1416
Carious areas can be located on different parts of the tooth, the most common is fissure caries - damage to the chewing surfaces of the teeth. How does the disease begin and progress? How does a doctor determine the degree of damage to tooth tissue and what will be the treatment?
What is fissure caries?
Fissures - this professional term refers to the natural pits and grooves that exist on the surfaces of chewing teeth. In these recesses, food debris clogs and accumulates, and therefore the fissures of the chewing teeth are vulnerable to caries. Therefore, it is so important to thoroughly brush your teeth and clean the fissures of your chewing teeth from plaque and food debris.
Fissure caries is clearly visible on the surface of the tooth, but only if the tooth has open fissures, that is, those natural depressions, the bottom of which is completely visible visually. But chewing teeth also have closed fissures: the structure of this type of fissure is very similar to the structure of a bottle. In closed fissures, only the upper narrow groove is clearly visible upon examination, but in depth it expands and forms a cavity. Diagnosing caries with closed fissures is a difficult task and, of course, you won’t find such caries on your own; you will definitely need to visit a doctor’s office.
In order to prevent fissure caries and begin its treatment in a timely manner, you need to undergo regular preventive examinations at the dentist’s office. Our VENSTOM dental clinic in Moscow uses the most modern diagnostic equipment and techniques to detect and treat caries on time!
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Fissure caries - what is it?
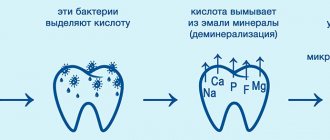
Fissure caries is a lesion of the natural grooves (fissures) located on the chewing side of premolars and molars. Fissures come in the form of grooves, cones and drops. The deeper and narrower the grooves, the higher the likelihood of developing pathogenic flora, since food particles get stuck in them during food consumption. And during chewing, food residues under pressure move even further and begin to decompose, providing a favorable environment for the growth of bacteria.
Another common cause of caries in the fissure area is weak mineralization of tooth enamel. Most often this occurs in children during teething, when the dental tissue has not yet fully formed.
If you delay the treatment of fissure caries, the disease can become more serious and lead to tooth destruction.
Why does fissure caries occur?
Fissure caries occurs for only one reason - poor dental and oral hygiene. If after eating you do not brush your teeth, do not rinse your mouth and perform dental hygiene less than 2 times a day, fissure caries will not keep you waiting, because plaque and food debris quickly accumulate in the pits and depressions on the surfaces of the chewing teeth. This environment is extremely favorable for the development of carious bacteria.
Bacteria will multiply, their vital activity will lead to weakening of the tooth enamel and when it becomes thinner to a certain extent, fissure caries will begin.
What are fissures
Fissures are anatomical grooves and grooves on the chewing surface of the crown. They are found on large teeth - premolars and molars. Depending on the structure there are:
- grooved;
- cone-shaped;
- drop-shaped.
Deep and narrow fissures are especially vulnerable to the influence of cariogenic bacteria. Microbes clog into the recesses and actively multiply in them. Even careful oral hygiene will be powerless, since it will not be possible to completely clean out the pathogenic flora from hard-to-reach areas.
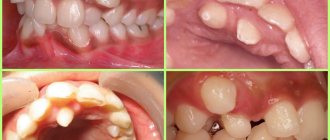
Signs of fissure caries
By what signs can you recognize the development of fissure caries? Fissure caries has the same symptoms as other forms of the disease:
1. With fissure caries in the staining stage on the chewing surfaces of the teeth, you can see a change in the shade of the enamel - it becomes whitish. Apart from whitish spots, fissure caries does not show itself in anything at this stage of development - the tooth does not hurt.
2. With superficial fissure caries, the spots become larger and darker, acquiring a distinct contour. Tooth sensitivity to hot/cold, sour/sweet foods may occur.
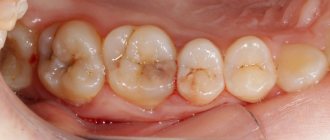
3. Average fissure caries already affects the dentin, so the destruction of the tooth will be clearly visible - a cavity will appear on the surface of the crown, which is popularly called simply “a hole in the tooth.” Unpleasant sensations may occur when eating, but usually they pass quickly - you just have to stop chewing on the affected tooth and rinse your mouth well.
If fissure caries is not treated, it will turn from medium to deep and the destructive process will reach the pulp (nerve) of the tooth. If the infection penetrates into the pulp, the dentist will no longer have to treat fissure caries, but its complication - pulpitis.
Any person can notice rare and deep fissure caries on their teeth during dental hygiene, but the diagnosis of fissure caries in the spot stage and fissure superficial caries requires a visit to the doctor’s office. Small specks of demineralized enamel may not be noticed under plaque, which is actively accumulating in the fissures, and even more so it will be impossible to independently detect caries if the fissures are closed.
Symptoms of fissure caries: how not to miss the disease
The manifestations of this type of pathology are the same as those of other variants of the disease. First of all, attention is drawn to the appearance of dark spots on the teeth (however, it is important to understand that darkening of the fissures is not always caries). If treatment is not carried out in a timely manner, the pathological process spreads deeper, affecting the dentin. As a result, complaints appear about the reaction to irritants (cold/heat, sour/sweet), and with further development of the disease - about constant pain.
Diagnosis of fissure caries: basic and auxiliary methods
The main diagnosis of fissure caries will consist of visual inspection and probing. If caries has affected the fissures, they will noticeably darken, the tissue in them will soften and the probe that the dentist uses during the examination will get caught on them. But if the caries is still in the staining stage or the tooth has deep and narrow fissures, additional diagnostic measures can be carried out:
- X-ray of a tooth. A fairly effective diagnostic method that allows you to detect fissure caries at the earliest stages of development, since carious lesions will be clearly visible on the pictures;
- Fissurotomy. A specific study that helps to see how deep the carious damage has gone in the tooth. Fissurotomy is carried out as follows: using a drill, the doctor opens the fissures to a small depth (up to 1 mm) and looks at how much caries has managed to destroy the tooth.
Diagnosis of fissure caries can be carried out using a laser. This is the most modern and effective method for diagnosing caries at any stage of its development: the laser is reflected differently from healthy and diseased tooth tissues. The difference in the reflections of the laser beam is noted by the device, which immediately sounds a sound signal. But laser diagnostics of fissure caries is carried out only in those clinics that have the appropriate equipment.
Diagnostics ↑
Most existing methods for diagnosing caries are ineffective, especially if the fissures are closed.
An alternative to a conventional visual examination using a dental probe is the X-ray diagnostic method and the detection of caries using a special device.
Visual inspection
This detection method is effective for teeth with open fissures.
Using a probe, you can examine the grooves and assess the condition of the enamel in them. But in the case of closed fissures, it is impossible to understand whether the tooth is damaged, either visually or with the help of a probe.
Photo: Visual examination of teeth
And since the thickness of the dental probe can exceed the width of the mouth of the barbs, there is a very high danger of damaging healthy tooth enamel. In such cases, other diagnostic methods come to the rescue.
Radiography
This method allows you to identify hidden fissure caries, even in the absence of clinical symptoms. Using the image, you can find out exactly how deep the areas of damage to dental tissues are. But x-ray examination is ineffective in the initial stages of caries.
Hardware diagnostics
Using a laser fluorescence apparatus, it is possible to very accurately diagnose hidden carious lesions.
This method is very effective at any stage of closed fissure caries. To date, this diagnostic method is the most indicative.
Photo: Device for hardware diagnostics of caries
How will fissure caries be treated?
After diagnosing and diagnosing “fissure caries,” a method of treating it is selected. Since patients usually come to dentists with moderate fissure caries, below we will describe all stages of its treatment.
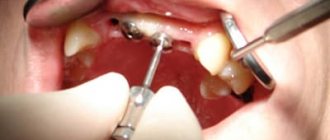
1. Pain relief. When treating medium fissure caries, the doctor will need to remove all affected and destroyed tissue with a drill. This can be unpleasant for the patient, so local anesthesia is given before treatment begins.
2. After the anesthetic has taken effect, a rubber dam, a special latex overlay, is installed on the area where fissure caries is treated. The rubber dam reliably isolates the area of treatment from saliva and moisture from the oral cavity, which may contain bacteria. In addition, careful isolation of the tooth from moisture is important for high-quality filling. If moisture gets into the cavity at the time of placing the filling, the adhesion between the filling materials and the natural tissues of the tooth will deteriorate and this can lead to the filling falling out.
3. After installing the rubber dam, the dentist will begin working on the tooth. When treating fissure caries, it is extremely important to remove all destroyed and damaged tissue. If this is not done, caries will continue to develop directly under the filling.
4. By removing tissue damaged by fissure caries, the dentist will form a cavity in the tooth for installation of a filling. This cavity is treated with a special etching solution that cleans the tissue, and then an adhesive composition is placed into it.
5. The dentist will restore >the crown of the tooth
The process of treating fissure caries is completed by grinding and polishing the installed filling.
If a tooth is severely damaged by fissure caries, then it is better to restore it not with a filling, but with a special restorative inlay, which can be made of different materials: gold, ordinary metal, ceramics.
Inlays are fixed in the tooth using special cement and differ from fillings in having a longer useful life, and in addition, in reduced risks of developing secondary fissure caries. In addition, fillings even made from the highest quality composites darken over time, but ceramic inlays retain their aesthetic appearance throughout their entire service life. Of course, restoring a tooth with an inlay after treating fissure caries will cost more, but the high cost will be justified by the durability and reliability of the restoration.
Methods of treating the disease
Treatment of the disease is usually carried out under local anesthesia and is performed according to the following scheme:
- mechanical opening of the gap and removal of all pigmented dental tissues using a drill;
- isolation of the causative tooth from saliva and oral fluid using cotton swabs or a cofferdam;
- etching of the carious cavity with orthophosphoric acid to form microcracks in the hard tissues of the tooth;
- installation of a filling made of solid or liquid photopolymer material;
- grinding and polishing the surface of the tooth being restored.
Isolation of the working field during fissure caries filling
Is it possible to cure fissure caries without drilling the tooth?
Fissure caries can be cured without drilling a tooth, but to do this you need to regularly visit the dentist’s office and undergo preventive examinations. If fissure caries is detected at the spot stage, it is treated without drilling the tooth, through remineralization or Icon technology.
From here we can draw a simple conclusion - if you want to treat your teeth without pain and drilling with a drill, you need to pay close attention to the prevention of caries.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
Prevention
It is not difficult to prevent the development of fissure caries; for this you need to follow simple rules of prevention:
- Visit your dentist regularly for preventive examinations;
- Keep your mouth clean. It is important not only to regularly brush your teeth with toothpaste and a brush, but also to periodically use dental floss to clean hard-to-reach places, as well as use special mouth rinses;
It is necessary to monitor your diet. By excluding from it harmful products that promote the growth of bacteria.
How to prevent fissure caries
The best prevention of fissure caries is regular and high-quality oral hygiene, as well as periodic professional teeth cleaning in the dentist’s office.
If you have deep, closed fissures, fissure sealing can be an effective method of preventing fissure caries. This is a simple event during which the fissures are sealed with a special sealing compound. Fissure sealing is carried out in both children and adult patients and helps to significantly reduce the risk of developing fissure caries.
An excellent method of preventing fissure caries is a course of remineralizing therapy. The essence of the procedure is to treat teeth with special compounds based on fluoride and calcium, which strengthen tooth enamel.
Do you still have questions about the treatment of fissure caries? Ask them in the chat on the website of our dentistry in Moscow - VENSTOM, or even better - come for a consultation with our specialists!
Rationale for choosing a sealant for sealing fissures of permanent teeth in children
An urgent problem in pediatric dentistry is the prevention of fissure caries in permanent teeth, especially during the period of their eruption and mineralization in school-age children. Today there is no doubt about the need to use fissure sealing to prevent caries on the chewing surface of permanent teeth, however, in terms of the scale of preventive measures involving fissure sealing, our country lags behind many regions in which fissure sealing is an integral part of national successfully implemented caries prevention programs [3, 6 , 7, 9, 13].
INTRODUCTION
Fissure caries is one of the earliest and most common forms of destructive damage to hard dental tissues [2, 3, 6, 13]. Early damage to fissures is associated with the peculiarities of mineralization of tooth enamel: active maturation of tooth enamel occurs in the first 12–24 months, and in the fissure area continues for another 2–3 years compared to smooth tooth surfaces [6, 8, 9]. The high incidence of fissure caries is associated with the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of fissures, the accumulation of food debris and the formation of aggressive dental plaque in the natural recesses of the tooth [5, 14].
According to various authors, in children aged 7 to 12 years, the chewing surfaces of the first permanent molars are most often affected by caries [1, 10, 12, 13]. When they erupt, active growth of the jaws is observed, and a second physiological increase in the bite occurs. The destruction of these teeth by the carious process and untimely treatment leads to dentoalveolar deformities and the formation of various occlusion pathologies [4, 10, 11, 15].
Reducing the level of dental morbidity in children and adolescents, primarily dental caries, is a priority direction of modern dentistry. Children's age is the most promising for obtaining high rates of preventive measures.
Purpose of the study: to justify the choice of sealant for sealing fissures of permanent teeth in children to increase the effectiveness of caries prevention.
Research objectives
- To study the prevalence and intensity of caries of permanent teeth in children 7-8 and 12-13 years old living in Omsk.
- To assess the hygienic status of the oral cavity of schoolchildren using the Green-Vermillion index.
- To determine the level of awareness of practical healthcare doctors about fissure sealing.
- Justify the choice of material for fissure sealing.
Materials and research methods
To achieve this goal, we conducted an oral survey and questionnaire of parents whose children sought dental care. Parents and patients were informed about the examination methods and the purpose of the work being carried out, and voluntary informed consent to participate in the examination was obtained. The examination was carried out using a standard set of dental instruments. When conducting a clinical examination of children, we used the Riga map. The Riga map is convenient and informative for such studies and includes the following indices: KPU+kp, kp, KPU surfaces and KPU cavities. The hygienic state of the oral cavity in children was determined using the Green-Vermillion hygiene index (1964), which allows one to assess the presence of not only plaque, but also tartar.
The electrical conductivity of hard dental tissues was measured using the Dentest device. To assess the thixotropy of the sealants, microphotography of teeth sections was carried out using an electron microscope.
Results
To solve these problems, we examined 64 children of Omsk aged 7-8 and 12-13 years, students of secondary schools No. 28 and 83. 38 girls were examined, 26 boys.
During a dental examination of schoolchildren aged 7-8 and 12-13 years, it was revealed that the prevalence of caries in permanent teeth is quite high and reaches 86%. The intensity of caries in permanent teeth (CPD) also increases with age and is: at 7-8 years old - 3.8, at 12-13 years old - 4.3. A structural analysis of the KPU indicators revealed that the growth of the KPU index is mainly due to the growth of the “K” indicators. In children aged 7-8 years it is 59%, in 12-13-year-old peers it increases to 69%. With age, there is a tendency for the “P” indicator to increase: for 7-8 year olds it is 41%, for 12-13 year olds it is 29%. However, in all age groups, the “K” component significantly exceeds the “P” component, which indicates untimely receipt of dental care. In the structure of the index of permanent teeth, there is an almost complete absence of “U” indicators in all age groups: only in 12-13 year olds it was 2% (Fig. 1).
Rice. 1. Assessment of indicators K, P, U depending on age.
At the same time, there is also a predominant lesion of the chewing surfaces (at 7-8 years old - 39%, at 12-13 years old - 46%) compared to the vestibular surface (at 7-8 years old - 18%, at 12-13 years old - 19%) , medial contact (in 7-8 years - 16%, in 12-13 years -11%), distal contact (in 7-8 years - 22%, in 12-13 years -17%) and oral (in 7-8 years old - 5%, 12-13 years old - 7%) (Fig. 2).
Rice. 2. Prevalence of caries on various surfaces of permanent teeth in children.
Using the Dentest device, the degree of mineralization of the enamel of permanent teeth (4.6 and 1.1) was determined in children 7-8 years old. The initial level of mineralization (ILM) of the 4.6 tooth enamel on the buccal surface averaged 7.4±0.8 (high ILM), and on the chewing surface - 22.5±1.5 (average ILM). For comparison, the IUM of 1.1 teeth was measured in the area of the cutting edge - 0.3±0.2 (high IUM), and in the cervical area - 6.4±0.7 (high IUM). Our results confirm the opinion of a number of authors [6, 8, 9] that the maturation of enamel on a smooth surface has a higher rate of mineralization compared to occlusal surfaces. In this regard, the occurrence of caries on the chewing surface can be predicted with a 50% probability [9]. High rates of caries damage to chewing surfaces and a low initial level of mineralization indicate the need to prevent caries in permanent teeth in children.
A fairly high intensity of caries damage to the chewing surfaces of permanent teeth was revealed against the background of unsatisfactory oral hygiene in the age groups studied. The value of the initial hygiene index in children 7-8 years old reached 2.7, in children 12-13 years old - 2.6. Thus, the high incidence of caries on the chewing surfaces of permanent teeth, combined with a low level of oral hygiene, confirms the need for schoolchildren to carry out preventive measures to prevent caries of chewing surfaces using the fissure sealing method.
To improve the hygienic state of the oral cavity, health lessons were conducted for schoolchildren, which included teaching schoolchildren how to brush their teeth with a demonstration of brushing teeth on models (Fig. 3) and dental education for 5 lessons.
Rice. 3. Teaching children oral hygiene.
The result revealed a significant improvement in the level of oral hygiene after 5 lessons; the index value decreased significantly in all age groups. In the first age group (7-8 years), the index decreased by 1.5 (56%) and amounted to 1.2. In the second age group (12-13 years), we observed a similar picture, the index decreased by 1.7 (66%) and amounted to 0.9.
To study the level of awareness of pediatric dentists about fissure sealing, we conducted a survey of 70 pediatric dentists in 4 public and 8 private clinics in Omsk. The doctors' work experience averaged 20±5 years. The following results were obtained during the study: 82% of doctors consider the use of sealants to be effective for the prevention of caries, 86% of dentists, using fissure sealing in their practice, stated that there was no caries damage to chewing surfaces.
However, only 27% of doctors use sealants in their practice quite often, 63% rarely, and 10% do not use them at all (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. Application of fissure sealing at a dental appointment.
There are a large number of different materials for sealing dental fissures; it is difficult for practicing dentists to navigate when choosing the most effective caries preventative agent. The most commonly used sealants are: Fissurit F, Fissurit FX, Ionosit Seal, Delton, Fissil - S, Fissulight LC (Fig. 5).
Rice. 5. Demand for materials for fissure sealing by dentists.
As the survey showed, the most commonly used sealant is Fissurit F, and the least used is Fissulight LC. To study the reason for this choice, it was decided to study one of the most important properties of sealants—thixotropy. To study the thixotropy of sealants, fissure sealing was carried out on extracted teeth. We studied 12 healthy teeth removed for orthodontic reasons. The extracted teeth were divided into 2 groups (6 teeth in each) depending on the sealant used. Sealants Fissurit F, “Fissulight LC” - light curing. After sealing, the tooth was sawed longitudinally and examined under an electron microscope. Photographs were taken from the samples obtained. The results of our electron microscopic study of the sealants Fissurit F (Fig. 6), “Fissulight LC” (Fig. 7) revealed that Fissurit F has the best thixotropy.
Rice. 6. Fissure sealing “Fissulight LC”. Rice. 7. Fissure sealing “Fissulight LC”.
The ability of the sealant to penetrate even into closed fissures provides a high caries-preventive effect, which explains the choice of Fissurit F by most of the doctors surveyed and gives grounds for recommending this sealant for sealing fissures.
Analyzing the results obtained, we can draw the following conclusions:
- the prevalence and intensity of caries of permanent teeth in children 7-8 and 12-13 years old in Omsk is high;
- the state of oral hygiene of schoolchildren according to the Green-Vermillion index is unsatisfactory;
- despite the high level of awareness of practical healthcare doctors about fissure sealing, this area of prevention is used in practice quite rarely;
- the choice of sealant for sealing fissures plays an important role in the effectiveness of the prevention; The most preferred sealant is Fissurit F.
LITERATURE
- Alimsky A.V., Fleisher G.L. Modern prerequisites and real opportunities for organizing hygienic training and dental education among the children's population of Russia. Medical alphabet // Dentistry. - III/2010.
- Boyarkina E. S. Development and evaluation of the effectiveness of minimally invasive methods for the treatment of fissure caries of permanent teeth in children (clinical and laboratory study): abstract. dis. ...cand. medical sciences - M., 2009. - 19 p.
- Bryanskaya M.N. Clinical and morphological rationale for the prevention and treatment of fissure caries of permanent teeth with immature enamel: abstract. dis...cand. honey. Sci. - Irkutsk, 2009. - 23 p.
- Vagner V. D., Distel V. A., Karnitsky A. V., Mateshuk A. I., Suntsov V. G. Guide to practical training in orthodontics. - Omsk: Publishing House Omsk State Medical Academy, 2009. - 372 p.
- Vlasova G. I., Lugovskov D. A., Silaeva O. A., Dudar S. V. Clinical assessment of the prognostic significance of informative markers in the practice of preventive dentistry // Ukrainian Medical Almanac. - 2008. - Volume 11, No. 5. - P.37-38.
- Zhorova T.N. The process of enamel maturation after eruption and the influence of various factors on it: Dis. Candidate of Medical Sciences Sci. - Omsk, 1989. - 24 p.; Leontyev V.K. Caries and mineralization processes: Abstract of thesis. dis. - Omsk, 1978. — 45 s.
- Kutsevlyak V.F., Polyakova S.V., Pushkar L.Yu., Varakuta V.V., Grishchenko V.V., Volkov S.N. Fissure sealing is a method of modern caries prevention.
- Leontyev V.K. Caries and mineralization processes: Abstract of thesis. dis. - Omsk, 1978. - 45 p.
Treatment
The traditional treatment regimen for fissure caries involves following the following steps:
- Removing affected parts of tissue using a bur.
- Treatment of the cavity with a special acid-containing liquid for etching (it cleans the tissue).
- Application of a composition with high adhesive properties (necessary for better fastening of the filling material).
- Filling. Optimally - using polymer materials.
- Correction of fillings with polishing.
Correction and polishing of the filling must be carried out as carefully as possible, because...
Poor treatment can lead to changes in the bite. Instead of a filling, you can use a ceramic inlay - a microprosthesis, individually selected for each client. The inlay is closely adjacent to the crown, and therefore provides higher guarantees of protection against microbes.
If acute focal pulpitis has developed against the background of fissure caries, at stages 2 and 3 it will be necessary to remove the pulp - the neurovascular bundle.
When contacted in the early stages of pathology development, treatment can be carried out without drilling. A polymer composition is applied to the stains, which “seals” the problem area and prevents bacteria from spreading to adjacent dental tissues. Other ways to treat caries without boron:
- Ozone therapy – the affected parts are sterilized with ozone.
- Laser – under the influence of a laser beam, infected areas evaporate (and only healthy parts remain). Read more details regarding laser treatment of caries in this article.
Treatment without drilling is the cheapest - from 1000 rubles for coating with polymer compounds and exposure to ozone. Laser therapy and installation of a photopolymer filling cost approximately the same - from 2000 rubles.