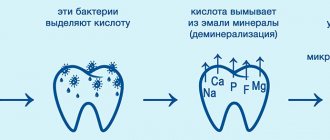
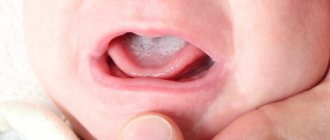
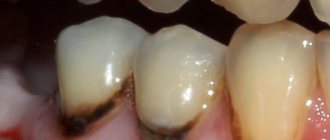
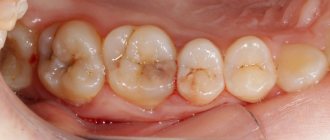
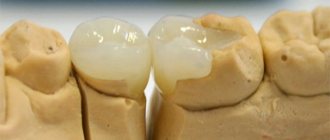
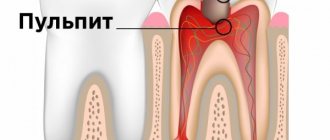
Bottle caries is a disease in young children (from 1 year to 3 years), resulting from the habit of drinking formula from a bottle before bedtime. This leads to food debris accumulating in the mouth. Lactose is a breeding ground for bacteria. The fermentation process starts, accompanied by the release of organic acid, which leads to the destruction of the enamel.
The disease can manifest itself in a child as early as 6–8 months, with the appearance of the first milk teeth. Bottle caries develops rapidly - the enamel can be destroyed almost to the base of the tooth crown in just a few weeks.
It is not uncommon for such a disease to develop in those children who are not bottle-fed at night. This happens for a number of reasons.
Causes of the disease
The causes of bottle caries may be as follows:
- a general decrease in the body’s defenses as a result of a severe infection, surgery, inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx, oral cavity, etc.;
- changes in the properties of saliva and its chemical composition: increased viscosity, decreased bactericidal characteristics. This may be due to the peculiarities of diet and child care, somatic and endocrine diseases;
- prolonged breastfeeding or prolonged use of a bottle or pacifier. The disease occurs in ¼ of children under the age of one and a half years; by the age of 2 years the rate increases;
- violation of oral care rules: improper brushing of teeth or lack of hygiene procedures, incorrect selection of hygiene products;
- genetic predisposition. It is usually possible to cope with this thanks to adequate oral hygiene, following doctor's recommendations, and a healthy diet.
Ask a Question
Causes of the disease
Carious lesions in baby teeth in infants are the same as in adults: uncontrolled proliferation of pathogenic microflora. The main source of nutrition for these bacteria are carbohydrates, which include lactose - milk sugar. There is a lot of it not only in complementary feeding formulas, but also in mother’s breast milk. The most widespread reason for the fermentation of leftover food in the mouth, therefore, is night feeding.
But here everything is not so simple. According to statistics, children whose parents did not teach them a feeding regimen have a 50% higher risk of caries in their baby teeth. The remaining 50% do not suffer from dental caries.
The point, as always, is a healthy immune system, which is initially inherent in the second 50%. Their teeth do not get caries, even if they are not brushed. The point is the bactericidal properties of children's saliva, which in completely healthy children successfully suppresses the activity of bacterial colonies in the mouth. Hence, it is true that if there is a lack of bactericidal properties, even timely oral hygiene after feeding and before bed will not guarantee the absence of caries.
Nutrition
The matter can be aggravated by errors in the preparation of children's diets. The inclusion of sweetened cereals, juices, and confectionery products increases the risk of caries many times over. You can improve the situation by including rough food in the menu as soon as the child’s primary molars erupt and become stronger in the gums after the incisors are formed. It’s even better if “eye teeth” have sprouted—fangs on the upper and lower jaws.
Rough food in the form of carrots or strong, “crispy” apples cleans bacterial plaque from teeth well, and the natural acids and vitamins they contain will have an inhibitory effect on bacteria. Including foods rich in phosphorus and calcium (fish, fresh cottage cheese) in a child’s diet already in the early stages of development will also be a factor in inhibiting the growth of lactic acid bacteria, thus preventing children’s “bottle” caries
Place of residence
Another problem, even with good immunity, can befall children who grow up in the Far North. One of the risk factors will be the low fluoride content in drinking water, and this is what the North is famous for. The basics of dentistry: without fluoride, tooth enamel loses about half its ability to resist aggressive acids released by bacteria in the mouth after eating. What can be done in this case? We deliberately do not consider the option of an urgent change of residence, because this is impossible due to the economic conditions of this family.
Using fluoride-containing pastes as recommended by a doctor and including a large number of dishes containing calcium in the diet will help. But in order for it to be absorbed normally, procedures involving quartzization of the child are necessary - that is, regular irradiation of it with non-hard ultraviolet light. Because without UV rays, no vitamins, including group D, which calcium is rich in, will be absorbed by the body!
Hygiene
No matter how confident you are in your child’s healthy immunity, in the sufficient bactericidal properties of his saliva, oral hygiene after feeding and before going to bed at night is much more likely to save you from the need to take your baby to the dentist.
Many parents “sin” on heredity in causing caries already in the first years of a child’s life. But in most cases, this is nothing more than an excuse for one’s own laziness and inability to find an approach to the child. What can you do to captivate and interest a child in such a situation?
- A child’s thinking is mythological to turn brushing teeth into an exciting game, so the inclusion of fairy-tale characters in this purely hygienic process will help develop healthy habits.
- A battery-powered electromechanical toothbrush with a rotating head and a funny buzzing sound, purchased for a child, can be a useful and favorite toy.
A healthy diet and basic hygiene habits can significantly reduce risks even if you have a genetic predisposition to caries. And also if there is a lack of fluoride in the area where you live.
Stages of disease development
The disease is classified by depth and distribution, taking into account the age of the child. There are four stages of bottle caries:
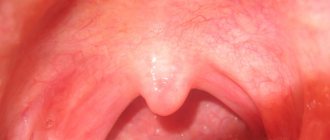
- 1. Initial stage. The child's age is from 6–10 to 20 months. Areas of tooth enamel lose minerals, white spots with a matte surface appear, indicating demineralization. A whitish line may appear at the edge of the gums of the front teeth. The child does not complain, since this stage is not accompanied by pain or increased sensitivity of the teeth. Treatment in this case is the simplest; it is possible to stop the pathological process and prevent the destruction of hard tissues. But only a dentist can identify the disease, which is why preventive visits to the doctor are so important.
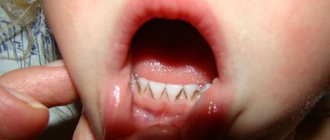
- 2. Superficial caries. The child's age is from 16 months to 2 years. At this stage, a section of enamel is destroyed and dentin is exposed. Pathological lesions may be light yellow or brownish. The child complains of discomfort while chewing, which is associated with increased tooth sensitivity.
- 3. Average caries. The child's age is from 20 months to 3 years. This stage is characterized by the destruction of both enamel and dentin. Lesions become noticeable and deep cavities appear. Sensitivity of teeth appears not only due to mechanical impact, but also due to the intake of sweet, sour, cold or hot food/drinks.
- 4. Deep caries. The child's age is from 30 months to 4 years. Damage occurs to the enamel and a larger area of dentin. Usually the upper incisors suffer - they are destroyed almost completely, while middle caries is observed on the molars and canines. The child complains of severe toothache, refuses to eat, and may have disturbed sleep at night.
How to treat caries in children at the following stages
Treatment of medium and deep caries is carried out through filling, depophoresis and preparation. Fillings are installed using materials that are softer in structure than teeth. Silicophosphate cements are usually used. Today they can also install a filling with fluoride: gradually it will move into the dental tissue and become part of it. Sometimes doctors use colored materials and even polymers with glitter to distract the child from the procedure itself.
Depophoresis is a method of treating dental canals in hard-to-reach places. The dentist injects a solution of copper and calcium into the carious cavity and carries out disinfection.
Preparation is the most common method of combating caries, during which the tooth is cleaned of necrotic tissue. The procedure is carried out by exposing the tooth to a powerful stream of water or air. sometimes with abrasive particles. After this, a seal is applied to the cleaned surface.
Treatment of childhood caries is carried out under local anesthesia. General anesthesia is used very rarely: only in cases where its use is really advisable.
Symptoms of bottle caries
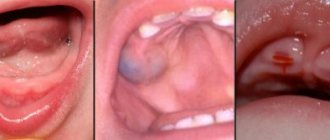
Clinical manifestations depend on the stage of disease development. First of all, the upper incisors and fangs are affected, which is explained by the sucking mechanism: when grasping a nipple or rubber nipple from a bottle, the tongue covers the lower teeth, and the upper ones come into direct contact with the milk - deposits accumulate on them faster.
The pathological process begins from the cervical region - the place where the gum is adjacent to the tooth. This is due to the low degree of tissue mineralization in this area. With further spread, the entire coronal part may be involved in the process.
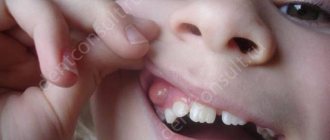
The enamel of baby teeth has a porous structure and small thickness, so the pathological process worsens very quickly. First, a white spot or stripe appears; there are no other symptoms of the disease. As caries progresses, the tooth is destroyed, yellow or brown spots appear, and increased sensitivity causes the child to experience discomfort while chewing.
Subsequently, sensitivity is observed to temperature and chemical influences: the tooth may react to cold air, ingestion of sour drinks or fruits, and sweets. After some time, acute pain appears, intensifying at night, as well as during eating.
Clinical picture of the disease
The disease is predominantly multiple in nature and affects the incisors and canines. In such cases, chalky and pigmented spots form in the cervical areas of the teeth. Soon, these primary carious lesions transform into enamel defects.
Bottle caries in the spot stage
Primary teeth are characterized by a rapid transition from the initial form of caries to deep lesions. This is due to the thin layer of enamel in baby teeth. Parents, as a rule, turn to the dentist when there is significant destruction of the crown of the tooth.
Diagnosis of the disease
Establishing a diagnosis of bottle caries is not particularly difficult. At this stage, the most important thing is for parents to contact the dental clinic in a timely manner.
Diagnosis of the disease consists of a thorough examination of the child’s oral cavity by a dentist. In this case, the doctor determines the stage of carious lesions and the viability of the pulp.
Classification of bottle caries
According to localization and prevalence, experts distinguish the following groups of carious lesions:
- initial caries in the form of a pigmented or chalky spot;
- superficial caries, which is characterized by the formation of a cavity within the enamel;
- medium caries - progressive destruction of dentin tissue;
- deep caries, in which doctors diagnose significant damage to the tooth while maintaining the integrity of the pulp chamber.
Deep circular caries
In most cases, bottle caries in children is detected by the doctor at the stage of a deep process. In this case, patients require immediate dental intervention.
Possible complications
Bottle caries has serious consequences. Many parents believe that it is pointless to treat baby teeth, because they will be replaced by permanent ones. As a result, the disease becomes advanced. It is important to understand that the infection can affect the rudiments of molars, which will erupt with caries. In addition, the pathological process on one milk tooth quickly spreads to the rest, and multiple caries appears. The infection can deepen, affecting the pulp (neurovascular bundle of the tooth) and peri-root tissue. As a result, the disease leads to premature loss of baby teeth, malocclusion, and impaired eruption of permanent dentition.
Causes and consequences
The main source of oral problems is poor hygiene. Many parents believe that baby teeth are a temporary phenomenon and there is no need to take special care of them. This practice is dangerous due to negative consequences:
- Decay in primary teeth causes discomfort to the child, causing him to be unable to eat cold, hot, or solid foods. This condition interferes with sleep, causes fatigue, and provokes crying. Against this background, immunity decreases, as a result of which the baby gets sick more often. In an advanced stage, the disease can negatively affect the rudiments of molars and soft tissues.
- Neglect of dental hygiene will form a bad habit in your child. In the future, it will be more difficult to teach your child to regularly care for his mouth.
But proper hygiene is not the key to healthy baby teeth.
Dentists identify a number of causes of bottle caries:
- Weakened immunity due to viral or systemic diseases is accompanied by a decrease in the protective properties of saliva. Due to the low content of immunoglobulin, it does not protect the body from pathogenic bacteria. They, in turn, release acid, which destroys the protective coating of the teeth.
- Poor nutrition - an abundance of sweets and flour products contributes to the proliferation of harmful microorganisms in the oral cavity.
- Lack or deficiency of fluoride in water and food, which strengthens tooth enamel.
- Poor feeding is partly due to hygiene issues. After night feeding, the child quickly falls asleep, food particles collect on the teeth and bacteria actively develop in this environment. At the same time, little saliva is released during sleep, which washes away plaque.
Diagnostics
Bottle caries is diagnosed by a pediatric dentist during a visual examination using a mirror and probe. A specialist can determine the disease at the chalk stain stage by drying the tooth surface, stomatoscopy in UV light, and also by using vital staining of the enamel.
There are several main criteria for diagnosing bottle caries:
- the child's age is less than 3–4 years;
- night breastfeeding or bottle feeding;
- damage to the upper incisors, canines;
- Poor oral hygiene: irregular or incorrect procedures.
In some cases, an x-ray is additionally required to make a diagnosis. It allows you to assess the depth of tooth damage and detect complications such as periodontitis or pulpitis. If the doctor has reason to suspect enamel hypoplasia or other types of caries, a differential diagnosis is carried out.
Prevention of caries in children
With the appearance of the first milk teeth, you need to take care of proper hygiene. For cleaning at first, you can use a fingertip with a brush, a bandage, or special bactericidal wipes. From the age of one year, you can teach your child to be independent and use toothpaste and a brush. Dentists advise adhering to a number of recommendations and rules:
- follow a proper diet without excess carbohydrates (sweets, flour products), eat solid foods (apples, carrots);
- establish a diet without night feedings; You can give your child warm water at night instead of milk and baby purees;
- own oral hygiene is not only a positive example, but also reduces the risk of transmitting bacteria;
- Traditional methods of treatment are good only after consultation with a specialist.
Proper care, timely treatment and regular visits to the dentist will help prevent bottle caries in children.
Calculator: calculate prices online
Light-curing fillings, caries treatment
The price is ALL INCLUSIVE except anesthesia, if necessary
Select the type of filling
0
Specify the number of fillings
Treatment methods
The treatment method for bottle caries in children is selected taking into account the stage of the disease, the age of the child, the number of affected teeth and other factors. Today, several methods are used in pediatric therapeutic dentistry:
- 1. Remineralizing therapy. At the chalk stain stage, it is possible to restore the normal structure of the enamel without filling. The doctor will apply a mineral composition to the tooth and also prescribe products for home use. The goal of therapy is to restore normal mineral balance and prevent further tissue destruction.
- 2. Silvering. Some pediatric dentists are skeptical about this method, since it leads to a decrease in the aesthetics of the smile - the teeth turn black. In addition, it is difficult to guarantee a positive effect using silvering. The essence of the procedure is to apply a 30% solution of silver nitrate to the enamel to neutralize pathogenic microorganisms and stop tooth decay. This method is used at the superficial stage of caries development. The procedure is quick and painless, but it is advisable only when it is not possible to use other methods.
- 3. Icon method. This is a way to treat bottle caries without drilling and conventional filling. It is used at the initial and superficial stage and does not provide pain relief. The doctor etches the pathological area with acid, dries it with air and applies a liquid filling that seals the tissue. Exposure to light allows the material to quickly harden. This method is designed to restore the normal shape of the tooth without classical filling and stop further tissue destruction. It is used in patients over 3 years of age.
- 4. Filling. Medium and deep caries require filling; a drill is indispensable. Treatment in this case is carried out in the usual manner: tissues affected by caries are removed by drilling, the crown cavity is washed with an antiseptic, then a filling material is installed - today glass ionomer is more often used. Fluoride in the filling is gradually released, which helps strengthen the tooth.
In pediatric dentistry, it is important to choose a material that will wear away along with the edge of the baby tooth in order to prevent disruption of jaw closure. Filling involves pain relief, the procedure takes up to 20 minutes. If the child is unable to sit in the dental chair for this time, or several teeth need treatment at once, the doctor may suggest anesthesia. For children over 1 year of age who have no contraindications, this decision is most often advisable, but the use of anesthesia requires prior consultation with a pediatrician and a comprehensive assessment of their health status.
How to treat the disease
At the earliest stages, it is much easier to cope with the consequences of destruction, since a preschool child psychologically tolerates painless procedures more easily. If you allow deep destruction of bone structures, surgical intervention, drilling with a drill, depulpation and extraction cannot be avoided. Fortunately, in modern dental clinics, including Dentika, it is possible to use sedation (medicated sleep), and the baby will not know what happened to him.
Thus, treatment of bottle caries in children depends on the causes and degree of neglect of the pathological process.
Deep strengthening (remineralizing therapy)
This method is effective only at the initial stage of the onset of the disease. The enamel layer is strengthened with the help of varnish compounds and gels.
The specialist additionally prescribes special pastes. It is necessary to periodically visit the dentist to assess the effectiveness of therapy.
Silvering
A special solution of silver nitrate is applied to the surface. Silver particles penetrate the enamel, strengthening it and protecting it from microbes. This method is effective in the first stages of the disease.
Flaws:
- the need to repeat the procedure;
- aesthetically unattractive appearance of treated teeth.
Classic and colored filling
Young children are most afraid of these manipulations. Adults should prepare the child for drilling so as not to cause fear before visiting a doctor.
For patients under 3 years of age, the most gentle methods of removing affected areas are used without turning on the drill. There are enough special tools that will not frighten the patient. Fillings are made from reliable, durable glass polymers.
Filling without drilling
Liquid filling material is poured into a syringe after cleaning the damaged structures, disinfecting and drying. The substance hardens under the influence of a light lamp. The result is observed only in the first stages of caries development.
Ozone therapy
Used in the early stages. Ozone is supplied through the tip of a special device under high pressure. It acts on affected surfaces, destroying bacteria and sterilizing tissue. There is no pain, as well as contact with the jaws. The procedure lasts no more than 10 minutes.
Icon method (infiltration)
One of the most modern techniques, which was developed in Germany just 10 years ago. Specialists use a special gel-like composition that seals cracks, chips and other damaged fragments, strengthens the enamel and prevents further spread of the disease.
To eliminate the consequences of the disease, just one procedure is enough. Healthy tissues are not subjected to mechanical stress and are protected from damage. This method has gained enormous popularity in Europe as the safest and most painless.
Removal of a tooth
This is the most radical measure. Doctors are trying to the last to heal the affected rows and prevent depulpation. However, it is not always possible to avoid torn incisors and fangs.
Dentures are placed in place of the removed teeth. If this is not done, serious problems with bite, crown position and speech subsequently appear.
Is it possible to be treated with traditional methods?
Home recipes are powerless in diagnosing bottle caries. No composition is capable of restoring damaged areas of enamel and dentin. However, there are methods that help stop the progression of the disease:
- increasing the amount of fish, dairy products, fresh seasonal fruits and vegetables in the diet;
- regular brushing of teeth with a piece of gauze or bandage soaked in a soda solution or herbal decoction;
- using lemon peel (you can let your child chew it if the baby is already 2 years old, and there are no allergic reactions or other side effects from eating citrus fruits).
In any case, without the intervention of a pediatric dentist, you risk only aggravating the situation.
Features of prevention
You can prevent bottle caries in children by following the following recommendations:
- careful implementation of hygiene measures: it is important to brush your teeth from the moment the first lower incisors appear;
- timely visits to a pediatric dentist or hygienist;
- compliance with the feeding regime, gradual abandonment of night feedings;
- diet correction: avoidance of large amounts of carbohydrates, preference for fresh vegetables, fruits, fish, meat, herbs.
Doctors at STOMA clinics are proficient in modern methods of treating bottle caries. You can bring your child to us for both a preventive examination and treatment. In our work we use advanced equipment and high-quality materials.