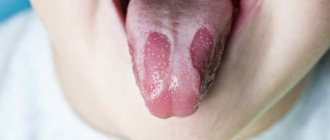
Stomatitis and tonsillitis are pathologies that often accompany each other. Moreover, often the first disease develops against the background of the second, although their simultaneous occurrence is not excluded.
It is not difficult to recognize and distinguish between these pathological processes, and they can be quite successfully cured. However, you cannot do without the help of a qualified medical specialist, otherwise you can aggravate the disease and cause unpleasant complications.
Can pathologies develop simultaneously?
As already noted, stomatitis and tonsillitis are diseases that often accompany each other. This may be due not only to previous viral or bacterial infections of the oropharynx, but also to an incorrect approach to the issue of therapy.
Sore throat and stomatitis at the same time are common occurrences in people who self-medicate. Often, patients cannot correctly determine which pathology they are suffering from, so they resort to very dubious, and therefore dangerous, methods of therapy.
But the worst thing is that some young mothers do not consider it advisable to take their children to the doctor, but use antibiotics at their own discretion. For this reason, sore throat, combined with stomatitis, develops more often in children than in adults.
Causes of the disease
- Untreated foci of infection in the mouth.
- Self-treatment of small infectious foci.
- Taking ineffective medications.
- Ignoring treatment.
- Weak immunity.
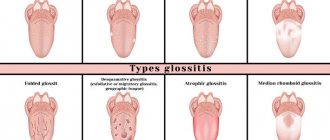
Kinds
Stomatitis, depending on the type of pathogenic flora, can be:
- Candidiasis (fungal infection develops most often due to long-term use of antibiotics).
- Viral (usually provoked by the Epstein-Barr virus or herpes).
- Aphthous (has an infectious-allergic nature).
- Bacterial (caused by streptococci and staphylococci).
- Chemical (burns of the oropharynx with acids and alkalis).
- Radiation (radioactive exposure).
The classification of sore throats is more complex, but according to the type of pathogen it can be divided into bacterial, fungal and viral.
Stomatitis tonsillitis does not have clear specific features; its clinical picture is a mixed version of primary and secondary infection.
What is stomatitis and how to detect it in time, watch our video:
Main signs
Sore throat and stomatitis have similar general symptoms, but some signs of pathologies still differ from each other, and it is these differences that need to be paid special attention to.
The general clinical picture of stomatitis with angina is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain in the oropharynx area,
- increase in body temperature,
- formation of ulcers and plaque on the mucous membranes of the oropharynx,
- chills,
- headache,
- difficulty swallowing food,
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes,
- increasing the intensity of salivation.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of stomatitis sore throat are a combination of signs of these two ailments. The patient can observe the following signs of this type of sore throat in the oral cavity:
- ulcerative lesions;
- redness and enlargement of the tonsils;
- inflammatory processes;
- increased salivation;
- presence of blood in saliva;
- specific smell when breathing;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- bleeding from the mouth.
Stomatitis sore throat is also accompanied by symptoms such as:
- severe pain when swallowing saliva or food;
- loss of appetite;
- weakness and aching joints;
- fever;
- pain in the neck and throat;
- nausea and abdominal pain;
- increased body temperature;
- hoarseness in the voice.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RIoKJ_pdP-8
It is important to know!
EVERYONE should know about this! UNBELIEVABLE BUT TRUE! Scientists have discovered a SCARY relationship. It turns out that the cause of 50% of all ARVI diseases, accompanied by elevated temperature, as well as symptoms of fever and chills, are BACTERIA and PARASITES, such as Giardia, Ascaris and Toxocara. How dangerous are these parasites?
.. »
Stomatitis and sore throat: causes of development
Often stomatitis with sore throat in children develops against the background of a bacterial infection - staphylococcal, streptococcal, etc. But sometimes the onset of the disease occurs against the background of uncontrolled use of antimicrobial agents for tonsillitis.
Factors predisposing to the development of stomatitis with angina in children and adults may include:
- failure to comply with oral hygiene rules,
- hypothermia,
- burn of the oropharyngeal mucosa,
- abuse of spicy and salty foods,
- injuries to the mucous membranes of the mouth or tonsils.
Sore throat and stomatitis at the same time in a child often occur due to the habit of putting fingers, toys and other foreign objects in the mouth. Moreover, stomatitis develops first, and already against its background a catarrhal or even purulent sore throat occurs.
Causes
There are several main factors that can provoke the occurrence of stomatitis sore throat, in which inflammation of the tonsils is a consequence of stomatitis. Among them:
- Weakened immunity.
- History of prolonged use of antibiotics.
- The presence of foci of infection in the oral cavity, for example, carious teeth, etc.
As for stomatitis, which is secondary in nature and occurs against the background of an existing sore throat or shortly after recovery, it is most often provoked by a strong drop in immunity and a violation of the full microflora of the oral cavity caused by taking antibiotics.
Diagnostic features
When tonsillitis develops along with stomatitis, a child, like an adult, requires qualified medical care. For diagnosis, it is often sufficient to conduct a thorough examination of the oral cavity and the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
A mandatory step is to conduct a general clinical blood test. With stomatitis tonsillitis, there is an increase in the number of leukocytes in the biomaterial.
Purulent tonsillitis and stomatitis in a child require special attention from the attending physician. In this case, a smear is performed for bacterial culture. Using bacteriological examination, the type of pathogenic microflora that caused the development of tonsillitis is determined.
Treatment of stomatitis sore throat
When stomatitis sore throat appears, treatment requires only as directed by a doctor ; the correct combination of both professional medications and “home” medicine is considered an effective method.
Along with gargling with medicinal solutions and homemade herbs, it is necessary to lubricate the affected areas with special products used for stomatitis sore throat. The doctor will recommend using a group of antibiotic drugs to stop the manifestations of inflammation and further progression of the disease. The most effective manipulations in treating the disease are the following steps:
- Prescription of Nurofen and other antibiotics that reduce fever and temperature.
- Treatment of the throat with Furacilin, ready-made preparations containing sea salt to alleviate the condition.
- The use of Strepsils, Lyzobakt, which eliminate painful spasms in the throat.
- Sprays based on Ingalipt, Miramistin solution for throat irrigation .
It would not be superfluous to prescribe a general strengthening complex of vitamins to maintain the body’s strength. In addition to the measures prescribed by the doctor, you can use home methods:
- Gargling with herbs based on chamomile and oak bark.
- Treatment of the intraoral cavity with hydrogen peroxide for disinfection.
- decoctions .
Measures for independent therapeutic manipulations must be agreed upon with the treating specialist .
It is necessary to pay attention to your diet, excluding irritating , for example, salty, spicy foods. Hot food is also not recommended during illness, and drinking plenty of fluids is mandatory. Brewed rosehip drink, chamomile infusions and teas with honey somewhat alleviate the general condition of the body.
Stomatitis and tonsillitis: how to distinguish between pathologies?
How to distinguish a patient's sore throat from stomatitis? To do this, you need to pay attention to the location of the foci of the inflammatory process.
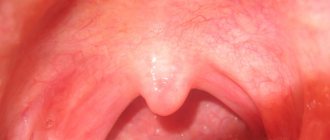
- With angina, ulcers, hyperemic areas and/or ulcers form exclusively on the surface of the tonsils. The mucous membrane of the larynx and palatine arch are red, nasal discharge may appear - transparent or yellowish.
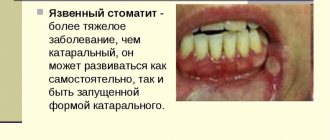
- Stomatitis differs from tonsillitis in that when it develops, aphthae or ulcers appear on the surface of the mucous membranes of the palate, the inside of the cheeks and lips. Possible formation of bubbles filled with cloudy or clear liquid. In this case, they speak of the presence of herpetic stomatitis.
Knowing how to independently distinguish stomatitis from a sore throat, you can promptly identify the pathological process and prevent its spread.
Sore throat stomatitis in children
Often, patients with tonsillitis are simultaneously diagnosed with stomatitis, an inflammation of the oral mucosa. Infection of the body begins to manifest itself with the symptoms of stomatitis, then signs of sore throat appear. As a rule, the disease develops due to decreased immunity or after acute respiratory viral infections. Tonsillitis and stomatitis, especially if the diseases are provoked by herpes, have fairly similar symptoms: the presence of erosions, plaque on the mucous membranes. Such manifestations are characteristic of both ailments. There is even a stomatitis form of tonsillitis, which combines the symptoms of two diseases.
A person can become infected with stomatitis during contact with a sick person. The disease develops gradually: two days or a couple of weeks may pass before the first signs appear. People are more likely to get sick during the off-season. The disease occurs in an acute form - a person’s body temperature may rise sharply, weakness, and painful sensations in the mouth may appear.
Symptoms of stomatitis sore throat: plaque, ulcers on the mucous membrane of the tonsils.
Experts say that the disease is caused by pathogenic bacteria that provoke stomatitis. Stomatitis and sore throat develop on the surface of the tonsils, as well as on the surface of the oral mucosa. A white or yellow coating appears on erosions. Ulcers form under the film on the affected tissues. Acute tonsillitis is severe, especially in children. The sick person's body temperature rises, swallowing food and drinks causes pain, and increased salivation appears. In some cases, the lymph nodes increase in size and hurt when touched. An increased content of leukocytes is sometimes found in the patient's blood. Often this form of tonsillitis lasts no more than fourteen days, but treatment of an advanced disease requires more time.
Stomatitis and tonsillitis affect a weakened body. In most cases, a simultaneous combination of diseases is diagnosed in representatives of the older generation, people with reduced immunity, and children.
Diseases affect the body of an exhausted person, and can also develop with dystrophy. In addition, illnesses arise due to poor hygiene and oral diseases (periodontal disease, etc.).
In addition to standard treatment methods, it is important to thoroughly lubricate oral ulcers. After treatment, treatment and prophylactic measures are necessary to help prevent subsequent infection. Treatment of a child must be especially thorough, since in children the disease often becomes chronic.
It is necessary to gargle with herbal decoctions or an antiseptic.
The patient must follow a diet and bed rest. The diet includes liquid cereals, fruits, herbal infusions, freshly squeezed juices, finely chopped food that will not irritate the mucous membranes. To quickly restore the body, you need to take vitamins. If the patient feels severe pain, the specialist may prescribe medications containing pyramidone. In addition, intramuscular injections of penicillin are possible. Doctors advise treating the affected mucous membrane of the mouth and tonsils with special means, gargling with an antiseptic solution or herbal decoctions. Antibiotics will help prevent a possible relapse of the disease (the disease can reappear in a couple of weeks).
Stomatitis often causes a sore throat, and sore throat often causes stomatitis. The clinical picture of these diseases has its own characteristics. So, with a sore throat, the patient feels pain only when swallowing food, and with inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth, food causes irritation throughout the entire cavity. Another sign is the location of symptoms. In a patient with tonsillitis, plaque and erosion appear in the tonsil area. Images of signs of the disease are available in the medical literature. With stomatitis, pathogenic bacteria primarily affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and lips. The acute form of stomatitis has few differences from tonsillitis. Especially if the infection was caused by herpes. Doctors often diagnose such stomatitis in children under three years of age. At this age, children have a reduction in the number of antibodies they received from their mother. It may take about a month to cure the disease in children. The disease sometimes occurs in a severe form. Therapy for stomatitis should be comprehensive. It is important both local treatment of ulcers and general restoration of the patient’s immunity.
Diagnostics should be carried out only by a competent specialist: he will examine the patient and prescribe tests. Diagnosis of the disease includes various studies (cytological, immunological, etc.), examination of the oral cavity. Comprehensive studies will help determine the cause of the disease, and then determine treatment methods and prescribe medications. When the first signs of inflammation appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. You cannot let the disease go on, as this is fraught with serious consequences. Self-medication is also extremely dangerous for the patient’s health. The treatment options prescribed by the doctor will depend on the cause of the disease and the patient's condition. Incorrect therapy will not help get rid of symptoms. Moreover, self-medication can significantly worsen the patient’s well-being. This significantly increases the risk of exacerbations.
Treatment of the disease should be carried out under the supervision of a specialist. However, if the patient wants to get rid of inflammation in the oral cavity and reduce pain, you can use universal remedies that will not cause harm to health. For example, a sick person can gargle with a decoction of chamomile or rose hips.
If you have symptoms of stomatitis, you need to hold the infusion in your mouth for a couple of minutes; if you have a sore throat, rinse your larynx. You can also treat the sores with a solution of blue or peroxide using a gauze pad. To relieve inflammation, doctors recommend using streptocide powder, sea buckthorn oil, aloe liniment and other means. In the initial stages of stomatitis or tonsillitis, swelling can be relieved with ointments with interferon. In particular, experts prescribe florenal ointment, Gossypol. Before lubricating mucous membranes and wounds, the patient should rinse the cavity with infusions of medicinal herbs or antiseptic solutions. It is also recommended to treat the mouth with enzymes, for example, Deoxyribonuclease in solution form. Painkillers are an integral part of therapy, but they should only be used after consultation with a doctor. He may prescribe trimecaine solutions, lidocaine spray and other medications.
Complex therapy for stomatitis sore throat includes antiviral medications, for example, Bonaferon. One cycle of taking the medication lasts five days. To get rid of toxins and strengthen the immune system, doctors prescribe antihistamines (diphenhydramine, suprastin, etc.), vitamins, and medications containing calcium. Experts also prescribe medications with prodigiosan and lysozyme injections. When treating the acute form of the disease, doctors recommend taking antibiotics.
The patient needs to eat fortified, high-calorie foods, drink warm drinks in large quantities, eat finely chopped non-hot foods, and rinse the mouth after each meal.
Sore throat or so-called acute tonsillitis is an infectious inflammatory disease that affects the tissue of the tonsils. The disease is widespread and often occurs in parallel with other diseases. For example, a fairly common form of this disease is stomatitis sore throat, a case in which sore throat and stomatitis occur simultaneously. What this is connected with and how to distinguish one disease from another is described in this article.
Their definitions alone help to understand how to distinguish stomatitis from tonsillitis. As mentioned above, tonsillitis is an acute form of manifestation of an infectious disease called tonsillitis. The causes of this disease are pathogenic microorganisms, which, depending on the type, can be viruses, fungi or bacteria. The most common causative agent of sore throat is considered to be the bacterium streptococcus, which, often for quite a long time, can be present in the tissues of the tonsils and upper respiratory tract without leading to disease.
The reason for the degeneration of a certain number of harmful bacteria into a dangerous infectious disease, which can have consequences for vital organs and even entire body systems, is the creation of appropriate conditions, one might say, an optimal environment for the development of sore throat.
That is why the list of causes leading to acute tonsillitis also includes additional factors. These include: weakened (for various reasons) immunity of the body, previous infectious diseases, high levels of stress, overwork, incompletely cured diseases of the oral cavity, the presence of bad habits (smoking, alcohol abuse).
Meanwhile, stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the oral mucosa. In other words, quite often, the presence of a disease such as stomatitis is a condition for the development of sore throat with incorrect or completely absent treatment.
Although, it often does not matter which disease develops first, stomatitis or tonsillitis. Just as acute tonsillitis can occur after inflammation of the oral mucosa, as a secondary pathology, stomatitis can develop after a sore throat. This is possible when inflammation spreads from the tonsils to the tissues of the oral cavity. In any case, the combination of such diseases complicates efforts to combat them.
Symptoms of a disease such as stomatitis tonsillitis are a combination of signs of two diseases. Namely, the signs of this type of sore throat include:
inflammation of the tonsils and oral cavity (tongue, lips); the formation of ulcers on the lips and tongue, purulent formations on the tonsils; temperature rise to 38-40? C; discomfort when eating, manifested in pain in the tongue and throat; irritability and fatigue.
The appearance of the first signs of inflammation requires immediate consultation with a doctor. Otherwise, incorrect treatment or self-medication of diseases can lead to serious complications. This is especially true in cases where stomatitis and tonsillitis are simultaneously observed in a child.
When stomatitis is also observed with angina, treatment of the disease, in addition to standard measures to combat acute tonsillitis, will also include procedures for treating mouth ulcers.
Since stomatitis and tonsillitis are very often observed in children, the treatment of these diseases involves the most gentle medications. However, when a bacterial form of sore throat develops, only broad-spectrum antibiotics can cope with it.
In general, doctors’ recommendations for recovery from tonsillitis, including stomatitis, include a whole range of measures. These include:
compliance with bed rest; isolation of the patient from contact with others; regular and balanced nutrition; plenty of warm drinks; carrying out medical procedures; taking medications according to the course prescribed by the doctor.
Carrying out medical procedures means daily gargling with special solutions and treating the tonsils. The course of taking medications to treat the disease usually includes antipyretics, antiseptics, and painkillers. And also, depending on the type of sore throat, antiviral, antifungal or antibacterial drugs can be used.
The entire process of diagnosis and treatment can only be carried out by a qualified specialist. Determining the type of disease and its stage is possible only through a medical examination and a series of tests.
Attention! All articles on the site are purely informational. We recommend that you seek qualified help from a specialist and make an appointment.
Sore throat is caused not only by bacterial, but also by all kinds of viral and candida (fungal) infections. Each type of pathogen manifests itself differently, so treatment is prescribed according to the type and extent of the lesion.
Often, pathological processes in the oropharynx are accompanied by concurrent diseases; sore throat can also manifest itself against the background of a primary infection that has developed in the oral cavity.
Inflammatory reactions in the oropharynx, including signs of tonsillitis and stomatitis, are called stomatitis sore throat in medicine. Bacterial tonsillitis (true tonsillitis) affects only the tonsils, developing as a result of focal accumulation of streptococcal flora on them.
Stomatitis is a dental pathology that manifests itself in the form of lesions of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and lips.
If stomatitis is not treated immediately, a sore throat may develop as a result. Advanced tonsillitis also leads to the development of stomatitis, especially in the presence of caries and problems with the gums. It is believed that stomatitis sore throat is caused by a symbiosis of several infections at once.
If the disease is to blame
herpes virus
, then it is quite difficult to distinguish stomatitis from manifestations of tonsillitis, the symptoms of both diseases are almost identical, therefore only a specialist can correctly diagnose stomatitis tonsillitis by comparing the clinical picture of the disease with data from other studies.
How to distinguish a viral sore throat from a bacterial one:
Kinds
Stomatitis, depending on the type of pathogenic flora, can be:
Candidiasis (fungal infection develops most often due to long-term use of antibiotics). Viral (usually provoked by the Epstein-Barr virus or herpes). Aphthous (has an infectious-allergic nature). Bacterial (caused by streptococci and staphylococci). Chemical (burns of the oropharynx with acids and alkalis). Radiation (radioactive exposure).
The classification of sore throats is more complex, but according to the type of pathogen it can be divided into bacterial, fungal and viral.
Stomatitis tonsillitis does not have clear specific features; its clinical picture is a mixed version of primary and secondary infection.
What is stomatitis and how to detect it in time, watch our video:
Sore throat, like stomatitis, develops most easily in a weak body. Therefore, the symbiosis of these diseases is most often observed in children, the elderly and patients with impaired immune defense.
Other factors can also provoke the disease:
Dystrophy. Avitaminosis. Stressful situations. Hypothermia. Smoking. Irregular oral hygiene. Allergies. Work activity in conditions of increased harmfulness.
In adults
Temperature increase. Inflammation of the oral cavity. Lack of appetite. White coating in the mouth. A sore throat. Severe malaise. Muscle aches. Ulcerative lesions of the oropharynx, lips. Swollen, reddened tonsils, purulent formations on them. Blood in saliva when it is secreted abundantly. Runny nose. Hypertrophy of lymph nodes. Cough.
How to distinguish a viral sore throat from a bacterial one
In children
Young children quite often get stomatitis sore throat. The disease occurs in a more severe and dangerous form than in adults, and therefore requires hospital treatment. In addition to the above symptoms:
Gastrointestinal disorders. Allergies. Convulsions due to high fever.
With the acute development of a mixed bacterial infection, the child may suffocate. This is the main danger of sore throat, so you should not try to treat children yourself.
At the first suspicion of a sore throat, you should consult a doctor. The clinical picture for mixed infections is usually not enough for a correct diagnosis; the following laboratory tests are needed:
Blood analysis. Throat swab. Serological research methods. Antibioticogram.
Manifestations of stomatitis may externally resemble foot and mouth disease, rhabdovirus, or herpetic sore throat. Therefore, when diagnosing, an analysis is sometimes needed to exclude these diseases.
During the first examination, the doctor focuses primarily on a description of the symptoms and a visual examination, and then refers the patient to certain tests.
The photo shows a throat affected by a sore throat.
As with ordinary sore throat, the patient should follow the following rules:
Bed rest. Isolation from close contact with others. Fortified diet, excluding heavy foods. Drink plenty of fluids.
Folk remedies
The most famous rinse products:
Lemon acid. Saline solution. Carrot and potato juice (work well separately or mixed). Beetroot juice with vinegar added. Elderberry decoction. Eucalyptus herb infused in boiling water. Egg whites beaten in a glass of water are good for reducing inflammation. A teaspoon of salt is added to it.
Increases immunity and has an antimicrobial effect by drinking herbal teas:
With rose hips. With cranberries and lingonberries. Linden with the addition of honey. With thyme. With lemon.
Inhalations made from pine buds, herbal infusions, garlic and Zvezdochka balm are popular among people.
They are especially popular for sore throats.
bee products
, based on them there are a huge number of recipes. But here it is important to understand that excessive consumption of honey in food is undesirable, it can cause allergic reactions and an increase in blood sugar levels.
How to cure a sore throat, watch our video:
An integrated approach to treatment reduces the likelihood of relapses and promotes a favorable prognosis. Therefore, after the acute symptoms disappear, the doctor may prescribe additional treatment in the form of the following physical procedures:
Magnetotherapy. Warming up. Phototherapy. Laser treatment. Electrophoresis. Ultraviolet irradiation of the tonsils.
Physiotherapy is contraindicated for pregnant women.
After a seriously ill illness, resort and sanatorium treatment is recommended.
In the later stages of pregnancy, stomatitis sore throat is less dangerous for the fetus than in the early stages. But it is necessary to follow all the doctor’s instructions, otherwise the consequences may be unpredictable.
Stomatitis tonsillitis in itself is a complication of an infection that is not cured in time.
Its further progression can lead to the following consequences:
Asphyxia. Rheumatic heart disease. Pericarditis. Pyelonephritis (kidney disease). Arthritis (complication of the joints). Abscesses of the oropharynx and neck area. Bleeding from the tonsils. Complications of stomatitis significantly expand the list of dangerous consequences: Scarring of the oral cavity (restriction of muscle mobility). Gangrenous stomatitis. Bechcher's disease. Visual disorders. Blood poisoning.
Medical preventive procedures include:
Vaccinations during the season of viral infections. Regular scheduled examinations. Conducting lectures in children's and public institutions.
Reduce the likelihood of disease:
Healthy lifestyle. Complete rest. Strengthening the immune system. Timely treatment of minor focal infections. Careful hygiene of the mouth and teeth.
Infants need to disinfect pacifiers, toys, and feeding bottles. This is especially important when the child is teething. In older children, the risk of microtrauma in the oral cavity increases, which can also lead to stomatitis, so monitoring the child is a necessary condition for maintaining his health.
Tips for preventing stomatitis:
Stomatitis and sore throat: treatment features
Treatment of stomatitis with tonsillitis in a child should be comprehensive. It is strictly forbidden to resort to antibiotic therapy on your own, as this can lead to side effects or significantly worsen the course of the disease.
So, for these pathologies it is shown:
- Rinse or treat the oropharynx with antiseptic solutions three times. For this purpose, the drug Miramistin has been successfully used.
- Rinsing the mouth and throat with herbal decoctions - chamomile, sage, marigold (prepared from calendula flowers).
- Taking vitamins aimed at speedy recovery of the body: Supradin, Revit, Multitabs.
Symptomatic treatment includes the use of painkillers (ibuprofen) and antipyretics (paracetamol, Panadol, Nurofen). Many drugs have both properties at once, that is, they relieve pain and reduce body temperature at the same time.
Purulent tonsillitis, occurring with signs of stomatitis, is treated with antibiotics of the penicillin group (Ampicillin, Penicillin, Amoxiclav) or cephalosporins (Ceftriaxone). Children are often prescribed the drug Cefixime, available in powder form for the preparation of an oral suspension. The course of therapy is 5–7 days.
Treatment
Treatment methods for stomatitis sore throat and stomatitis that occurs against the background of tonsillitis are selected exclusively on an individual basis. Treatment depends on the type of disease, the causes of its occurrence, accompanying symptoms and the age of the patient. Most often, patients with stomatitis on the tonsils are recommended:
- Stick to a healthy diet.
- Use symptomatic medications (to reduce fever and combat pain).
- Organize complete antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity.
- Use medications to fight infection.
- Use drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration.
- Strengthen immunity.
You should not get carried away with self-medication. Each type of stomatitis requires its own correct therapy.
General recommendations
To make painful ulcers in the mouth and tonsils go away as quickly as possible, you must:
- Stick to bed rest. Physical activity, hot baths and overheating are prohibited.
- Follow a fairly strict diet: refuse any rough food, cold or hot, eat more fruits and vegetables (it is better to cook them in the form of purees), as well as dairy products.
- Drink plenty of liquid - regular warm water, tea, compote, herbal decoctions and infusions.
- Brush your teeth regularly and rinse your mouth after every meal.
- Get separate dishes and pour boiling water over them after washing.
- Do not contact healthy people around you.
If you do not adhere to the basic rules of treating stomatitis, you simply will not be able to get rid of the disease quickly. And even vice versa, neglecting simple recommendations is fraught with the development of complications.
Drug therapy
Basically, various local drugs are used to treat stomatitis:
- With this diagnosis, the oral cavity should be regularly rinsed with antiseptic solutions. You can give preference to any available product that is at hand: soda or saline solution (you should add a couple of drops of iodine to it), Miramistin, a weak solution of calendula or propolis tincture, furatsilin, etc. Rinsing should be done at intervals of half an hour.
- To treat affected areas, you can use sprays with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory components, for example, Chlorophyllipt, Ingalipt, Proposol. Hexoral spray can be an excellent find - it will relieve pain and destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
- Doctors also often recommend dissolving tablets with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, for example, Strepsils, Lizobakt, Faringosept.
- To reduce fever and eliminate pain, it is worth using ibuprofen or paracetamol in an age-appropriate dosage.
- If stomatitis is of a bacterial nature, you cannot do without antibiotics, and if the disease is fungal in nature, you should take antimycotic drugs prescribed by your doctor.
- To strengthen your immune system, recover faster and prevent relapses of the disease, you should take multivitamin medications.
- To accelerate the healing of mucous membranes during stomatitis, it is worth lubricating the affected areas with Solcoseryl or Actovegin gel.
Folk remedies
When treating stomatitis sore throat or stomatitis that has developed against the background of tonsillitis, you can resort to the use of various alternative medicines, namely:
- Rinse with infusions of herbs, such as chamomile, calendula or yarrow. 1 tsp. dried herb, brew 1 tbsp. boiling water and leave for 30 minutes. for insisting. Strain the finished medicine and use as directed.
- Rinse with a decoction of oak bark. This is a very effective medicine for stomatitis, and it is very simple to prepare. You need to take 1 tbsp. l. raw materials, brew 1 tbsp. water and put on fire. After the mixture boils, you need to boil it for 10 minutes. Cool the medicine to a warm temperature, then strain and use.
- Chewing aloe or kalanchoe. Pour boiling water over the leaf and simply chew thoroughly for 3-5 minutes. You can use these plants to obtain juice and use it for rinsing.
- Resorption of honey or propolis. Honey should simply be placed on the tongue and dissolved, and a small piece of propolis should be placed behind the cheek or under the tongue and left for 20 minutes.
- Rinse with a decoction of onion peels. Brew 100 grams of dry raw materials with 0.5 liters of boiling water and boil for 15 minutes. Leave the product to cool, then strain. Use for rinsing.
- The use of flaxseeds. To prepare this medicine, take 1 tbsp. l. flax seeds, brew them with 1 tbsp. boiling water and cook for a couple of minutes. Cool this medicine and strain. Afterwards, use the decoction to rinse your mouth at least three times a day. During the procedure, keep the medicine in your mouth so that it has time to take effect. Flax is able to quickly and gently relieve inflammation and promote rapid regeneration of mucous membranes.
When treating with folk remedies, you need to be careful. Any of the listed medications can provoke reactions of individual intolerance and other side effects.