Features of the disorder
Stomatitis refers to inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa. The disorder occurs in numerous forms and occurs due to the action of various provoking factors. Thanks to timely treatment procedures, the disease disappears after a few days or weeks . Under the influence of certain factors, symptoms may recur, causing discomfort.
Glossitis
1. Superficial. Only the mucous membrane of the tongue becomes inflamed. Soreness, swelling and redness appear. This type of glossitis can be caused by the following factors:
- sore teeth or gums;
- poor oral hygiene;
- drinking alcohol and smoking.
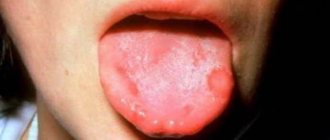
2. Catarrhal. It is superficial. Inflammatory process with pain and burning, aggravated by eating and mechanical irritation. The tongue becomes covered with a white coating, it swells, thickens, mobility is lost, salivation increases, and the patient ceases to feel taste. Catarrhal glossitis is accompanied by rejection of the mucous membrane, and red spots appear in its place. This type of glossitis may indicate the presence of diphtheria, measles, and scarlet fever.
3. Deep. Inflammation that forms deep in the tissues of the tongue. It proceeds as purulent inflammation - phlegmon or abscess occurs. In both cases, the pain is concentrated deep in the tongue. The spread of purulent inflammation leads to pain in the neck or chin. Next, the microbes can invade the lymph nodes, they become enlarged and extremely painful. The pathology causes a jump in temperature, weakness, and headaches. Surgical treatment is indicated.
Classification of the disease
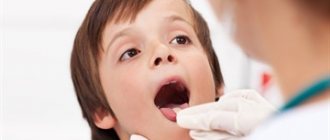
When inflammation appears on the oral mucosa, you need to consult a specialist for treatment. It will help determine the nature of the development of the disease and select the correct treatment method. For normal diagnosis, a scraping is made from the inflamed area.
Based on the nature of the pathogen, the following types of disease can be distinguished:
- Vesicular stomatitis develops under the influence of viruses. Infection occurs after the bite of an infected insect.
- Herpes occurs after herpes enters the circulatory system.
- Aphthous is a complication of the herpetic form, which manifests itself as a result of improper treatment.
- Viral can appear after influenza, smallpox, measles, and other viruses.
- Candidiasis appears as a result of infection of the oral mucosa by pathogenic microflora.
- Bacterial is caused by staphylococcal and streptococcal infections, factors that provoke gonorrhea and diphtheria.
- In addition, the causes of stomatitis include an allergic reaction to certain types of products.
- Catarrhal manifests itself with different symptoms.
- Ulcerative stomatitis occurs as an independent disease or a complication after the catarrhal form.
Causes
The condition of the oral mucosa is determined by the substances that make up saliva, which has antiseptic properties. Therefore, pathogenic microbes are suppressed in the mouth. One of the main reasons for the appearance of stomatitis is a change in the properties of saliva . Such changes are often made during the process of dehydration, when children are not given enough liquid or there is low humidity in the room where they are located.
When a child is dehydrated, he is constantly thirsty, his mouth is dry, and he urinates infrequently. The urine becomes darker, tears do not flow while crying, the face turns pale, circles appear under the eyes.
Among the common factors that provoke diseases are:
- The immune system is weakened due to frequent colds or other disorders, lack of vitamins, and unsuitable living conditions.
- Inadequate oral hygiene , neglect of the need for treatment.
- Use of antibiotics and other drugs.
Infectious infections become the main causes of the development of the disease. This happens if personal hygiene rules are not followed. The infection process develops when children bite their cheeks and injuries appear on the gums and lips when brushing their teeth. With the development of infectious disorders, microbes penetrate the mucosa through the lymphatic vessels.
Infection can be transmitted through the respiratory tract after a sick person coughs or sneezes, or after sharing a pillow, towel or cutlery. Children are often infected by kissing. Saliva containing germs enters the mouth.
Sometimes stomatitis causes a burn from tea or porridge; irritation can be caused by garlic and pepper. The allergic form occurs after taking medications or food to which the immune system reacts poorly.
When should you sound the alarm?
If home remedies have been tried but are not successful, you should consult a doctor. A signal to visit a specialist can be pain, as well as traditional symptoms of irritation - coating on the tongue, ulcers and bumps, burning. To make a diagnosis, the doctor sends the patient for tests - smears, blood, biopsy, allergy test, acidity test, anxiety and depression levels.
Discomfort and persistent pain in the tongue, especially if the cause is unclear, is a clear signal to visit a doctor. Most likely, the doctor will prescribe medications and prescribe procedures to alleviate the condition.
Diseases of the muscular organ in the human mouth are a dangerous condition that can cause complications. This is especially dangerous for a child, since excessive swelling of the tongue may block the supply of oxygen, which will cause suffocation. There are cases when you need to see a doctor immediately:
- raising body temperature to 40 degrees;
- body temperature is 39 degrees or above for more than three days;
- inflammation of the papillae of the organ, which is visually manifested by a profuse rash;
- bleeding;
- cases when parents do not know about the nature of the disease;
- a sharp loss of strength in the child;
- possibility of bacterial inflammation;
- the appearance of formations in the mouth that are unknown to the parents.
Weak immunity
Frequent occurrence of stomatitis in children may indicate poor functioning of the immune system. More often this happens to babies who have had the herpes form of the disease. When the immune system is weakened, herpes appears and provokes symptoms of the disease.
The protective functions of the child’s body are weakened by the following factors:
- Jar of Hearts.
- Intellectual or physical activity.
- Failure to adhere to sleep patterns.
- Overheating or hypothermia.
- Allergic reactions.
Parasites
Through dirty hands or unwashed food, it is possible to introduce not only microbes into the body, but also worms. Their eggs can be laid in seafood, meat dishes, vegetables, etc.
Due to the work of worms, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract deteriorates . Dysbacteriosis and problems with the acid-base balance appear. Initially, the disorders spread through the digestive system, then into the oral cavity.
Parasites can also weaken the immune system, provoke gastrointestinal disorders, reduce iron levels in the body, and contribute to the development of anemia, diarrhea, and dehydration. All these factors can provoke a new attack of stomatitis.
Why does my cheek hurt?
There are a lot of factors that can provoke pathological processes in the cheek area. Here are just a few of them, the most common:
- allergies to food or body care products,
- teething,
- a piece of food that gets into the gum pocket and causes suppuration,
- stomatitis,
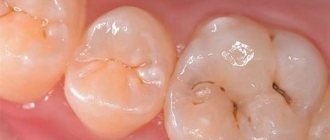
- deep caries,
- pulpitis (inflammation of the dental pulp),
- periodontal disease (damage to periodontal tissues),
- periodontitis (inflammation of the tooth root membrane), gumboil (suppuration in the periosteum),
- gingivitis (swelling of the gum tissue),
- not completely removed nerve in a dental unit,
- inflammation of the facial nerve or lymph node,
- injury due to the child hitting or accidentally biting the inside of the cheek,
- sinusitis,
- mumps (popularly called mumps),
- temporal tendonitis (inflammation of the tendons of the masticatory muscles),
- temporomandibular joint disease,
- tumor,
- a bite of an insect.
It can be difficult to determine on your own what exactly the problem is. However, the baby is suffering and adults must take immediate measures to relieve the pain symptoms.
Poor nutrition
Frequent stomatitis in children occurs due to poor diet. The consequence of this is a lack of nutrients in the body.
The diet should include: vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs, fish, meat, dairy, cereals, nuts, honey.
During the cold season, a multivitamin for babies allows you to compensate for the deficiency of nutrients. You can use medications only with the permission of a doctor.
Symptoms
The incubation period of the disease lasts from 4 days to a week. The first signs resemble a mild form of ARVI: high fever, chills, general weakness, nausea, vomiting, lymphadenitis, rhinitis, conjunctivitis.
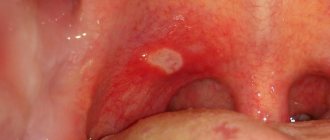
A plaque appears on the mucous membrane, not always the same color. Then small ulcers and blisters form.
Stomatitis differs in clinical signs:
- With the viral form, bubbles with a cloudy liquid appear, which burst and then form round ulcers. When small formations come together, large erosive areas are created that are covered with plaque. The mucous membrane begins to become hyperemic.
- With herpetic stomatitis, a marble pattern forms on healed ulcers.
- The primary manifestation of candidal stomatitis is dryness in the mouth, which is accompanied by pain or burning. You may notice a sour odor from your mouth. Then the mucous membrane becomes covered with white spots. When formed in large quantities, they visually resemble a curd coating. Bleeding erosion appears after removal of such plaque.
- The bacterial form is characterized by redness of the mucous membrane with superficial erosions. Yellow crusts often form on the lips, gradually drying out. The secretion of saliva is taken into account, and a rotten smell is formed.
- Aphthous stomatitis differs from other types of the disorder in the formation of an ulcer with a white center and redness along the edges. The disease can develop into a chronic form and manifest itself as an allergic reaction.
Acute herpes stomatitis
We got sick on Friday, and our pediatrician said that my throat was red - SARS. She prescribed antibiotics, but today it turned out to be stomatitis, the gums were swollen terribly and were bleeding. Let's go to the dentist. and she is shocked by the prescription of antibiotics - they provoke thrush in case of stomatitis. So we were not treated, but maimed. I found a good article about this. Maybe it will help someone recognize the disease in time.
The baby cries and worries, constantly puts his hands in his mouth... And the reason for this is not at all due to teething, but due to stomatitis. And older children are not immune from this trouble. Dentist Tatyana Zinchenko will tell us what kind of disease this is and how to treat it.
– What do parents need to know about stomatitis and what can cause them?
Stomatitis
is an inflammation of the oral mucosa of various nature. Let me list the most common causes of stomatitis point by point. This:
– How to determine that a child has stomatitis?
Clinical manifestations of stomatitis are varied. The child suddenly became irritable and capricious, his sleep apparently worsened, he refused to eat, and complained of pain in his mouth. Body temperature may rise, dyspeptic disorders may occur: bloating (flatulence), diarrhea, pain, rumbling in the stomach, etc. This is a sufficient reason to pay close attention to his oral cavity.
– And what can mom see there?
First, palpate the child's submandibular and anterior cervical areas. Most often, small swellings can be found there - enlarged lymph nodes, painful or painless.
In the child’s mouth, you will notice various kinds of redness, plaque, ulcers (aphthae) with or without plaque, blistering rashes, etc. on the mucous membrane.
- How to proceed then?
If you notice these symptoms in your child’s oral cavity, you should seek help from a dentist. General treatment, if necessary, is prescribed by a pediatrician.
– We already know that there are different types of stomatitis. What type of illness do children get most often?
Infectious stomatitis of a viral nature - herpetic stomatitis.
– It’s more common, of course, to find herpes on the lips...
Nothing like this. Herpes
(from the Greek herpes - fever) is the most common viral infection in humans, existing for a long time in the body. Moreover, mainly in a latent (hidden) form. No infection has such a variety of clinical manifestations as the herpes virus. It can cause damage to the eyes, nervous system, internal organs, mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, oral cavity, genitals, can cause cancer, and has a certain significance in neonatal pathology and the occurrence of hypertension.
– And in dental practice?
Most often, there are two main forms of herpes infection: primary
, occurring as acute herpetic stomatitis (AHS), and
recurrent
- in the form of chronic recurrent herpetic stomatitis (CRHS).
– At what age can babies get sick?
The frequency of primary herpesvirus infection increases in children after 6 months of life, when antibodies received from the mother disappear. The peak incidence occurs at the age of 2-3 years. Herpes virus infection often occurs in newborns.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can distinguish stomatitis from other diseases. You cannot carry out any procedures at home without the participation of a specialist. You should consult a doctor immediately after symptoms occur.
Diagnostic procedures:
- Analysis of blood, urine, feces.
- Study of mucosal scrapings.
- Cytological diagnosis.
- Check for viruses.
- Detection of bacteria.
- Analysis of the state of the immune system.
Such activities are carried out to recognize factors that provoke negative symptoms.
Treatment
Many people try to treat stomatitis without going to a medical facility. This kind of practice is prohibited. Only a doctor can prescribe a suitable therapeutic method.
When treating stomatitis, the following is performed:
- Relief of symptoms with antiviral drugs.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptics after eating.
- Painkillers.
- Healing ulcers using ointments and toothpastes.
- Use of medical sprays. Such products are prohibited for use by children under 1 year of age.
Help relieve pain: sea buckthorn oil, rosehip-based gel, anesthetic substances.
If stomatitis reoccurs in an infant, you will have to urgently consult an immunologist. The doctor should monitor the treatment process for one-year-old babies.
Herpetic stomatitis requires hospitalization when its severe form develops. The disease can spread throughout the body due to increased intoxication. Mild and moderate forms of the disease do not require hospitalization. For effective therapy, an antiviral agent and the following procedures are prescribed:
- The oral mucosa should be lubricated with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide with the addition of furatsilin. Then you can use herbal decoctions if you are not allergic to the components.
- Lugol's solution is used as an antiseptic to eliminate infection.
- Since herpetic stomatitis causes severe pain in the mouth, anesthetics and local anesthetics of mixed action are used.
- Medicines for herpes and other antiviral drugs are used
- In case of acute development of the disease and constant relapses, you can use prescription antiherpes medications
- Oil solutions are used to improve mucosal regeneration.
During therapy, you need to follow a gentle diet, do not eat spicy, sour foods, or drinks that are too hot or cold. For preventive purposes, the child should be given separate dishes.
ethnoscience
If a 5-year-old child has a sore cheek, traditional medicine can alleviate the condition. Cold compresses are considered effective, in which ice must be wrapped in a cloth and applied to the sore area. This allows you to relieve discomfort. Instead of ice, you can apply half a raw potato with the cut side to the skin.
Antiseptic rinses with a baking soda solution help. For this, 1 tsp. The product is dissolved in a glass of warm boiled water. Herbal infusions based on chamomile, calendula, green or black tea, oak bark and other herbal infusions have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effects. Preparation is carried out by brewing 2-3 tbsp. l. raw materials with a liter of boiling water.
Prevention
Parents should be responsible for carrying out preventive measures. Let's figure out what needs to be done:
- Children need to be protected from injuries at home.
- Eliminate infections and viruses in a timely manner.
- Check your oral cavity regularly. This is especially important in the first 3 years.
- Disinfect nipples before breastfeeding.
- The child's hands should always be clean.
- When teeth erupt, you need to send your child to the dentist more often.
- It is necessary to provide your baby with a nutritious diet containing plenty of calcium and other useful minerals.
- All diseases should be treated only by a doctor.
How to recognize and treat stomatitis in a child - video
Recommendations from Dr. Komarovsky on how to detect the presence of stomatitis in time and treat it correctly.
Lack of proper treatment of mild forms of stomatitis in children develops into complex and chronic forms. It is more difficult to fight such diseases, so at the first suspicion you need to contact a specialist for help. Frequent stomatitis in a child indicates other problems with the body. Often pain increases due to a weak immune system.
Mouth pain in children
Pain in the mouth is an unpleasant and dangerous symptom that interferes with eating, swallowing normally, and even speaking.
Most oral discomfort is related to dental problems, but it doesn’t have to be. This sign can indicate many serious illnesses. And since it is through the mouth that we take in food, without which we cannot live, it is necessary to solve the existing problem as soon as possible. Soreness in the mouth is possible at any age. The discomfort may be accompanied by other symptoms, including fever.