Advantages of titanium implants
Implants made of pure titanium do not cause allergic reactions and successfully take root in bone tissue with minimal risk of rejection. The material has a sufficient degree of strength and resistance to mechanical loads. This design can last for many years without the slightest complications. The method itself is the most preferable for restoring teeth. It allows you to achieve maximum comfort and naturalness - from both physiology and aesthetics.
Such an implant will be a complete replacement for a living root. It will transfer the load from the crown or prosthesis directly to the bone tissue, which will support metabolic processes in it and prevent it from atrophying. Today, leading manufacturers and modern dental centers offer a lifetime warranty on their products and services.
Implants are becoming full-fledged replacements for tooth roots
Experts in the field of implantation and prosthetics highlight a number of specific features and advantages characteristic of this material:
- no risk of allergies or metallic taste,
- high viscosity and plasticity,
- accelerated osseointegration with bone tissue,
- resistance to mechanical loads,
- no toxicity to the body,
- minimal risk of rejection,
- service life of structures from 30 years,
- the ability to undergo CT and MRI without the risk of heating the material.
Titanium as a basis for creating artificial roots has virtually no disadvantages. However, you need to understand that restoring teeth using this method is a full-fledged operation. Like any other surgical option, it also comes with some risks.
The engraftment of structures is influenced by many factors, ranging from the quality of the product and its performance characteristics to the attitude of the patient himself towards oral care and compliance with all doctor’s instructions - both immediately after the procedure and in the long term. Symptoms of rejection are redness and swelling of the mucous membrane, severe pain, and purulent discharge. In such a situation, emergency medical intervention is required.
Implantation is a full-fledged operation
Titanium dental crowns and bridges
Titanium crowns and bridges are not very often used in dentistry. The main reason for their unpopularity is poor aesthetic performance. Titanium is a rather inconspicuous material, and structures made from it look unnatural. However, titanium alloys are very strong, durable, and also have high biocompatibility.
Titanium is widely used for the manufacture of permanent dental structures. In addition, it is the main material for the production of dental implants.
Fixed dental structures include crowns and bridges. Crowns are placed on individual teeth, and bridges (bridges) replace lost units.
Titanium bridges are several crowns connected together, the outer ones are hollow and are placed on the supporting teeth, and the middle ones imitate lost units
The positive properties of titanium include:
- Biocompatibility. The material is well tolerated by the body and is not rejected
- Infusibility
- Durability
- Not susceptible to corrosion
All these properties make titanium suitable for use in medicine, in particular in dentistry. For the production of crowns, pure titanium or titanium alloys with the addition of molybdenum, aluminum, and vanadium are used.
In some cases, the inner surface of the product is coated with gold plating to give it antimicrobial properties. The outer part of the crown is covered with ceramics to create an aesthetic appearance.
As mentioned above, products made from this material are not popular.
Patients with money prefer metal ceramics based on cobalt-nickel alloys, ceramics or zirconium.
Poorer patients choose metal and metal-plastic structures.
Although titanium products are not in demand, they have a number of advantages:
- High strength, wear resistance
- Long service life. Titanium crowns or bridges can last at least 12 years
- Corrosion resistance. Titanium, unlike many other materials, does not rust
- Antimicrobial properties. Pathogenic bacteria do not multiply on this metal, therefore the risk of crown destruction and the development of inflammatory and carious processes in the mouth is reduced
- Hypoallergenic and non-toxic. Titanium does not cause allergies and has no harmful effects on the body. It also doesn't leave a metallic taste in your mouth.
- No negative impact on neighboring teeth. Titanium crowns do not destroy neighboring teeth, do not injure gums, and do not cause inflammation
- Ease. Despite its high strength, titanium is very light. The weight of the crowns is not felt at all on your teeth
- The ability of a metal not to reflect x-rays. Therefore, during an X-ray examination, you can see the condition of the tooth under the crown.
Titanium is perfectly compatible with living tissues! It is even suitable for children if they need temporary or permanent dentures.
Due to its many positive properties, titanium is used to make dental implants. It is also recommended for use in prosthetics on implants.
Titanium alloys make good crowns and bridges for chewing teeth. They are lightweight, so they do not load the supporting units, but they last much longer than other types of structures.
Like any material, titanium has its drawbacks. Let's look at them.
- It is impossible to make cast crowns from it. Due to its characteristics, titanium is not used for casting. Structures from it are made using the milling method. The technique for their manufacture is quite complex, but it is impossible to obtain products that would fit perfectly to the edge of the tooth. There remains a small gap between the tooth tissues and the crown, into which food particles get packed and microbes enter
- It does not adhere well to ceramics. Ceramic coating does not adhere very well to titanium surfaces. Chips and scratches quickly appear on it. In addition, low-temperature ceramics are used for lining titanium crowns, which are not used with other metals
- It looks unaesthetic. Titanium structures are not similar to natural teeth. They are not placed in the frontal zone, since they stand out strongly against the background of other teeth. A low-temperature ceramic coating does not look as beautiful as a regular one
Recently, thin-walled titanium dentures have been made because they fit more tightly to the teeth, allowing the gap to be reduced to a minimum.
It is recommended to install titanium prostheses to restore severely damaged or removed teeth. They restore the aesthetic and chewing function of teeth. Also, titanium crowns or bridges are indicated in the following cases:
- Increased tooth wear
- Abnormal development or congenital absence of teeth in children
- Tooth injuries, chips, cracks and other damage
- Severe destruction of the coronal part of the dental unit
- Replacement of crowns or bridges made of other materials if they break or the patient requires their removal and re-treatment of teeth
If the tooth is destroyed to the very root and it can no longer be restored, then titanium crowns are not used. It is not recommended for children to have dentures until all their teeth have grown out.
CAD/CAM technology is used to manufacture the titanium frame of the structure. First, the prosthesis is modeled on a computer, and then it is cut out of a solid metal block using special equipment.
Installation of titanium prostheses includes the following steps:
- Diagnostics. The doctor examines the patient and sends him for an x-ray. The picture shows the condition of the teeth and gums, the presence or absence of diseases
- Sanitation of the oral cavity. If the patient has caries or other diseases, they need to be cured
- Depulsion of the tooth under the crown, filling of the canals. This is done if necessary. In some cases, repeated endodontic treatment is required (if the tooth has already been treated previously, but problems have arisen again)
- Grinding the tooth. If its coronal part is severely damaged, use a special titanium inlay
- Taking impressions and sending them to the laboratory
- Trying on and fitting the prosthesis
- Ceramic cladding. The color of the ceramic is matched to the shade of adjacent teeth.
- Crown installation and fixation
Typically, the entire prosthetic process takes from two weeks to one and a half months. The greater the number of teeth and the amount of work (preliminary sanitation, etc.), the longer the process takes.
Some time after installation, the patient comes for a follow-up examination with a doctor. If discomfort and unpleasant sensations occur, the prosthesis is adjusted.
If you properly care for crowns and dentures, they can last not the stated 12 years, but more - 15 or even 20 years
The prosthesis will last a long time only if the preliminary preparation is carried out in compliance with all the rules.
If the doctor did not cure caries, pulpitis, or poorly cleaned or filled the canals, then you should not hope for a long service life of the crown - after a while problems will begin.
The second factor influencing the service life of crowns is the actions of the patient himself. If he leads a healthy lifestyle and takes care of hygiene, then there will be no problems.
Doctors recommend adhering to the following hygiene rules:
- Daily brushing of teeth morning and evening
- Rinsing your mouth after every meal
- Cleaning teeth and tongue from plaque
- Using dental floss, brushes, and irrigator
- Using mouth rinses after brushing
- Chewing sugar-free gum after eating without being able to brush your teeth or rinse your mouth
- Preventative examinations with a doctor every six months
- Professional teeth cleaning once or twice a year
In addition, patients with crowns or dentures should not chew hard objects or create excessive chewing load. You need to chew on both sides to load all the teeth.
Titanium products have a relatively low cost. They are one and a half to two times cheaper than metal-ceramic ones. On average, the following prices apply in Moscow:
- 3,000 – 4,500 rub. – titanium crown with aluminum, molybdenum or vanadium
- 6,000 rub. – crown made of pure titanium
- 6,500 – 7,000 rub. – product with gold plating inside
This cost does not include pre-treatment costs. Here everything is calculated individually depending on the volume and complexity of the work.
Related Articles
Why old dental crowns can be harmful to your health
Titanium dental implants
Zirconium dioxide dental crowns
Add a comment Cancel reply
Titanium and its alloys - characteristics of materials
Titanium is the most suitable material for creating artificial roots. It is completely bioinert, fuses with bone tissue and is not rejected by the body. However, not all titanium alloys are used in dentistry. Only suitable connections are described below:
- pure titanium grade 4 (ASTM standard) - contains about 99% titanium and literally 0.5% iron. In total, there are 4 classes of commercial titanium, which contains virtually no impurities. And even those that exist remain in minimal concentration and are completely safe for the body. But grades 1, 2, 3 have a significantly lower iron content, which makes the material too soft - this is not a suitable option for implants that must withstand quite intense and constant chewing load,
- Grade 5 alloy is a compound with impurities in which titanium makes up the main volume - 88%, and aluminum (up to 6.75%) and vanadium (up to 4.5%) are added to it in small concentrations. This alloy is several times stronger than Grade 4, and its production is significantly less expensive financially. Implants made from it are often made with compression or aggressive threading - they are suitable for implantation into dense basal layers of bone tissue. However, vanadium has a certain degree of toxicity, which inhibits the process of osseointegration (fusion with bone).
Titanium is the most suitable material.
After special treatment, a titanium dioxide film is formed on the surface of the implants - it protects the material from destruction and does not allow vanadium impurities to negatively affect living tissue. This is a kind of protective barrier that is bioinert. Titanium implants are produced by the world's leading manufacturers, such as Nobel Biocare, Straumann, OSSTEM, Oneway Biomed and many others. Today it is the most popular and in demand material in implantology practice. In addition, it is the most studied, and its reliability and safety have been confirmed by many studies conducted over 60 years of observations.
Indications for installation
As mentioned above, this restoration method is optimal from the point of view of physiology and aesthetics. Experts recommend resorting to it if there are the following indications:
- inability or unwillingness to wear a removable denture,
- missing one tooth,
- scattered defects,
- missing segment of teeth,
- complete or almost complete edentia,
- impossibility of installing a bridge due to the lack of supporting elements,
- allergy to polymers and other materials from which removable orthopedic structures are created.
As an alternative, similar products can be distinguished, only created from special high-strength ceramics or zirconium. These models are suitable for single restorations in the smile area. Titanium models are an ideal option for restoring molars, that is, chewing teeth.
Implantation will help solve the problem of missing teeth
They are also suitable for restoring jaws that are completely or almost completely edentulous. Today, for this purpose, one-stage treatment protocols are more often used - when a complete fixed prosthesis is fixed with a screw or cement method on implants in the amount of 4, 6, 8-12 pieces installed per row. In this case, prosthetics are carried out shortly after installation - the prosthesis stabilizes the implanted structures, and this has a positive effect on the process of their osseointegration. In addition, most one-stage protocols make it possible to avoid building up atrophied areas of bone, including through inclined installation of implants in the lateral sections.
“It took me a long time to get implantation; I had to prepare not only financially, but also psychologically. I had to restore my entire upper jaw, and I was very worried. The specialists at your center helped me cope with these fears – I thank them so much for that! The procedure itself was quite easy, I didn’t even expect it. There was no pain at all! In other clinics they convinced me that it was necessary to build up the bone, and that due to the removable denture it was badly resorbed. But in the end there was no need to do anything like that. I was implanted using the all-on-4 method, only 4 implants were implanted and the prosthesis was firmly attached to them. During rehabilitation there was swelling and a fever, but these were all minor things, these symptoms quickly passed. Now I’m happy with my smile, it’s very comfortable, my teeth are like my own! Thank you for doing such important and necessary work!”
Anastasia Nikolaevna V., 57 years old, review on the website of one of the Moscow dental clinics
Among the most popular one-stage methods are Trefoil (all-on-3, lower jaw), all-on-4 and all-on-6 on 3, 4 and 6 Nobel Biocare implants, respectively, as well as Pro Arch and Pro Arch TL on 4 and 6 designs from Straumann. There is also the option of basal implantation for cases of complete adentia against the background of severe atrophy and inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues, of course, after the acute condition has been relieved. A cement-based prosthesis is fixed on 8 or 12-14 implants - products from Oneway Biomed are considered preferable for this concept.
Indications
The main area of application of crowns made of titanium alloy is the restoration of the functionality of the dentition in situations where individual elements have been subjected to mechanical damage. Installation of dentures allows you to normalize chewing and speech functions. In addition, indications for installation of the structure are:
- Insufficient level of mineralization of tooth enamel;
- The need to close extensive fillings;
- The need to protect abrasive hard tissues;
- Thinning of the walls of a dental unit under the influence of caries or stress;
- Long-term wearing of orthodontic systems;
- Dysplasia, hypoplasia and aplasia, which result in damage to baby teeth.
Titanium is very popular in dentistry. Its qualities make it possible to create crowns and prostheses with high levels of reliability, stability and durability.
Manufacturing and installation of a titanium crown using cad/cam technology
One of the advanced methods for restoring dentition is cad/cam technology. Digital prosthetics is an opportunity to quickly restore the functionality and aesthetics of a smile by performing all the necessary manipulations in one day.
The procedure is carried out in two stages:
- Preparation and diagnostics. Forget about impressions and plaster - the dentist conducts a full scan of the oral cavity, identifying possible anomalies. Based on the results obtained, a three-dimensional model is formed.
- Manufacturing and installation of a prosthesis. The procedure for creating a crown is carried out in a laboratory and takes no more than an hour, after which it is transferred to the dental office for fixation. All work is carried out only with a dental microscope - the technology guarantees an accurate fit and a minimum duration of the adaptation period.
Service life, recommendations and cost
Prices for titanium crowns are determined not only by the performance characteristics of the material, but also by its durability. This is one of the most durable elements, the service life of which exceeds twenty years - without restoration or replacement. Recommendations for hygienic care are standard: brushing teeth, using floss and mouthwash, as well as reasonable load distribution help avoid problems with the restored element.
In our clinic, the cost of a titanium crown installed using cad/cam technology starts from 10 thousand rubles. Considering how long-term and reliable this investment in your own health is, the choice seems obvious!
Contraindications to the installation of titanium “screws”
As mentioned above, implantation is a full-fledged surgical intervention, and such operations are not always possible. The following are the main absolute contraindications to the installation of titanium roots:
- severe forms of periodontal disease,
- hemophilia and other pathologies of the hematopoietic system,
- oncological neoplasms,
- tuberculosis,
- HIV infection and AIDS,
- serious pathologies of the cardiovascular system,
- some connective tissue diseases,
- nervous system disorders,
- dysfunction of the endocrine glands,
- mental illness.
Some diseases of the body may be contraindications for installation.
Relative contraindications, experts include caries, pulpitis, stomatitis, gingivitis and other dental diseases that first need to be cured. The operation can also be postponed due to diseases of the ENT organs in the active phase, diabetes mellitus until it is brought into a stable, controlled form. Such procedures are not performed on women during pregnancy, or on children under 18 years of age, since at this age the skeletal system is still developing.
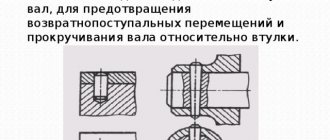
Types of titanium implants
To begin with, all dental implants can be divided into 2 types: intraosseous and extraosseous. The first ones are intended for implantation into the jawbone. The classical method places high demands on the condition of the bone tissue - it must be dense and of sufficient height. Otherwise, it will be necessary to build it up, for example, by grafting a bone block or performing a sinus lift on the upper jaw.
Important! One-stage techniques for complete implantation often allow one to abandon this measure, since they involve the implantation of structures on the sides at an angle (this increases the area of contact of the implant body with living tissue and increases its primary stabilization) or the use of elongated models, for example, zygomatic for the upper jaw.
Extraosseous models are fixed in other structures of the oral cavity, for example, in the periosteal layer or directly in the supporting teeth. They are more likely to be auxiliary components, and their installation does not require serious manipulation. In fact, such products are used quite rarely, since they are not very reliable and are often unpredictable in the long term.
Root-shaped models
This is a classic model, exactly identical in shape to a natural tooth root. It is durable and resistant to mechanical loads, ensures uniform pressure distribution. Such implants are used to restore any number of teeth, are practically not rejected and are characterized by low trauma during installation.
Such structures are shaped like tooth roots
Plate structures
An outdated option is a porous plate combined with an abutment. Previously, such systems were fixed when the width of the bone tissue was insufficient. But the installation process itself was very traumatic and often led to the development of complications. Today such models are not used.
Such designs are already outdated
Combined option
The symbiosis of root-shaped and lamellar implants is a complex branched structure. The system was immediately implanted into three points on the jaw, and it is obvious that this process was also too traumatic and dangerous. Like the previous option, combined models are now a thing of the past.
Endodontic stabilization
They are not intended to replace the root system of the tooth, but to strengthen it. They are used in cases where the root remains in satisfactory condition - they act as pins. The product is implanted into the jawbone, but through the tooth root. It takes root quickly, usually does not cause complications, but has a short service life.
Stabilization products are implanted into the existing tooth root
Intramucosal structures
The products are intended for implantation into the oral mucosa to provide additional support for a removable denture and improve its fixation. This is a suitable option for cases where the patient is completely edentulous, but it is not possible to install classic intraosseous structures. With such implants, the removable denture will stay in place better than simply by being suctioned to the gum. However, the products themselves are small, not strong enough, are demanding on the condition of the mucosa and are usually fixed for a short period of time.
This is what intramucosal implants for removable dentures look like
Orthodontic – to correct the bite
These systems are not intended for dental restoration. They are installed temporarily as part of orthodontic bite correction. In this case, small screws serve as supports to support additionally installed elements of the orthodontic structure. They are used to correct complex pathologies of occlusion, crowding, and also to stimulate the growth of impacted incisors.
Orthodontic implants are designed to correct the bite
In their shape, mini-implants are similar to root-shaped ones, but are smaller in size. Their diameter usually does not exceed 2 mm, and their length varies from 6 to 10 mm. The thread is made symmetrically; special stoppers are located above the neck to prevent the growth of the mucous membrane. There is a small hole in the working head through which the ligature1 is passed.
Such models allow you to shorten the correction period, safely increase the load on the teeth in order to correct their position, and avoid removing healthy elements to free up space in the row.
Subperiosteal subperiosteal
The structures visually resemble plate models, but are designed for implantation into the space between the jaw bone and gum - into the periosteum. Such models were used for severe atrophy of bone structures, which is usually observed in elderly patients. The system itself is quite complex and voluminous; it includes a metal mesh and an abutment. Naturally, its installation was quite traumatic, so such structures are not used today.
Such models were used for severe atrophy of bone structures
Transosseous models
Another not very common model, which is characterized by a complex traumatic installation. Such systems were installed only under general anesthesia. In appearance, it is an arched metal plate designed to be fixed with long pins on the chin. Each such pin comes out of a through hole in the bone and serves as a support for installing artificial crowns.
This system is fixed using long pins on the chin
Zygomatic implants
Zygomatic (transzygomatic) models are usually used as part of the complete restoration of the upper jaw in case of acute atrophic processes in the lateral regions. They are significantly longer than standard root-shaped structures and, when installed, pass through the entire jawbone, go further into the depths and are fixed in the zygomatic bone of the skull.
The photo shows zygomatic implants
The first zygomatic implants were developed by P.I. Branemark, and the patent for them belongs to Nobel Biocare. Produced under the Zygoma brand. Their length reaches 52 mm and their diameter is 4.2 mm2. Such systems are used as part of one-stage implantation protocols, for example, all-on-4 or all-on-6, or to restore the lateral segments of missing teeth. Their use makes it possible to avoid bone augmentation in the upper jaw.
Basal systems
Basal models are designed for implantation into deeper areas of the jawbone, including the cortical and basal layers. They are distinguished by elongated dimensions and more aggressive carvings. Modern basal implants are smooth and have an antibacterial coating, which allows you to stop the further spread of inflammatory processes. Such implants are used for complete jaw replacement. They are similar in shape to classic root-shaped ones and can be implanted through punctures in the mucous and bone tissue.
Basal implants are designed for deeper layers of bone
Disadvantages of titanium crowns
Unfortunately, titanium crowns also come with a number of disadvantages.
These include:
- low accuracy of fitting of the prosthetic device, due to the high complexity of the titanium milling process (it is undesirable to cast this metal, since at a temperature of 800 degrees it loses its biocompatibility properties).
- In addition, titanium crowns are not always suitable for use as frames for standard metal-ceramic prosthetic structures. The low level of adhesion between titanium and ceramics in almost all cases leads to rapid chipping of the outer coating from the crown. Therefore, for the manufacture of metal-ceramic crowns on a titanium frame, only special low-temperature ceramics can be used, which are significantly inferior in aesthetic properties to standard veneers.
Many patients consider the disadvantages of titanium crowns to be their relatively high price. Meanwhile, dentures of this type are much cheaper for clients of dental clinics than products made from other high-quality hypoallergenic materials.
How is installation carried out - stages
The classical method and one-stage technologies have some differences. However, the process of restoring teeth using titanium screws can be described by a universal scheme. Let's look at it using the example of installing one implant:
- initial consultation, diagnosis and tests: first, the specialist conducts a visual examination and necessarily sends the patient for an X-ray examination (in case of multiple and complete implantation using the one-stage method, a CT scan is required). The doctor also questions the patient about chronic pathologies, carefully examines the x-ray, assesses the condition, height and thickness of bone tissue, location of nerves and other important internal structures. The patient must undergo urine and blood tests to exclude possible contraindications. If necessary, he is sent for consultation to other specialized specialists,
- preparation: at this stage it is important to stop all pathological processes in the oral cavity, including healing caries, and also bring inflammation of the mucous membranes into a stage of stable remission. The operation can be performed only after prof. hygiene – removing plaque and deposits, removing diseased, rotten and severely damaged teeth,
- bone grafting: there are different ways to carry it out, among which are directed regeneration, autotransplantation of a bone block, sinus lifting on the upper jaw, replanting of bone replacement chips, including during implantation of the structure, for example, with simultaneous implantation,
- implant installation: a specialist makes an incision on the mucosa, removes a flap of tissue, uses a special bur to form a bed under the artificial root, screws it in and then tightly sutures the mucosa. This is a classic patchwork method, which, however, is considered quite traumatic. With a one-stage technique, implants can be implanted in a minimally invasive way, that is, through punctures in the gums and without sutures. There is also an option for immediate implantation - into the hole immediately after tooth extraction,
- plug, gum former, abutment: the classic method involves installing a special plug on the top of the product. After complete engraftment (about 3 months on the lower jaw or 4-5 months on the upper jaw), the doctor removes the plug and literally installs a gum former for 2 weeks, if the restoration is carried out in the smile area - this detail will allow you to form an even and aesthetic gingival contour so that the smile looks naturally. After 2 weeks, the specialist will replace it with an abutment on which an artificial crown will be installed.
With a two-stage method, the process of installing implants can last several months.
One-stage treatment protocols are most often used without preliminary bone grafting, and the specialist must very accurately calculate the places suitable for implantation of structures. Therefore, each stage is carefully planned and worked out using modern software and mandatory 3D visualization of the upcoming process.
Warranty and service life
Modern implants from the world's leading brands successfully cope with their immediate tasks for many years, right up to the end of the patient's life. On average, their service life starts from 20 years. The important factors influencing this indicator are the following:
- quality of designs, reliability, safety and resistance to constant mechanical stress - all this must be confirmed by clinical studies,
- the patient’s compliance with all doctor’s recommendations during the period of preparation and rehabilitation,
- completeness of preparation and correctness of the operation, adherence to the technology for implementing each stage of treatment,
- the patient’s oral cavity and health condition after surgery and rehabilitation,
- correct choice of implant models and places for their implantation.
Modern implants successfully cope with their tasks for many years.
This is not a complete list. But if you choose a doctor and clinic responsibly, and strictly follow all the doctor’s instructions, the risk of problems in the future will remain minimal. You will need to ensure good quality hygiene and regularly see your dentist for preventative care.
What are the service life and care recommendations?
Titanium crowns are the most durable. Judging by the reviews, they last at least 12 years. And with proper care, the service life reaches 15-20 years.
The service life of the prosthesis itself is indicated with ideal pre-treatment. If the dentist missed inflammatory processes, did not eliminate carious lesions, or poorly obturated the root canals, there is no point in hoping for a long “life” of the structure.
How long titanium dentures last also depends on the patient and how carefully he maintains oral hygiene. Recommend:
- brush your teeth at least twice a day, ideally after every meal;
- clean not only the crowns, but also the tongue, the inside of the cheeks, and gums from plaque;
- use dental floss, brushes or an irrigator to clean the interdental spaces;
- at the end of each cleaning, rinse your mouth with disinfectant solutions;
- if it is not possible to fully brush your teeth, use a mouthwash, floss, or chewing gum - they will eliminate some of the bacterial plaque and food debris;
- undergo a dental examination every six months;
- Remove plaque and stone 1-2 times a year.
Another tip is not to overload the teeth under dentures: evenly distribute the load when chewing on both sides, do not chew hard objects, etc.