane of the affected organ (pharynx, larynx, mouth, etc.). The disease progresses, and the ulcers deepen, destroying soft tissues (tonsils, mucous membrane, soft palate) and even bones. A characteristic sign of cryptococcosis is that the patient’s body temperature remains normal, regardless of the severity of the disease. Isolated mucosal cryptococcosis responds well to treatment.
It is worth noting that cryptococcosis of the throat is rarely primary; more often it appears as a result of the spread of infection from the lungs, brain or other internal organs.
- Histoplasmosis
Systemic mycosis caused by a fungus of the Histoplasma genus. Infection occurs by inhaling spores from the soil. First of all, the pharynx is affected, as well as the gums and palate. Lumpy, extensive ulcers appear on the mucous membrane. The infection may spread to the lower respiratory tract.
- Zygomycosis
Mucor and Rhizopus are the most common representatives of zygomycetes. These fungi are ubiquitous - they are found in soil and decomposing food. In healthy people, spores of these fungi are present in the nasopharynx almost constantly, without causing illness. If a person becomes ill with zygomycosis, he must be tested for HIV infection (it is precisely those with immunodeficiency who often suffer from zygomycosis). The disease is difficult. When the pharynx is affected, soft tissues are destroyed, then bones.
Fungal diseases of the throat are dangerous but rare diseases. It is worth emphasizing that they develop only in individuals with severely weakened immune systems.
Why is it dangerous?
Thrush is a disease that should not be underestimated. With constant inflammation of the larynx and lack of adequate therapy, the fungi become overly active and aggressive.
Cells of the affected mucosa begin to die, forming ulcers on the surface into which pathogenic microbes easily penetrate. This is fraught with the accumulation of secondary infection, suppuration and the formation of an abscess.
The infection can also spread to the respiratory organs - trachea, bronchi and lungs, resulting in a generalized form of inflammation with symptoms of sepsis.
Attention
This complication is especially dangerous for patients with a critical decrease in the body’s defenses. In case of a generalized infection of the respiratory system, the patient must be urgently hospitalized.
And the least dangerous, but unpleasant consequence is considered to be relapses of fungal infections of the throat. Therefore, it is important not only to eliminate the pronounced symptoms of candidiasis, but also to increase immunity to prevent the reactivation of mycotic pathogens of thrush.
Symptoms
The main symptoms of fungus in the throat:
- Painful sensations in the throat, worse when swallowing,
- Hyperemia of the throat mucosa,
- Oral hypersensitivity,
- White cheesy discharge on the surface of the mucous membrane due to candidiasis,
- Yellow coating on the tongue and back of the throat in the presence of mold fungi,
- Cracks, blisters, small ulcers and erosions in the throat,
- Swelling of the nasopharynx and tonsils,
- Intoxication - fever, weakness, loss of appetite.
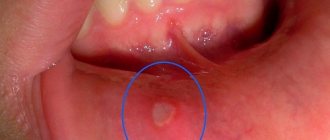
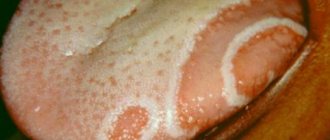
photo: manifestation of fungus in the throat
A curdled coating on the mucous membrane is a hallmark of a fungus in the throat. Discharge accumulates and rises above the surface of the tonsils, posterior wall of the pharynx, tongue, and palatine arches. White dots and grains are clearly visible on the bright red inflamed mucous membrane. The discharge may take the form of films or plaques that tend to merge. The plaque is removed with great difficulty, and erosions and ulcers form underneath. In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, the infection spreads lower and affects the esophagus, organs of the respiratory and digestive systems.
In a child, the clinical manifestations of candidiasis are much more pronounced. Intoxication and sore throat predominate. After removing the plaque, wounds form on the mucous membrane, from which droplets of blood are released.
When the palatine, pharyngeal or lingual tonsils are involved in the infectious process, fungal tonsillitis develops. The pharyngeal ring turns red and is covered with a white coating on top, spreading to the cheeks and tongue. In this case, the clinical signs are slightly expressed. Acute pain and intoxication are often absent. Patients experience discomfort and discomfort in the throat, malaise, headache, lymphadenitis. Children become moody and restless due to a sore throat.
Throat candidiasis is usually combined with candidal stomatitis, glossitis, and cheilitis. A complication of the disease is secondary infection, leading to the formation of ulcers and abscesses. In persons with weakened immunity, generalization of infection with the development of sepsis is possible.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact if I suspect a fungal infection of the larynx? The child should be shown to the pediatrician, the adult should visit the local therapist.
1
Next, the patient is referred to an ENT doctor, who examines the throat and scrapes the surface of the mucous membrane. The patient donates blood and urine for laboratory analysis, which clarifies the presence of inflammation in the body.
2
A smear examination allows you to identify mycotic cells and fungal spores (yeast or mold). The cultural method takes longer, but allows you to accurately identify the type of pathogen and assess its resistance to antibacterial agents.
3
The smear is also examined using a screening method; the patient may be offered to donate blood for PCR diagnostics, which will 100% confirm the fungal etiology of the disease.
4
To find out the reason why the Candida microbe was activated in the throat, especially if this is not the first relapse of the disease, consultation with an immunologist and endocrinologist is necessary.
5
Often, during such examinations, adult patients are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, hepatitis and other concomitant diseases that cause fungal infection of the larynx.
Throat fungus: diagnosis
Treatment of fungal throat diseases is a complex process that must begin with a correct and accurate diagnosis. A correct diagnosis is also important because the symptoms of the disease are similar to viral and bacterial infections. The drugs prescribed in both cases are most often ineffective against fungal microorganisms.
Diagnostics includes the following procedures:
- examination by an otolaryngologist. The doctor studies the patient's medical history, collects an anamnesis, and then examines the oral cavity and pharynx. The visual diagnostic method allows you to identify swelling, redness, the presence of purulent plaque or infiltration;
- analysis of a smear from the throat and other parts of the oral cavity. The doctor takes the biological material, places it on a sterile surface and examines it under a microscope. If necessary, a cultural examination is carried out when the smear is placed in a nutrient medium. However, this method takes about 2 weeks and is prescribed only when absolutely necessary;
- general research to identify the cause of the disease. The patient donates biological material - blood, urine, feces - for testing for HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, diabetes.
Diagnosis is important for many reasons. But first of all, to prescribe the correct treatment for throat fungus. We recommend not to self-medicate - such tactics can lead to complications.
How to treat throat fungus in an adult?
The doctor decides how to treat the yeast-like fungus Candida. Therapy is based on three points:
- mandatory withdrawal of antibiotics if they provoked activation of microbial flora, use of local and general antimycotic agents;
- restoration of full intestinal microflora - for this, probiotics and preparations based on live bacteria Bifidumbacterin, Linex, Hilak Forte, Lactobacterin, Bifiform are used;
- increasing immunity - the patient is prescribed Interferon or Viferon in a monthly course. Interferon acts in the nasopharynx, and Viferon is more convenient to use in the form of suppositories.
Be sure to gargle 4-6 times a day with antiseptic solutions. Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Rotokan, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and sage are suitable for this. For external treatment, Lugol, methylene blue solution, and powdered sugar are prescribed.
For severe pain in the larynx, antiseptics are recommended - Lizobact, Septolete, Strepsils, Hexoral, Kameton, Tantum Verde sprays. If the patient complains of body aches and discomfort caused by high fever, he is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs Nimesil, Ibufen, Nurofen, Paracetamol.
Drug therapy
Uncomplicated infection is treated as follows:
- The oral cavity is alkalized by repeated rinsing every day. To do this, use a 10% borax solution or a regular baking soda solution.
- The oral cavity is treated with an antifungal agent twice a day. Most often, “Amphotericin” is used for these purposes - a concentrate for preparing a solution that can destroy any fungal infections.
- Fungicidal medications (antimycotics) are prescribed for oral administration. Their active components penetrate the fungal cell and inhibit the development of the pathogenic microorganism. The choice of drug is made on the basis of bacteriological culture transcripts.
- To prevent bacterial complications, medications with antiseptic properties (Miramistin, Lugol's solution, Natamycin) are sprayed into the throat several times a day. Alternating them, you need to treat the back wall of the pharynx and rinse the tonsils.
- If the disease has become chronic, to prevent relapses, you need to take prophylactic antifungal drugs (the dosage is developed by the attending physician), multivitamin complexes, probiotics (Bifiform) and immunomodulators (Polyoxidonium).
In children, treatment of pharyngomycosis is carried out according to a different scheme. To treat the oral cavity, decoctions of oak bark or borax solutions are used. Among the medications prescribed, Pimafucin drops, Nizoral spray, Miramistin solution, Clotrimazole ointment are prescribed.
Traditional medicine in the fight against fungus in the throat
Some folk remedies help enhance the drug effect and reduce the drug load.
Even doctors often advise their patients to use:
- Decoctions of chamomile, sage and calendula for gargling. They help stop the inflammatory process, relieve swelling, which significantly alleviates the patient’s condition.
- Golden mustache juice. It can be dropped into the nose or used to prepare solutions for gargling. It has a pronounced antimicrobial effect.
- Lingonberry fruit drinks. Their use improves the functioning of the immune system.
- Pumpkin juice. It has antipyretic and tonic effects.
- Propolis infusion. The product has a pronounced anti-inflammatory and restorative effect.
When choosing folk remedies for the treatment of pharyngomycosis, it is important to remember that they can only be part of an auxiliary therapy. The basis of treatment for fungal infections should be medications.
If you have pharyngomycosis, you should not warm your throat, use warming alcohol compresses or steam inhalations. This can provoke fungal activity and the spread of infection. You should not choose products that contain yogurt, kefir and honey to treat the disease.
Doctors categorically prohibit all their patients from smoking, drinking alcohol, or eating foods that contain yeast and large amounts of sugar. The success of treatment largely depends on how strictly patients follow the instructions of the attending physician.
How to treat fungus in a child's throat?
In children, thrush less often becomes chronic, since parents immediately take the baby to the doctor and manage to start therapy on time. To cure laryngeal candidiasis in a child, local methods are usually sufficient:
- the use of antiseptic solutions for gargling if the child is over 3-4 years old and can gargle on his own;
- treating the affected areas with a soda solution (yeast-like fungi are afraid of an alkaline environment);
- identification and elimination of the main cause that caused candidiasis of the tonsils - strengthening the immune system, curing concomitant diseases;
- balanced diet high in vitamins and protein;
- maintaining hygiene when caring for infants.
You cannot use antibiotics yourself; they will not help eliminate the fungus, but will also worsen the child’s condition. When thrush transitions from acute to chronic form, the pediatrician will select systemic agents to stop the proliferation of yeast throughout the body.
Features of the treatment of fungal throat infections in children
After discovering a fungal infection in a child’s mouth, you cannot begin treatment on your own. All measures must be agreed with a doctor. After examining the baby, the specialist will prescribe treatment of the oropharyngeal mucosa with decoctions of medicinal herbs, solutions of baking soda or borax with glycerin. In addition, the child may be prescribed one of the following pharmaceutical drugs:
- Pimafucin (drops);
- Clotrimazole (ointment);
- Nizoral (spray);
- Tea tree oil;
- Miramistin (antiseptic solution).
Newborns with oropharyngeal thrush should not be weaned. The mother should treat the nipples and areolas with an antiseptic before each feeding. If the baby is bottle-fed, then all nipples and bottles should be thoroughly sterilized. For children of preschool and school age with oral thrush, spicy, sweet, sour and spicy foods are excluded from the diet. A gentle diet is needed to prevent irritation of the pharyngeal mucosa. Young patients are also recommended to drink plenty of fluids (herbal infusions, compotes, teas, still mineral water).
Antifungal throat spray
The use of drugs in the form of sprays has many advantages. Sprays act locally, immediately eliminating the cause of the disease, without penetrating into the general bloodstream and without having a systemic effect on the body.
The medicine is convenient to carry with you and use according to medical advice. In addition, preparations in the form of aerosols gently cleanse the mucous membranes and have an analgesic and disinfectant effect.
The best sprays for laryngeal mycosis:
- Angilex (Hexoral) – has an antifungal and antibacterial effect, relieves inflammation and pain, suppresses the growth and reproduction of yeast microorganisms;
- Inhalipt is a spray with a disinfecting, anti-inflammatory and fungicidal effect. The therapeutic effect is achieved due to the presence of mint and eucalyptus extracts in the medicine;
- Stopangin - slows down the proliferation of pathogenic flora on the laryngeal mucosa and reduces the level of inflammation due to the content of clove, menthol and mint oils;
- Lugol is a drug proven over the years that heals wounds and ulcers that often accompany infections of the mucous membrane. Eliminates pain, reduces body temperature, acts against inflammation.
Bioparox spray also has a powerful antimicrobial effect, including antifungal. But it can be used strictly on the recommendation of an otolaryngologist, if candidiasis is not caused by a history of antibiotic abuse.
Thrush in children
A person can live with Candida mushrooms without even knowing about their presence. They cannot be gotten rid of; they are found everywhere in the environment, including on human skin. Infection occurs through contact with various objects, soil, plants, and animals. In children, mycosis of the throat is more often observed, because they are more active, like to play in the sand, pick flowers, and pet animals. Children get their hands dirty faster and do not wash them promptly. This is one of the reasons why throat thrush or mycoses of other organs occur in young children, especially since their microflora is not stable and their immunity is not yet strong.
Medicines for throat fungus
A systemic antifungal drug should be prescribed by a doctor, since drugs of synthetic origin can cause side effects on the kidneys.
Remember
Long-term use of medications leads to complications, so candidal tonsillitis is treated with antimycotics for no longer than 10-14 days.
For this purpose, the following groups of means are used:
- polyenes - Nystatin, Amphotericin B. They destroy the cell membranes of fungi, causing their death;
- allylamines – Naftitin, Terbinofine. They have a powerful antifungal effect and allow you to quickly cope with the signs of thrush in the throat;
- azoles – Bifonazole, Mycospor. They stop the active reproduction of yeast and mold spores, preventing their further spread throughout the mucous membrane of the larynx, respiratory tract and nasopharynx.
The drug Fluconazole is effective in the treatment of yeast infections; it belongs to the group of triazoles. A similar substance contains tablets Flucostat, Mycoflucan, Fucis, Flucoside, Fungolon and others.
The drugs are well tolerated and rarely provoke allergic reactions. The dosage and duration of the course are determined by the attending physician.
Prevention
To avoid the appearance of fungus in the throat, it is important to strengthen the body's protective functions. If you adhere to a healthy lifestyle and avoid hypothermia, the risk of contracting pharyngomycosis will be much lower. Prevention of throat fungus includes the following measures:
- Maintaining general hygiene. In case of infection with a fungus, the patient must be isolated from relatives who live with him, so as not to transmit the infection to them.
- Timely detection and treatment of sinusitis, caries, purulent tissue damage.
- Hardening the body. Rubdowns, sports, contrast showers, dousing with water, visiting the pool, etc. are suitable for this. It is important to note that hardening procedures should not be carried out during exacerbation of fungal tonsillitis.
- Maintain personal hygiene. Each family member should have separate dishes, slippers, towels and toiletries.
- Balanced diet. The diet should be compiled in accordance with age and individual characteristics. A person must receive the right amount of proteins, carbohydrates and fats so that all body systems function normally.
- Strengthening the immune system. Immunomodulators (Bronchomunal, Ribomunil), vitamins, drugs for stimulating cellular and humoral immunity (Licopid, Interferon, Timalin), and probiotics are suitable for this.
Treatment with folk remedies
It’s worth mentioning right away that it is impossible to completely cure pharyngomycosis using folk remedies. But they alleviate the symptoms of the disease by removing toxins and antibodies of yeast microbes that poison the body from mucosal tissues.
Parsley, calendula, bird cherry and lingonberry have a pronounced antimycotic effect - decoctions and tinctures are prepared from the plants, which are taken orally and used for rinsing.
Here are a few recipes that are effective in relieving the symptoms of laryngeal thrush:
1
St. John's wort grass and lingonberry leaves are crushed, taking 5 grams each. raw materials, pour a glass of boiling water and leave for several hours. After infusion, rinse with the composition 3 to 5 times a day;
2
dried calendula flowers and mint leaves are mixed in equal parts (a tablespoon each) and poured with 1.5 glasses of water. After boiling for 3-5 minutes, cool the composition and strain it, using it to rinse the pharyngeal mucosa three times a day;
3
20 gr. parsley (roots along with leaves) pour 0.5 liters of water and boil for several minutes over low heat. Gargle with a warm solution four times a day for a course of 7-10 days.
Regular use of these compositions helps relieve inflammation, disinfects mucosal tissue, cleanses of white loose plaque and heals. In addition, you can take freshly squeezed lingonberry juices internally, make fruit drinks from the berries and cook compotes. This remedy strengthens the immune system and fights the cause of the disease from the inside.
Treatment
Professional antimycotic therapy can cure a patient in an average of 2-3 weeks. In severe pathogenesis, surgical removal of the affected mucosa and endoscopic sanitation of the nasal sinuses are performed.
To avoid relapses, a re-examination is scheduled after 4 months, but no later than six months.
Medicines
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, treatment takes place at home. Local drops and ointments and nasal spray are prescribed.
Antifungal drugs include a group of azoles that destroy fungal cells: Intraconazole, Fluconazole, Bifonazole, Clotrimazole. If Staphylococcus aureus is detected, Nystatin and Levorin are used. Sinuses affected by histoplasmosis and mucormycosis are sanitized with a solution of the drug Amphotericin.
To neutralize an allergic reaction, desensitizers are prescribed, to facilitate breathing - vasoconstrictor aerosols, and to increase the body's resistance - vitamin complexes.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=eH8GbkJLKhk
Traditional methods
The combination of pharmacy and home antifungal remedies speeds up recovery.
- It is useful to rinse the sinuses with herbal decoctions. Steam a tablespoon of dry string herb, oak bark, chamomile flowers, rose hips, calendula (optional) with a glass of boiling water, leave for 3 hours. Use the filtered liquid to rinse your nose 3-4 times a day.
- Freshly squeezed carrot or beet juices work as antifungal nasal drops; they are instilled up to 4 times a day.
- If you make oil applications daily, the peeling of crusts and wound healing will accelerate. Cotton or gauze wicks are dipped in sea buckthorn oil, a mixture of tea tree and olive oils. Inject into each nostril and hold for half an hour.
- To disinfect and relieve swelling, rinse the nasopharynx with a weak soda or saline solution (a quarter teaspoon of dry ingredient per glass of water). Each type of rinse can be alternated. 5-6 sessions are recommended. Treatment of the nasal sinuses with a solution of the same amount of sea salt and a couple of drops of iodine works well. The liquid is drawn into a small rubber bulb or syringe (injected into the cavity without a needle).
Diet and prevention
Following a diet during the treatment of laryngeal candidiasis is an important point in complex therapy. Proper nutrition speeds up the process of removing toxins and decay products of pathogenic microbes from the body, improves immunity and makes the patient feel better. The following foods are allowed during therapy:
- lean meat and fish;
- porridges and cereal soups with lean broth;
- fruits;
- chicken eggs;
- bell peppers, onions and garlic, cucumbers, cabbage.
Alcoholic beverages, fermented milk products, sauerkraut, baked goods, sweets, honey, rice and barley cereals are prohibited.
You should limit the amount of table salt and avoid sugar altogether. Bakery products are also prohibited because yeast is used in their preparation.
Preventive measures for throat candidiasis include:
- refusal of unnecessary use of antibiotics and corticosteroids (monitoring the condition of the throat mucosa during drug treatment);
- maintaining oral hygiene - the paste should include antimicrobial components, after eating you should rinse the mouth;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases (gastrointestinal tract, thyroid gland, tuberculosis, bacterial infections);
- increasing local and general immunity.
To maintain a healthy immune system, you should walk in the fresh air more often, provide a diet with sufficient vitamins, and follow a daily routine. You should also avoid excessive physical exertion, hypothermia and frequent viral infections.
Varieties
For a fungus to affect the oral cavity, several factors must contribute to this. Based on the general condition of the fungus carrier, candidiasis of the oral mucosa has a different course and localization.
Thrush most often occurs in infants and older people. When the body is weakened by frequent colds, the patient has chronic diseases, then the immune forces are not able to resist pathogenic microorganisms - candidiasis affects the oral cavity.
Oropharyngeal thrush
Oropharyngeal candidiasis usually occurs after taking antibiotics. If dosages are not observed or treatment is prolonged, the beneficial microflora of the oral cavity is suppressed under the influence of medications, and pathogenic microorganisms take its place. That is why patients who are treated with aggressive therapy become carriers of the oropharyngeal type of the disease.
If thrush is in the initial stages of development, identifying it is extremely problematic. There are no pronounced signs; areas covered with a gray-white coating do not exceed 3 mm.
Treatment in this case is not required. As soon as the patient stops taking antibacterial drugs, the body's immune forces will allow you to get rid of thrush. In case of severe disease, it is necessary to take antifungal drugs, use antiseptics to suppress foci of fungal infection, and adhere to a special diet.
Mycosis of the gums
Young mothers often find a white coating in the mouth of newborns, implying that this is the remains of curdled milk. In fact, in most cases, this symptom indicates gum candidiasis. This is a common occurrence associated with infection of the fetus by Candida fungi during pregnancy or during childbirth.
Adults can also suffer from gum candidiasis. Mycosis occurs due to poor oral hygiene, smoking or taking oral contraceptives. People with dentures also experience discomfort from thrush.
Damage to the corners of the mouth
The corners of the mouth are rarely affected by candida fungus. A person notices how small cracks form in the affected area, which begin to grow over time.
Sometimes painful areas become covered with a white coating. As the fungal infection develops, when opening the mouth, the cracks bleed and the patient experiences discomfort. Treatment is prescribed by a highly qualified specialist. Often, candidiasis of the corners of the mouth is treated with ointments and creams (Nystatin, Fluconazole). The doctor may also recommend taking vitamins and immunostimulants.
FAQ
Patients with symptoms of throat candidiasis often ask otolaryngologists and therapists the following questions:
What should you not do when you are sick?
During the period of treatment for laryngeal thrush, you should not overcool, experience physical exertion, or use antibacterial drugs. You should also give up alcohol and smoking, follow a diet and careful oral hygiene.
Fungal tonsillitis: Treatment of the disease
Any type of sore throat requires a special approach to treatment. Since fungal tonsillitis appears as a result of an imbalance in the species composition of the microflora, the greatest attention should be paid to this particular reason. When fungi begin to develop due to the use of antibiotics, it is necessary to include antifungal drugs (Nystatin or Fluconazole), adjust the treatment regimen, completely cancel or change antibacterial drugs, and change dosages.
To replenish vitamins in the body, the patient’s daily menu must include vegetables and fruits, protein foods, and fermented milk products. Proper treatment of this disease includes the following methods:
- treatment of the mouth and throat with antiseptic agents (lubrication, irrigation, rinsing);
- use of antimycotics;
- taking vitamin complexes;
- use of immunostimulating drugs;
- in case of bacterial infection, use of antibacterial agents;
- physiotherapeutic methods of treatment, for example, ultraviolet irradiation of the sky and tonsils.
Afterwards, to form a healthy microflora in the patient’s body, he is certainly prescribed probiotics . This is a very important step during treatment and prevents the appearance of chronic candidiasis and relapse of the disease.
Is it necessary to lower the temperature?
With fungal sore throat, an increase in body temperature occurs infrequently. Symptoms such as fever, fever and chills usually appear when a secondary bacterial infection is attached. Then, to eliminate body hyperthermia, measures are taken and medications are adjusted.
For the patient, low-grade fever (38 degrees) is not dangerous, but if the patient feels unwell, fatigue, heaviness in the joints, headache, weakness, then anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs will be useful. Nurofen, Ibuprofen and other drugs in this group will significantly alleviate the patient’s condition and normalize the temperature.
When is hospitalization required?
Fungal tonsillitis is a harmless disease. But there are some risks for patients with immunodeficiency conditions and in advanced stages , when a person should not be left for a long time without medical supervision. These conditions include:
- spread of the inflammation process throughout the body;
- deep infection of the tonsils, which requires surgical intervention;
- abscess or cellulitis;
- there is unstoppable bleeding on the tonsils;
- swelling in the larynx.
Features of the treatment of fungal tonsillitis in newborns
The immunity of an infant is low. The first interaction with pathogenic organisms, which occurs in the first year of life, may go unnoticed, but the risk of fungal infection is quite high. The main danger of advanced infection in newborns is the development of rheumatism and disruption of internal organs. Therefore, treatment of fungal tonsillitis in children should be carried out only under medical supervision, and immediately after detecting the first symptoms, seek medical help.
The main treatment methods are the same as for adults:
- use of antifungal agents, probiotics;
- balanced diet;
- treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions;
- local treatment with rinses.
Nystatin is usually used to treat fungal infections in children. Treatment is carried out in courses of 1-2 weeks. The dose of the drug is prescribed by the doctor, taking into account the weight and age of the child.
Gargles
Rinsing is one of the main methods of treatment. For rinsing, you can use pharmaceutical solutions , products made from improvised materials at home.
- The first remedy is a soda solution. It helps during fungal tonsillitis, since yeast-like pathogenic organisms do not tolerate an alkaline environment.
- Calendula decoction worked well. It disinfects and softens the mucous membrane of the throat, and also has a healing effect.
- Honey mixed with one spoon of lemon juice and warm water alleviates the disease and relieves pain.
- Infusions of Kalanchoe, aloe, and propolis have an excellent disinfecting effect. To achieve the desired result, you need to gargle with a solution of any of this infusion three times a day for a week.
- For rinsing, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used: St. John's wort, chamomile, string, violet, pine needles, etc.
- Garlic infusion copes very well with various fungal infections.
- Of the pharmaceutical drugs, Miramistin, Furacilin, Tantum-Verde, Chlorphilipt, Chlorhexidine, Hexoral, Iodinol have proven themselves to be excellent.
After rinsing, you should not eat food for about half an hour.
If a sore throat develops during early pregnancy, only a doctor can prescribe the necessary treatment. Otherwise, the disease may cause complications for the fetus .
Treatment of the disease in a newborn up to one year of age consists of antibacterial therapy. For infants, microflora is the most dangerous, since immunity is just beginning to form.
Prevention of fungal sore throat
To prevent the disease, you need to maintain immunity, follow simple rules of general and personal hygiene, harden yourself, promptly identify and treat foci of infections in the body, lead a healthy lifestyle and eat right . All these measures must be performed not only to prevent fungal tonsillitis, but also during its treatment, only in this case the disease recedes more quickly.
It is very important to supplement your daily menu with proteins and vitamins, and to include fermented milk products in your diet, since they help restore the natural microflora in the intestines. During the off-season, to strengthen the immune system, you can, in consultation with your doctor, use drugs that stimulate cellular immunity, vitamin complexes and immunomodulators .
In matters of prevention and treatment of fungal tonsillitis, you must trust a professional doctor. Self-treatment leads to dire consequences and can be dangerous. Only by taking the right actions and strictly following the doctor’s instructions can a positive effect be achieved.
Fungal tonsillitis