In this article
- How does caries develop?
- What are the stages of caries?
- How does caries appear in the spot stage?
- How can caries be detected in the chalk spot stage?
- How is dental caries diagnosed in the chalk spot stage?
- How is caries treated at the spot stage?
- Ozone therapy and laser treatment of caries
- Measures to prevent dental caries in the stain stage
It is easier to treat early-stage caries than the advanced form of the disease. Often you can do without drilling your teeth. Unfortunately, many people turn to the doctor much later, when preparation and filling of the carious cavity is no longer possible. In this article we will talk about the benefits and methods of treating caries in the white spot stage.
How does caries develop?
The human oral cavity contains many bacteria that actively participate in the decomposition of food. When we eat large amounts of carbohydrates, cariogenic bacteria ferment the sugars and convert them into acid. It has a damaging effect on enamel, dentin and other dental tissues. As a result, a disease such as caries develops.
In most cases, dental caries does not occur overnight. This process is relatively slow and sluggish. However, if nothing is done, then gradually the initial caries, in which the damage is insignificant, will go into a deep stage or even into pulpitis and periodontitis. In this case, complex treatment is required and there is a risk of infection or tooth loss.
Dental problems
Dental diseases have been known since ancient times. Thus, the characteristic cavities on fossilized teeth found during excavations eloquently indicate that ancient man suffered from toothache.
How quickly does caries develop? To begin with, it is worth deciding directly on the concept itself. So, caries is the process of destruction of tooth tissue under the influence of pathogenic microorganisms. Today, the chances of encountering such a problem are quite high: poor environment, refined nutrition and, of course, insufficient oral hygiene. The last factor creates the prerequisites for the development of caries in infancy (there is even a special medical term - bottle caries).
In fact, the main factor that triggers the development of tooth decay is food left in the mouth. The longer it stays there, the faster bacteria multiply, which in the process of their vital activity release aggressive acids that lead to the destruction of dental tissue.
What are the stages of caries?
In caries, according to the depth of damage to dental tissues, different stages are distinguished - chalk spots, as well as superficial, medium and deep caries.
They are characterized by the following types of destruction:
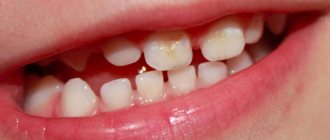
- With caries at the spot stage, a white spot appears on the surface of the enamel, which is also called chalky. This is a zone of demineralization. That is, the enamel in this place is actively losing minerals, in particular calcium, but a carious cavity has not yet formed in the tooth.
- With superficial caries, the destruction is already more significant: a carious cavity forms in the tooth, but so far its localization is limited to the top layer - the enamel - and does not affect the dentin layers.
- Middle caries is the third stage of destruction of dental tissue. The carious cavity increases in size and penetrates into the dentin - the hard tissue of the tooth, which makes up its main part.
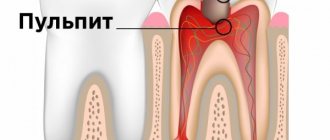
- At the stage of deep caries, the cavity with destroyed tissue is still located in the dentin, but it is already as close as possible to the pulp. That is why deep caries is often complicated by pulpitis - inflammation in the neurovascular bundle of the tooth.
You can count on the most favorable prognosis, simple and painless treatment, and minimal financial costs if a person begins to treat dental caries in the stain stage. The later he goes to the doctor, the more complex manipulations will be required for treatment and the more expensive it will be.
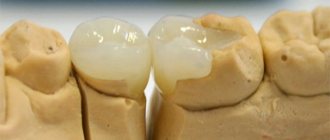
Signs and appearance of teeth with deep caries
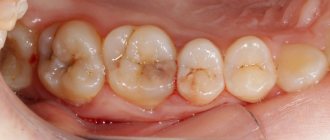
The photo below shows internal caries on the tissues under the destroyed enamel. This is a typical type of disease that develops inside the tooth. The dark areas of the affected dentin are clearly visible:
It is the changed color of tissues damaged by caries that is the main diagnostic sign of the disease. In the vast majority of cases, it is precisely by the black dots on the enamel or on the fissures that the doctor clearly diagnoses “caries”.
From the practice of a dentist
Black dots on teeth can indicate either congenital or acquired (most often) pigmentation (“smoker’s plaque”, etc.), but more often – hidden caries. When you start to drill out such points, they go so deep that 70-80% of the points within the enamel are completely removed, and 20-30% reach the dentin, and sensitivity appears (if the patient, due to refusal of anesthesia, asked to manipulate the conditions, until it becomes painful). Since the patient is always right, we act according to the situation: it becomes painful - we agree and administer anesthesia to the brave client according to the protocol.
Sometimes even severely damaged teeth with internal caries can appear completely healthy. So, if the surface from which the damage began is tightly adjacent to another tooth, caries can develop deep in the internal tissues, and even with a close examination of the oral cavity with the naked eye it remains unnoticed. The situation is similar when caries inside a tooth develops from damage in the enamel located below the soft gum tissue (root caries).
In most cases, at the first examination of teeth, their walls (surfaces) affected by caries are striking. These are often not carious cavities at all, but simply gray, tarnished enamel that has lost its healthy appearance due to demineralization.
Often, the dentist sees a certain “tunnel” in the space between the teeth, but the probe may, due to the density of the interdental space, not pass into the hidden internal carious cavity. Usually, the doctor shows the patient in the mirror the grayish shades of the enamel against the background of developed internal caries and begins treating the tooth after anesthesia.
When a bur touches gray enamel, in almost 90% of cases it breaks off within a couple of seconds and the bur falls into the internal cavity with an abundance of carious, pigmented, infected and softened dentin. If the anesthesia is administered correctly by the doctor, there is absolutely no pain.
The doctor cleans and seals the tooth strictly according to the caries treatment protocol. If the tooth already has a connection with the pulp chamber (the cavity where the nerve is located), then the doctor performs depulpation and filling of the canals, followed by a permanent filling in one or two visits.
The photo below shows a tooth in which deep internal carious cavities are visible under bright light:
The following photo shows fissure caries, that is, localized in the area of the natural relief of the teeth. Such darkening inside also often hides significantly destroyed tissues that are not immediately detectable during a normal examination:
It is also useful to read: The danger of caries localized under the gum and the features of its treatment
At home, such “internal caries” is almost impossible to detect. It will reveal itself only if there is extensive damage to the dentin and pain appears in the tooth when the pulp is included in the pathological process. That is why preventive visits to the dentist are so important, who, using special methods, will be able to detect caries in any location and treat the tooth before it requires pulp removal (nerve removal).
How can caries be detected in the chalk spot stage?
Most often, a person goes to the dentist if a tooth bothers him - it hurts, aches, reacts to cold or hot. However, at the initial stage, caries may not manifest itself in any way. The tooth does not cause concern and in most cases does not hurt. Therefore, detecting dental caries in the staining stage is more difficult than it seems. In order not to miss the onset of the disease and stop the process of carious damage to teeth at an early stage, it is recommended to regularly examine the enamel surface for discoloration, and also visit the dentist twice a year, even if there are no complaints.
Rules for treating the disease
In all cases of caries development inside a tooth, its treatment requires opening the enamel, removing the affected dentin and filling the cleaned cavities. In its advanced form, internal caries leads to the need to remove the nerve and fill the canals.
It is also useful to read: About advanced caries: what to do if almost all teeth show signs of destruction
Even more serious are situations when a very significant amount of tissue is damaged by caries from inside the tooth, and it either after their removal or simply due to softening, splits. In this situation, it is often necessary to remove a tooth according to indications, followed by installation of an implant at the request of the patient, or to make do with modern prosthetic techniques.
On a note
There is a difference between a split and a split, so tooth-preserving techniques may involve, for example, restoration of a tooth on a titanium (anchor, fiberglass) pin after thorough intra-canal treatment + installation of a crown (metal-ceramic, stamped, solid-cast, etc.), may involve tooth preparation under the tab, installing the tab + crown. There can be many options.
Sometimes the damage is quite extensive, but it is possible to save the roots of the tooth by removing the pulp from them. In such cases, it is possible to get by with installing a crown.
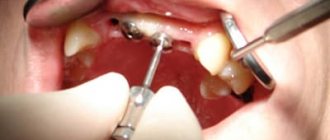
In any case, after detecting a carious cavity, the doctor cleans it out with a bur. If such tissues come close to the pulp, their removal can be painful and is most often done using local anesthesia.
From dental practice
There are ambiguous situations when the pulp area has not yet been opened when cleaning the carious cavity, but the patient already begins to experience pain during the doctor’s work. It is impossible to say for sure whether it is worth carrying out depulpation here or not. Without depulpation after installing the filling, when chewing, it may begin to disturb the nerve endings and cause pain. Some doctors are inclined to depulpate such a tooth so that they do not have to carry out repeated work if, after installing the filling, the patient begins to experience pain. Other dentists explain the situation to the patient in detail and make a decision together with him. It should be borne in mind that many patients are very sensitive to the preservation of their teeth in a “living” form and are willing to take risks in order to walk around with a tooth with preserved pulp for several more years, if after a simple filling there is no pain.
In general, even with deep caries, the nerve has to be removed, according to statistics, in less than a third of cases, and the removal of the tooth itself due to deep caries is generally a rather rare situation.
How is dental caries diagnosed in the chalk spot stage?
There are different methods for diagnosing caries at the stage of spots on the enamel surface. One of the most informative and frequently used methods is testing the enamel for integrity using dyes - carmine, tropeolin, methylene red or blue. The latter is used especially often. The essence of diagnostics using a dye is that a dye solution is applied to the surface of a cleaned and dried tooth and washed off after a few minutes. If traces of dye remain on the enamel, it means there is a carious lesion.
There are other diagnostic methods:
- Drying. The tooth is treated with hydrogen peroxide and dried with a warm air stream. Areas of enamel with white spots immediately appear.
- Radiography. An x-ray shows the affected enamel as a small speck. Most often, this diagnostic method is used for contact forms of caries.
- Diagnosis using a stomatoscope. The accumulated plaque is first removed from the enamel surface, after which the teeth are illuminated with a special device. UV radiation helps to determine exactly where the carious lesion is located and accurately determine its boundaries.
- After diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a suitable treatment method for caries.
Features of symptoms
The insidiousness of initial caries is that it is asymptomatic, i.e. almost invisible to humans. There will be no pronounced defects - strong darkening, visible or open cavity in the tooth. There is no pain either. The mouth may feel sore, as if there is something astringent or sour in the mouth. Upon closer examination in the mirror, you can see spots on the enamel - white, yellow, dark. Let's consider this feature further.
White spots on enamel
Chalk spots indicate an active form of initial caries, which progresses rapidly. The lesions are single, have a matte smoothness (no natural enamel shine). The shape of the formations is uneven.
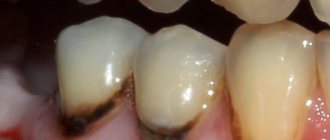
Darkening of the enamel
Sometimes an examination reveals yellow, brown and black areas of pigmentation - this is how the early carious process manifests itself in the dark spot stage. The lesions become stained due to the penetration of bacteria and the deposition of plaque in areas of increased enamel permeability. This is a chronic process that has a long course.
How is caries treated at the spot stage?
There are several methods to treat caries in the initial stages.
- Borovsky-Leus method.
This method is widely known, although today dentists increasingly prefer other methods of treatment. The method involves cleaning the tooth from plaque, treating it with hydrogen peroxide and sequentially applying solutions containing calcium and fluoride. The most commonly used are sodium fluoride and calcium gluconate. The essence of the method is that the components of the compositions penetrate deep into the tooth enamel, restoring its structure. The duration of the therapeutic course is from one to one and a half months, and the procedures are performed every other day.
- Fluoridation is simple and deep.
The essence of the treatment method is to saturate tooth enamel with fluoride and other minerals. During the procedure, the enamel is coated with a special fluorine-containing composition, which may also include calcium, magnesium, and potassium. The compositions disinfect tooth enamel, strengthen and restore its structure due to fluoride ions. Fluoride prevents the further development of caries, helps reduce tooth sensitivity, and evens out the color and surface of the enamel.
Fluoridation can be simple or deep. With simple fluoridation, a thin film of fluoride varnish or fluoride gel is applied to the teeth. It remains on the surface of the tooth enamel without penetrating into its pores. This method is often used for preventive purposes. If the structure of the enamel is damaged and a more intensive therapeutic effect is required, deep fluoridation is carried out, in which fluoride-containing compounds penetrate into the enamel and seal its pores. Deep fluoridation is carried out after professional teeth cleaning, since the microbial film can prevent the penetration of beneficial substances deep into the enamel.
- Treatment of early caries using ICON technology
A relatively new method that is widely used in modern dental clinics as an alternative to fluoridation. Treatment of dental caries in this way is absolutely painless and very effective, provided that the caries is in the spot stage and there is no carious cavity. Tooth decay is promoted by bacteria in the oral cavity, which convert sugars into acids that eat away at the enamel. These acids enter the pores of the enamel and corrode it. The essence of the ICON method is to seal the pores with a special polymer gel and prevent acids and toxins from penetrating into them. This method of treatment is called infiltration. It helps make the enamel denser, stronger and more resistant to microbes. After the procedure, the white spots disappear and the enamel acquires a natural shade.
Treatment is carried out according to the Ikon method in several stages:
- clean the tooth surface from plaque;
- they isolate it using a rubber dam - a special insulating plate that protects against saliva;
- an etching gel is applied, the task of which is to ensure the penetration of the infiltrant into the affected area;
- after thoroughly removing the etching gel, treat the enamel with a drying compound, ridding it of moisture;
- An infiltrating composition is applied that closes the pores of the tooth enamel.
After applying each layer, it is illuminated with a special lamp.
This forms a complete protective layer that prevents the negative effects of acid on tooth enamel and allows you to stop carious destruction at an early stage.
Clinical manifestations of pathology
It is believed that with initial caries, the standard symptom is a person’s periodic feeling of a sore throat in the mouth, which occurs when sour, sweet or salty foods come into contact with the teeth. At the same time, strong painful sensations, as for example in the case of dentin caries (the main tooth tissue located under the enamel), do not occur, which is the peculiar insidiousness of initial caries - a person can walk with it for a long time, not even suspecting that the enamel his teeth are gradually being destroyed.
However, in practice, patients do not always complain of a feeling of soreness, especially in the early stages of initial caries.
On a note
Tooth enamel is devoid of nerve endings and consists of almost 97% inorganic substances. The thickness of the enamel in different parts of the tooth varies significantly, almost disappearing at the neck of the tooth. Accordingly, strong pain during caries will be felt only when the carious process reaches through the enamel below, to the dentin, penetrated by microscopic tubules with nerve endings.
However, tooth sensitivity can be caused not only by the appearance of zones of demineralization, but also by increased abrasion of the enamel (when brushing teeth and pressing the brush in the cervical areas), as well as a banal violation of the density (or structure) of the enamel, when, without the appearance of initial caries, a process of “conductivity” occurs » cold and hot from the enamel into the underlying tissues.
The enamel itself, of course, does not have nerve endings, and its structure is constantly changing even without initial carious zones. However, for some people it is enough to press excessively on the cervical areas with a toothbrush for a couple of days, so that for the next 2-3 days they are afraid to even touch sensitive areas.
Clinical manifestations of initial caries also include changes in tooth color, as discussed above. In this case, the following shades are observed as the pathological process develops:
- natural tooth shade, but matte;
- white;
- beige;
- light brown;
- dark brown;
- black.
It is also useful to read: Average caries
You may be surprised, but black dots or stripes on the teeth in the area of fissures (the natural relief of the tooth surface) do not mean that the tooth is irreparably rotten and everything is very bad with it. There really are problems with it, but this condition may well be one of the clinical manifestations of initial caries. And, as you remember, in some cases it can be completely reversible.
The photo below shows approximately the initial caries in the fissure area of the tooth:
From the point of view of a professional dentist, the clinical picture of initial caries is complemented by a number of significant nuances. So, for example, the doctor will definitely check the condition of the enamel using a dental probe - with initial caries in the white spot stage, the tip should slide over the surface, since the enamel still retains a fairly high hardness.
With a more advanced demineralization process, probing may reveal some roughness and reduced hardness. The patient may experience slight pain.
Ozone therapy and laser treatment of caries
In some clinics, initial caries is treated with ozone therapy. The affected area of the tooth is exposed to ozone, which causes the death of pathogenic microorganisms, neutralizes the damaging effects of organic acids, and helps restore the mineral balance of the enamel.
The procedure does not cause pain, so it does not require anesthesia. The duration of treatment with ozone is less than a minute. Typically, ozone therapy is combined with remineralizing measures or sealing fissures (natural grooves on the teeth).
Another method is laser treatment. The affected tissue is exposed to a laser beam, which destroys bacteria and stops the proliferation of microbes. Laser treatment is painless, does not leave cracks in the enamel coating of the tooth, and is suitable even for children.
How best to treat a particular patient’s teeth and which method to choose is decided by the dentist after a preliminary diagnosis.
Further development of caries
If you do not stop the process of destruction of tooth enamel, it will begin to thin out in places where acids are aggressive. At this stage, more noticeable damage can be determined: stains become clearly visible, and increased sensitivity of the teeth to hot or cold occurs. Caries has not yet spread that much, but its presence is becoming more and more noticeable. This stage can last from several weeks to several months.
The third stage of disease development corresponds to moderate caries. The changes affect not only the enamel, but also the dentin - the cavity grows quite quickly, the tissue becomes much softer and more vulnerable. Painful sensations occur when inhaling air. Bad breath also causes significant discomfort. Some 2 months pass, and the tooth is almost completely destroyed.
The very last stage is complete tooth destruction. Here you will have to use special tabs in order to somehow restore the affected areas. The tooth crumbles, which causes significant inconvenience during treatment. Acute pain can occur even in the absence of any impact. At this stage, caries has managed to get close to the soft tissues, which contributes to the development of pulpitis.
As mentioned above, the main condition for the development of caries is insufficient oral hygiene, as well as a lack of calcium and fluoride.
Measures to prevent dental caries in the stain stage
Initial dental caries, which at the first stage looks like a barely noticeable speck of white color, progresses if left untreated and turns into a dark spot on the enamel. A change in color means that bacteria have entered the pores of the tooth enamel, the destruction process is very active, and soon caries will move from the initial stage to the superficial one.
The following methods of caries prevention will help stop the pathological process, as well as maintain dental health after treatment procedures:
- Brush your teeth twice a day using a toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Your doctor will help you choose a toothpaste with the appropriate composition.
- After brushing your teeth, clean the spaces between your teeth with floss, dental floss, or a waterpik to remove food debris from even the most difficult to reach areas.
- Eat a balanced and varied diet. Make sure your diet includes fish, meat, vegetables, fruits and other foods rich in calcium, fluorine and phosphorus. Avoid eating sweet, starchy and other carbohydrate foods in large quantities.
- Visit your dentist twice a year and have your teeth professionally cleaned.
Such prevention of caries in the stain stage will help prevent or stop tooth decay, maintain their health and beauty.