How does papilloma form in the throat?
A similar pathology occurs when papillomavirus enters the human body. A person may not even be aware of the presence of the virus that causes the disease for a long period of time, until the disease manifests itself and tissue proliferation begins. Can such growths be safe?
Important! If a papilloma is discovered during an examination by an otolaryngologist, treatment should be started immediately. In addition to the fact that the formation tends to grow and can block the airways, a tumor from benign can quickly turn into malignant and an oncological disease will develop.
What is also dangerous about such formations in the throat is that as a result of the activity of the virus, serious complications of the disease can appear. Naturally, the question arises: is human papilloma contagious?
The virus that causes it is transmitted in various ways:
- airborne (from an infected person whose mouth contains growths caused by the activity of the virus);
- vertical – intrauterine infection from the mother’s body to the fetus. Infection of the fetus can occur through the placenta or during passage through the birth canal;
- contact – sexual or contact-household route.
In rare cases, when the immune system is weakened, the infection can spread from a virus carrier who does not have any external manifestations of the disease.
Often the appearance of a lump in the throat and pain when swallowing, loss of voice, and the appearance of a lingering cough are confused with the symptoms of a common cold. But all these phenomena can be signs of the formation of papillomas; therefore, if you suspect an infection, you should immediately consult a doctor to make a diagnosis, and not self-medicate.
Attention! If strange growths and lumps appear in the oral cavity, do not remove them yourself, using advice received from reviews on a medical forum! Only a doctor can prescribe the correct treatment after conducting a preliminary examination.
Can they appear in the sky?
Modern medicine knows more than a hundred types of HPV, including oncogenic ones.
The virus is highly contagious, with about 80% of humanity now infected. External signs of papillomavirus are warts of the skin, mucous membranes - condylomas, papillomas, including squamous cells - developing on the palate and the entire oral cavity, larynx. Papillomas of the palate are located on a narrow or wide base, the growths are multiple and sometimes spread to the larynx. According to medical facts, among patients with benign tumors of the pharynx, men aged 20 to 45 years predominate. Appearing on the soft or hard palate, growths often cause severe discomfort to the patient and require prompt removal.
Microscopically, oral papilloma is a tumor of highly differentiated stratified squamous epithelium with symptoms of keratinization. The membranes are intact, the polarity of the cells is not changed, but there is an imbalance of the structural elements of the epithelium and connective tissue framework, and a focal infiltrate of inflammation.
There are soft papillomas, pinkish doughy in consistency, hard ones - gray dense to the touch. The former often recur, bleed easily when injured, and grow well into nearby tissues. They tend to resolve themselves under a number of conditions. Solid types do not bleed, and no new appearance is observed after removal.
The growths are fixed on:
- amygdala;
- upper soft palate;
- uvula (papilloma of the uvula is rare in practice).
Sometimes papillomas of the soft palate are represented by a single element, but papillomatosis of the throat also occurs, which is characterized by groups of many formations. They (especially in children) can cause obstruction of varying severity - from slight hoarseness of the voice, shortness of breath to asphyxia, which can be fatal.
If you experience discomfort in the throat and pain, even periodic, it is better to consult a specialist. Such sensations are often caused by growths in the throat, which can be dangerous formations. In any case, a growth in the throat can create unpleasant sensations when swallowing, even the urge to vomit, and make breathing difficult.
Chronic pharyngitis.
Groups of follicles in the form of red grains form on the back wall of the throat, and a purulent mucous secretion covers the pharynx. Pain during swallowing is typical, and swallowing saliva is more painful than food. The timbre of the voice changes, a runny nose appears, and body temperature rises.
Peritonsillitis.
Most often it is a consequence of chronic or acute tonsillitis, in which the tissues surrounding the palatine tonsil become inflamed. In severe cases, a cavity with pus forms near the tonsil. This causes severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, high body temperature, and bad breath. Sometimes it is impossible to open your mouth completely.
Throat abscess.
An inflammatory process in which a purulent complication appears in the area of the lymph nodes.
Usually this is a consequence of a previous sore throat, but the cause can be pharyngitis and injuries to the mucous membrane of the throat.
At the same time, the body temperature rises sharply, an acute sore throat and headache appear, saliva accumulates in the mouth, breathing becomes difficult, the neck area is swollen, the lymph nodes are swollen and painful.
Syphilis of the larynx.
At the initial stage of infection of the larynx with Treponema pallidum, a chancre can be mistaken for a growth. If the disease is not diagnosed, in the secondary period a rash accumulates around the larynx, body temperature periodically rises, headaches and general weakness are constantly bothering.
Benign formations.
Most often these are papillomas, cysts, lipomas, angiomas. These formations look like normal growths in the throat, but there is no discharge from them. They do not cause harm to the body, but cause unpleasant sensations of a dry or sore throat and discomfort during swallowing.
Malignant formations.
Their symptoms are difficulty swallowing, a feeling of a stone stuck in the throat, unpleasant breathing, and bloody discharge from the mouth.
How to treat growths?
Patients should understand that growths in the throat must be treated or removed surgically.
For bacterial acute pharyngitis, a course of antibiotics is indicated; for viral pharyngitis, treatment is symptomatic, gargling with antiseptic solutions.
For paratonsillitis, a course of antibiotics is prescribed, and the growth itself is surgically opened. If he breaks through on his own, it will have bad consequences.
Treatment of syphilis of the larynx is carried out using specific therapy.
Benign formations are removed surgically if they have grown to a large size. Small formations are left under medical supervision. Papillomas are removed in any case due to the risk of developing papillomatosis.
Malignant growths in the throat require urgent attention to a specialist.
In fact, there are many conditions that can lead to noticeable changes in the condition of the mucous membranes of the mouth. These can be infectious diseases, benign and malignant tumor processes, etc. The healthy mucous membrane of the mouth and throat should be smooth, and if any changes are visible on it, it is better to play it safe and contact an otolaryngologist as soon as possible.
Tonsils are important organs, collections of lymphoid tissue. Their main function is the formation of immunity. Sometimes strange neoplasms appear on such organs, which can be:
- Traffic jams. Such cones have a yellowish, gray, brown or red color. At their core, they are accumulations of calcified substance that collects in the recesses of the tonsils. Their occurrence is a characteristic sign of chronic tonsillitis.
- Benign tumors, such as lymphangiomas. Such growths arise from the proliferation of lymphatic vessels passing inside the palatine tonsils. This is a fairly rare disease that can be found on the tonsil with equal probability on both the right and left. The tumor is manifested by a foreign body sensation, difficulty swallowing and sometimes moderate pain.
- Retention or dermoid cyst. Such neoplasms can be spherical, soft and mobile, or dense. They do not cause any discomfort at first, but can grow and cause difficulty swallowing and breathing problems.
- Cancerous tumor. Such a neoplasm may have the appearance of a dense tumor with blurred boundaries. The tumor usually causes severe discomfort when swallowing and disturbances in the timbre of the voice, and can provoke bad breath.
The mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the larynx can suffer not only from papillomatosis. Unknown neoplasms of such localization may also be:
- Manifestations of granulomatous pharyngitis. This is a chronic inflammatory process in the pharynx, which is characterized by the formation of reddish nodules on the mucous membrane. The disease also manifests itself as dry mouth, soreness and soreness. Patients complain of a feeling of a foreign object in the throat.
- Manifestations of GERD. This is a disorder of the digestive tract, which consists of incompetence of the lower alimentary sphincter. With this disease, the contents of the stomach enter the esophagus. The acidic contents can reach the larynx and cause inflammation and irritation. Patients complain of heartburn, cough, hoarseness and pain when swallowing.
- Abscess. This disease develops with suppuration of the lymph nodes, as well as the fiber of the retropharyngeal space. Most often, an abscess occurs as a complication of influenza, measles or scarlet fever. Manifested by high fever, pain when swallowing, and breathing problems.
- Benign or malignant tumor. Typical symptoms of tumor diseases are breathing and swallowing problems. Painful sensations may occur.
Unexplained neoplasms can also appear on the root of the tongue. They have this localization:
- Benign tumors (hemangioma, neurofibroma, etc.).
- Malignant tumors (squamous cell, glandular or adenoid cystic cancer).
Tumors on the root of the tongue at an early stage of development do not cause any significant specific complaints. They are often disguised as chronic inflammatory processes, so the diagnosis may be made incorrectly. Typical signs of cancer include:
- Pain at the root of the tongue.
- Foreign body sensation.
- Blood in sputum.
With benign tumors, the following symptoms come to the fore:
- Foreign body sensation.
- Hoarseness.
The uvula is a small conical process located on the posterior edge of the soft palate. It consists of connective tissues and plays a very important role in the process of sound production. Sometimes strange neoplasms may also appear on such an organ:
- Symptoms of inflammatory throat diseases. Sometimes bumps and rashes appear on the tongue with a sore throat (especially with herpetic sore throat). As a rule, they are supplemented by the classic symptoms of ARVI and go away on their own after recovery.
- Cyst. Such a neoplasm may have the appearance of a small pea. The patient may constantly cough and complain of discomfort in the throat area.
Cancers and benign tumors are extremely rarely localized on the uvula. Such an organ can become swollen due to various dental diseases, ailments of the oropharynx and nasopharynx, etc. But at the same time, it becomes completely inflamed, not partially.
Doctors' opinions on the most effective methods of treating warts and papillomas
The chief physician of Moscow City Hospital No. 62 describes his vision on this matter. Anatoly Nakhimovich Makhson Medical practice: more than 40 years.
“I have been treating people’s papillomas and warts for many years. I’m telling you as a doctor, papillomas along with HPV and warts can really lead to serious consequences if they are not dealt with.
The human papillomavirus is present in everyone on whose body there are papillomas, moles, warts and other pigmented formations. According to rough estimates, 80-85% of the planet's population has it. By themselves they are not dangerous. The problem is that an ordinary papilloma can become melanoma at any time.
These are incurable malignant tumors that kill a person in just a few months and from which there is no salvation.
Unfortunately, in Russia and the CIS countries, pharmaceutical corporations sell expensive medications that only relieve symptoms, thereby hooking people on one drug or another. That is why in these countries there is such a high percentage of cancer diseases and so many people suffer from “non-working” drugs.
The only drug that I want to recommend, and it is also officially recommended by WHO for the treatment of papillomas and warts, is Papinol. This drug is the only remedy that has an effect not only on external factors (that is, it removes papillomas), but also acts on the virus itself. At the moment, the manufacturer has managed not only to create a highly effective product, but also to make it accessible to everyone. In addition, within the framework of the federal program, every resident of the Russian Federation and the CIS can receive it for 149 rubles.”
To find out more, read this article.
Reasons for appearance
The causes of the disease are known - it is infection with human papillomavirus, which is characterized by ease of infection. It causes changes in the nature of epithelial tissues, and neoplasms appear on the mucosa.
Under the influence of HPV, not only papillomas are formed, but also warts, genital warts and cancerous tumors. The danger of the virus lies in the fact that it can remain dormant for years.
Infection occurs through close contact with a carrier:
- Through kisses.
- When using shared items.
- Through the birth canal from mother to child.
- Sexually.
- Transfer from other parts of the body.
Related article:
Lapis pencil in the treatment of warts and papillomas
With strong immunity, signs of pathology do not develop. When the body's defenses decrease, a period of active division of microorganisms begins.
The following factors lead to this:
- Frequent use of antibiotics. Even the simplest runny nose can greatly reduce immunity
- Respiratory diseases accompanied by inflammation of the nasopharynx.
- Avitaminosis.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Neglect of oral hygiene rules.
At risk are children under 5 years of age due to insufficient immunity and adults from 20 to 40 years of age due to their high social activity. If a person practices promiscuity, the risk of developing pathology increases 3 times.
Causes of papillomas in the throat and their characteristics
The appearance of papillomatosis can be caused by a number of reasons:
- Infection. The human papillomavirus is already in the body, but has not yet manifested itself in any way. It is restrained by the body's defense mechanisms.
- Decreased immunity. As a result of this phenomenon, microorganisms begin to actively multiply. In this case, the epithelium grows pathologically and papillomas will appear.
- The presence of infectious diseases (measles, scarlet fever).
- Chronic infectious diseases of the ear, nose and throat, such as otitis media, tonsillitis, laryngitis, and rhinitis, can trigger the appearance of papillomas. Chronic tonsillitis is a common cause of tumors appearing on the tonsils.
- Taking antibacterial drugs.
- Diseases of the endocrine system.
- Hormonal disbalance.
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene standards and casual relationships.
- Heredity.
- Drinking alcohol and smoking.
In the throat, growths form primarily in the front of the vocal cords. In cases of severe damage to the mucous membranes, formations can grow over the entire surface of the larynx, trachea and bronchi, which causes a feeling of discomfort. Localization of multiple growths in the trachea can cause an attack of asphyxia (suffocation).
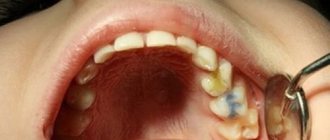
What papillomas look like depends on which particular strain causes it. Papilloma can be whitish, pale pink, or even red in color. In appearance, it resembles a papilla or wart, mulberry or pea, tubercle or cockscomb. Papillomavirus rarely causes single papillomas. It mainly promotes the formation of multiple growths.
Who is at risk?
Often, HPV in the throat occurs in children who suffer from infections associated with the ENT organs. These include pharyngitis, tonsillitis, tracheitis, purulent otitis media, laryngitis.
Papillomatosis of the throat is most widespread among people aged 20 to 45 years.
A risk factor is a person who has bad habits, constantly experiences stress, and leads an unhealthy lifestyle.
There are a number of indirect factors that can provoke the development of papillomas of the throat:
- taking hormonal pills;
- living in an area with high levels of air pollution;
- passive smoking;
- violations in oral care;
- hormonal imbalance in the body;
- the presence of hereditary factors;
- stress.
At the first symptoms, consult a doctor
Features of the appearance of papillomas in the throat and tongue
Papillomas can affect different places in the oral cavity. They form on the mucous membrane of the larynx wall and deep in the throat:
- on the tonsil;
- at the root of the tongue near the larynx;
- on the palatine arch;
- on the tongue;
- on the lateral walls of the pharynx;
- on the vocal cords;
- in the trachea.
It is characteristic that papillomas most often affect the tonsils, palatine arches and vocal cords. Very rarely, growths appear on the tongue.
What is papilloma?
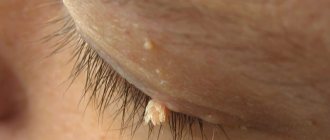
Papilloma is a benign neoplasm that is found on the mucous membranes and internal organs. The virus affects the larynx, esophagus, soft palate and uvula .
In appearance, papillomas are similar to warts, attached to the surface of the epithelium by a thin or thick stalk. They are round and flat in shape, sometimes resembling a pea. If a lot of tumors appear, the condition is called papillomatosis. It makes speech difficult and interferes with proper breathing.
Attention! Papillomas rarely lead to cancer , but degeneration of the growth is possible.
A person may experience the formation of single warts or entire scatterings. Due to the predominance of connective tissue elements, papillomas in children are pink in color.
Photo on the left: healthy throat. Photo on the right: papillomas in the throat
In adults, epithelial structures predominate, so the color of the neoplasms is white or gray. They are dangerous when they appear on the larynx or trachea, as they provoke breathing problems in large accumulations.
In young children, growths cause suffocation with every respiratory illness. Without proper treatment, the risk of death from asphyxia increases.
be careful
The presence of papillomas and warts on the body is the first sign of malignant melanoma!
We hasten to warn you that most drugs that “treat” warts and papillomas are a complete deception of marketers who make hundreds of percentage points on drugs whose effectiveness is zero. They do not cure the disease, but only mask the symptoms.
The pharmacy mafia makes huge money by deceiving sick people.
But what to do? How to treat if there is deception everywhere? Doctor of Medical Sciences Anatoly Makhson conducted his own investigation and found a way out of this situation. In this article, the Doctor also told how to 100% protect yourself from melanoma, for only 149 rubles! Read the article in the official source via the link.
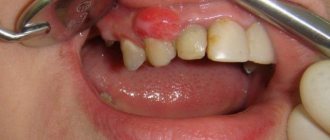
What to do if the papilloma in the throat changes color and hurts
Benign growths have a soft structure. As a rule, they are flesh-colored or slightly darker. If the tumor turns black and begins to hurt, it is imperative to identify the cause of this condition. Sometimes the papilloma turns black when tissue degeneration occurs. Perhaps it's cancer. It is necessary to see a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe timely treatment. At the same time, this needs to be done as quickly as possible because:
- The process of degeneration of papilloma cells into malignant formations (malignization) develops very slowly and imperceptibly;
- The transformation begins from the central part of the growth, gradually spreading to the remaining cells;
- Gradually, adjacent areas of the mucosa undergo malignant changes.
Attention! Under no circumstances should papilloma be removed on your own! Damage to the tumor can trigger the mechanism of cell degeneration. If the papilloma is oncological in nature, pathogenic cells can spread to other tissue areas.
Features of the development of papilloma of the throat in men
In an adult man - 20-30 years old, the papillomavirus usually affects the epithelium of the larynx. Apparently, sex hormones—androgens—play an important role here, which explains this peculiarity of tumor localization. The causes of the disease in men can be:
- decreased secretion of sex hormones;
- chronic diseases of the larynx;
- bad habits: smoking and excessive alcohol consumption;
- high levels of stress;
- poor nutrition;
- poor oral hygiene;
- visiting public bathing places (swimming pools, saunas, baths).
Causes of papilloma in the throat during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body undergoes serious hormonal changes. As a result, the immune system weakens. The female body becomes especially susceptible to infection by various viruses or the activation of existing ones that have not manifested themselves. One of these pathogens is papillomaviruses. An increase in their activity causes the appearance of growths in the oral cavity of a pregnant woman.
If a woman had papillomas before pregnancy, then during pregnancy there is a high probability of their growth and an increase in the number of tumors.
Laryngeal papillomatosis
Oral papilloma is most often caused by just a few strains of HPV. The growths of epithelial cells in the oral cavity have a variety of sizes; at the beginning of their formation they practically do not bring any discomfort.
But due to the peculiarities of this location, there is a high risk of injury and infection of the growing papilloma, which in turn leads to an inflammatory reaction. In this regard, papillomatous growth of the oral cavity is recommended to be removed at the initial stages of occurrence.
The formation of any type of papillomas on the skin and mucous membranes occurs when the human papillomavirus enters the body.
This microscopic pathogen easily enters epithelial cells through small cracks in the body. When choosing a localization site, it is not the method of penetration of the viral agent that matters, but its strain.
If papillomatous growth affects any area of the oropharynx, then 6,11, 2, 30, 13 or 32 types of virus are detected.
Activation of changes in the epithelial cells of the oral cavity can be provoked by:
- Injury to the mucous membrane - prostheses, dental procedures.
- Decreased local and general immunity.
- Bad habits, which include constant consumption of hot food that burns the mucous layer.
- Long-term use of strong antibiotics and hormonal agents.
- Chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Hormonal imbalance.
The average age of patients with benign viral growths in the oral cavity is 35 years. The disease often occurs in young children.
It is impossible to become infected with papilloma, you can only become infected with a virus, and how it behaves in the future depends on many external and internal factors.
Conducted research has helped to reveal that HPV is present in the body of almost 90% of the population of the entire planet. Infection is possible at any age and in several ways.
If we are talking about the development of papillomas in the mouth of children, then infection most often at this age occurs through vertical and household contact.
The vertical route is the transmission of the virus from a sick mother to her newborn child as it passes through the birth canal. At this time, the microorganism is able to get on the skin of the face, mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
Among children, the most common route of transmission of HPV is still considered to be through household contact - transmission occurs through close contact, through toys, and when using the same hygiene items.
Children often drink from the same cup, use the same spoon or fork, and can eat the same piece of fruit for several people - HPV is found in saliva and therefore in such cases it easily spreads and leads to infection.
The virus can enter the body anywhere in the body, but this does not always mean that it will be activated in this area and cause changes in the epithelium.
In addition to sexual transmission, household transmission is also common. The virus feels great and remains active for a long time in a humid and at the same time warm environment. In this regard, there is a high probability of infection when being in public places - baths, sports complexes with swimming pools, saunas.
Several types of papillomas are detected in the oral cavity, these are:
- Epithelial hyperplasia. This type is manifested by the appearance of small growths, their color is reddish, and upon palpation they are felt as soft and mobile formations. They are localized mainly on the lateral surfaces of the tongue.
- Vulgar or simple papilloma. The growth has a pineal shape with a flat base; such a papilloma is mobile and often grows on the soft palate.
- Flat papillomas mainly form on the gums. Their surface is granular, and the color matches the pink tint of the mucous membrane.
- Filiform papillomas have a thin stalk and are easily injured.
- Genital warts occur if infection occurs through sexual contact. It is these growths that are characterized by merging and the formation of a large tumor with an uneven, bumpy surface.
Papillomatous growths on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity can grow in almost any area. Most papillomas are found on the palate, palatine sacs, followed by the prevalence of the process on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, and tongue. Changes in the mucous layer under the influence of the virus are found in the throat and larynx.
At the initial stages of the growth of papilloma in the mouth, a person does not show any complaints. In the future, the symptoms of papillomatosis mainly depend on the size and location of the wart.
If it is located on the tongue, the mucous membrane of the cheeks, or the hard palate, it is easily irritated by hot, spicy food, which causes injury, bleeding, infection, and an unpleasant odor.
When papillomas are located on the gums, they are subject to injury when wearing dentures or while brushing teeth, which also affects the appearance of discomfort. Constant infection and inflammation create conditions for the degeneration of epithelial cells into cancer cells.
The growth in the oral cavity may initially be a single growth, but the spread of the virus from the initial focus leads to the growth of an unlimited number of warts, which can make eating and even breathing difficult. In advanced cases, large areas of growth are detected in people, covering the entire oral cavity up to the tonsils and with tumors moving to the throat.
Other benign or malignant tumors can also form in the oral cavity. Papilloma can be distinguished from them by several signs:
- Dimensions not exceeding one centimeter.
- Attached to the mucous membranes using a thin stalk or wide “sole”.
- Painless and soft to the touch.
- The color is pinkish, matching in shade with the main part of the oral cavity, or pale.
HPV on the tongue
Most often, papillomas on the tongue occupy the lateral surface of the organ or its tip; in the middle and under the tongue, viral formations grow less frequently. Such neoplasms look like papillary growths that are reddish in color; their surface looks like an accumulation of small grains. This type of papillomatosis is referred to as epithelial hyperplasia.
Photos of genital papillomas on the tongue
Papillomas localized on the tongue are often secured with a small stalk. The size of the growths varies; they can be either tiny teardrop-shaped growths or pea-shaped tumors.
Epithelial hyperplasia on the tongue leads to unpleasant sensations when eating. Constant irritation causes pain and an inflammatory response. Neoplasms with a similar location often undergo malignant transformation in the absence of timely therapy.
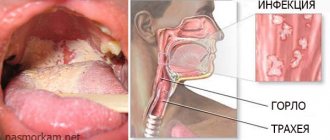
In the throat and larynx
Papillomas growing in the throat may remain undetected for a long time, as they do not give a clear clinical picture.
A person may only periodically feel a slight soreness and irritation in the throat, which is attributed to colds and respiratory phenomena.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5j8gcj5il6I
With a noticeable increase in growing tumors or with a large number of them, eating becomes noticeably difficult - the food bolus does not move well, and a feeling of a foreign body arises. When swallowing solid foods, the papilloma is injured, which is expressed by pain and the appearance of a cough with ichor.
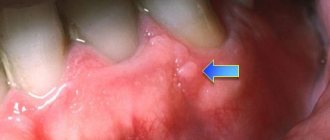
Photo of papilloma in the throat
Laryngeal papillomatosis is considered a rather dangerous disease. The thing is that growing warts break the lumen and interfere with normal breathing.
Papillomas on the larynx and cleft are sometimes found in newborns, and in this case the most likely source of infection is the sick mother, from whom the virus was passed to the baby during childbirth.
You can pay attention to the baby’s cough, some hoarseness, and in case of respiratory diseases, rapidly increasing swelling leads to difficulty breathing.
Removal of papilloma in the throat
How are growths usually removed? If there is no other option left to get rid of papillomas, then several methods are used for this:
- The method of surgical intervention is used - an operation is performed to destroy the tumor using a scalpel;
- Electrocoagulation - cauterization of papillomas occurs by applying current to the affected area. It is noteworthy that if a tumor is removed using this method, almost no traces remain on the freed area of skin;
- Using a laser. Removing growths using a laser is a very effective method. After its use, tissue scarring does not occur;
- Radio wave therapy. When it is used, a crust appears at the site of the papilloma. It disappears without leaving a trace after a few days;
- Application of the cryodestruction method. The formation is cauterized using liquid nitrogen. This method does not require pain relief. Overgrown areas are frozen. After some time, the dead papillomas disappear on their own.
The method of surgical intervention is rarely used because:
- after such operations, scars remain at the site of the removed growths;
- there is a high probability of recurrence of the disease.
However, if the tumors are located very deep, modern endoscopes with attachments can be used, with which you can reach the most inaccessible places in the oral cavity and carry out surgical procedures there most accurately. To reduce the recurrence of the disease, the doctor prescribes restorative and antiviral drugs.
Important! During pregnancy, as a rule, doctors do not use surgical methods to get rid of papillomas. Surgery with anesthesia is used only after the birth of the baby. But if necessary, for example, when a tumor grows in the larynx or trachea and there is a risk of an attack of suffocation, surgery is also performed during pregnancy.
Treatment with folk remedies
There are a number of folk medicines, using which you can get rid of papillomas in the throat. They are based on natural herbs and plants. A simple remedy is to eat 1 large spoon of fresh honey daily.
An infusion of bay leaves will also help cope with the problem. They are poured with boiling water and kept in a thermos overnight. The resulting medicine is drunk within 24 hours. The course of treatment with the drug is 2 weeks.
An effective recipe is a mixture of chopped horseradish and honey. The ingredients are taken in equal parts. You need to take a spoonful of the product per day. The pulp is placed on the tongue, and after a couple of seconds it is washed down with water.
Since ancient times, people have treated papillomas localized in the throat by drinking a decoction of a mixture of bird cherry, thyme, licorice, black currant, raspberry, coltsfoot, and plantain. The drug is taken an hour after eating for 3 months.
You cannot treat the problem with folk recipes. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the sooner he will receive highly qualified care, which will help avoid consequences.
What treatment is prescribed for papilloma in the throat?
If a disease occurs or you feel a lump forming in your throat, you should immediately consult a doctor and not self-medicate to prevent the condition from worsening. The otolaryngologist will perform an examination and decide how and with what to treat papillomatosis. Traditional methods of getting rid of tumors can only be used in addition to the main therapy. Treatment with folk remedies involves the use of decoctions of medicinal herbs to cleanse the body.
Important! You should only use the treatment method prescribed by your doctor! You cannot cauterize papillomas yourself using traditional medicine, for example, celandine. This plant contains poison! Only a specialist can remove any growths!
A cardiac method for the treatment of papillomatosis has not yet been developed and the main way to combat formations is removal. Before this operation is scheduled, medications are used:
- Acyclovir (tablets) is an antiviral drug. It is prescribed before and after surgery, if there is no risk of suffocation and the airway is clear.
- Ribavirin is an antiviral drug in tablets. It quickly penetrates the body and inhibits the activity of viruses and other infections.
- Interferon is an immunostimulating drug with general protective properties. Interferons are produced by the cells of the human body themselves and stop the penetration of the virus. It is known that interferon can slow down the growth of pathological cells and tissue proliferation.
- Amiksin is a low molecular weight synthetic interferon inducer. Promotes the formation of this substance in the body, which slows down the growth of papillomas. The accumulation of interferon can lead to remission.
We invite you to watch a video of how a papilloma in the larynx is surgically removed.
Features of laryngeal papillomas in children
In children, the disease develops more rapidly than in adults and is more aggressive. Respiratory dysfunction due to stenosis of the vocal lumen in children under 3 years of age occurs many times faster than in adults.
Papillomas in children provoke various manifestations of hypoxia, shortness of breath, and spasms. The rapid development of the disease is dangerous due to attacks of suffocation and asphyxia, even death. Therefore, treatment of the child should begin at the first signs of discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the throat area.
The pathology can spread to the trachea, lungs and bronchi, causing bronchitis and pneumonia.
The development of growths on the mucous membrane in children is accompanied by a decrease in the body’s immune forces and hormonal imbalances.
Respiratory failure in a child entails the occurrence of the following pathologies: dysfunction of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system, delay in psychological and physical development.
Diagnostics
Diagnostic measures include:
- Laryngoscopy. The procedure is carried out using a laryngoscope and consists of a visual inspection of the affected area;
- Biopsy, endofibrolaryngoscopy. Research allows us to study the body of the papilloma and determine the level of oncogenicity;
- X-ray;
- CT and MRI of soft tissues of the affected area.
Treatment of papillomas in the larynx
The doctor determines what to do for papilloma in the throat and prescribes treatment aimed at solving the following problems:
- Destruction of papillomas;
- Elimination of narrowing of the airway lumen;
- Restoration of voice-forming function;
- Preventing the development of pathology;
- Strengthening the body's immune forces and minimizing relapses.
The chronic nature of the disease makes it necessary to treat papillomas in the throat both externally (external medications, surgery) and internally (pills, injections). Complex therapy is used.
First, the doctor conducts a preliminary examination of the throat. For a more detailed examination of areas affected by papillomavirus, a laryngoscope or operating microscope is used.
At this stage, a biopsy of the outgrowths is performed in order to study the biomaterial in the laboratory. Blood is also taken to determine the type of virus.
To identify disturbances in the functioning of the vocal apparatus, stroboscopy is used - a study of vibrations of the ligaments.
Tomography and x-rays are used as an additional measure to detect developing pathology in time. Studying the vibrations of the ligaments will also help to recognize malignant neoplasms.
After surgery, a histological analysis of the removed papillomas is carried out to confirm or exclude the malignant genesis of the formations.
What is papilloma
Prevention
Preventive measures combine activities that prevent factors that contribute to the occurrence of outgrowths of the laryngeal mucosa:
- Prevention of acute and chronic ENT diseases. Treatment of the respiratory tract area must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor, since the uncontrolled course of ENT diseases is fraught with serious complications and consequences, one of which is the development of formations;
- Measures to prevent infectious diseases of childhood (measles, whooping cough, scarlet fever);
- Strengthening the immune system (physical education, hardening, diet);
- Maintaining oral hygiene;
- Regular examination by an otolaryngologist of a child in case of prolonged acute illness of the upper respiratory tract. Since the detected “young”, recently emerged formations are easier to treat;
- Children who are diagnosed with the disease should be observed in a dispensary at least once every 3 months.
HPV is widespread among children. It can be infected not only in public places, but also at home. Therefore, to prevent the papillomavirus from entering the child’s body, you should follow some rules:
- wash your hands after walking, visiting the toilet, communicating with other people;
- avoid bad habits - finger sucking, nail biting;
- eat well;
- avoid injury to the throat and mouth;
- strengthen the immune system (carry out hardening procedures, take the necessary vitamins);
- do not wear other people's clothes, especially underwear;
- Use only your own hygiene items.
Papillomas in the throat are dangerous because they can degenerate into a malignant tumor, or grow, thereby blocking the airways.
Therefore, if a suspicious growth is detected, it is recommended not to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a doctor. After diagnostic measures and tests, the doctor will prescribe the correct therapy.
How is tonsillar HPV infection detected?
There is no test that will find early signs of an HPV throat infection. Cancerous or precancerous HPV lesions of the tonsils are discovered during screening or examination by a dentist or doctor. Most papillomas are found by testing individuals who have already had signs or symptoms of infection.
To check hard-to-see areas of the throat, larynx, voice box, and base of the tongue, doctors use instruments (laryngoscope or pharyngoscope).
For some structures in the throat that cannot be viewed with these instruments, flexible laryngoscopes and pharyngoscopes are used. They penetrate deeper, which allows the doctor to see the lesion or absence of papillomas.
The doctor will order a biopsy for any growths that look suspicious. Papilloma particles are collected using a hollow needle. The cells are then examined under a microscope to look for or rule out cancer.
Symptoms of pathology and what to do
The infection will not always recur if there is a virus in the body. It all depends on the general health of the person and the activity of his immune system. When the body's protective function weakens, the virus begins to accumulate in a specific place on the mucous epithelium, triggering the process of improper cell division and leading to the appearance of growths.
Papilloma on the uvula (photo
) or on the walls of the larynx does not always give a clear clinical picture.
When the formation is small, a person simply will not feel it in the throat, but if the wart is actively growing, dysphonia or dysphagia may appear. That is, the patient will begin to experience difficulty swallowing food, drinking, talking, and breathing. People begin to show symptoms in the form of shortness of breath, wheezing, wheezing, and coughing. If laryngeal papilloma occurs,
what are its
symptoms and what to do
in this case? You definitely need to see a doctor and get examined.
During a visual diagnosis, the doctor will note inflammation, swelling and enlargement of the tonsils. If the tumor is actively growing, you will experience a strong cough with sputum containing blood. Next, hyperkeratosis of the vocal cords will appear, and the timbre of the voice will change. Shortness of breath and cough will worsen after exercise.