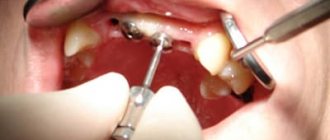
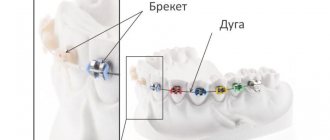
Elimination of pathology
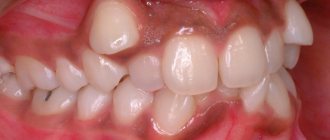
As a rule, extra units grow outside the dentition, which affects a person’s appearance.
They are especially visible when smiling or communicating. In some cases, even with a closed mouth, a person has protruding lips or an extended jaw that does not close. If you have supernumerary teeth, you may experience a lisp and speech problems. Hyperdontia also affects the formation of bite. Indeed, with such a pathology, difficulties arise with chewing and biting food, and the molars also become displaced. Due to excess dental elements, problems arise with performing regular hygiene procedures in the oral cavity. And without proper care, various oral diseases appear.
Quite often, the mucous membrane of supernumerary teeth is damaged, which leads to inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Due to crowding of teeth, a person’s dentition is formed incorrectly and the bite is disturbed.
Treatment of hyperdontia depends on many factors - the inclination and location of the supernumerary tooth, the degree of disturbance that it provokes, as well as the period of formation of the bite.
Removal of a supernumerary tooth is performed in the following situations:
- The extra unit erupts in place of the molars.
- Additional bone formation caused the formation of bite pathologies, both deep and open.
- The supernumerary dental elements are impacted and there is no chance of their eruption (distal, mesial, vestibular or palatal inclination).
By the way, quite often just removing an extra tooth is not enough. To restore the integrity of the dentition, they resort to the use of orthodontic appliances.
Treatment
Today, absolutely everyone is treated, including supernumerary teeth. Such treatment directly depends on the location of the supernumerary tooth and, of course, its effect on the position of normal teeth. Supernumerary teeth undoubtedly disrupt the process of teething and the correct construction of the dentition. Therefore, they should be removed in the same way as teeth that appear on the roof of the mouth.
Removing impacted supernumerary teeth, such as a tooth on the palate, is associated with very significant difficulties, which are caused by the great depth of occurrence or closely spaced rudiments of adjacent teeth or irregularly shaped roots. In such cases, it is very important to determine the most rational surgical approach to the supernumerary tooth on the palate. X-ray or orthopantogram is of great help in this.
After removing the supernumerary tooth, its shell is also carefully removed. As a rule, the postoperative period is favorable, especially if the patient consults a doctor in a timely manner.
Supernumerary teeth are an anomaly in the development of the dental and jaw system, which is based on the excess number of teeth in the oral cavity. The norm is 20 milk and 32 permanent teeth. Additional teeth are localized in front of the dentition, but there are exceptions when others erupt near the last teeth. To save the patient from this dental pathology, it is necessary to carry out treatment, which is based on the removal of excess processes. Polyodontia occurs in both adults and children.
Concept and signs of supernumerary teeth
Hyperdentia (hyperdentia from hyper and lat. dens, dentis tooth) is an anomaly in the number of teeth.
Up to a certain age, children should ideally have twenty milk teeth, which are gradually replaced by permanent ones, and there are 32 of them. With hyperdontia, these numbers shift by one or more positions in a larger direction, since in this case there are one or several more tooth buds than normal.
Supernumerary teeth, as a rule, erupt after the main teeth, but there are exceptions when the supernumerary has erupted and taken the place where a normal tooth should be. As a result, teeth shift and bite changes. Only in rare cases does hyperdontia make itself felt during the period of milk eruption. Most often, this anomaly occurs among men, which accounts for about 65% of the total number of such cases.
In 15% of cases of this anomalous phenomenon, more than two supernumerary teeth erupt on the gum or palate. The most common phenomenon among hyperdontic anomalies is the eruption of supernumerary teeth in the area of the lateral incisors on the upper jaw, and less often on the lower jaw. Such teeth may differ from normal ones in shape, structure, color, which indicates their abnormal origin.
Symptoms
The shape of supernumerary teeth can be very different; it may well correspond to the anatomical shape of an ordinary healthy tooth or resemble drops, entire conglomerates of tooth-like formations, or individual crowns. Sometimes such teeth emerge from the palate or are fused to healthy permanent teeth, which has a negative impact on the proper development of healthy teeth.
Supernumerary teeth can be located outside the dentition (oral, vestibular) or in the dental arch. It also happens that such teeth are located between the upper central incisors, thereby disturbing the correct position of healthy teeth and incisors. With a significant jaw size, a supernumerary tooth in the palate may not affect the shape of the dental arch at all, but with a small jaw, as a rule, anomalies in the position of individual teeth occur.
Supernumerary teeth: causes of appearance
The exact cause of this anomaly is still unknown. However, scientists suggest that polyodontia occurs as a result of splitting of the tooth germ or as an atavism.
The appearance of excess bone formations in the mouth is explained by the fact that the dental system is trying to return to the original number of units that were provided by nature. Our ancestors had 6 incisors on the upper and lower jaws. That is why many doctors are inclined to believe that hyperdontia in some people is nothing more than an atavism.
According to another hypothesis, extra dental units appear when tooth germs split. Hyperdontia in this case appears due to impaired jaw development in the unborn baby during the embryonic period. A supernumerary tooth can also appear due to poor ecology, viral infections, drug and alcohol use by the expectant mother, illegal medications during pregnancy and other factors.
Scientists continue to investigate the reasons for this anomaly. They cannot accurately explain the development of polyodontia, but most of them are inclined to the second hypothesis.
Many people with hyperdontia have only one extra tooth, but in 25% of cases there are several such elements, most often located in the dentition. Moreover, approximately every fifth person with this pathology is found to have a supernumerary impacted tooth.
We suggest you read: What color is the tongue of a healthy person?
Causes
There are only theories about the origin of this anomaly. According to the knowledge of embryology, teeth develop from the dental plate. For some inexplicable reason, it produces not 32 rudiments, but more. Some people think that the reason for this is the mother’s illness during pregnancy, others point to food with GMOs causing mutations, others blame the poor environment, others consider it a consequence of endocrine diseases, and others talk about heredity. There is also an idea that a supernumerary tooth arises as a manifestation of ancient genes inherited from ancestors. They had more teeth, which is why sometimes homo sapines has a blast from the past. Just like some people have a tail growing from the coccyx (the coccyx is precisely a reduced tail).
Hyperdontia in an adult
In adults, hyperdontia is much more common than in children. Additional teeth are mainly located in the palate or on the gums, which is unnatural and contrary to the norm. The eruption of an “extra” tooth can cause the following symptoms:
- Impaired diction. The person begins to burr and vaguely pronounce some sounds and sound combinations.
- A feeling of discomfort caused by the abnormal position of supernumerary teeth. Such teeth provoke curvature of the dentition.
- Malocclusion. This problem entails a number of dental diseases, such as pathological tooth wear, impaired diction and others.
- Damage to the oral mucosa with subsequent inflammation;
- Impaired chewing function, which leads to gastrointestinal problems.
This type of anomaly often causes nervous breakdowns and mental disorders. Due to the displacement of the dentition, healthy teeth lose their strength and begin to loosen under the pressure of the growing supernumerary rudiment. The jawbone swells, which leads to pain. Constant aching pain leads to irritability, apathy and deterioration in general well-being.
Causes
As for the causes of this pathology, it is very difficult to name them, but in modern dentistry there are the following assumptions about this:
- Atavism. Few doctors adhere to this theory, since it is based on the echoes of time. It is also unable to explain why polyodontia occurs both at the beginning and at the end of the dentition.
- Incorrect embryonic development. Many doctors believe that during uterine development the plate split into a large number of parts in the fetus, which provoked this pathology. This theory explains the appearance of additional teeth at the end of the dentition. However, it is not able to explain why some people have extra teeth but are missing some rudiments.
- There are experts who are of the opinion that the anomaly occurred during the first trimester of pregnancy, when a negative impact was exerted on the pregnant woman’s body.
The above reasons are rather arbitrary and therefore cannot be considered correct when making a diagnosis.
Types of hyperdontia
Depending on the location of the supernumerary teeth, several types of polyodontia are distinguished:
- Conical or awl-shaped tooth. In this case, excess rudiments erupt between the upper central and lateral incisors. The name of the anomaly comes from the peculiar shape of the supernumerary tooth, which looks like an awl. This form of hyperdontia is dangerous because the sharp end of the tooth often injures the mucous membrane, which is why an inflammatory process develops when an infection gets there.
- Additional molars. Such teeth grow between the main molars, displacing the dentition from the correct position.
- Extra fangs. This type of anomaly is typical for the upper jaw.
- Supernumerary premolars. These additional teeth are located on the lower jaw. Each type of anomaly looks different depending on where and how the extra teeth are located. These differences can be clearly seen in the photo.
This anomaly is classified into types according to several characteristics. Hyperdontia is distinguished:
- Atypical. Supernumerary units appear outside the alveolar sockets, dentition, and sometimes even outside the oral cavity.
- False. The development of polyodontia is associated with the eruption of fused or double bone formations, as well as with a delay in the loss of primary teeth.
- True. The formation of supernumerary indigenous units is observed.
- Atavistic (typical). Additional dental elements are located within the dentition.
Types of supernumerary
Extra teeth in the mouth can develop in a variety of ways. Therefore, in dentistry it is customary to classify them according to a number of characteristics and distinctive features.
Based on its origin, polyodontia is divided into two types:
- False
. do not fall out, but are firmly located in the bite of people of any age. This anomaly can also be observed in the case of fusion of several adjacent bone processes. - True
. Supernumerary teeth develop due to genetic predisposition or the influence of negative factors during the intrauterine development of the fetus. Accompanied by the formation and eruption of excess tooth germs.
The following types of disease are distinguished by location:
- Typical
. Diagnosed in patients with the presence of extra teeth located in the main row and not extending beyond its boundaries. - Atypical
is detected less frequently and is characterized by the appearance of bone processes outside the dentition.
Photo shows supernumerary teeth on x-ray
When a patient is diagnosed with polyodontia, the doctor determines treatment methods, which depend on the type and complexity of the disease, as well as the location of the extra teeth. Possible ways to eliminate this anomaly are:
- procedures that help facilitate teething;
- removal of supernumerary teeth;
The process of teething in adults occurs with virtually no symptoms. Usually problems arise only in children.
Antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. This helps relieve pain and inflammation of the soft tissues of the palate and gums. Medicines are used in the form of a suspension or suppositories. For severe pain, an anesthetic effect can be achieved using gels and ointments.
Sometimes baby supernumerary teeth do not fully erupt in children, and some of them remain in the jaw tissues. Therefore, you have to influence them with the help of electrical stimulation and special massage.
The need to remove extra teeth arises when they are present in the primary dentition, due to the risk of improper development of the jaw bones. You should also get rid of bone processes located outside the dentition, including those that have not yet erupted.
Afterwards, the child may need the help of an orthodontist. This is necessary for:
- proper jaw growth;
- avoiding problems with;
- adjustments to the dentition.
When molars are removed, the patient undergoes bite restoration. Various types and removable plates are used. This treatment is long-term and should be prepared in advance, first of all, mentally. After all, you will have to constantly wear a corrective device for a long time.
Hyperdontia is an abnormality in the number of teeth in a person, expressed by the presence of supernumerary teeth. According to statistics, the frequency of supernumerary teeth averages 2-3% in individuals with dental anomalies. This disease also includes such an anomaly as a tooth on the palate.
The nature of hyperdontia (dental anomaly), which, of course, includes the appearance of bone dental tissue on the palate, has not been fully studied. Presumably, this anomaly is directly related to a violation of the mechanism. The most common occurrences of supernumerary teeth are:
- on the upper jaw (molars, incisors, canines, premolars);
- on the lower jaw (incisors, canines, premolars);
- in areas of the dentition;
- sometimes the tooth grows on the palate;
- with a permanent bite, but less often with a milk bite.
Supernumerary teeth can cause deformation of the dentition, so in most cases they must be removed, including the tooth on the palatal surface.
Hyperdontia in children
Sometimes the eruption of extra abnormal teeth in children is almost asymptomatic. The only sign of polyodontia is the number of teeth erupted, which exceeds a certain norm for a particular age. Most often, this anomaly is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms, which should cause concern among parents and become a reason to consult a dentist.
Signs of polyodontia in children:
- a rapid increase in temperature, which is difficult to bring down and lasts from one to several days;
- a strong aching or throbbing pain is felt at the site where the irregular tooth erupts;
- there is a feeling of discomfort when talking, eating, drinking;
- a slight swelling of the cheek and even the wing of the nose is noticeable on the side where the extra element erupts;
- due to excessive salivation as a reaction to an irritating factor, a wet cough and difficulty breathing may occur;
- gastrointestinal disorder as another reaction of the body to the inflammatory process and high temperature.
The symptoms of the eruption of supernumerary teeth in children are similar to those observed when the first milk teeth appear, only in this case the situation is a little complicated by the fact that the germination of an extra tooth is not something normal and inherent in nature. This makes it more difficult for the child to tolerate this phenomenon than the eruption of healthy baby teeth.
The main symptoms of polyodontia
The eruption of supernumerary units may have different signs in children and adults. For example, some babies are already born with such teeth. It becomes very difficult to feed them, as they injure the nipple during breastfeeding.
When a supernumerary tooth grows in an older child, symptoms may include:
- the appearance of pain at the site of eruption;
- temperature increase;
- in rare cases – stomach upset;
- swelling of the upper respiratory tract;
- salivation.
The most difficult thing to endure is the eruption of excess teeth on the upper palate. When the baby begins to talk, polyodontia has a negative effect on the pronunciation of sounds. On top of that, the tongue and oral mucosa are constantly injured, which provokes the development of inflammatory processes.
We suggest you read: How many teeth should a person have?
Symptoms
In adults
They differ greatly depending on which of the three positions the tooth is in. If there was excess space in the dentition, then it will simply “compact” the neighbors and stand quietly, violating the aesthetics. If the position is crowded, a scenario of traumatic eruption arises, and the tooth rests against the cheek, then in the mouth there will be constant sluggish inflammation with attacks of exacerbation, a non-healing ulcer or erosion, the skin around will be swollen and hyperemic. If it is impossible for a supernumerary tooth to erupt in adults, it can either “sit quietly” or try to erupt and become inflamed. Then the corresponding side swells, pain and enlarged lymph nodes are noted. Even suppuration and odontogenic osteomyelitis of the jaw may occur.
In children
A supernumerary tooth in a child manifests itself according to similar rules, only small patients react more severely. Where an adult will simply have swelling, the baby will have a fever of 38-39, a severe headache, tears and snot. However, in one aspect they were lucky. Supernumerary teeth in children do not cause as many problems if there is no space. The fact is that an adult’s jaw has nowhere to grow, and there will be no extra space unless a healthy tooth is removed. Whereas the child’s growth phase has not yet ended, and there is always the opportunity to correct the situation with a little effort. The development of the situation must be monitored by an orthodontist to prevent crowding of teeth or traumatic eruption.
Causes of jaw abnormalities
To date, doctors have not reached a unanimous opinion about the causes of such an anomaly as hyperdontia. There are different hypotheses about this:
- Atavism. Historians have proven that primitive people, due to the way of life they led, naturally had 36 tooth primordia. The results of studies of the remains of those times indicate that people had six incisors on the upper and lower jaws. Therefore, polyodontia is a kind of genetic anomaly that makes itself felt after thousands of years;
- Many doctors are inclined to the theory that one embryo splits into several in the womb, when, in fact, they begin to form. This theory also states that an anomaly can develop throughout pregnancy if it was quite severe, the woman suffered serious illnesses or led an unhealthy lifestyle (bad habits, drugs, alcohol and others);
To date, research continues to establish the true cause of hyperdontia. Based on these data, modern doctors are more inclined to the second version than to the first.
Why does excess stuff come out in my mouth?
Modern medicine cannot give a definite answer about the reasons for the appearance of supernumerary teeth. However, there are several hypotheses that explain the etiology of this anomaly:
- Atavism
. It is assumed that polyodontia is a return to the original structure of the dentition, when an increased number of teeth was natural for the ancient ancestors of humans. It is considered probable that they have six incisors on the lower and upper jaws. - Diseases in the mother during pregnancy.
During the maturation of the embryo, a disturbance occurs in the development of the dental plate, which leads to hyperdontia. This is due to problems of the endocrine system and various infectious diseases in the expectant mother. - External factors
. Deviations in the formation of tooth germs during intrauterine development can be affected by medications, drugs, alcoholic beverages, and smoking.
The exact causes of the disease continue to be studied. But most experts are inclined to the version of splitting of tooth germs during the development of the embryo.
How to relieve the unpleasant symptoms of teething?
This is relevant for young children, since adults in most cases do not feel any discomfort when additional dental elements appear in the mouth. Since the supernumerary tooth erupts with the same symptoms as the primary tooth, the treatment for possible complications will be the same.
If a child has a high fever during teething, you should give him Ibuprofen or Paracetamol in the form of an oral suspension. These medications help not only reduce fever, but also eliminate pain, as well as symptoms of inflammation of the soft tissues of the palate or gums.
It is also recommended, when teething a supernumerary tooth, to use local agents with an anesthetic effect in the form of an ointment or gel: Solcoseryl, Dentinox and Kalgel. They have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Children over 2 years old are allowed to be treated with alternative medicine: bee products (propolis and honey), decoctions of medicinal herbs (calendula, chamomile, lemon balm). It is also recommended to rinse your mouth with solutions made according to folk recipes. They relieve discomfort and prevent the development of inflammation. But before such treatment, you must definitely consult a dentist.
Sometimes a temporary supernumerary tooth erupts only partially, and part of its crown remains in the tissues of the jaw. To make this germ grow, a special massage, vibration or electrical stimulation is performed.
What can you see in the sky during the day?
Sun
, the main object for observation is the Sun. It is important to take precautions when observing the Sun. Under no circumstances should you look at the Sun directly during the day when the sun is high in the sky. Moreover, you cannot look at the Sun through an ordinary, unprotected telescope - you can go blind.
There are special methods and instruments for observing the Sun.
Solar eclipses
During a total solar eclipse, the Moon blocks the disk of the Sun from us and the solar corona - the outer layers of the Sun's atmosphere - becomes visible. Photo: Fred Espenak
Solar eclipses occur several times a year - one of the most unusual, fantastically beautiful and exciting astronomical phenomena. During a total solar eclipse, the Moon completely obscures the Sun from us. In the middle of broad daylight, night suddenly falls, stars and planets appear, and the Sun itself looks like a black disk surrounded by a beautiful luminous halo. Nature immediately calms down.
Solar eclipses are short - all this beauty lasts no more than 7 minutes; In addition, the band of a total solar eclipse is very narrow and the chance that it will pass over your city is small. Therefore, many astronomy enthusiasts go on special trips to see the eclipse with their own eyes.
Partial solar eclipses are easier to observe, but they are not as impressive as total eclipses. Is it strange to see the Sun, and not the Moon, in the form of a luminous crescent.
Partial solar eclipse. The Sun is not completely hidden behind the Moon and appears in the form of a luminous sickle. Photo: Evan Zucker
As with the Moon, the Sun can be the source of unusual and varied atmospheric phenomena. We are talking about halos, rainbows, antihelia and other interesting things. All of them are somehow related to the refraction of sunlight on tiny ice crystals floating in the Earth's atmosphere. Some of these phenomena are very impressive. For example, parhelium is the appearance of three suns in the sky, two of which are false. They are located on the sides at the same distance from the real Sun, creating a stunningly beautiful picture.
Three Suns in the sky is a fairly rare atmospheric phenomenon called parhelium. Photo: Erik Axdahl/Wikipedia
Diagnostic measures
Any disease from the above lists must be diagnosed and treated in a timely manner. A person should periodically examine their teeth, since the appearance of noticeable symptoms - pain, fever, swelling, putrid breath - is characteristic of the later stages of diseases, at which it becomes more difficult to treat the disease.
If signs of dental disease have already appeared, you need to contact the dentist. After examining the dentition, the dentist may prescribe additional examinations to clarify the diagnosis:
- X-ray.
- MRI.
- Electroodontodiagnostics.
If the doctor suspects the presence of internal diseases that could provoke dental diseases, he will refer the patient to the appropriate specialist: a pediatrician or therapist, endocrinologist. In this case, the list of examinations may be supplemented with blood tests, urine tests and other studies.
To detect excess teeth in the oral cavity, the dentist only needs to perform a visual examination and listen to the person’s complaints. But if the supernumerary unit has not erupted, a specialist takes x-rays to fully study the picture. This study allows you to visualize all dental elements, even supernumerary ones, and also find out the features of their location.
If it is necessary to study the problem area in different planes, as well as detect inflammatory processes, the specialist conducts additional diagnostics using computed tomography.
Pemphigus
Photo of pemphigus on the sky
Children are most susceptible to developing pemphigus. It pops up in the shape of a white ball at the top of the mouth. The bumps are a consequence of erosion and later develop into ulcers. When pressed it bleeds and hurts. Diagnosed by visual examination and using the Nikolsky method.
If the tumor is not removed, erosion will develop into massive exfoliation of the oral epithelium, disruption of digestive processes, and general weakness. If there is no treatment, the bumps become widespread. Pressure causes rupture of tumors, the contents of which cause intoxication of the body.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of polyodontia is carried out exclusively by a specialized doctor - an orthodontist, who conducts a preliminary examination of the oral cavity and dentition, refers the patient to x-rays (orthopantomography) and analysis of anthropometric casts of teeth made of plaster. Such models are made for a more detailed study of a specific anomalous phenomenon, on the basis of which a diagnosis is then made and treatment is prescribed.
Table of normal human teeth.
Deviation from the norm - polyodontia When examining plaster models made on the basis of dental casts, the doctor measures the size of the teeth, and then analyzes the data obtained based on a special table by Wetzel and Ustimenko. The length of each row of teeth must be measured. This indicator may fluctuate depending on such characteristic individual characteristics of a person as crowding of teeth or the presence of large gaps between them.
We suggest you read: Why and how to clean a person’s tongue
Treatment of diseases
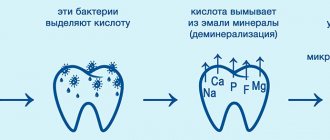
If inflammation of the palate occurs as a result of injury or burn, it hurts a lot, what to do? The oral cavity must be treated with antiseptics (Chlorhexidine, Miramistin), you can treat it at home with decoctions of medicinal herbs, a solution of baking soda and salt. The procedures kill pathogenic microflora and promote rapid wound healing.
The hard palate in the mouth hurts, the reasons are tooth decay due to pulpitis and periodontitis, what treatment is necessary? With the development of pulpitis or periodontitis, the nerve bundles surrounding the tissues around the tooth become inflamed, purulent masses can form and accumulate in the deep layers of the jaw.
What to do?
The presence of supernumerary teeth is an abnormal phenomenon, so the issue of eliminating this problem must be resolved. How, this is another question, to give an unambiguous answer to which is impossible. As a rule, there can be several ways to solve a problem. The choice of treatment method depends on where the extra tooth is located, what shape it is, and what stage of eruption it is at.
Drug treatment allows you to relieve unpleasant and painful symptoms during the eruption of excess buds. This option is the only one for children with baby teeth if the tooth is only at the eruption stage. When it finally germinates, it will be necessary to use more radical methods. The dentist prescribes medications that will help relieve pain, reduce fever and stop the inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the gums.
Surgery. This method is the fastest and most effective, since removing an extra tooth easily solves the problem and relieves a person from unpleasant sensations and discomfort. This treatment method is used when there is too little space in the dentition for an extra tooth or there is no space at all.
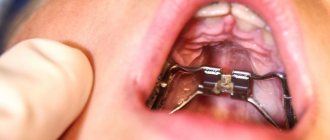
Orthodontic treatment is a method that involves correcting the bite, straightening the teeth, etc. The result is achieved by installing braces or other orthodontic structures that allow you to straighten crooked teeth and return them to their place, where they should be. The duration of wearing braces depends on many factors:
- the age of the patient (children have their own specifics);
- complexity of the situation;
- locations of supernumerary teeth and others.
At the first and second stages of the disease, the doctor may decide to install special expansion plates or aligners. Can also apply the separation method.
If the treatment is not well-carried out, impacted teeth will continue to interfere with the normal development of the bite and dentition, which causes a violation of chewing ability, leading to a number of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and impaired diction, which negatively affects pronunciation and pronunciation. Also, after unsuccessful treatment, healthy teeth that are located next to the additional one may begin to deteriorate.
The essence of preventing dental anomalies is to eliminate the possible causes of their appearance even at the stage of formation of rudiments, that is, all responsibility for possible dental anomalies depends entirely on the child’s mother. To prevent this unpleasant phenomenon, you need to eat right, food should be balanced and healthy.
Treatment depending on the cause of swelling
Effective therapy of the pathology is possible only with the correct determination of the root cause of the edema itself. If the swelling is minor and is not accompanied by any additional symptoms, treatment may consist of periodically rinsing the mouth with self-prepared infusions of medicinal herbs such as chamomile or sage. An alternative to pharmaceutical herbs can be a decoction of oak bark, which must be prepared in a water bath. Only a doctor can tell you what to do and in what dosages to use this or that drug after a thorough examination and additional examinations.
| Cause of swelling | Therapeutic recommendations |
| Stomatitis | It is imperative to use medications with an antiseptic (disinfecting) effect, for example, Chlorophyllipt, Lidochlor, Chlorhexidine or Rotokan. In the latter case, the medicine is intended for rinsing the mouth. |
| Mechanical injuries with violation of the integrity of the integument | The use of decoctions and infusions from traditional medicine, as well as the use of pharmaceutical drugs, should be strictly controlled by a doctor. This will speed up the healing process and prevent the development of infection. |
| Fungal infections | In such cases, anti-inflammatory treatment is necessary, for example, with Pimafucin, Mycosan, Clotrimazole or Nystatin ointment. |
| Sore throat, accompanied by enlarged tonsils | The doctor may recommend antibacterial pharmaceutical drugs in addition to decoctions of medicinal herbs. |
| Dentistry | If there are dental problems, it is extremely important to first remove the cause itself, for example, cure caries or eliminate pulpitis.
|
| Allergic reaction | To begin with, it is extremely important to determine what exactly provokes the allergic reaction, and then eliminate its impact. |
| Tumor | In such cases, it is important to eliminate the risk of cancer. Therapy in this case is possible only in the form of surgical intervention. |
Self-administration of any drugs with a dosage not specified in advance can cause increased swelling, as well as the formation of dangerous tumors that tend to degenerate from benign to malignant (oncology).
The sooner you consult with your doctor, the greater the chances of quickly and effectively getting rid of the problem itself, avoiding dangerous complications.