Factors promoting development
The main reason for the development of gumboil remains the presence of carious, untreated teeth. With an inflammatory lesion, periostitis develops. Therefore, before starting pregnancy, it is imperative to visit a dentist and treat all carious teeth, check existing fillings and eliminate other defects in the oral cavity. If you plan your pregnancy in advance, you should treat all existing inflammatory processes and undergo a course of restorative therapy for the smooth bearing of the baby.
An important factor in the occurrence of the disease is poor personal oral hygiene. Bad habits and physical trauma to the gums, followed by infection in the wound.
Symptoms of syphilis during pregnancy
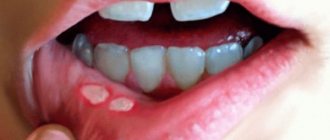
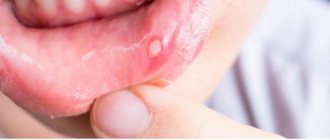
The disease can manifest itself with typical symptoms or be hidden. The first symptom of primary syphilis is a painless chancre (ulcer). It is a raised, reddened, rounded area with a diameter of up to 2 cm. The edges of the chancre are raised, scanty discharge is observed, and a crust may form on top. Localized on the genitals, lips, rectum, tongue, cervix, tonsils, mammary glands, fingers and toes.
After about 6 weeks, a scar forms at the site of the chancre. The disease becomes latent. A pregnant woman may feel weakness, headache, fever, and malaise.
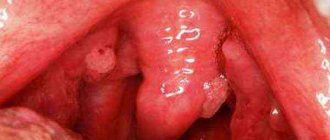
A symptom of secondary syphilis is a rash on the body, soles, and palms. The patient feels fatigue, fever, and headache. During this period, hair loss and enlarged lymph nodes are possible.
In the late stage (tertiary syphilis), damage to the heart, nervous system, eyes, liver, bones, spinal cord, joints, and brain is observed. All this leads to bone deformation, mental disorders, blindness, paralysis, deafness and death.
Manifestations of flux
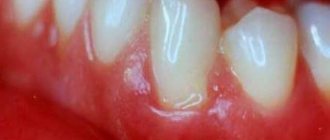
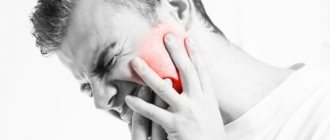
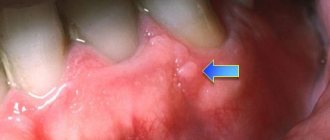
The process of flux formation occurs with the unfolding of a pronounced picture of the disease. There is a sharp increase in body temperature to 380, symptoms of general intoxication (weakness, lethargy and drowsiness). Locally it is indicated by severe pain in the localization of the flux, especially when pressing on the affected gum. Externally, swelling of the cheek is noticeable, and if the maxillary region is affected, the nose and lower eyelid swell. Regional lymph nodes correspond to the inflammatory process: palpation reveals an enlarged node, a mobile, elastic formation that is painful when pressed. The patient cannot eat, and sometimes speech suffers due to severe pain in the affected tooth.
When examining the oral cavity, a focus of inflammation is visualized in the form of swelling and hyperemia of the gums; in some cases, it is possible to detect a fistula (a canal with inflammatory contents), upon exposure to which it becomes white.
Causes in pregnant women
Against the background of a significant decrease in immunity in a pregnant woman, the symptoms of the pathology appear much more clearly. In this case, the patient’s body temperature can reach 39 ºС, which is a dangerous condition for the fetus.
As for flux itself, the main reasons for its formation are, first of all, dental problems:
- xerostomia, or lack of sufficient saliva in the mouth;
- advanced, untreated caries;
- periodontitis;
- pulpitis;
- pathologically deep periodontal pockets;
- violations during endodontic treatment;
- mechanical tooth trauma;
- gum disease;
- poor oral hygiene.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is not difficult. The diagnosis is made based on the collection of complaints, examination, palpation and x-ray of the jaw. Pregnancy is not a contraindication due to low radiation exposure to the jaw. During the examination, the woman's abdomen is protected with a lead apron, but unless absolutely necessary, X-rays are not used. The CBC will show the presence of an inflammatory process in the body.
Stomatitis on the palate - what are the causes and ways to combat the disease
Can tests always confirm the presence of syphilis?
Diagnosis of syphilis is based on the results of serological tests, which demonstrate the presence or absence of antibodies to the causative agents of this disease.
There are two types of tests. The nontreponemal test will always be positive for syphilis infection. This test may appear to be a false positive for syphilis because the result may indicate the presence of another disease.
However, during the treatment of syphilis, only these tests can have a negative result, indicating successful treatment. The treponemal test exclusively indicates the presence of syphilis. But it may indicate syphilis, which the patient suffered from in the past, and not now.
Therefore, to accurately determine the disease and conduct serological studies (non-treponemal and treponemal tests) of the venous blood of the mother and her child, comparisons are made of their indicators.
If excesses (AT titers) occur in the baby’s blood, then congenital syphilis can be diagnosed.
The likelihood of the baby becoming ill becomes greater if the mother was treated inadequately for syphilis during pregnancy. For example, late (after the 32nd week), without following instructions and with drugs not based on penicillin.
In this regard, it would not be amiss to recall that pregnant women should be screened for syphilis during the 27th – 30th weeks and again: 36th – 40th weeks. As well as newborn children of mothers who did not undergo treatment during pregnancy.
Treatment
Fluxes have occurred during pregnancy and what should the patient do? Self-medication is out of the question. Flux is a serious disease, prone to serious complications that threaten the life of not only the pregnant woman, but also the fetus.
Treatment with antibiotics in this situation is not acceptable; it will have a detrimental effect on the health of the fetus. You should contact a specialist for help as soon as possible. Treatment of a pregnant woman is complex and carried out in a hospital setting under joint management with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
Gum diseases
Permitted types of anesthesia
As a rule, during the treatment of flux, the use of painkillers is inevitable.
During pregnancy, it is necessary to use only those products that cannot penetrate the placenta and harm the fetus.
The drugs Ubistezin or Ultracain D-S are usually prescribed. These drugs are non-toxic, but they are contraindicated in case of anemia and bronchial asthma. Doctors prescribe painkillers, taking into account the individual characteristics of the pregnant patient.
The use of drugs that negatively affect the child and can lead to developmental pathologies is not allowed.
Among the dangerous drugs:
- Lidocaine;
- Imudon;
- Septanest.
To relieve pain at home, it is allowed to take Paracetamol, Nurofen, No-shpu, Spazmalgon.
Features of the treatment of periostitis: what should the doctor do
Based on a clinical examination and medical history, the doctor will plan further actions and determine how to treat flux in a pregnant woman. All procedures must be as gentle as possible. The dentist is required to provide therapy, including the following features:
- Minimize the effects of x-ray exposure. It is advisable to carry out diagnostics using modern devices with minimal radiation: radiovisiograph, orthopantomograph. If the clinic only has outdated equipment, E-grade film is used and the abdomen is covered with a lead apron.
- Use safe painkillers. Treatment will consist of either preserving the tooth or removing it. In any case, it is necessary to drain the gums and ensure the outflow of purulent exudate. Regardless of what therapeutic measures the dentist takes, all manipulations must be carried out under anesthesia. For pregnant women, drugs that do not contain adrenaline are used to avoid vasoconstriction and increased heart rate.
- Carefully monitor the patient's condition. The risk of losing a child is especially high in the 1st and 3rd trimesters. In the last months of pregnancy, all interventions are carried out only in a hospital under the supervision of a group of doctors: a dentist, an anesthesiologist, a gynecologist, and sometimes a cardiologist and an endocrinologist.
- Find an alternative to antibiotics. They are necessary for purulent and inflammatory processes to get rid of infection. However, all antibiotics affect the fetus. Therefore, in pregnant women they try to replace them with multivitamin complexes and immunostimulants so that the body can cope with pathogenic microorganisms on its own. But if there is an urgent need, drugs that are safe for pregnant women are prescribed: Amoxicillin, Ampicillin, Cephalexin, Ceftriaxone (contraindicated in the early stages), Macropen.
Additional Information! When contacting a dentist, it is necessary to tell about the symptoms, when they occurred, tell the exact timing of pregnancy and the specifics of its course, especially if there are complications.
Self-medication is unacceptable!
How to avoid flux: preventive measures
It is best to ensure that flux does not occur during pregnancy. Since it appears due to dental diseases, weakening of local and general immunity, preventive measures include:
- Carrying out sanitation of the oral cavity. It is highly advisable to cure caries, gum inflammation, and remove tartar before planning a pregnancy.
- Timely elimination of any diseases of teeth and gums. While carrying a child, it is necessary to pay attention to even minor symptoms and treat any diseases in a timely manner, even if it is just plaque or caries at the white spot stage.
- good oral hygiene. You should brush and floss your teeth at least twice a day and use an antiseptic rinse after every meal.
- Strengthen immunity. The diet should be balanced, with a high content of calcium, fluorine, iron, selenium and vitamins B, C, A. It is also necessary to take recommended vitamin complexes and immunostimulants.
Timely treatment of dental diseases is the best prevention of complications.
Treatment of flux during pregnancy is complicated, since it is impossible to use standard drugs: anesthesia containing adrenaline, antibiotics. Any surgical interventions are also undesirable. Therefore, it is easier to prevent periostitis: carry out preliminary sanitation of the oral cavity, get rid of dental diseases in a timely manner and strengthen the immune system.
Symptoms of the disease and its forms
If we consider the question of whether it is possible to get pregnant with syphilis, the answer will be positive. In addition, many women infected with Treponema pallidum discover their problem during pregnancy, during a medical examination. The sooner the disease is identified, the lower the price for the unborn baby.
The difficulty lies in the fact that it is not always possible to notice the symptoms characteristic of this particular disease.
This is due to the variety of forms of pathology:
- Incubation. Covers the first month from the moment of infection.
- Primary . The appearance of the first symptoms is observed after about 1 month, this phase lasts about 40 - 50 days.
- Secondary. The average duration of this form of the disease is 2 - 4 years.
- Tertiary. Occurs from the 5th year after infection in the absence of quality treatment.
- Hidden . It is divided into early and late, depending on the duration of infection. There are no obvious symptoms; nonspecific manifestations may be observed in the form of fever to subfebrile levels, weakness, and loss of appetite.
The presence of Treponema pallidum in the body provokes the appearance of ulcers on the skin, namely in the area through which the infection occurred. Subsequently, infectious granulomas and scars form in the tissues, and the functioning of various body systems is disrupted.
Treponema pallidum provokes the development of the disease and the manifestation of its characteristic symptoms.