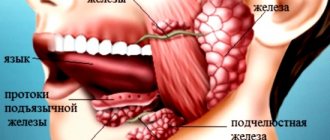
Saliva in the human body is produced by 600–1000 small and three large (submandibular, parotid, sublingual) glands. These formations are evenly distributed in the oral mucosa, located on the palate, tongue, larynx, pharynx, and paranasal sinuses.
Benign or malignant tumors can appear in the salivary glands under the influence of certain conditioning factors. Thus, according to medical statistics, about 80% of all formations occur in the parotid, 10–15% in the submandibular glands, and the rest in the sublingual and small glands. Pleomorphic salivary gland adenoma is the most common benign epithelial formation. It can appear in patients of any age, but most often affects people 30–60 years old.
Classification
There are several forms of ASL:
- adenolymphoma;
- pleo- or polymorphic;
- greasy;
- mixed;
- basal cell;
- canalicular;
- monomorphic.
Pleomorphic ASJ grows slowly, can reach gigantic sizes, and has a tuberous structure. Most often localized in the parotid salivary gland. In the final stages of tumor development, the risk of malignancy increases sharply.
How tumors manifest depends on the degree of neglect of the process.
Basal cell formation is a small node with a homogeneous dense structure. This form of ASJ practically does not recur, but is prone to malignant degeneration. The canalicular tumor contains particles of epithelium, which, gathering in bundles of different sizes, resemble beads to the touch. In most cases, patients aged 60–65 years suffer from this type of ASC; the disease is asymptomatic.
Diagnosis and treatment
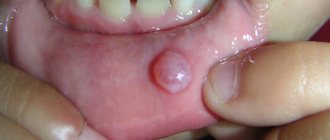
Diagnosis begins with examination and palpation of the tumor. The neoplasm has a lumpy surface to the touch and a dense, elastic consistency. It is movable, slightly shifts with lateral pressure relative to the lobe. Adenomas of the ear (parotid gland) are connected only to the organ on which they are located.
The skin is not changed, it folds freely.
If an adenoma is suspected, the doctor prescribes additional studies for differential diagnosis:
- Ultrasound;
- tomography (computer or magnetic resonance imaging);
- X-ray contrast study;
- puncture biopsy and cytology (to determine the nature of the tissue).
Treatment is carried out exclusively by surgical methods.
Operation
The growth into neighboring areas and organs, which is uncharacteristic for a neoplasm, makes tumor removal a relatively simple procedure. The complexity of the intervention is determined by the need to separate the branches of the facial nerve from the tissues of the affected gland. The volume of tissue removed depends on the degree of development of the tumor:
- If the tumor is located in the lower part, it does not affect the area of the nerve bundle and is excised completely, along with the capsule.
- If localized in the pharyngeal region or extensive lesion, parotidectomy is performed (complete removal of the salivary gland). The facial nerve is carefully isolated, trying not to damage its branches.
- The adenoma in the anterior section is excised along with the capsule, making an incision over the nerve.
With any method of removing a tumor, it is recommended to excise part of the healthy tissue: through the openings of the capsule, tumor cells enter the glandular epithelium. Such relapses occur in approximately 50% of cases. After removal, a tumor develops again from the remaining cells, and the affected salivary gland has to be completely excised.
If there are no complications after surgery, the person recovers. Complicated course of the postoperative period can occur for the following reasons:
- Damage to the autonomic nerves (Frey's syndrome). Signs of complications will be redness of the skin and increased sweating on the side of the operated gland.
- Feeling of dry mouth after parotidectomy.
- Paralysis and paresis of facial facial muscles. This can happen as a result of traumatization of the branches of the facial nerve by the surgeon.
In case of a complicated period after surgery, and especially if the facial nerve is damaged, it is better to consult a doctor immediately.
Main symptoms
Pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland grows slowly, is quite painful, and can develop over several years. Signs of tumors depend on their location. If the formation transforms into malignant or is quite large in size, patients exhibit symptoms of neuritis of the facial nerve (with its characteristic asymmetry of the facial muscles).
Pleomorphic ASJ is confirmed by histological method
If the pathological process develops in the deep lobes of the affected glands, patients may experience dysphagia, the tumor interferes with speech, and pain occurs in the retropharyngeal region. Upon visual inspection and palpation, salivary gland adenomas (hereinafter referred to as ASG) are detected as one dense node that has clear boundaries and moves freely. The size of a pleomorphic adenoma can be insignificant (several millimeters) or reach several tens of centimeters.
Symptoms of malignancy (malignancy) of ASJ:
Blastoma of the mandible
- the tumor rapidly increases in size;
- the formation is not mobile, fuses with the surrounding soft tissues;
- the adenoma can grow into the lymph nodes, affect the facial nerve, and affect the skin (ulcerated lesions appear).
You should consult a doctor immediately if:
- visually or by touch in the neck, parotid area, swelling or a formed tumor is determined;
- the patient is bothered by attacks of pain of unknown etiology, localized in a given area for more than a month (the results of otoscopy are within normal limits).
Radiation therapy
Treatment of pleomorphic adenoma of the salivary gland sometimes involves a course of radiation - you should not be afraid of this. This is necessary to prevent consequences such as tumor malignancy and the appearance of new nodes.
Therapy is carried out in courses of 3-7 days, which are repeated after 2 weeks. It is possible that after such a course a feeling of dry mouth, acne and blisters on the skin will appear. Over time this will pass. What to do in this case? Doctors recommend waiting - you should not refuse a course of radiation therapy if you have a strong desire to defeat the disease forever.
Possible complications
If diagnosed untimely and untreated, an adenoma of the submandibular salivary gland can result in damage to the facial nerve passing through the area where the tumor is located (during the growth of the tumor or after surgery).
Diagnosis of suspected malignancy of ASJ begins with a biopsy
Important! Regardless of the cause of salivary gland adenoma, it can transform into carcinoma (malignant neoplasm).
The main symptom is the rapid growth of a tumor that was previously stable. In the postoperative period, patients with ASC may develop the so-called Frey's syndrome. This disease is manifested by hyperemia and increased sweating in the submandibular region when eating.
A pathological process develops due to damage to para- or sympathetic nerve fibers. Radiation therapy may subsequently result in a decrease in the intensity of salivation (xerostomia) and increased dryness of the oral mucosa.
When is it necessary to remove the salivary glands?
The main reason for surgical intervention is pathological conditions of organs that are not amenable to drug treatment. These include:
- Sialadenitis is an inflammation of the salivary glands. Occurs due to damage to organs by bacteria or viruses. It manifests itself as enlargement, pain, decreased saliva production, and general weakness.
- Sialolithiasis is a salivary stone disease. Surgery is prescribed when the sialolith exceeds 1 mm in diameter, clogs the duct and cannot be washed out with conservative treatment (diet and drugs to increase salivation). Symptoms include a feeling of fullness, swelling, an unpleasant taste, periodic acute pain, and difficulty swallowing. In the later stages – general intoxication.
- Mumps - mumps. Occurs as a result of an infectious lesion. Accompanied by swelling of the exocrine glands, high fever (from 38°C), decreased appetite, weakness, and headaches.
- Sialodochitis is a pathological change in the excretory ducts (expansion or narrowing). It occurs with increased secretion of saliva with a salty taste, swelling, a feeling of fullness, discomfort while eating, and stuffy ears.
- Sialadenosis (sialosis ) is bilateral swelling without tumor or inflammatory etiology. Accompanied by local pain, changes in the composition of saliva, disruption of the functioning of the facial nerve, and enlargement of paired organs.
- Mikulicz disease – gradual painless enlargement of the excretory organs. It is a type of sialosis.
The operation is performed for pathologies that are not amenable to conservative treatment.
Important! In the last two cases, surgery is used extremely rarely. The reason for surgical intervention is excessive enlargement of the salivary glands, leading to facial asymmetry.
Diagnostics
To determine the location of the tumor, its size and growth into adjacent soft tissues, as well as timely detection of signs of malignancy, the following is used:
- Ultrasound examination (in the initial stages of development).
- MRI or CT – for deep localization of the pathological process.
- Fine needle aspiration biopsy is a method of obtaining a tumor sample for further histological examination.
- Sialography is a technology for contrast study of the salivary ducts.
Home treatment
As an auxiliary treatment for ASJ, you can also use proven folk remedies. So, 3 tbsp. l. crushed dried celandine is poured into 300 ml of boiling water. Then they are sent to the fire to boil for another 10–15 minutes. As soon as the medicine is prepared, remove it from the stove and leave for at least 3 hours. How to use: swelling goes away if you regularly apply a cloth soaked in a decoction of celandine to the affected gland. The procedure can be performed up to 4 times a day.
Surgical intervention for pleomorphic ASJ - a stage of complex treatment
Compress with hemlock:
- 10 g of plant seeds and its crushed leaves are poured with 40 ml of medical alcohol;
- the composition is infused for 2 weeks, filtered when ready;
- before applying a compress to the affected area, hemlock tincture is mixed in equal proportions with grated carrots;
- leave the bandage on for at least 2 hours. The procedure is carried out twice a week.
Natural homemade ointments also help to cope with ASJ. Take 100 g of any animal fat, which is heated in a water bath, combine it with 20 g of crushed camphor, bring the mass to a homogeneous consistency and lubricate the affected gland (after a few hours the mixture is washed off with warm water). Birch branches are burned, and the resulting ash is sifted through a fine sieve. After 1 tbsp. l. powder mixed with 3 tbsp. l. birch tar. Directions for use: The resulting ointment is used to treat the swollen gland daily for a month.
Important! Cosmetic Vaseline and tar, mixed in a ratio of 1:10, is an effective remedy for ASJ. The treatment regimen is similar to the previous recipe.
The juices of celandine and St. John's wort are combined in equal parts, a double portion of rendered animal fat is added to them, and applied daily to the “affected” gland. A diet for ASJ involves avoiding fatty, salty, overly spicy foods and any food that causes excessive salivation (including in the postoperative period).
Forecast
If an adenoma is detected in the initial stages of its appearance and removed surgically, the patient, as a rule, makes a full recovery. Relapse most often occurs with pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland. Most often, this phenomenon is associated with the entry of adenomatous cells into the surgical wound, the growth of the formation beyond the capsule, and the rupture of this membrane during surgery.
In most cases, with relapse, multinodular neoplasms appear. So, ASC is a benign formation, which, with timely diagnosis, responds well to treatment. With correct surgical intervention, the prognosis for patients with such tumors is favorable.