The difference between stomatitis and thrush
One of the common diseases of the oral cavity in children is stomatitis, but only a doctor can correctly distinguish whether thrush or stomatitis is bothering the baby. Identifying white plaque in a baby's mouth confuses many young mothers. A non-serious attitude and lack of adequate treatment threatens the disease to become chronic. If you understand the causes of this disease and learn to navigate the symptoms, the risk of relapse can be minimized.
Compound
The active component of the drug is clotrimazole. It is considered an imidazole derivative and the pharmacological effect occurs due to a failure in the formation of ergosterol. This component is a component of mushrooms. Subsequently, the nutrition of the cell is disrupted and its elimination occurs. Dispensed from Candide pharmacies for stomatitis in the form of:
- tablets;
- ointments;
- powder;
- solution.
When treating oral candidiasis, the most effective and convenient for use is a solution, especially when the oral mucosa is affected in children. Some doctors prefer to use the drug in tablet form.
The drug is indicated for infection with yeast and mold fungi and a number of other pathogens:
- microsporia (mycotic disease of the skin, hair and nail plates);
- ringworm (appears as a result of a fungal infection and can affect the skin, hair, eyelashes and nails);
- trichophyton;
- epidermophila;
- lichen (a skin disease that is caused by viruses or fungi, transmitted from humans or animals by contact);
- vaginal trichomanas;
- Gardnerella vaginalis (conditionally pathogenic bacteria that are part of the normal microflora of the urogenital tract).
This medication in small dosages has a fungostatic effect, and in high concentrations it has a fungicidal effect. This helps to use it not only for the treatment of the disease, but also for its prevention. “Candide” for oral stomatitis receives good reviews.
What is the difference?
Stomatitis is not just a disease; this term combines a number of pathologies of the oral cavity, sometimes having the same symptoms. For more accurate information, it is necessary to establish what exactly caused the disease. There are more than enough factors that cause the development of inflammation; they have their own differences and influence the final diagnosis.
Stomatitis is classified according to its symptoms:
- Aphthous. The result of infection of the body with a viral infection, allergic reactions, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Pathological lesions appear in the mouth - aphthae, causing pain and discomfort to the patient. Accompanied by profuse salivation and bad breath.
- Catarrhal. A common type of oral lesion. This pathology occurs without visible defects in the inflamed areas. Accompanied by hyperemia (redness) of the affected tissues and severe swelling.
- Ulcerative. More often it is an advanced form of catarrhal stomatitis. Signs that allow one to distinguish an advanced form from a mild one are inflamed tissues that become covered with ulcers, sometimes bleeding.
- Candidiasis or thrush. A consequence of the activity and growth of yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. A white or yellow coating forms in the oral cavity, accompanied by itching of the affected areas.
Return to contents
What are the symptoms of stomatitis
To identify stomatitis in a child, it is important to have some information and be able to recognize its symptoms.
Sometimes this is not so easy to do, since such a small patient cannot yet talk about his feelings. But an experienced therapist will recognize stomatitis in a newborn and infant quite quickly. Symptoms of stomatitis:
- The gums become swollen and red;
- The baby sleeps poorly and restlessly;
- He becomes moody and cries often;
- The temperature rises;
- Salivation increases;
- The baby refuses to eat;
- Bad breath appears;
- The oral mucosa becomes covered with ulcers. They can have different shapes. It all depends on the specific type of stomatitis;
The listed symptoms are quite arbitrary. They can manifest themselves in different ways. Some may not appear at all, while others become more pronounced. For example, high temperatures are not always observed. The severity of symptoms will depend on how severe the disease is.
The main reasons that lead to stomatitis in infants
In children, stomatitis develops for the following reasons:
- Some kind of infection has occurred. It can be fungal, viral or bacterial.
- The baby has a weak immune system. Even local weak immunity can lead to this disease.
- There are serious systemic diseases: diabetes, HIV, diseases of the endocrine system.
- After undergoing antibiotic treatment.
- Hygiene in the home is not strictly adhered to, and the baby’s oral hygiene is also compromised.
- Pacifiers, bottles and toys are not sterilized correctly.
In babies under 12 months of age, stomatitis caused by a fungal infection is manifested by the appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa. They are painful and covered with a white coating that looks like cottage cheese. The plaque can be removed with gauze, and then a wound that bleeds is visible underneath. Due to the great pain of such ulcers, a baby with stomatitis behaves restlessly, does not want to eat and cries a lot when they want to feed him.
Thrush should have symptoms other than white plaque
Symptoms of thrush and stomatitis
Symptoms in each individual case are different, it all depends on the form and severity of the disease, as well as foci of inflammation. In a child, the first symptom of stomatitis is most often fever. Also observed:
- apathy;
- lethargy;
- decreased appetite or complete refusal to eat;
- moodiness, nervousness;
- bad dream.
Candidiasis is slightly different in symptoms. When examining the oral cavity, redness, swelling, white or yellowish plaque, small ulcers and round wounds are detected. The course of the disease in children is often acute. Because of the itching in the mouth, the baby tries to scratch the inflammation with something and puts everything in his hands into his mouth.
Only a dentist can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe effective therapy. You should not self-medicate, as it is unsafe.
Causes of the disease
The causes are varied, since the development of various forms of stomatitis is influenced by many factors. Common reasons:
- poor oral hygiene;
- mechanical injuries;
- very hot food and drink;
- bacterial or viral infections;
- chronic forms of diseases;
- taking antibiotics;
- teething;
- dehydration;
- allergy;
- lack of vitamins;
- weak immunity;
Return to contents
Candidiasis in children: causes and signs
Candidal stomatitis affects children of different age groups, but in most cases it occurs in children in the first few years of life. Sometimes its development is provoked by other health conditions. Thrush is often passed on to a baby during childbirth from an infected mother. Infection is possible if hand hygiene rules are not followed after playing in sandboxes or walking.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Candidal stomatitis (fungal), thrush in the mouth - causes, symptoms, treatment
Candidal stomatitis in children can occur in mild, moderate or severe forms. The last two types are characterized by an increase in body temperature to 39°C. Sometimes parents do not pay attention to a mild form of pathology for a very long time, since the infant, although capricious, cannot talk about what is bothering him.
The reasons for the development of thrush are:
- improper metabolism, especially diabetes;
- long-term use of antibacterial agents;
- weak immunity;
- dysbiosis of the oral mucosa.
Symptoms of oral candidiasis include:
- the appearance of a white cheesy coating on the palate, inside of the cheeks and tongue;
- soreness of the affected areas;
- formation of bleeding wounds when removing the film;
- swelling and hyperemia of the oral mucosa.
In the absence of timely treatment, the baby develops the following signs of pathology:
- loss of taste;
- formation of cracks in the corners of the lips;
- feeling that the tongue has become “cotton”;
- pain or discomfort when eating and drinking.
What treatment is prescribed?
For candidal stomatitis
It is worth remembering that only a doctor can prescribe correct and effective treatment. In mild cases of candidiasis, it is prescribed to rinse the mouth with a soda solution - chamomile decoction, a weak solution of potassium permanganate. If the child is very small, mothers are advised to wrap a bandage around their finger, which must be sterile, soak it in the solution and remove the white coating. The drug “Nystatin” helps well, which is mixed with water and wiped over the infected areas. If the thrush is advanced, inflammation appears under the white layer, and even wounds or ulcers, then antifungal drugs are prescribed, in which case it is recommended:
For other varieties
A clear definition of the form of stomatitis allows you to select effective treatment. Depending on the cause of the disease, different drugs are prescribed. For catarrhal stomatitis, mouth rinses, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic sprays, and pain relievers help. For aphthous stomatitis, in addition to oral irrigation, medications with interferon and antihistamines are prescribed. Treatment for ulcerative stomatitis is prescribed individually and in combination with other drugs; self-medication is not enough. If symptoms appear, it is important to immediately consult a specialist.
Treatment of thrush
Treatment of thrush in newborns is complicated by the fact that the baby cannot yet speak and is not able to describe his complaints and sensations to adults. Therefore, mothers of newborns need to be extremely careful and seek help from a doctor if any symptoms occur.
If thrush appears due to frequent regurgitation , then the cause of this phenomenon must be determined and eliminated. It is likely that the baby does not latch onto the pacifier or nipple correctly during feeding, resulting in air getting into the intestines. Follow the feeding technique, and be sure to carry the baby in a column after any meal, this way excess air comes out.
Local treatment of thrush in newborns
To remove the fungus, you need to treat the child’s oral cavity with such means.
Dilute one teaspoon of baking soda in a cup of warm water. Soak a cotton swab in this solution and clean your mouth with it. Everything needs to be treated: cheeks, tongue, palate, gums. Try to perform this procedure as often as possible during the day. If you identify thrush at an early stage, then there is a great chance of getting rid of the disease with the help of these simple manipulations in one week.
How can simple soda help get rid of fungus in the mouth? The soda solution makes the oral lining alkaline, which is unfavorable conditions for the life of the fungus. It cannot develop here and dies over time.
In the same way, you can use a light composition of potassium permanganate.
As a rule, treatment of infants is performed only by local treatment of the oral cavity and shows excellent results. Antifungal drugs are rarely prescribed to these babies.
Treatment of children from six months of age
Many remedies for the treatment of oral thrush are used for children from the age of 6 months. Until this age, only local treatment is recommended.
When thrush has become severe, often the only effective treatment is to take antifungal agents, as well as drugs containing iron . The principle of operation of antifungal agents is based on the destruction of the membranes of the viral fungus.
Fungal stomatitis in children
This pathology occurs in all age groups . If immunity is normal, the course of the disease is mild, responds well to treatment and causes virtually no complications .
- Infection occurs when a child passes through the maternal birth canal .
- Under one year of age: immature immunity, habit of licking toys and other foreign objects.
- Long stay of the baby in the hospital.
- Artificial feeding.
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules by the mother during breastfeeding.
- When artificially feeding, use mixtures with a high sugar content .
- Uncontrolled use of antibiotics leads to disruption of microflora .
- Oncohematological formations.
- Therapy with cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs.
The diagnosis is made based on a doctor’s examination , analysis of accompanying symptoms, history taking and scraping from the tongue (to determine the presence of a fungus).
Why is it dangerous?
Repeated occurrence of such a disease in a child may warn of the presence of other serious health problems. These are leukemia, diabetes and even HIV . Complications of fungal stomatitis include: candidosepsis, vulvitis and balanopostosis (candidiasis of the genital organs), visceral candidiasis (microabscesses of the brain, esophagitis, enterocolitis, osteomyelitis, ventriculitis).
How is it different from thrush in a child's mouth?
Thrush is often called candidal stomatitis. a white coating appears in the child’s mouth due to the Candida fungus . But inflammation of the mucous membrane and the development of stomatitis can be caused by bacteria (staphylococci and streptococci), viruses, aggressive allergens or mechanical injuries.
Important! Treatment of this disease must be mandatory and timely to avoid complications.
Candida drops - benefits and harms
Yes, this is a really effective remedy that helps remove fungal stomatitis, however, as you know, every medal has 2 sides.
We found out above that Candida drops are used today in the form of drops. In rare cases, ointment is used to treat the oral cavity.
Why? This ointment has ceased to be a popular treatment for stomatitis due to its bitter taste.
Moreover, it is absorbed much more slowly than drops. The main active component of Candida is a substance that has a destructive effect on fungal cell membranes.
This is what makes this antifungal medicine effective. As a result of the inhibitory effect of drops on pathogenic microorganisms, they quickly die, which stimulates the patient’s recovery.
Doctors recommend using this remedy for medicinal purposes only if the disease was caused by mold or yeast-like fungi.
Only a doctor can determine the pathogenic bacterium that provoked swelling and irritation of the oral mucosa.
Therefore, before purchasing Candida, we recommend being diagnosed in a hospital.
Since the medicine has pronounced antifungal activity, the results from its use will not be long in coming.
As for viruses and infections, these drops do not suppress them. Therefore, in the instructions for it you can find information that Candida drops should be used to relieve symptoms exclusively of fungal stomatitis.
Its main advantage is excellent and rapid absorption. That is why the therapeutic effect occurs very quickly.
A huge advantage is that stomatitis can be treated with this remedy for children, even small ones.
It is worth noting that the active components of this product cannot be detected in biological fluid 30 minutes after its use.
Due to this, Candida is recommended to be used to relieve the symptoms of fungal stomatitis even in infants.
But not everything is so perfect. Unfortunately, many patients purchasing this medication for medicinal purposes complained of severe mouth pain.
Such a symptom can actually appear in the first seconds of applying the product to the oral mucosa.
Moreover, the more stomatitis pimples in the patient’s mouth, the stronger he will experience a burning sensation.
However, this is not a “stone in the garden”. The fact is that with a fungal infection of the mouth, it becomes very inflamed and painful, which means that a person will experience severe pain from any irritant.
In this case, such an irritant is a stick dipped in medicine. If after the first procedure you feel a slight burning sensation, then you should not refuse the medicine.
Gradually, negative manifestations will be minimized, and soon you will not feel any discomfort at all.
However, mothers who treat their children with Candida should exercise caution. It is recommended to monitor his condition in the first days of therapy.
If after the second application the baby’s well-being has not worsened, continue treatment.
If the situation is the opposite, be sure to consult a pediatrician.
Finally, I would like to say a few words about the prevention of fungal stomatitis. It has been proven that a person with strong immune defenses tolerates diseases more easily.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with Iodinol or Betadine - All about the fungus
Therefore, if your immunity is weakened, take measures to strengthen it. The easiest option is daily charging.
She also recommends consuming plenty of vitamins found in vegetables and fruits.
This will help you always stay healthy!
Symptoms and stages of development
- At the first (mild) stage , excessive dryness of the mucous membrane, burning sensation, unpleasant taste and bad breath appear . Infants behave restlessly, lose appetite, and sleep poorly.
In the second degree (moderate severity), small whitish dots form , which over time begin to merge and form a profuse, foul-smelling coating.
The temperature rises to low-grade levels , general weakness is observed, and the child refuses to eat.
- In severe cases of stomatitis, the plaque acquires a dark gray tint , it is difficult to remove, and the mucous membrane underneath it begins to bleed . The temperature rises to high levels, the lymph nodes become inflamed, drowsiness and lethargy appear, and immunity decreases. Against this background, the child may simultaneously become infected with other infections .
- Children wearing orthodontic appliances are at risk of developing an atrophic form of candidal stomatitis. It has less pronounced symptoms : dry mucous membrane, redness, burning sensation. Plaque forms in the folds of the lips and cheeks.
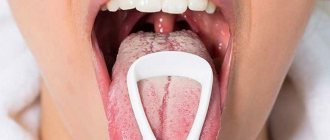
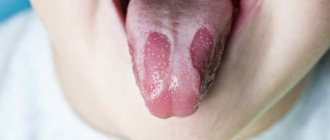
What does candidal stomatitis look like on the tongue?
Photo examples
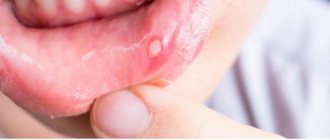
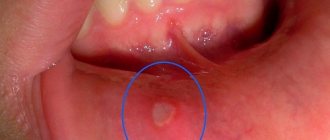
Photo 1. An example of a copious amount of white plaque in a small child with stomatitis.
Photo 2. Candidal stomatitis, or in other words, thrush in the oral cavity of a child in infancy.
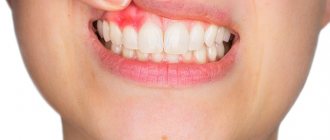
Photo 3. Several foci of inflammation of purulent stomatitis on the lower lip on the inside of the mouth.
Indications for use
Most often, drops are prescribed to children with oral lesions from Candida fungi.
Candide quickly suppresses the development of pathogenic microorganisms, which helps to quickly cure candidiasis (thrush) and fungal stomatitis in children.
The medicine can help children with weakened immune systems, so it is prescribed to patients with diabetes, patients with oncology and immunodeficiency conditions.
Candida with stomatitis in children is able to block the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids and ergosterol in fungal cells. It damages the cell membranes of fungi, which leads to their death. If you treat your child's mouth daily according to the instructions for use, you can quickly overcome thrush.
Treatment
Therapeutic actions must be carried out strictly in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. Treatment cannot be interrupted independently until the end of the course , as this is fraught with the development of pathogen resistance.
Therapy for stomatitis is divided into local and general . Antifungal drugs are available in various forms: ointments, sprays, lozenges. When prescribing them, the doctor is guided by the age of the child.
Attention! Self-medication is prohibited ! Before consultation with a specialist (pediatrician or ENT specialist), the baby is only allowed to be given an antiseptic and pain reliever .
How to treat children under one year old?
Only local treatment is allowed . To treat the oral cavity, preparations are used that create an alkaline environment.
The most common option is a solution of soda in a proportion of 1 tbsp. water: 1 tbsp. l. soda _ Another drug is a solution of boric acid 2% .
Depending on the prescription of the attending physician, treatment of the oral cavity can be performed up to 5 times a day. Breastfed babies need to be put to the breast more often , and the mother's nipple must be treated.
Formula-fed babies should be given formula only after boiling the dishes and nipples first . During treatment, you should not start complementary feeding.
Therapy for older people
It is carried out using a methylene blue solution (blue). Candida drugs (Fluconazole or Diflucan) are also widely used . The dosage is determined only by a specialist. Children over 4 years old Hexoral Tabs lozenges .
Teenagers are prescribed antibiotics, antiseptics, antifungals, painkillers and immunomodulators , ultraviolet irradiation of the mucous membrane and heparin ultraphonophoresis. Vitamin A is used to improve epithelization .
During illness, it is worth paying close attention to the teenager’s compliance with hygiene procedures . For all types of stomatitis, the use of the herbal collection Stomatofit gives a positive result. It is recommended to drink plenty of calendula and chamomile tea , as well as other herbal infusions.
How is stomatitis treated?
As soon as you notice the first signs of stomatitis in an infant, immediately seek help from a pediatrician or pediatric dentist. Do not try to deal with this problem on your own. The recommendations that we give below can only be an addition to the main treatment. In addition, there are many types of stomatitis. Each of them requires specific treatment.
For example, with candidal stomatitis, you can try to remove plaque from the tongue using sterile gauze or a bandage soaked in a soda solution. You need to dilute a teaspoon of soda in a glass of warm boiled water. Wash your hands well and wrap a piece of sterile bandage or gauze soaked in this soda solution around your finger. Make sure that the threads from the bandage do not get into the child’s mouth.
As we have already mentioned, it is important to tell the pediatrician in a timely manner that the baby may have stomatitis. The doctor will prescribe all the necessary tests, examine the child, and then prescribe specific treatment.
There are rules that, if followed, will help avoid stomatitis in infants:
- The children's room needs to be thoroughly wet cleaned every day;
- Try to carefully care for your child's oral cavity;
- The mother should keep her nipples clean. It is recommended to wash them with warm water before feeding. Once a day you need to wash your nipples with soap.
- Pacifiers and bottles must be thoroughly sterilized;
- Wash toys with baby soap more often;
- Soft and warm foods are suitable for feeding an infant. Such food is easy to swallow and does not injure the mucous membrane.
Soda solution helps well with stomatitis, but only at the beginning of the disease. Soda can also be replaced with chamomile decoction. The procedure must be repeated until the symptoms of stomatitis go away.
Stomatitis is often caused by a virus. This infection can be treated with special ointments. If the doctor allows, the baby’s oral cavity can be treated with acyclovir, tebrofen or oxolinic ointment. Only a doctor should select a specific drug and determine the method of its use! Don't risk your baby's health!
If the doctor has determined for sure that the cause of stomatitis is a fungus, then it will be necessary to use antifungal drugs. This can be an aqueous suspension of levorin or nystatin, a solution of candida or nystatin in drops. A specialist prescribes a specific drug.
If the baby is clearly bothered by pain, then Kamistad gel can come to the rescue. It has a pronounced analgesic effect. In addition, it copes well with inflammation. But it can only be used from three months of age. Moreover, it is allowed to apply it to the mucous membrane no more than three times a day. The final regimen of use should be prescribed by a pediatrician.
In order for the tongue to heal as quickly as possible, the doctor must prescribe drugs that can regenerate the mucous membrane. This could be Shostakovsky balm or Solcoseryl. These medications can be used up to 5 times a day.
The following groups of drugs are used to treat stomatitis in infants:
- Antifungal.
- Antiviral.
- Painkillers.
- Products that speed up the healing process.
They are most often prescribed in combination. Their combination may vary. It all depends on the specific form of stomatitis, on what pathogen caused it.
Each of the listed medications has serious contraindications and conditions of use. Therefore, only a physician has the right to prescribe them! In addition, there is a whole list of drugs that absolutely cannot be used in the treatment of stomatitis in infants. Such dangerous drugs include Metrogyl Denta, Fluconazole, Cholisal, Lidochlor. To treat ulcers, you should never use brilliant green or hydrogen peroxide!
Before feeding, lesions on the mucous membrane should be treated with agents that provide an analgesic effect. These can be special gels with anesthetics, which are used when teething.
Treating the baby’s mouth with a soda solution is highly effective against oral thrush, the main purpose of which is to create an alkaline environment in the mouth:
- A teaspoon of soda dissolves in a glass of heated boiled water.
- Then the mother wraps her finger in gauze or a bandage, dips it in a soda solution and carefully wipes the baby’s mouth. In this case, there is no need to try to remove the white coating; the mother should simply moisten the affected areas and gently wipe them, without causing bleeding wounds.
- The procedure is carried out 4-5 times a day.
If the baby is not at risk of an allergic reaction, areas of inflammation can be treated with honey diluted in water. A teaspoon of this sweet delicacy is diluted in two teaspoons of water, and then the child’s mouth is treated up to 5 times a day in the same way as soda is treated.
Most often, when treating thrush, the oral cavity is treated with special preparations.
Treatment of acute and chronic cases
Therapy should be aimed at stopping the inflammatory process and increasing the resistance of the whole organism .
Local therapy includes anesthesia, antiseptic treatment and mucosal cleansing with a combination of antibiotics with proteolytic enzymes and keratoplasty.
Polyene antibiotics are prescribed orally or topically . At the final stages of therapy, sanitation of the oral cavity is necessary .
The pathology can become chronic. In this case, the symptoms change : there is a feeling of difficulty swallowing, a burning sensation turns into constant pain.
If left untreated, the chronic form may damage the intestines, esophagus, larynx and other organs. The entire range of drugs listed above is also used for therapy. The doctor individually determines the duration of treatment.
What are the basics of prevention?
The basis for preventing this disease is hygiene . bottles and toys well , boil pacifiers. Maintaining hygiene of the mother's breasts and nipples is also important. From childhood, a child must be taught consistent oral care. To prevent the disease, it is recommended to carefully select a course of vitamins and minerals , as well as a special diet that limits the consumption of “fast” carbohydrates. In case of frequent relapses, additional consultation with a doctor is necessary .
Prevention
There are quite simple and very effective methods to reduce the risk of developing this disease. First of all, to ensure that oral candidiasis never bothers a person, care must be taken to strengthen the immune system. It is very important to take pharmacy multivitamins, eat right, exercise and exercise.
To ensure that candidiasis in the oral cavity never bothers a person, he needs to pay due attention to hygiene. Regular brushing of your teeth and tongue can reduce the risk of this problem. In addition, it is required to undergo regular routine examinations, including dental examinations. If you have dentures, you must carefully monitor their cleanliness. So, the treatment of oral candidiasis involves a comprehensive treatment.
Differences between stomatitis and thrush
The oral mucosa reacts sharply to fluctuations in acidity levels, mechanical and physical influences, bacterial or viral infections. In the case of thrush, a white coating can be found in the child’s mouth - it is caused by a fungus from the genus Candida.
Thrush is also called candidal stomatitis . But other factors may also cause inflammation of the mucous membrane and the development of stomatitis. For example, these could be bacteria (most often staphylococci or streptococci), viruses (usually herpes), mechanical injuries or strong allergens.
Candidiasis in a child
Before starting self-treatment, you should definitely consult a pediatrician or pediatric dentist to identify the cause of the inflammation and receive the correct therapy. Concomitant diseases that suppress the immune system can also intensify the inflammatory process.
Factors that provoke the development of different types of stomatitis and thrush:
- development of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity;
- unwashed fruits and vegetables;
- weak local immunity;
- taking antibiotics by both the child and the mother;
- damage to the mucous membrane, due to the fact that the baby puts everything he sees into his mouth;
- teething;
- dry mucous membrane;
- lack of hygiene;
In healthy children with strong immunity, thrush or candidal stomatitis with mild symptoms may disappear on their own, without treatment. And in weak and sickly babies, a white coating can be found throughout the mucous membrane, on the tongue, gums, and pharynx. This creates difficulties when sucking and swallowing, and appetite is disrupted.
Such babies may not latch onto the breast, be capricious, and cry. Many doctors say that one of the main reasons causing stomatitis or thrush in children is an imperfect immune system and, accordingly, weak antiseptic properties of saliva in children.
The mucous membrane in the oral cavity is thin and sensitive, and it is quite easy to injure it, but then it is much more difficult to restore it.
It is necessary to determine the type of infection and the accompanying factors that provoked it in order to quickly select the correct treatment and improve the patient’s well-being. Thrush most often affects children from birth to 3 years of age.
Allergic stomatitis affects primary school students with weakened immune systems. Bacterial stomatitis can occur in children of any age, and viral stomatitis often affects children from birth to 3 years of age.
Stomatitis in a child
This disease is accompanied by painful sensations throughout the mucous membrane, burning, dryness, decreased appetite, anxiety and irritability. The entire mucous membrane is swollen, red, blisters, erosions and ulcers may occur.
It is necessary to start treatment in a timely manner so as not to aggravate the situation and prevent the appearance of small plaques with a white border (aphtha). The child constantly cries, does not eat and loses weight, and a high temperature may rise.
Drug treatment of candidal stomatitis
How to get rid of thrush in the mouth should be decided only by a doctor who examined the areas of the mucous membrane affected by the fungus. First of all, antifungal drugs for oral administration are selected. In most cases, medications in tablet form are used, such as:
- Itraconazole
- Fluconazole.
- Mikosist.
- Irunin.
Since any person wants to cure oral thrush forever, it is necessary to follow the course of drug treatment prescribed by the doctor. In order for candidal stomatitis to disappear, it is often necessary to use these drugs for at least 1 week. If the inflammatory process spreads to the lip area, they need to be treated with Levorin or Nystatin ointments, which have a pronounced antifungal effect.
Treatment of oral candidiasis in adults and children involves the use of local antiseptics. Treatment with such agents as Dimexide, Miramistin or Furacilin should be carried out at least 8 times a day. Rinsing with these solutions also eliminates the existing symptomatic manifestations of the disease.
Treatment of oral thrush in adults with dentures is complemented by intensive hygiene. This allows you to quickly destroy bacteria and pathogenic fungi that may be hiding in hard-to-reach places. Since it is desirable to cure candidiasis completely so that the disease does not become chronic, it is necessary to immediately begin taking vitamins and minerals to maintain immunity.
In especially severe cases, when a person has primary diseases that greatly affect the functioning of defense mechanisms, the use of immunomodulators may be indicated. Treatment of oral candidiasis requires an integrated approach. The standard course of therapy can be supplemented with a special diet on the recommendation of a doctor. In addition, in some cases, correction of the treatment of primary disorders is required.
Therapy for different types of stomatitis
For different stomatitis, therapy is prescribed depending on the type of pathogen . These could be: bacteria, viruses, allergens. An analysis may be required to determine the causative agents of candidiasis, herpes, or bacterial culture.
To successfully treat stomatitis, you need to undergo an examination, follow all the pediatrician’s prescriptions and oral hygiene, and also drink plenty of chamomile or calendula tea.
Sometimes inexperienced young mothers do the wrong procedures or take medications on their own, which further aggravates the situation. In this case, before consulting a pediatrician or ENT specialist, you can only take painkillers and antiseptics.
Such drugs for stomatitis are prescribed containing benzocaine, chlorhexidine, lidocaine. If stomatitis is of viral etiology, the doctor will prescribe antiviral drugs. With bacterial stomatitis, symptoms depend on the type of microorganism. In cases of mild to moderate severity, antiseptics, painkillers and antibiotics will suffice.
You can use a spray containing lidocaine , however, for children under 2 years of age, this product only treats erosions and does not irrigate the oral cavity. After 4 years, children can dissolve Hexoral Tabs tablets. For all types of stomatitis, you can use the herbal mixture "Stomatofit", and do not forget to treat the oral cavity with a soda solution.
Hexoral Tabs tablets
With catarrhal stomatitis, the mucous membrane is not severely damaged; it occurs as a side infection of measles or scarlet fever. Rinsing with a solution of carrot, beet and cabbage juices with warm boiled water gives good results.
Traditional medicine recommends herbal infusions, Kalanchoe and aloe juices. Propolis tincture has pronounced antimicrobial properties.
Signs and treatment of viral stomatitis
In order to correctly prescribe treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of the inflammatory process.
The most contagious types of thrush or stomatitis in children are of fungal, viral, bacterial etiology; they most often affect children from birth to two years.
How is stomatitis different from thrush? Stomatitis can also be caused by influenza, chickenpox, herpes, enteroviruses and adenoviruses. Almost 90% of the population are carriers of the herpes virus , and the disease develops only in people with weakened immune systems. Herpetic stomatitis is most often diagnosed in children.
It causes the following symptoms:
- the appearance of swelling and redness;
- the appearance of small bubbles (vesicles);
- body temperature up to 40 o C;
- subsequently the vesicles burst and liquid flows out of them;
- formation of ulcers and erosions in the mouth;
- Huge discomfort in babies, which is caused by burning, dryness, and pain.
In complex forms of herpetic stomatitis, nausea, vomiting, fever or headache may occur. Up to 20 vesicles may appear in the mouth.
In mild cases, the temperature remains at the subfebrile level and the blisters are slightly, no more than 6. For treatment, antiviral drugs with interferon, oxolinic ointment and Cholisal gel are used.
For high temperatures, antipyretics are used, and for itching and burning, antihistamines are used in the form of drops for children under 5-6 years of age, and in the form of tablets for children older than this age. We also monitor personal hygiene and control nutrition.
Treatment of thrush
Stomatitis or thrush in infants can cause a rapid increase in temperature and inflammation of the lymph nodes. Foci of thrush localization occur on the lips, cheeks, and tongue, but can also cover the pharynx.
The mucous membrane becomes covered with a cheesy, white coating. In the initial stages of the disease, it can be easily removed with a bandage soaked in a soda solution. All the mucous membrane underneath will be red and inflamed.
In case of mild illness, the temperature may not rise or be low-grade. A child who is bothered by thrush eats poorly and experiences pain.
Itching, dryness, burning, inflammation cause a lot of discomfort and trouble for the baby. Parents have a question: when can a child feel relief?
With normal care, following all doctor's recommendations and treating the oral cavity with soda solution, symptoms may disappear after 3-6 days.
In breastfed children, after each feeding, the mucous membrane in the mouth and the mother's peripapillary area should be treated with a soda solution.
If necessary, your doctor may prescribe antifungal medications. Candide lotion and Miconaz gel have proven effectiveness; they are approved for use from birth.
A fungal infection lowers the pH level , and an acidic environment only promotes the development of fungi. To neutralize the acid and restore the alkaline environment, treatment with a 2% baking soda solution is necessary.