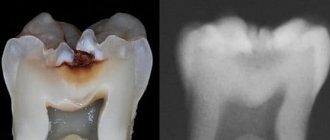
Characteristics of the initial stage of caries
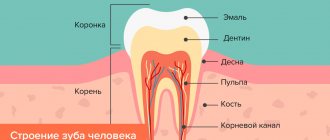
Initial caries (spot stage) is characterized by destruction of the surface of the enamel layer. This form has a peculiarity - since the destruction has barely begun, and the infection has not penetrated deep into the tooth, a carious cavity does not form. But this is only as long as the enamel has sufficient resistance.
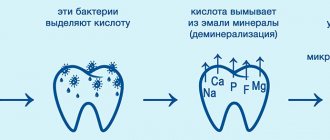
Interesting to know! Enamel is the hardest substance in the body. 95-97% of it consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, which contains a large number of calcium and phosphorus atoms.
At the initial stage, calcium is washed out of surface molecules - this process is called demineralization. Externally, the changes look like a white or chalky spot.
Causes
To understand how the onset of caries develops, you should remember the anatomy of the tooth and the structure of its tissues. Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body. It consists of 96% inorganic component, 3% water and 1% organic binder. In the structure of the crystal lattice, the main place is occupied by calcium hydroxyapatite; in addition, the covering dental tissue consists of phosphorus, fluorine and other microelements.
In the absence of proper hygienic care for the oral cavity, as well as with frequent consumption of carbohydrate foods, sugar particles settle on the surface of the enamel and stick to each other. Carbohydrates are a substrate for the reproduction and growth of pathogenic bacteria, which lead to the development of caries.
During their life, microbes produce organic acids, which lead to the leaching of the most important structural elements from the surface layer of the tooth. The process of demineralization occurs - the destruction of the enamel crystal lattice due to the removal of inorganic components from it. This is considered the main cause of initial caries.
There are many factors that increase the risk of dental caries:
- Heredity. The structure of the enamel is formed during the period of intrauterine development of the child, so if the mother’s nutrition at this stage is inadequate (it lacks vitamins, minerals, dairy, meat products, fruits and vegetables), most likely the baby will have weak enamel,
- Poor dental care. The role of oral hygiene in the fight for dental health cannot be overestimated. In the accumulation of food debris on the teeth, bacteria develop that produce acids that destroy the hard tissues of the tooth.
- Food. To replenish the crystal lattice, calcium, fluorine, phosphorus and many other trace elements are needed. In addition, solid rough food promotes mechanical cleaning of teeth.
- Characteristics of saliva. Viscous and thick saliva does not cope well with the task of washing teeth. If the mineral composition of the physiological fluid is disrupted, it can provoke tooth decay.
- Irregular visits to the doctor. Without professional examinations and teeth cleaning procedures, it is difficult to prevent the development of caries. Frequent visits to the dentist will allow you to notice the occurrence of demineralization in a timely manner and stop it.
Causes of caries
The etiology (causes) and pathogenesis (mechanism) of caries at the spot stage lies in the interrelation of several factors. The main ones are bacterial and chemical. What happens here is the following: due to poor hygiene or weak protective properties of saliva, soft plaque, plaques and hard stone (which consist of bacteria and food debris) accumulate on the teeth. Most often, the cervical part of the tooth near the gum or the interdental spaces where food gets stuck is affected.
Next, bacteria (streptococci, staphylococci, etc.) produce acids that destroy the enamel structure. The aggressive impact of microbes is aggravated, again, by poor hygiene (when food particles remain in the mouth) and the consumption of large amounts of simple carbohydrates (sugar, sweets, baked goods), which are quickly absorbed by bacteria and contribute to their growth.
Among the causes of caries are crowded teeth and hereditary characteristics of the enamel, when it is poorly mineralized due to problems in intrauterine development.
Important! Enamel caries in the spot stage in children, if left untreated, very quickly develops into more serious forms and can cause complications. Baby teeth differ from adult permanent teeth in their fragility and lower density. Therefore, carefully monitor your child’s oral hygiene and proper nutrition.
Is it necessary to treat enamel caries at the spot stage?
Now we know how to treat caries in the spot stage, but is this necessary? Indeed, there are cases when the enamel is naturally saturated with calcium due to the composition of saliva, and the problem disappears. However, this does not happen too often due to insufficient hygiene and monotonous nutrition, which does not meet the body’s need for minerals. Therefore, it is better not to rely on chance and consult a doctor, otherwise early stage caries will develop into a full-fledged defect.
Classification of the disease
Classification of early stage caries is carried out in several directions - by zone of penetration and by location.
By penetration zone
- superficial: the structure of the enamel is still preserved, but its increased permeability is observed. A pellicle, a thin layer of microbial-free film, swells on the surface,
- subsurface or “damage body”: demineralization is observed - the loss of minerals in enamel prisms is about 20%. The permeability between fibers increases sharply - by 25%,
- zone of reduced mineralization: located under the “damage body”, i.e. the destruction deepens,
- zone of increased mineralization: located closer to the enamel-dentin border, has a transparent structure.
By location
- cervical: the pathological focus is localized near the gums (near the neck of the tooth),
- fissure: located in fissures - thin natural depressions between the tubercles of the chewing teeth,
- interdental: on the contact areas of adjacent teeth.
Other purposes
In the complex treatment of carious spots, calcium and phosphorus preparations are prescribed orally, a special diet, vitamin preparations, etc. according to indications.
Treatment of common diseases, against which caries has developed, is carried out by appropriate specialists. According to the results of our clinical observations obtained in the long term, spots disappeared in 5.8%, decreased in 15.9%, did not change in 66.7% and turned into cavities in 11.6% of cases.
The disappearance of carious spots occurred in cases of single lesions of the frontal group of teeth (from 2 to 4 lesions) in the cervical area, found under a layer of thick soft dental plaque. Most of the disappeared carious spots were diagnosed as subsurface, that is, they appeared only when the surface of the tooth dried. A decrease in carious spots occurred with single and multiple lesions and was characterized by the appearance of clearer, strictly limited contours against the background of more extensive blurry spots, i.e., normal enamel was restored along the periphery of the center of the spot.
Stabilization of carious lesions was the most common result of their conservative treatment. Its signs were the constancy of the boundaries of the lesion and the appearance of a shiny surface, which before treatment was matte and dull.
In cases where the stains did not stabilize, microdefects appeared in the center, and then a cavity within the enamel, which was subsequently ground off or filled. In 3 patients in this group, enamel defects arose simultaneously with signs of stabilization of the process (a glossy surface around the defect appeared). We consider these cases as a relative stabilization of caries, which occurred already at the stage of enamel formation, i.e. treatment was started late, but had a positive effect. In these cases, we did not prepare the cavity, but sanded off the affected enamel and then carried out repeated remineralization therapy.
In patients who did not show a tendency to stop dental caries, their lesions were multiple. They have a high CPU index. When examining this group of patients, concomitant general diseases were identified (diseases of the nervous system, diabetes, thyrotoxicosis, hyposalivation, etc.). As carious cavities developed, these patients were treated with conventional methods, including prosthetics. Consultations and treatment were also provided by other specialists according to the existing disease. In some cases, failure was attributed to patients' failure to comply with oral hygiene and dietary instructions.
Thus, according to our observations, the application method of treating the initial stages of caries (at the white spot stage) is effective in 88.4% of cases. In most cases, treatment provided stabilization of white carious spots, and in some (5.8%) - their complete disappearance.
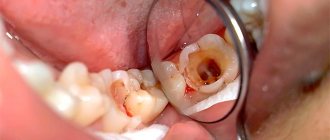
Superficial caries defects located within the enamel do not require filling. In such cases, it is enough to grind off the affected surface and treat it with medication. If the pathological process reaches the enamel-dentin border and affects dentin, one cannot count on a good result of conservative treatment.
Features of symptoms
The insidiousness of initial caries is that it is asymptomatic, i.e. almost invisible to humans. There will be no pronounced defects - strong darkening, visible or open cavity in the tooth. There is no pain either. The mouth may feel sore, as if there is something astringent or sour in the mouth. Upon closer examination in the mirror, you can see spots on the enamel - white, yellow, dark. Let's consider this feature further.
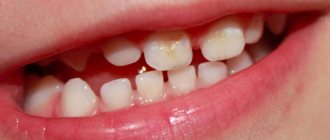
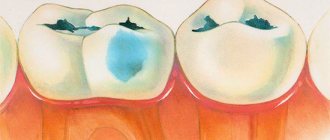
White spots on enamel
Chalk spots indicate an active form of initial caries, which progresses rapidly. The lesions are single, have a matte smoothness (no natural enamel shine). The shape of the formations is uneven.
Darkening of the enamel
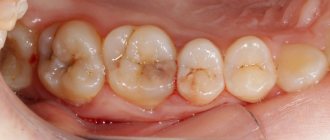
Sometimes an examination reveals yellow, brown and black areas of pigmentation - this is how the early carious process manifests itself in the dark spot stage. The lesions become stained due to the penetration of bacteria and the deposition of plaque in areas of increased enamel permeability. This is a chronic process that has a long course.
Features of the course of acute and chronic initial caries
Chronic initial caries is characterized by an almost complete absence of pain. Patients mainly complain about the appearance of yellow or brown spots on their teeth. Brown, brown or brown-black spots form on the surface of the enamel in places where food debris accumulates. After drying with air, their surface becomes matte; upon probing, the spots are painless and have a somewhat rough surface. The density of their surface is almost no different from the density of the surrounding healthy enamel.
G.N. Pakhomov (1968, 1976) distinguishes several types of carious spots depending on their color and distribution on the surface of the tooth crown. They have different pathomorphological picture and depth of enamel damage. The author identifies white, brown with varying degrees of prevalence, and black spots. Such gradation may have clinical significance due to different prognosis and further progression of carious demineralization. It is believed that white spots are a sign of progressive demineralization of the enamel, light brown spots are variable (alternating, intermittent) and dark brown or black spots are a sign of stationary caries. The larger the area of the stain, its depth and the intensity of the pathological process, the sooner it will lead to disintegration of dental tissues (carious defect).
White spots are quite dynamic in their development, and with a gradual increase in their size, an enamel defect is formed in the center of the spot (transition to superficial caries). On the other hand, when the general condition of the body improves, they undergo remineralization and may disappear completely. Brown spots progress to a lesser extent and not as quickly; black spots can generally be a sign of so-called stationary caries (the most mineralized). When stationary caries appears, protective mineralization develops in the spot area, it becomes dense and shiny, but the pigmentation does not disappear.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of caries in the spot stage is aimed at determining the depth of destruction (based on this, the dentist will choose a treatment method). You should also find out whether the patient really has caries, and not some other pathology - fluorosis or enamel hypoplasia. For this purpose, differential diagnosis is carried out. For example, caries often manifests itself as a single lesion with unclear edges, while fluorosis is characterized by multiple and clearly defined lesions. And with hypoplasia, dots and grooves appear on the enamel. Let's consider ways to diagnose initial carious lesions:
- identification of dull spots: the tooth is treated with hydrogen peroxide and dried with a stream of air,
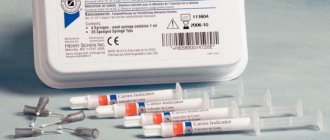
- use of caries markers: a solution of methylene blue is applied, which colors only carious defects blue,
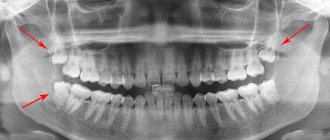
- X-ray diagnostics: not informative for non-carious diseases, and the defect itself will be clearly visible - especially if there is an infected cavity under a small spot on the surface,
- transillumination: transillumination of the tooth with a special lamp shows darkening in the area of the spot,
- ultraviolet lamp: the pathological focus will not luminesce, and healthy tooth tissues will be illuminated.
“I noticed white spots on my youngest’s teeth; they were not cleaned with a brush and gradually became larger. We decided to go to the dentist with this problem, otherwise you never know. The doctor asked how long ago these spots appeared and whether they were right after teeth erupted. I understand that there are congenital diseases that are similar to caries - non-carious. The teeth then erupt with stripes or spots. And if it turns white after teething, then it’s caries. We were prescribed treatment at home: apply pharmaceutical gel. It seems to be better now.”
Polina, review from otzovik.com
Treatment of early stages. Remineralizing therapy
The principle of remineralizing conservative therapy for caries is to replace the mineral elements lost by the enamel during the period of previous partial carious demineralization.
Since the main components of tooth enamel are calcium and phosphorus, they also form the basis of mineral (remineralizing) solutions. The ions of mineral elements that have penetrated into the enamel are sorbed on the organic matrix, forming an amorphous crystalline substance, or they replace free spaces in the unbroken crystals of enamel apatites. Although complete restoration of demineralized tooth enamel is impossible, in practical terms, the effect of partial remineralization makes it possible to stop the carious process and preserve tooth function.
When treating caries at the spot stage, remineralizing solutions are used, injected into the lesion using application and electrophoretic methods. The most widely used are 10% solution of calcium gluconate, 2-10% solution of acidified calcium phosphate and Vorovsky-Pakhomov remineralizing liquid. Indications are single and multiple white, light brown carious spots on the smooth surfaces of teeth.
The surface of the teeth is cleaned of plaque with a toothbrush or cotton swabs moistened with hydrogen peroxide, and then dried with a gauze cloth or a stream of warm air. The teeth are isolated from the mucous membrane with cotton swabs or lignin turundas, or, even better, a rubber dam. Cotton swabs moistened with remineralizing liquid are applied to the surface of carious spots. Duration of application is from 5 to 20 minutes (the longer the better), on average 15 minutes.
During this time, tampons can be replaced with fresh ones every 5 minutes. After removing the tampon with the remineralizing liquid, cotton swabs moistened with a 2% sodium fluoride solution are applied to the tooth surface. The duration of application of the solution is 2-3 minutes. The patient is advised not to drink or eat for 2 hours.
A course of remineralization therapy consists of 15-20 applications, depending on the activity and extent of the pathological process, but in some cases, with extensive multiple lesions of the teeth, up to 30 applications are made. Procedures should be done daily (every other day is acceptable), preferably in the morning. In case of a forced break in treatment, the course is started again.
During remineralization therapy, its effectiveness is monitored by staining tooth surfaces with methylene blue. As a rule, after 3-5 applications, the intensity of staining of carious spots noticeably decreases, which indicates partial remineralization of the demineralized carious lesion.
After a course of treatment with remineralizing solutions, subsurface carious spots disappear, and the surface ones decrease and acquire shine, which indicates stabilization of the pathological process. This can be confirmed by re-staining the tooth. If necessary, a second course of treatment can be carried out (usually after 6 months). Indications for repeated courses of therapy and their timing are also established by the method of vital staining of teeth.
In some patients, further development of the carious process and the occurrence of defects in the enamel are observed, which, as a rule, is associated with neglect of recommendations regarding hygienic dental care, non-compliance with nutritional recommendations, as well as a violation of the body’s condition, especially accompanied by impaired salivation.
Oral and dental hygiene is an integral part of the complex treatment of initial caries. As a rule, in persons with an active form of caries the hygienic index is high (2-3 units). They should be prescribed teeth brushing twice a day (morning and evening) with a soft toothbrush made of natural bristles using “Pearl” toothpaste or fluoride-containing toothpastes and creams. It is mandatory to repeatedly re-determine the hygienic index during treatment in order to monitor the effectiveness of hygienic procedures prescribed by the doctor.
The hygienic index is determined before the start of the treatment procedure. In cases where it is more than 1.0, it is recommended to brush your teeth longer (up to 5 minutes) and more thoroughly. Individuals with multiple caries and a high hygiene index should brush their teeth after every meal (3-4 times a day). When treating children, parents, with whom the doctor must have close contact, play an important role in monitoring tooth brushing.
Diet is a very important factor in the pathogenesis of caries, so its nature cannot be ignored. When treating caries in the spot stage, the doctor’s recommendations regarding diet should be aimed at reducing carbohydrate and acidic foods in the diet, as well as maintaining a certain diet. It is necessary: 1) exclude (at least temporarily) sweets from their diet, especially sweets, cakes, cookies, etc., replacing them with dairy products.
Sugar can only be taken in dissolved form (with tea) and after eating sweets, rinse your mouth with water. Acidic foods should be replaced with non-acidic fruit juices and drunk through a straw, and then rinse your mouth with water; 2) do not allow the consumption of any foods, and flour and sweets, especially in the intervals between set meal times, i.e., follow a certain regime.
Disordered nutrition contributes to the deposition of plaque, an increase in microflora in the mouth, fermentation of carbohydrates, a decrease in the pH of oral fluid and dental plaque, i.e., it creates a cariogenic situation in the mouth, favorable for activating the process of demineralization of enamel in the lesion. The effectiveness of remineralization therapy for caries is significantly reduced or eliminated altogether.
How can you cure
Is it necessary to treat caries at the spot stage? Here you should know that if a carious defect has already appeared, it will not go away on its own. Therefore, dental treatment is mandatory for enamel caries in the stain stage. Depending on the nature of the lesion, treatment can be conservative (remineralization) or with the installation of a filling.
Remineralizing therapy
Local treatment of caries in the spot stage is optimally carried out according to the principle of deep fluoridation. This method is much more effective than applying fluoride varnish or remineralization with calcium gluconate. Deep fluoridation is carried out by a dentist and involves alternate application of an enamel-sealing liquid containing 2 active ingredients - based on fluoride and calcium.
The result of the interaction of these substances is the formation of calcium fluoride ions and a helium component that fills the voids in the enamel. Fluorine is fixed in the gel and starts the process of hydroxyapatite formation. This way the enamel is completely restored. And you don’t need to drill anything or install a seal. But it should be understood that this therapeutic measure will only help at the white spot stage.
When to place a filling
Treatment of caries in the dark spot stage using the principle of deep fluoridation may not give the expected result, since bacteria have already penetrated the enamel surface and a bacterial film has formed. Here the dentist can offer the option of a “liquid filling” (Icon technology). Its advantage is that it does not require a drill.
How does the treatment work? The doctor removes plaque using instruments, then dries the tooth and etches the pathological area with hydrochloric acid. After this, a liquid infiltrate is applied, filling the enamel micropores and hardening under the action of a blue light lamp. Then the filling is finished polished.
Interesting fact! Similar treatment can be used in children starting from 3 years of age. This is the optimal replacement for outdated silver plating, which stains baby teeth black and practically does not prevent the development of carious lesions.
Prevention of caries in the spot stage
Avoiding the development of a disease is always easier than treating it later. Dental caries in the staining stage can always be prevented. To do this, you need to follow several rules:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day, choosing high-quality toothpaste and a brush that is not too hard. It is better to ask your dentist to select hygiene products for you.
- Use dental floss and a special mouthwash after each meal.
- Rinse and dry your toothbrush well to prevent the growth of pathogenic bacteria in its bristles.
- Eat nutritiously, do not overindulge in frequent snacks, drink enough water.
- Quit smoking, as it causes the thinning of tooth enamel.
- Visit your dentist regularly for a preventive examination and removal of dental plaque.
Enamel caries in the white spot stage is dangerous because it can quickly progress, developing into superficial, and then medium and deep caries. The sooner a patient begins to take care of oral hygiene, the less likely he is to lose a tooth in the foreseeable future.
Complications without treatment
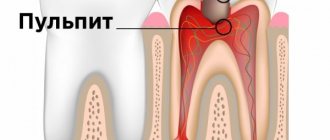
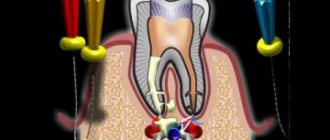
Initial caries is the only completely reversible form of this disease. And if you do not resort to treatment in time, the process will go deeper into the enamel, into the dentin, and can infect the pulp. In all these cases, you will have to drill and install a large filling. And with pulpitis, it is necessary to remove the nerve, which will ultimately affect the life expectancy of the tooth. Therefore, pulpless teeth need to be covered with crowns.
If pulpitis is not treated in a timely manner, the patient may develop more serious complications - periodontitis, periostitis (flux), abscess, osteomyelitis of the jaw. Here the treatment will be very long (several months) and costly from a financial point of view. Therefore, do not delay visiting a doctor if disturbing symptoms appear.
Stages of development of initial caries
A person’s teeth do not deteriorate immediately. Pathology arises, then passing through certain time periods or stages. As you move from one of them to another, the degree of tooth damage increases. As a result, in the absence of treatment, the so-called point of no return occurs. It is characterized by the appearance of large voids in the tooth tissues. And this will require serious treatment.
What stages does the initial stage of dental caries go through (photo below)?
Among them:
- A stage called the “chalk spot.” At this stage, pathology is determined by the presence of a white area. This stain is lighter when compared to the rest of the enamel.
- The stage of the so-called dark spot. This form of the disease is more serious. The pathological process penetrates deeper into the enamel. Food coloring easily lingers in this area. It is because of this that stains on the teeth turn brown or turn brown.
Let's take a closer look at the stages of initial caries, and start with the first stage.
Preventive measures
Most patients go to the dentist only if they have pain. But to prevent the disease, regular visits to the clinic are simply necessary - the doctor can identify the problem in time and quickly eliminate it. It is recommended for adults to visit the dentist once every six months, and for children twice as often.
And if the patient has healthy teeth, then professional dental cleaning can be performed (using ultrasound or Air-Flow), then undergo a course of enamel remineralization or deep fluoridation. This will increase the resistance of the enamel to hazardous factors.
Don’t forget about daily oral hygiene, after which carefully examine your smile in the mirror - in case there are already problems, but you haven’t noticed them yet.
Treatment
Drilling of bone tissue is rarely used in the initial stages of diseases. As a rule, the initial destructive process can be treated with conservative methods. If plaques form due to insufficient mineralization of the teeth, the patient is prescribed a dental procedure to strengthen it using preparations containing calcium and fluoride. He will also be prescribed a course of vitamin and mineral complexes.
The procedure for restoring the enamel structure is called remineralization. It is carried out using special varnishes and gels that supply the upper layers of the teeth with the necessary microelements.
Several decades ago, gluconate tablets were used to restore damaged elements, which were crushed into powder and rubbed into carious lesions. This method was not particularly effective, since calcium gluconate could not dissolve into the ions necessary to fill microcracks in the teeth.
Modern preparations for remineralization are manufactured in such a way that during use the latter disintegrate into ions and can penetrate into the deep layers of bone tissue. Drugs dissociate into ions when interacting with a moist environment (saliva). The active substances in remineralization preparations are calcium and fluorine. The concentration of these components in dental products is much higher than in restorative toothpastes. Thanks to this, the process of remineralization of bone tissue occurs much faster.
Dental
The dentist does not use a burr to treat caries at the spot stage. In such cases, he performs the remineralization procedure according to the following algorithm:
Anti-caries paste
- whitens the surface of affected units;
- treats the enamel with a weak acid solution;
- Apply an application of a 10% concentration of calcium hydrochloride solution or Remodent to the problem area.
To enhance the effect of the procedure, therapeutic measures can be supplemented with electrophoresis. On average, the remineralization procedure lasts for 10 days.
The next stage of dental treatment includes replenishing fluoride deficiency on the enamel surface. Medicines are rubbed into the surface of the bone tissue, and their remains are removed using a cotton or gauze swab. The remaining product is washed off with a soda solution. To achieve results, 7–10 sessions of the procedure are required. After this, the person will need to take vitamin and mineral complexes.
Dark spots are more difficult to treat. It is not always possible to eliminate them using remineralization and infiltration. In such cases, doctors resort to preparation and polishing of the problem area. The lesion is disinfected with boric acid and then filled with composite materials. To correct the front teeth, light filling materials are more often used, since they are less noticeable to others and do not have the property of changing color over time.
To combat white and dark spots on the surface of the enamel in children, the silvering procedure is used. During the work, the doctor applies a silver nitrate solution to the surface of the enamel of baby teeth, which fills microcracks in the enamel and helps restore the enamel. In addition, silver-based preparations prevent the activation and reproduction of pathogenic flora. The procedure is prescribed to children once or performed twice a year to prevent caries.
Dental treatment with silvering in children
Homemade
A white spot on the surface of the dentition can be eliminated independently using a remineralization procedure. Before choosing a particular drug, it is advisable to consult a dentist. He will choose the optimal remedy based on the structure of the patient’s dentition and his individual reactions to medications. It is advisable that before the home procedure, the dentist removes plaque and tartar from the surface of the elements. After professional cleaning, the effect of remineralizing compounds will be more pronounced.
After the enamel is restored, you will need to closely monitor the condition of your mouth for several weeks. It will be necessary to remove food debris and plaque from hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity. Different models of brushes differ from each other in the size of the working part, color and design. It is advisable to choose products with synthetic pile, as pathogenic microorganisms will accumulate less on it.
After each meal, it is advisable to use dental floss or floss. Without the use of additional dental care products, standard oral cleaning will not bring the desired result in caries prevention.
Drugs used
Preparations used to remineralize enamel should include calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. These substances are characterized by rapid absorption and complete penetration into the structure of bone tissue. After using medications, a protective film is formed on the surface of the row, protecting the teeth from negative external influences.
It is recommended to use gels only after thoroughly brushing your teeth. For this purpose, toothpastes that do not contain fluoride and calcium are used.
List of drugs used to combat caries in the spot stage:
- ROCS Medical Minerals. There are 2 types of drugs, one of which is used in the morning, and the other in the evening. The drug is used to prevent carious destruction of enamel and to combat the signs of an incipient disease. The product contains amino fluorides and sodium fluorides in a concentration of 500 ppm. The product is used for remineralization of enamel as applications or as a paste for cleansing the oral cavity. Brushing your teeth with gel takes less than 3–4 minutes. Otherwise, it will not be possible to achieve significant results from its use.
- Elmex gel (manufacturer Germany). The drug has a high concentration of fluoride and is used to clean the elements of the oral cavity. The fluoride level in Elmex is 12,500 ppm. To eliminate caries at the spot stage, use the gel no more than 2 times a week before bedtime. In addition to the gel, it is recommended to use toothpaste from the same manufacturer, the fluoride concentration of which is 1400 ppm. The paste can be used daily for therapeutic and prophylactic purposes.
Prevention of white spots
People's teeth often deteriorate for reasons beyond their control. These are genetic preconditions, polluted atmosphere and other similar factors. However, even in this case, it is necessary to pay attention to your teeth, recognizing areas of demineralization on them. Otherwise, contacting a specialist will require quite serious treatment.
What to do to prevent initial caries? To do this you need:
- brush your teeth in the morning and evening;
- rinse your mouth after eating or carry chewing gum with you;
- purchase dental care products containing fluoride;
- use dental floss or irrigator to remove food debris;
- balance your diet by reducing the amount of food high in sugar;
- contact the dentist not only when a source of pathology is detected, but also for preventive purposes (at least once every six months).
Giving up bad habits will also help fight caries. Smoking and alcohol have an extremely negative impact on dental health.