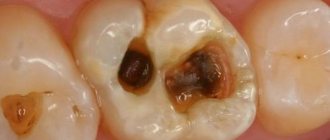
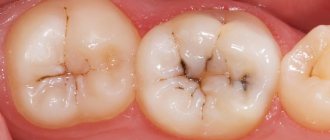
The process by which the color of tooth enamel changes and the hard tissues of the tooth are destroyed is called caries. This is the most common dental disease. Various factors lead to damage to the tooth surface; in first place in popularity is non-compliance with hygiene standards.
There are several stages of development of dental caries, and the stages of treatment depend on their severity. The easiest to treat is first-degree pathology – superficial. If the disease is advanced, the tooth is most often removed.
Spot
The root cause of this condition is poor oral hygiene. It is this circumstance that leads to the concentration of pathogenic flora, which provokes the appearance of caries.
In addition to hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, strong immunity and proper nutrition help to curb the proliferation and spread of microorganisms. If for any reason one of the mentioned limiting factors is excluded, microbes will intensify their activity and lead to caries.
It is quite difficult to identify the disease on your own at this stage, since it does not manifest itself in any way . This can only be done by an experienced specialist. But its presence can be suspected by the weakening of the tooth shine. In this situation, the gloss does not disappear from the entire tooth surface, but only on a small area of it.
Small shapeless white or matte spots will subsequently form on it. Their appearance indicates the development of demineralization, which quickly covers all units. Over time, the enamel of demineralized teeth begins to thin, and the stains themselves darken and turn brown. This change sets many patients on edge.
Important: at this stage, the affected unit does not respond to stimuli. There is no discomfort or pain.
Using a methylene solution will help diagnose caries at the initial stage. It tints problematic units blue. Instrumental diagnostics are powerless, since in destructive areas the enamel is still smooth and the probe slides over it.
We will be told about the treatment of caries at the spot stage in the following video:
Treatment of carious teeth excludes the use of preparation and filling. Their therapy consists of enriching the enamel with the necessary ions of calcium, magnesium, potassium (remineralization). The procedure itself is performed in the following sequence:
- local anesthesia is performed (if necessary);
- professional cleaning of the oral cavity is performed;
- the affected tooth is polished and isolated from access to saliva;
- one of the remineralizing agents is applied to its dried surface.
Caries at the 1st stage is a reversible process, subject to timely contact with a specialist and treatment.
We will tell you what dental phobia is and how to deal with it in our next article. From this review you will find out which medicine for toothache is the most effective.
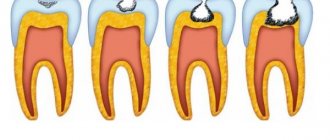
Stages of development
- Stage 1 – external damage to tooth enamel. The appearance of caries in the form of white or dark spots, barely noticeable during a superficial examination of the teeth. At this stage, it is impossible to detect any signs of destruction of tooth enamel.
- Stage 2 – initial form of caries. Formation of a defect outside the dental covering, without destruction of the dentin located under the enamel.
- Stage 3 – the middle stage of caries development. The disease progresses, affecting dentin, but not affecting the deep tissues surrounding the pulp.
- Stage 4 – deep stage of caries manifestation. Destruction spreads close to the tooth pulp, affecting and deforming dental tissue.
If you do not prevent the development of the disease even after the fourth stage, then complications are possible in the form of diseases such as pulpitis and periodontitis. The first causes inflammation of the pulp, the second causes inflammation beyond the boundaries of the tooth (periodontal abscis).
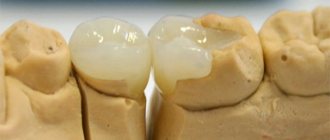
Surface
Left untreated, the initial stage tends to develop further. The stain begins to quickly increase, changes color, but does not affect the deeper layers of the enamel. The greatest intensity of the process is observed on its lateral and internal surfaces.
The superficial stage is characterized by the following manifestations:
- the structure and structure of the enamel changes: it becomes porous, uneven, rough;
- the color of the spots themselves changes: from matte (white) it changes to brown or even black;
- Depressions, cracks, and chips become clearly visible on the stains;
- a nagging, short-term painful reaction to irritants develops (especially from hot, sour, sweet, cold foods), and with the additional presence of a source of infection, discomfort is observed from brushing the teeth or pressing on them with a finger;
- plaque accumulates in the pregingival area;
- inflammation of the papillae develops (rarely).
Superficial caries is easily diagnosed by visual inspection or probing.
It is impossible to return enamel to its original state using remineralization. At this stage, dentists apply direct action on the tooth itself, and the sooner it is started, the significantly less effort required to restore it.
Treatment of superficial caries consists of:
- treating problematic surfaces;
- grinding of altered enamel;
- coatings with an adhesion-increasing composition;
- filling.
Upon completion of the procedure, the filling must be polished, adjusted to the bite, and fissures (lumps) are formed on its surface.
Average
At this stage, the disease is visible visually, so ignoring its presence is pointless and dangerous. Every day the discomfort and pain will manifest themselves more and more.
Average caries is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Sharp, but not intense pain that appears when exposed to irritants : brushing teeth, eating, contrasting air temperature.
The pain goes away almost immediately after eliminating the irritating factor. In isolated cases, it may be completely absent due to the fact that the dentinoenamel junction has been destroyed and replacement dentin has formed. It weakened the sensitivity of the pulp to the action of irritants. - Increased area of damage , covering most of the tooth. Caries affects the middle layers of enamel and invades dentin.
- Noticeable aesthetic disturbances. A dark carious spot appears on the dental cavity, the enamel on the affected unit loses its shine and becomes rough.
- The solid walls of the emerging cavities.
- Unpleasant odor coming from the mouth . Its appearance is associated with rotting and decomposition of food debris accumulated in carious cavities. Daily hygiene cannot completely clean them out, which is why the food begins to rot.
For a detailed study of the oral cavity, an x-ray, visual (mirror) and instrumental examination are used. The examination reveals a characteristic carious spot, brown (less often gray and beige), a carious cavity of varying depths.
Does a loved one grind their teeth in a dream? Let's figure out how to deal with this. At this address: https://dentist-pro.ru/lechenie/bolezni-polosti-rta/v-chem-prichiny-ploxogo-zapaxa.html you will learn about chronic bad breath.
And here you can find instructions for using dental drops.
The use of a probe makes it possible to determine the degree of coverage of the enamel by the pathological process, the depth of the cavity, and sensitivity on those teeth that are poorly visible visually.
Based on the results of the data obtained, appropriate treatment is prescribed. If you do not delay visiting the doctor, caries at this stage can be easily stopped. His treatment regimen is as follows:
- Anesthesia is given.
- Infected tissues are eliminated.
- Aseptic treatment is carried out using fluoride and calcium-containing preparations (their use strengthens tissue and prevents the development and spread of caries in the future).
- An insulating pad is applied.
- A filling is placed.
- The tooth is polished and ground.
Important: usually such caries is treated in one visit. The patient still has a chance to save his tooth, which cannot be done at the next stage.
Deep
Unfortunately, this is the stage of the disease that is most often detected. Fear of the dentist makes many people put off visiting him, which leads to further spread of the disease and worsening of the condition: the development of secondary diseases, loss of the tooth itself.
The pathology is characterized by the following symptoms:
- voluminous deep carious cavities extending to the dentin (but they do not affect the pulp);
- sharp, long-lasting pain, which can develop not only from the action of irritants, but also at rest (pain sensations often appear in the evening and at night);
- affecting the dental nerve;
- the affected areas become black;
- The tooth and subgingival area are gradually destroyed.
Treatment of caries at this stage is a long process and may take more than one visit to the dentist.
It is carried out in the following order:
- Local anesthesia is given.
- Using a mirror and probe, the doctor examines the carious cavity, determines its depth, and explains the course of treatment to the patient.
- Necrotic, carious soft and hard tissues are removed.
- A cavity is formed.
- Aseptic processing is carried out.
- A medical pad is placed on the bottom of the cavity to prevent the development of complications.
- After it, an insulating gasket is laid to secure the first one and protect it from the ingress of the composite.
- Adhesive material is applied to the walls.
- A filling is placed.
- The tooth is being restored.
If the treatment takes place in 2 stages, then instead of a permanent filling, a temporary filling is placed. This is done if the patient complains of pain, the disease progresses to pulpitis, the dentin is very thin or absent, and the pulp chamber is open.
What determines the cost of caries treatment?
In addition to the level of the clinic, the cost of caries treatment depends on the condition of the tooth itself.
There are two main factors:
- Depth of caries damage to hard tissues. Caries can be superficial, medium and deep, and the deeper it is, the higher the price.
- The degree of destruction of the tissues of the tooth crown from the outside. Caries can be superficial, but it destroys a large amount of tissue, and it will take a lot of time and effort to restore the tooth to its original form. This also increases the cost of treatment.
Let's look at how the price changes depending on the depth of the lesion.
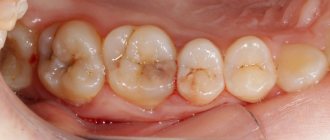
Multiple
An acute stage of the disease, in which 6 or more units are immediately susceptible to destruction, and several “holes” may be present on one at the same time. It manifests itself in the presence of neurosomatic, endocrine, infectious and other chronic conditions.
Among the “unfavorable” factors leading to this condition are a lack of vitamins and minerals in consumed foods and water, poor environment, stress, diet, work in hazardous industries, heredity, etc.
A characteristic sign of pathology is its rapid development and spread. So, in just a year, almost all of a person’s units can be destroyed. Simultaneously with the development of the pathological process, a person experiences viscous and high viscosity of saliva, poor salivation, and dry mouth.
Other clinical signs of caries include:
- slight destruction of enamel with extensive damage to dentin;
- the appearance of several cavities on one tooth;
- rapid appearance of plaque;
- simultaneous presence of caries at different stages of development.
Another sign of the disease is the loss of relatively fresh fillings. This is explained by the development of a secondary focus of caries underneath them, as a result of which the enamel becomes soft and the fixation of the composite weakens.
Treatment for multiple stages includes:
- removal of affected dentin;
- formation of cavities;
- their treatment with antiseptics;
- filling.
The success of treatment directly depends on how successfully the underlying disease that caused multiple caries is treated. Additionally, the patient is recommended to take medications that enhance immunity and restore mineral balance. A diet is being developed that includes foods rich in proteins, minerals, and vitamins.
Physiotherapy procedures give good results: fluoridation, silvering, calcination of teeth with special means or electrophoresis.
How to properly prevent caries
To get rid of problems with caries forever, you need to regularly visit a dentist . In addition, a number of preventive measures must be taken:
- Eat right. It is advisable to eat fruits, vegetables, fish, seafood, and dairy products, because dental tissues need fluoride, calcium, phosphorus and other minerals for normal development and functioning.
- Avoid eating hot and cold food at the same time, otherwise you can damage the enamel. The outer shell of the tooth gradually collapses after large temperature changes.
- Check with your dentist at least once every six months to check for dental-related diseases.
- Maintain oral hygiene and use effective products to combat plaque. Choose a toothpaste with comprehensive protection, and sometimes use an antiseptic rinse to remove harmful microorganisms.
Thanks to such simple tips, the condition of your teeth will be ideal, and you will not need treatment for deep lesions of dental tissue, which costs a lot of money.
Recurrent
It arises and develops in a sealed tooth (under the filling itself or at the edge of the sealed cavity). Pathology can be recognized by the darkening of the filling along its edge, the appearance of visible cracks or chips in the enamel.
Several reasons can lead to its development:
- incorrect transition of the filling material into the tooth (with a joint);
- the outer tooth surface is poorly prepared for the application of a composite;
- The carious cavity was not completely cleaned out during the first filling.
Important: to prevent the development of recurrent caries, you must periodically visit the dentist to check the condition of existing fillings.
If unevenness or roughness of the filling is discovered, especially in the place where it connects to the tooth, the doctor, using polishing, will return it to its original appearance and protect it from caries. If the disease occurs, treatment consists of replacing the filling.
Carious tooth decay can be stopped at any of the above stages . The main thing is to identify and eliminate the cause of the disease in time.
User reviews about treatment methods
Inna, Voronezh: “Naturally, in the last stages of the disease, folk remedies will no longer help. Only a visit to the dentist can solve the problem. At one time, a tincture of fir oil helped me a lot. It’s good that I discovered the formation of a stain on the tooth wall in time.”
Svetlana, Kaluga: “My daughter got caries at the age of 8. If we hadn’t noticed the dark spot on the tooth, we would have had to go to the dentist. A friend told me that her son had a similar problem and advised him to apply propolis, saying that this remedy is best suited for children. We started taking it. After some time, the spot disappeared.”
Denis, Tver: “When I was a student, I ate a lot of sweets. Over time, problems with teeth began. I started going to the dentist for examinations and doing preventative care, but the disease became more and more intense. I learned from a friend with whom I served together that application napkins with the application of fluoride-containing paste help a lot. Successfully prevented dental caries. I recommend"
Ekaterina, Moscow: “After giving birth, complications began related to pain near the tooth. I started looking for traditional medicine on the Internet and found information that sage tincture helps with aching pain. I took it for about 10 days - the pain first subsided, and then went away completely.”
By location
Based on this symptom, the disease is divided into 4 types:
Fissure (occlusive)
The most common type that affects the natural recesses of the chewing dental surfaces: fissures. It is in these depressions that the most deposits accumulate, and it is not always possible to completely clean them out.
Interdental (approximal)
Destroys the contact surfaces of teeth and is not visualized for a long time. Its “hiddenness” is explained by the peculiarity of the development of the pathology: affecting the masticatory units, the disease develops towards their center, while the carious cavity itself remains covered for some time by the preserved enamel. An x-ray allows you to detect its location.
Cervical (cervical)
The source of the disease is located in the area near the gums (in the neck). It may be covered for some time by the reddened gum area.
Atypical
A rare species, located at the cutting edge of the teeth or their protruding part.
Reviews
Caries is a dangerous and insidious disease that, if left untreated, leads to tooth loss. Only adequate oral care and regular visits to the dentist will help stop this pathological process at an early stage and save you from unbearable suffering and expensive long-term treatment.
You can share your experience of treating him and the effectiveness of various therapy methods on him by leaving a comment on this article.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.