Causes
Stomatitis on the tonsils can be caused by various reasons. Let's conditionally divide them into 3 groups:
- The pathology is provoked by an allergic reaction to food and personal hygiene products. Aggressive environmental influences also cause the development of the disease.
- Infection of the mouth and throat (flu, ARVI, sore throat, purulent diseases of the teeth and gums). The herpes virus, which lives in the body of almost every person, is capable of becoming more active at some point, infecting the oral cavity.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane of the throat, tonsils of various origins (cuts, burns).
Stomatitis on the tonsils mainly occurs due to a weakening of the body's protective functions. Immunity is significantly reduced in cases of oncology, fungal infections, pathologies of the digestive system, and HIV.
Which doctor should I contact?
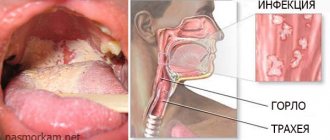
Stomatitis is a disease of the oral cavity of a viral, fungal or bacterial nature.
It is manifested by severe inflammation and the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane. The pathology may be accompanied by high fever, sore throat, poor appetite, and weakness. Young children often suffer from stomatitis due to reduced immunity.
Many parents who notice signs of such a pathology in their child do not know which doctor to contact. It is recommended to visit a pediatrician at your local clinic. The doctor will conduct a survey, examine the baby’s throat, measure the temperature and make a preliminary diagnosis. To confirm the existing pathology and identify its etiology, the doctor will refer the small patient for examination.
A pediatrician is a general practitioner, so he is able to select an effective treatment regimen for stomatitis. In severe and advanced cases, consultation with a dentist, immunologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist, or otolaryngologist may be required. Also, if there are signs of stomatitis, you can immediately contact a dentist at a public or private clinic. A doctor of this specialization treats pathologies of the oral cavity.
If ulcers appear on the tonsils, on the back wall of the throat, then you should visit an otolaryngologist.
Classification
Depending on the etiology, stomatitis of the throat can be of several types:
- The catarrhal form is more common than other types and is considered the easiest to treat. The main reason for the appearance of inflammation on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity is the unsatisfactory hygienic condition of the teeth and gums.
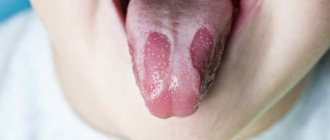
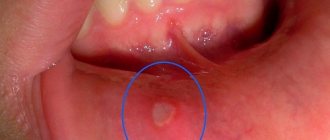
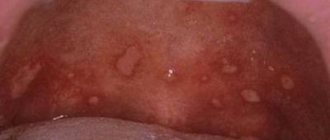
- The aphthous form is manifested by the formation of blisters on the throat and tonsils. After they burst, the mucous membrane ulcerates. This type of disease is most often localized in the throat.
- Candidal stomatitis is caused by fungi, popularly called thrush. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of a white, thick coating on the affected areas of the mucous membrane. Most often found in the area of the tongue, palate, inner cheeks, and lips. Sometimes candidiasis can also be in the throat.
Necrotic, herpetic, and ulcerative stomatitis are extremely rare. Regardless of the form of the pathology, it can occur in acute and chronic stages.
Folk remedies
To get rid of the disease in folk medicine there are a huge number of recipes. When choosing the right one for yourself or your child, you need to take into account the individual characteristics of the body and age.
- After each meal, rinse your mouth with clean warm water.
- Dilute 1 teaspoon of hydrogen peroxide in 100 ml of warm water. Used for rinsing and lotions.
- Treat the affected areas with aloe or Kalanchoe juice, or simply chew the leaves.
- Lubricate the mucous membrane with propolis tincture or honey.
- A few cloves of garlic are turned into a paste, add 1 tbsp. a spoonful of kefir or homemade yogurt. Hold in the mouth, distributing it throughout the entire cavity with the tongue. Repeat up to 6 times a day.
- Rinse your mouth with potato juice and apply the pulp to your gums.
- Fresh carrot juice is mixed in equal proportions with warm water and rinsed.
- Prepare a decoction of chamomile, sage, and calendula. Add 4 g of boric acid to the glass and use it for rinsing. The product has an analgesic effect.
- Treat the oral mucosa with sea buckthorn and calendula oil.
- Dissolve a furatsilin or streptocide tablet in warm water and use it for rinsing.
- Dissolve 0.5 teaspoons of baking soda, salt in a glass of water, add 5 drops of iodine. Gargle. Particularly effective for candidal stomatitis.
Folk remedies are used 3 to 6 times a day. Before active treatment, you should consult a specialist. At the same time, you should stick to a diet, eat more fermented milk products, take vitamins and probiotics.
Signs
Stomatitis on the tonsils causes significant discomfort to a person. Therefore, the disease is difficult to detect. Consider the symptoms of the pathology:
- Burning sensation in the mouth and larynx.
- Hyperemia of the mucous membranes (slightly swell and turn red).
- Breath becomes stale (a sign indicating chronic inflammation).
- Eating becomes difficult. Children with stomatitis have no appetite.
- Sometimes the body temperature rises and headaches occur.
- Saliva is released much more intensely than usual.
- The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged.
- The affected areas become covered with a white, grayish coating or ulcers.
In addition to the listed symptoms, the patient feels a general malaise. The symptoms cannot be ignored. The sooner you begin to treat stomatitis in the throat, the sooner recovery will occur.
Symptoms of the disease
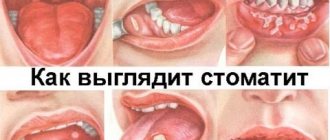
The development of the disease begins with redness of the throat, initially reminiscent of signs of a common sore throat. After a few days, the pain intensifies, and a characteristic plaque and blisters appear. Symptoms of stomatitis in children are more pronounced, but externally the damage to the oral cavity is no different.
Signs in children:
- Redness of the throat, tissue swelling;
- The mucous membrane of the throat becomes covered with a yellowish coating;
- Sores are found to be located in groups or alone;
- Lymph nodes enlarge.
You can see what stomatitis looks like in children in the photo below. The development of the disease is accompanied by a deterioration in overall health.
- Temperature rises to 39 degrees Celsius.
- Increased salivation, sore throat.
- Decreased appetite.
- Itching.
- Capriciousness, tearfulness of the child.
- Headache, weakness, apathy.
- Sour breath.
The nature of the development of the disease depends on the strength of the immune system and the age of the child. There may be minor damage to the throat or a serious inflammatory process in the entire oral cavity - throat, gums, palate.
Symptoms in adults:
- Redness, swelling of the mucous membrane;
- Yellowish or white coating;
- Ulcers of different sizes and numbers;
- Slight increase in body temperature up to 37.5 degrees;
- sore throat, difficulty swallowing;
- Itching;
- Lack of appetite;
- Increased salivation;
- Headache;
- Bad breath;
- Weakness;
- Decreased ability to work.
What rashes look like in adults is shown in the photo below. Lymph nodes do not enlarge, the extent of damage to the oral cavity is somewhat less than in children. The disease causes discomfort, unpleasant sensations, disrupts sleep, and irritates the nervous system.
Diagnostics
The presence of pronounced symptoms in the throat in the form of ulcers, hyperemia of mucous tissue, plaque allows the doctor to diagnose the pathology after a visual examination. But in order to know how to treat stomatitis, it is important to classify it.
Conclusions depend on several factors:
- condition of mucous tissue;
- shapes, boundaries of ulcers;
- presence of plaque, its characteristics.
Laboratory testing involves taking a smear for bacterial culture from the throat and a general blood test.
When re-diagnosing the disease or when stomatitis is chronic, additional examination of the patient is required:
- Blood test for sugar, biochemistry.
- Saliva is collected to determine the causative agent of stomatitis.
- An immunoenzyme test is prescribed to determine the activity of the body's defense system.
Treatment
Stomatitis in the throat in children and adult patients is treated comprehensively. In addition to drug therapy, the doctor recommends following a diet. Aggressive foods (spicy, sour, sweet) are excluded from the diet. Preference is given to boiled, warm, soft food.
Approximate treatment regimen:
- Treatment of stomatitis in the throat of a child involves treating the oral cavity with antiseptic agents (Furacilin, Chymotrypsin). Lidochlor-gel, Baby-dent, Kalgel are used as painkillers. If the pathology is viral in nature, then it is advisable to include Acyclovir, Florenal, Bonafton in therapy. For candidiasis in a child, Candide is prescribed. And to speed up the regeneration processes, the affected areas are treated with Solcoseryl or rosehip oil. An elevated temperature is brought down with antipyretic drugs (Panadol, Ibuprofen).
- Stomatitis on the tonsils in adults is treated according to the same principle, only other drugs are selected. The doctor recommends treating the affected areas with antiseptic solutions (Miramistin, Hexoral, Chlorhexidine). For fungal infections, mycoseptic drugs (Fluconazole, Candide) are prescribed. Regeneration of affected tissues is ensured by sea buckthorn oil, Solcoseryl, Karotolin. If the pathology is provoked by a virus, then appropriate therapy is prescribed that inhibits their reproduction (Acyclovir, Immunal). In rare cases, antibacterial treatment is required (Amoxicillin, Ofloxocin, Gentamicin). If allergic reactions occur, antihistamines (Claritidine, Diazolin) are recommended.
It is necessary to clarify the regimen and combination of drugs with your attending physician. With proper therapy, acute stomatitis can be stopped in 5–10 days.
Causes of stomatitis in the throat
Stomatitis is a disease whose mechanism of occurrence is that the human immune system reacts to irritants in an atypical way, resulting in ulcers in the mouth and throat. This reaction of the immune system can be triggered by bacteria, viruses, fungi and other microorganisms. Therefore, stomatitis in the throat is often a concomitant disease that occurs against the background of another infection.
Based on this, we will name the following causes of stomatitis ulcers in the throat:
- Bacterial infection of the oral mucosa
. Most often, the causative agents of infection are various strains of microorganisms such as streptococci or staphylococci. If a person neglects oral hygiene, or if, for example, he gets a bacterial sore throat, this can trigger the development of stomatitis in the throat. - Viral infections.
In most cases, the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the mouth is provoked by the herpes virus, which penetrates the human body and develops as a separate infection. In this case, small bubbles appear in the throat, which are located in groups. The occurrence of herpetic ulcers is accompanied by itching, pain and redness. - Fungal infection of the oral mucosa.
A fungus of the genus Candida most often develops in the human mouth. Normally, it is always present on the mucous membrane, but weakened immunity, stress, long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs can provoke its growth. As a result, a white coating appears in the throat, palate or tongue of a person, which indicates a fungal infection. The development of stomatitis against the background of a fungal infection is also quite common.
Weakening of the human immune system. The immune system of an adult is weakened by stress and somatic diseases. The child’s immunity is weakened in principle, since it is not yet fully formed and is just learning to fight infections. Stomatitis in this case either occurs as a separate disease or becomes a consequence of some current illness. Avitaminosis. A lack of various vitamins and microelements in the human body can also provoke the formation of stomatitis ulcers in the throat.
Allergic reaction. Allergies to certain foods (chocolate, citrus fruits, peanuts) or the substances they contain (for example, gluten, which is rich in cereals) provoke the appearance of stomatitis ulcers in the throat and on the oral mucosa of a person.
Possible complications
If acute stomatitis is not cured in a timely manner, the disease transforms into the chronic stage. In addition, damage to the pharynx and tonsils is already considered the clinical stage of the disease. Bacteria, viruses or fungi will quickly spread through the esophagus to the internal organs of the body.
Untreated stomatitis provokes a secondary infection. The risk of developing ENT diseases and dental pathologies increases.
Like all inflammatory processes, pathology significantly undermines the immune system.
Prevention
There is a set of rules, the observance of which will minimize the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process in the oral cavity:
- Carefully monitor the hygiene of your teeth and gums.
- Treat caries and other dental diseases in a timely manner.
- Having noticed that any products have an aggressive effect on the mucous membrane, their consumption is reduced or stopped altogether.
- Avoid contact with infected people.
- Strengthen your immune system with a healthy diet, exercise, and walks in the fresh air.
- You should get rid of bad habits.
Paying attention to your health also means responding in a timely manner to disruptions in your body’s functioning. Visiting a doctor at the first symptoms allows you to diagnose the disease at an early stage and quickly treat it.
Author: Tatyana Grosova, nurse, especially for Moizhivot.ru