1658
Despite the enormous possibilities of therapeutic dentistry, saving a tooth is not always possible.
Some diseases require mandatory surgical intervention. These include inflammation of the roots of the elements of the jaw row, the formation of cysts and granulomas near them.
For this reason, dentists perform a procedure to maximize the integrity and functionality of teeth - hemisection.
The essence of the operation
Hemisection, also called resection of the root apex, is an operation to amputate the root and the associated coronal part of the tooth, which is carried out when one of the roots of the molars is inflamed, as well as the localization of various neoplasms in their area.
The use of this procedure is justified if the source of inflammation is located at no more than one root. This allows you to preserve the body of the molar as much as possible and use it in the future for orthopedic treatment.
Hemisection is applicable both during permanent dentition and during its formation in adolescents. The operation makes it possible to preserve the healthy area of the tooth without resorting to its removal.
Thanks to this, there is no empty space in the jaw row, which could result in the movement of existing teeth.
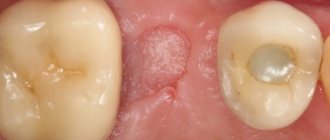
Hemisection of tooth
Before hemisection, the dentist will certainly fill the root canals, which must be preserved. The patient is then given anesthesia. After which the doctor separates part of the crown. Next, the specialist carefully removes one of the roots of the tooth along with the adjacent coronal part using forceps and curettages the hole. He also carries out hemostasis and, with the help of burs, smoothes the overhanging edges of the coronal part of the tooth adjacent to the wound. The specialist fills the hole formed at the site of the removed root with artificial bone tissue. After this, he places a sterile gauze ball on the wound for a few minutes. After two weeks, the stitches are removed. In particularly difficult cases, the doctor has to peel off the mucoperiosteal flap and then remove the damaged root using a drill. The patient can also undergo amputation of the tooth root, or rather the removal of the entire root while preserving the crown part of the tooth. The procedure is performed for the same reasons as hemisection, but on the molars of the upper jaw. First, the doctor peels off the mucoperiosteal flap along the periodontal margin. After cutting off the root with a bur, he removes it using forceps. The specialist places the mucoperiosteal flap in the correct position and applies sutures. After the hole has healed, the remaining crown and roots of the teeth can be used for further prosthetics as supports.
In some cases, the specialist resorts to coronoradicular separation, which involves dissection of the lower molar in the bifurcation area, followed by curettage of the interroot area and further closing of each segment of the coronal part of the tooth with a crown. It is performed when radiologically detected pronounced destructive changes in the hard tissues of the tooth and bone tissue in the bifurcation area. Replantation of the tooth is not excluded, namely the return of the tooth to its own socket after medical treatment. This type of procedure is carried out when conservative treatment of the tooth is impossible and in case of complete post-traumatic dislocation of the tooth from the socket. The duration of the hemisection operation depends on the complexity of the clinical picture. But, as a rule, it does not exceed two hours. If hemisection of the tooth root is successful, the recovery period lasts no more than five days. However, the patient should remember that after hemisection, the root can last only 1-2 months, since its integrity is damaged during the operation: it loses the stability that it had before.
Advantages and disadvantages
The key advantage of hemisection is the possibility of preserving the tooth or part of it and then using it as a support for fixing the prosthesis.
This not only guarantees an even distribution of the chewing load, but also prevents the possibility of bone tissue atrophy.
Another important advantage of this operation is its safety, which is manifested in a minimum number of complications when the procedure is carried out well.
At the same time, dentists note that hemisection can have significant disadvantages:
- the loss of one of the roots of a molar leads to a decrease in its stability , which often entails the inability to withstand previous mechanical loads;
- presence of risks. If surgical intervention is performed unprofessionally, the patient does not comply with recommendations in the postoperative period and the rules of oral hygiene, a person may develop various complications.
Pros and cons of hemisection
Root hemisection is considered a tooth-preserving operation. This is its main advantage. The ability to save a severely damaged unit prevents some of the problems associated with amputating the entire tooth. This prevents bone tissue atrophy, which affects the aesthetics of the smile. And, of course, after treatment the tooth can serve as a support for dentures.
Experts consider the fact that the result cannot be predicted and the long-term functioning of the causative tooth cannot be guaranteed as a huge disadvantage of the operation. Having lost a segment of the stabilization system, the unit sometimes cannot withstand heavy mechanical loads. Therefore, the operated tooth must be treated with great care.
Indications
A tooth-saving operation called hemisection is indicated for patients for a number of reasons. Most often, dentists resort to it in the following cases:
- the need for surgical intervention in patients with a developing occlusion - under the age of 25 years;
- the presence of various neoplasms in the area of the tooth root;
- fracture of one of the molar roots;
- chronic inflammation of periodontal tissues, which cannot be eliminated by conservative methods of therapy;
- inflammation or infection of a tooth area with the formation of purulent contents inside the root;
- the impossibility of cleaning dental canals as a result of the complex anatomy of the structure of the root system of the tooth;
- breakage of a part of a dental instrument in the canal during cleaning and the impossibility of removing it.
Recommendations for the period after complex wisdom tooth removal and possible complications.
Let's find out together here what to do if your gums hurt after tooth extraction.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/chem-mozhno-poloskat-rot-posle.html we will tell you how to rinse your mouth after tooth extraction.
Indications and contraindications for intervention
An inflammatory process in the root area that affects or may affect the jaw bones in any case requires intervention. The difference is whether this procedure will be tooth-saving or not.
Hemisection is a relatively labor-intensive operation, which is advisable only if the molar is valuable for occlusion or future prosthetic structures. In other cases, it makes more sense to remove the tooth and install an implant.
In general, the operation is possible if one root of a multi-rooted tooth is damaged; the others must be intact and also available for re-treatment of the canals. Among the specific indications for the procedure :
- the impossibility of treating a dental canal in one root due to obstruction or anatomical features - the source of infection can only be eliminated by removing the root;
- anomalies in root topology (curvature, separation);
- root growth into a cyst or granuloma by more than a third - resection of the apex will not be enough, the entire root must be removed;
- fracture of one root;
- granulomas or cysts of significant size;
- inflammation of the root with the addition of infection and the development of an abscess - purulent softening of tissue;
- local inflammation of the periodontium (the set of tissues that hold the tooth);
- deep intraosseous pockets - formed by abscesses and cysts;
- destruction of the bone of the interroot septum of the tooth.
Hemisection is especially appropriate in patients under the age of 25 in order to preserve the bite before implant placement.
From a medical point of view, the procedure is impossible or inappropriate if there are:
- fusion of roots - it is impossible to separate them without damaging the tissues;
- the degree of tooth destruction at which even partial preservation is impossible;
- anatomical features associated with the localization of the maxillary sinuses or the alveolar canal of the lower jaw - unintentional perforation is possible during the process of hemisection;
- short roots - the two remaining roots will not be able to “work” adequately, and the tooth will become loose under load;
- insufficient volume of gum tissue in the area of the affected molar.
Among the general restrictions to hemisection:
- bleeding disorder or allergy to pain medications;
- severe chronic pathologies - due to the risk of exacerbation;
- sexually transmitted diseases, including HIV;
- the presence of malignant processes - both the disease itself and anti-cancer therapy cause low immunity of the patient, which can lead to complications and difficult rehabilitation after the intervention;
- old age - in patients over 60 years of age, recovery processes occur slowly, and complications, on the contrary, develop more often.
Among the relative contraindications:
- decompensated diabetes mellitus (slow healing plus risk of complications);
- cardiovascular disorders or the recovery period after them, which do not involve planned interventions;
- disorders of the psyche and functioning of the nervous system during an exacerbation;
- acute inflammatory processes in the mouth and throat;
- multiple caries;
- respiratory tract infections.
It is not advisable to carry out the procedure during menstrual bleeding in women. During pregnancy, surgery is permissible in exceptional cases.
Contraindications
Despite the obvious advantages of hemisection, the possibility of saving a tooth as a result of it does not always exist.
Dentists focus on diseases in the presence of which surgery is strictly contraindicated:
- nervous system disorders;
- uncompensated diabetes mellitus;
- blood clotting disorder;
- venereal diseases, HIV;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system that exclude surgical interventions;
- malignant neoplasms;
- intolerance to anesthesia;
- chronic diseases that may worsen as a result of surgery.
In addition to general diseases, the dentist will not undertake the procedure for certain features of the patient’s dental anatomy.
These include the following structural anomalies:
- excessively close location of the maxillary sinus or mandibular canal - the operation can lead to their unintentional perforation;
- strong fusion of dental roots , which makes it impossible to separate them without negative consequences;
- high degree of destruction of the bone tissue of the tooth , as a result of which there is no possibility of preservation;
- the roots are too short - as a result of removing one of them, the rest may not be able to cope with the resulting load, which will lead to loosening and tooth loss;
- reduced volume of gum tissue in the surgical site.
In addition to the above circumstances, dentists note that hemisection is impossible if there is an incorrectly installed filling on the tooth to be sawed.
In this situation, they often resort to removal of the affected molar followed by implantation or prosthetics.
Indications for treatment
Since treatment with this method can only be performed if the tooth is permanent, the patient must be at least 10–12 years old. The most common indication for hemisection of a tooth is periodontitis (inflammation of the periodontium, accompanied by damage to nearby soft tissues and ligaments). At the initial stage, periodontitis can be eliminated therapeutically, but in advanced cases, only surgical intervention remains.
Indications for hemisection also include:
- the need to preserve the tooth to avoid malocclusion;
- formation of basal and root neoplasms;
- a fracture that occurred at the root;
- purulent processes affecting the roots;
- complex structure of the root system;
- fracture and leaving the tip of the tool during root treatment.
Hemisection is mainly used in pediatric dentistry, since the installation of permanent dentures is impossible, and the preservation of the molar is necessary, since it plays the most important functional role in the entire dental composition. Surgery is not recommended if a number of dental pathologies develop.
Stages of the procedure
Modern dental practice involves hemisection using two methods - patchwork or resection of the root apex.
These procedures differ in the different preservation of the body of the affected tooth and the degree of trauma.
The choice of a specific surgical procedure depends on the anatomy of the elements of the jaw row and the amount of affected tissue.
Patchwork method
Performing hemisection of any of the existing techniques begins with the preparatory stage. The dentist determines the presence of contraindications and carefully examines the patient’s oral cavity for concomitant diseases.
If necessary, at this time the oral cavity is sanitized, as well as the remaining root canals of the molar that will be treated are cleaned and filled.
Hemisection using the flap method involves making an incision and removing a flap of gum tissue to provide maximum access to the affected root.
This makes it possible to preserve a significant volume of the molar body, but increases the traumatic nature of the procedure and complicates the recovery period.
The flap hemisection method involves the dentist performing the following actions:
- Injection of an anesthetic drug into the operated area of the jaw row.
- An incision is made in the gum tissue and a flap is removed to provide access to the affected root.
- Sawing off the damaged root and removing it from the soft tissue, as well as removing an existing cyst or granuloma using special tools.
- Cleaning the resulting cavity from bone fragments and disinfecting it.
- Filling the cavity with artificial bone material and placing a special protective membrane.
- In some cases, to avoid rejection of synthetic bone tissue, a material made from plasma, which is isolated from a person's donated blood, is used.
- Placement of the detached flap of soft tissue in its original place and fixation with suture material.
The flap method of hemisection is quite traumatic because it requires incisions in the gum tissue. For this reason, it takes 3 to 5 weeks for it to heal completely.
Root apex resection
Carrying out hemesection by resection of the root apex is a less traumatic option, since it does not require cutting the gum tissue. The disadvantage of this method is the removal of a large volume of the molar body.
Surgical intervention consists of the following stages:
- Anesthetizing the area of the mouth where surgery will be performed.
- Sawing the body of the molar along one of the natural division lines to the beginning of the root system.
- Extracting a section of the tooth along with the affected root using dental forceps or other suitable instruments. At the same moment, the existing tumor is removed.
- Treatment and cleaning of the cavity formed in the bone tissue , as well as filling with special material and medications to prevent the germination of gum tissue.
- Restoring the integrity of a prepared tooth using a composite material or an artificial crown.
The duration of the surgical intervention does not exceed 1-1.5 hours.
The video shows a diagram of saving a tooth with a root fracture.
Progress of the operation
Since tooth root hemisection is a surgical procedure, it requires the use of anesthetics. For this, local anesthesia or general anesthesia is used.
- Before directly removing part of the tooth root next to it, a flap is formed from the mucous membrane, which is processed and peeled off.
- The hard tissue of the tooth is prepared.
- The tooth crown is separated to the point where the tooth root bifurcates.
- The crown and the root affected by the carious process are removed.
- The tooth socket is treated, gradually filling it with special material.
- The surgical site is treated with an antiseptic solution and covered with a flap.
The condition of the operated tissues is checked the next day. In order to prevent complications, antibiotics must be prescribed. Recovery time ranges from 5 to 10 days.
Possible complications
Hemisection is a fairly safe operation, but the patient’s well-being after it depends both on the competent actions of the dentist and on the accuracy of following his recommendations during the recovery period.
The procedure is often accompanied by the following complications:
- swelling of the gum tissue;
- bleeding gums in the operated area;
- suture material dehiscence;
- inflammatory process at the site of the removed root;
- damage to healthy roots or adjacent teeth during surgery;
- increased mobility of a molar whose root has been removed.
The occurrence of these complications is a reason for an unscheduled visit to the attending physician, since the lack of timely treatment can have serious consequences, including tooth loss.
What treatment is used after tooth extraction to avoid complications.
In this publication you will find reviews about tooth extraction under general anesthesia.
Here https://zubovv.ru/hirurgiya/udalenie-zubov/stoit-li-boyatsy-retinirovannogo-mudrosti.html we will calculate the price of removing an impacted tooth depending on the complexity of the case.
Possible complications of hemisection
All dental operations can cause various complications, including hemisection. Most often, the causes of unpleasant consequences are an increased content of pathogenic microbes in the mouth or weak immunity.
The most common complications include the following:
- bleeding begins;
- great swelling;
- seam divergence;
- inflammatory process due to wound infection;
- injury to a neighboring healthy unit;
- instability of the remaining tooth segment.
Sometimes a repeat operation is performed. During this procedure, the remaining segment is amputated.
Doctors pay attention to the fact that timely treatment of all dental diseases allows you to maintain the health and beauty of your smile. Preventive visits to the clinic twice a year will significantly reduce the likelihood of a situation requiring hemisection.
Author: Tatyana Grosova, dental assistant, especially for Karies.pro
Recovery period
The course of the rehabilitation period depends not only on the quality of the surgical intervention, but also on the actions of the patient himself during the operation.
To avoid the development of complications and speedy healing of the wound surface, dentists recommend following these rules:
- Do not eat any food for 3 hours after surgery.
- For the first 2-3 days after surgery, you should avoid eating hot and cold, spicy, salty, and sour foods.
- Drinking alcohol is strictly contraindicated during the entire recovery period. The ban also applies to any solid food products.
- The first days after hemisection, it is necessary to refrain from physical activity so as not to have additional impact on the sutures.
- The toothbrush should be replaced with a product with soft bristles. This will prevent gum damage and infection of the treated areas of soft tissue.
- It is necessary to appear for postoperative examinations at the time prescribed by the dentist. This allows for timely detection of complications of the procedure.
- After each meal, it is necessary to rinse the mouth and treat the suture area with special antiseptic solutions.
Another important rule that should be followed in the postoperative period is regularly taking anti-inflammatory, painkillers and antihistamines prescribed by the dentist.
If you experience any discomfort, you should report it to your doctor - this will allow you to take timely measures to eliminate the problem.
Postoperative period
In the first 3 hours after surgery, eating is prohibited, but you can drink water at room temperature. You should not be afraid of the recovery period, however, you should not neglect measures that speed up healing and reduce the risk of complications . Among them:
- Refusal of hot/cold, spicy and sour foods, solid or tough foods, alcoholic beverages, smoking - from 3 to 10 days, depending on the presence of stitches.
- Attention to everyday oral hygiene - immediately after surgery, the brush should be replaced with a softer one. This will help avoid injury and prevent bacteria accumulated on the old brush from entering the wound.
- Minimizing physical and emotional stress that causes muscle tension in the head and neck area - this will protect against damage to sutures or tooth displacement in the surgical area. This regimen should be followed for 3 to 14 days.
- Antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity. After each meal (water with added salt or soda is suitable here), as well as after each cleaning, solutions of Furacilin or Miramistin are appropriate here. Rinsing should be done for 5–10 days.
- Additional treatment of seams with an antiseptic using a sprinkler - also for 5 days, then - according to indications.
- Avoiding overheating of the operating area - you should not heat the area of the face and teeth in isolation; it is better to avoid baths and saunas for at least 3-5 days.
- Scheduled visits to the surgeon for examination and x-rays. As a rule, the examination is scheduled on the 3rd and 5th day after the procedure, but the schedule may be different.
- Taking prescribed medications - postoperative therapy includes antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs; antihistamines are prescribed less frequently to prevent rejection of bone replacement material.
- Taking painkillers is appropriate for moderate pain and stable positive dynamics.
The following phenomena are considered normal after hemisection::
- pain – usually the “peak” of discomfort occurs 6–12 hours after surgery, then the pain decreases;
- minor bleeding - up to a maximum of 24 hours (if the patchwork method was used);
- swelling in the operating area – up to 7 days;
- discomfort when opening the mouth, chewing, talking is a consequence of anesthesia, which should be eliminated within 5 days.
If the symptoms intensify or other alarming symptoms appear, this is a reason for an unscheduled visit to the doctor.
As the wound closes and the bone replacement material heals, the load on the tooth can be slightly increased. However, it should be understood that the molar will not have full load-bearing capacity - even if the outer part of the crown remains intact .
A tooth after hemisection is, first of all, an opportunity to preserve its appearance, avoid changes in bite, and also more evenly distribute the load during prosthetics.
Price
The cost of hemisection of a tooth varies significantly in different clinics in large cities of Russia, as well as in less densely populated regions.
In the capital of the country, you will have to pay from 3,500 to 8,000 rubles for the operation. In the provinces, the price for the same procedure can be about 1,500-2,500 rubles.
In addition to the location of the clinic, the final price is also influenced by factors such as the quality of the material used, the newness of the equipment and instruments, as well as the reputation of the dentist himself. In the video, find out a specialist's opinion about the operation.
Reviews
Hemisection is a very popular procedure in dental practice, as it allows not only to eliminate the existing problem, but also helps to save your own tooth.
The effectiveness of the operation, as in most cases, depends not only on the qualifications of the specialist, but also on the timeliness of the patient seeking professional help.
To help readers of the article cope with the fear of waiting for this procedure, share your experience of undergoing it, as well as the peculiarities of the recovery period in the comments section.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags: tooth hemisection, tooth extraction surgery
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet