How are baby teeth different from permanent teeth?
There are significant differences between primary and permanent teeth:
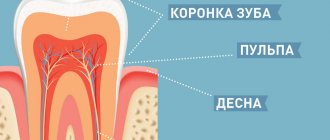
- Root. In temporary occlusion units, the canals are very wide, as a result of which the inflammatory process and pathogenic microorganisms quickly penetrate the jaw bone and periodontium. This can provoke the development of periodontitis, and then periostitis. Diseases can lead to damage to the molar tooth germ located under the root of the milk tooth, and it will subsequently die or grow, but will have defects.
- Crown. In a temporary tooth it is larger and has a convex shape. The width of the unit is greater than the height. By the time the bite changes, the tubercles and cutting edges of the baby tooth are gradually erased.
- Enamel and dentin. The tissues of baby teeth contain less minerals, which means they are less durable and more susceptible to caries and abrasion. Due to the thin walls of the crown and the large volume occupied by the pulp, caries in children develops at lightning speed. The disease often affects the tooth from all sides, and not from one, as in permanent ones.
Temporary units differ from primary units in that they have roots that can be absorbed by the time the bite changes. The canals with nerves and blood vessels disappear - only the crown remains of the tooth.
Can baby teeth hurt?
There are still myths and misconceptions that many parents willingly believe. When asked whether children’s baby teeth hurt, they will confidently answer “no.” They believe that primary teeth do not have nerves, so developing caries will not be painful.
Even the smallest child can have toothache. The structure of the mammary units does not differ from the primary ones, and the absence of discomfort during a strong inflammatory process indicates that the nerve has already been fundamentally destroyed. Also, pain syndrome may be absent at the initial stage of caries, but the disease will make itself felt when a cavity forms in the unit and bacteria reach the pulp.
An affected baby tooth in a child hurts periodically, just like a permanent tooth in an adult. It can react to air, cold, sour, etc. food. Caries and pulpitis are the most common dental diseases in children. The main reasons for their development are poor tissue mineralization, a thin layer of enamel and poor hygiene.
Can excessive acid microflora cause a hole in a child’s baby tooth?
An excess of carbohydrate and protein foods increases the acidity of the oral cavity. Another factor influencing the formation of pathogenic microflora is the presence of food debris in the interdental space.
The most dangerous for the formation of bacteria are pieces of meat food and sweets. As a result of the activity of anaerobic bacteria, pathogenic microflora develops, causing holes in baby teeth, which leads to the development of caries.
- Disruption of the digestive system is the third cause of the disease.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are as follows:
- diagnosing gastritis;
- liver inflammation;
- hereditary predisposition to gastrointestinal diseases.
All this leads to the formation of plaque on tooth enamel, yellow and brown spots. The first signs of caries form under them. Moreover, the development of the disease provokes the further spread of infection, as a result of which diseases of the stomach and intestines become acute. Poorly processed food enters the stomach, which contributes to the development of gastritis and inflammatory processes.
If your baby’s tooth is not yet loose, you should urgently consult a dentist, since it is still possible to cure it. If a molar begins to form under the baby tooth, there is no point in saving the first one, since it will fall out after some time. Accordingly, if holes form in the teeth of small children, and because of this the baby feels severe discomfort, in most cases removal is performed. In this case, removal is possible even without anesthesia, since the loose fang will fall out without pain.
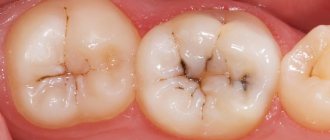
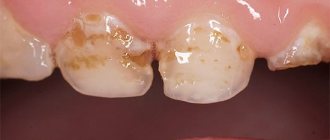
What does caries look like in a child?
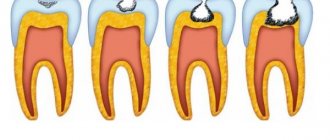
Caries in children goes through 4 stages of development:
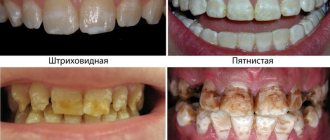
- Initial. White spots or stripes appear on the teeth. The enamel becomes rough, losing its shine at the site of the lesion. This occurs due to the loss of calcium and fluoride from the area of the tooth. At this stage, the tissue is not yet shrinking - demineralization can be stopped.
- Superficial. Irreversible changes occur in the enamel, its top layer is damaged. The carious spot becomes noticeable, acquiring a light brown tint. Such teeth hurt when chewing sour, sweet, salty foods, and also react to thermal irritants. A child with a high pain threshold may not have any complaints of discomfort.
- Average. Microorganisms have already destroyed the hard tissues of the tooth and penetrated the dentin. Parents can determine the presence of a problem by visual inspection - a dark recess is formed. Food particles become lodged in it, causing pain. The process of development of the disease accelerates, discomfort is felt not only when exposed to thermal irritants, but also when chewing.
- Deep. A hole appears in the tooth. A thin layer of bone tissue remains between it and the pulp. Food gets stuffed into the hollow, causing acute pain. While eating, the child tries not to chew on the sore side. The deep stage of the disease in children is rare, since only 2–4 months pass from the initial form of caries to pulpitis.
Children aged 3–4 years usually cannot point to a specific tooth that causes discomfort, and due to the fact that the disease is at the initial stage of development, it is impossible to see the affected areas. You should pay attention to the symptoms: if the baby cries while eating, refuses it, or touches his teeth or lips with his fingers, action must be taken.
Diagnostics
Dental treatment for a child aged 3 years begins after diagnostic measures. Their caries develops rapidly and aggressively, even compared to adults. This is due to the fact that the enamel of baby teeth is weak and includes micropores where bacteria can easily enter. After the development of the carious process begins, the tooth is destroyed within a few months. Therefore, it is important to visit the dentist every 3-4 months.
We suggest you read: White film in the mouth of an adult. A white ulcer appears in the mouth: how to treat it correctly
Symptoms of caries depend on the stages:
- Elementary. First, white spots appear on the enamel. Then they become yellowish and the surface will be rough. The child does not feel pain, but a reaction to hot and cold food is likely. This stage is treated without drilling with a drill. In this case, a filling is not needed.
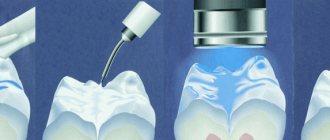
- Average caries. In this case, the enamel layer is destroyed and a “hole” appears. Sharp pain occurs when exposed to mechanical or chemical factors. At the bottom of the cavity there is an accumulation of softened dentin and food debris. Gentle methods and prevention do not help - it is necessary to install a filling. The dental cavity will be open; it should be hermetically sealed with filling material.
- Deep. The “hole” becomes large and noticeable. Enamel and dentin are damaged. When probing the bottom of the cavity, a lot of softened dead tissue is noticeable. Deep caries is treated with filling. But often the enamel is so destroyed that it is impossible to install a filling, and the baby tooth is removed.
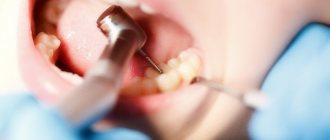
How teeth are treated for 3-year-old children depends on the stage of caries. To do this, it is enough to carry out a visual inspection and probing. But often the carious lesion is located in a hard-to-reach place. Then you need an x-ray or an intraoral camera.
If it is difficult to determine initial caries, the doctor uses a caries detector. This liquid turns infected tissue blue or pink. This drug is safe for children.
How are teeth treated for young children?
If the baby complains of discomfort, he should be shown to a pediatric dentist. He will conduct an inspection and find out how damaged the unit's tissues are. He will also decide whether to treat baby teeth using conservative methods, or whether a more serious intervention is necessary with the installation of a filling. A professional will be able to win over the child and make sure that he is not afraid of dentists in the future.
Silvering and fluoridation
One of the methods of dental treatment is silvering. The procedure is performed on children under 3 years of age and is necessary to stop the spread of caries, but can only be used at the initial stage of its development. To coat the units, the doctor uses a 30 percent solution of silver nitrate, which has an antibacterial effect. The method has many advantages:
- painless and safe for the child;
- affordable price of the procedure;
- stopping the development of caries;
- reduction of plaque formation;
- speed of implementation.
The main disadvantage of silvering is that it stains teeth gray, but kids don’t pay attention to this. Many doctors believe that this procedure is useless, but if no other therapeutic procedures are performed, silver plating will have an antimicrobial effect for some time.
During the procedure, the doctor applies a solution to the child's teeth using a cotton swab. To achieve the desired effect, you will need to coat the units 3-5 times with an interval of 1 day. Six months later, silvering is repeated.
Anesthesia
How else do children 3 years old get their teeth treated? The use of anesthesia is effective if the child is very restless and hyperactive. And some may be afraid of dentists. You should not be afraid of this method; it is actively used in Western countries for treatment from 1 year.
We suggest you read: White plaque on the tonsils without fever - how to treat it in an adult, what to do if the tonsils are covered on one side
Some parents worry that anesthesia affects the child's memory or impairs speech development. Theoretically this is allowed, but in practice it is rarely observed. The complication does not arise from the anesthesia itself, but due to the child’s stress in dentistry or a chronic disease in combination with general anesthesia. For bottle caries, anesthesia is considered the only method of performing manipulations in 1 procedure.
How are teeth treated for 3-year-old children under anesthesia? Before this, surrender is required:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- biochemical blood test;
- blood sugar test;
- electrocardiography.
You can’t eat 6 hours before anesthesia, and you can’t even drink 4 hours before. The child goes into a sleep state. You can wake him up at any time, you just need to increase the dosage of oxygen. Within 15 minutes, all reflexes are normalized.
Maybe it's better to wait until they fall out?
Many parents wonder whether it is necessary to treat baby teeth, because nature intended that they are only a temporary replacement for permanent ones. Dentists are unanimous in their opinion: it is worth carrying out not only treatment, but also prevention of caries, because this is the key to a beautiful smile in the future. A number of arguments can be made in favor of carrying out therapy instead of extraction:
- Under the temporary teeth are the rudiments of the molars. An infected milk unit can irreversibly damage the permanent one.
- Loss of canines and incisors leads to diction problems. The baby simply cannot pronounce some sounds. In addition, the child will be forced to bite off food with the help of molars, which will lead to their rapid wear.
- A diseased tooth is a source of infection. It leads to the spread of caries to healthy temporary and root units, which are especially vulnerable within a couple of years after their appearance. It can also provoke the development of diseases of the throat, gastrointestinal tract, and heart.
- The affected units are destroyed over time to the base, which leads to improper formation of the bite.
- A child whose teeth are covered with carious black spots is embarrassed to smile and grows up with a complex.
It is worth remembering that after suffering from pulpitis or periodontitis, resorption of the roots of temporary units may not occur. In this case, they will need to be removed. To prevent illness, the baby should be taken to the doctor for the first time at the age of 1–1.5 years.