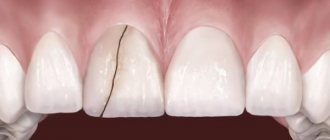
Difference from other types of disease
Regarding the part of the tooth that is affected by caries, this disease is divided into the following groups:
- dental crown;
- cervical;
- root;
- basal.
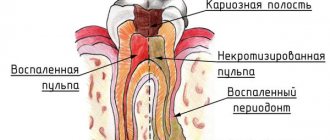
Most of the patients affected by tooth root caries are people over 60 years of age. The main difference between root caries and the basal and cervical varieties is its location deep under the gum.
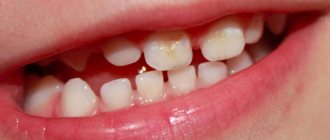
Disease of the cervical region of the tooth is characterized by the location of caries cavities at the edge of the gum on the side of the buccal or labial surface of the tooth enamel. They are easy to see upon inspection. Root disease affects areas along the tooth root that are exposed. The destroyed areas are clearly visible.
Root caries is an invisible disease hidden under the gums, which makes it the most dangerous and capable of causing serious problems.
Is it possible to diagnose the disease at home?
Even a qualified dentist cannot make an accurate diagnosis based solely on examination and probing, so it is impossible to determine the disease at home without the use of instrumental diagnostic methods. However, it is possible to detect signs of pathological processes in the basal and cervical zone, which almost always occur simultaneously with deep root caries.
Destruction of root cement
To do this, you need:
- brush your teeth and wash your hands thoroughly;
- take a thin toothpick;
- Gently draw a toothpick along the line between the gums and the teeth, pressing lightly.
If painful sensations appear during the procedure or deformed areas (chips, cracks), roughness are found, you should urgently consult a dentist for a comprehensive examination.
Panoramic photo of teeth
Causes
Most often, older people face this problem. Of the 10 pensioners who sat in the dental chair, 7 are diagnosed with dental root caries. Due to age, many experience some changes in the periodontal tissues, namely: their blood supply and nutrition deteriorate.
As a result, the gums, deprived of proper mineral nutrition, recede and expose the root of the tooth. In this unprotected position, he becomes very vulnerable to the harmful effects of the acid produced by bacteria.
Toothpaste for caries
Much less frequently, but young people may also need treatment for root caries. They may be at risk for the following reasons:
- insufficient hygiene;
- inflammation of periodontal tissues;
- error in dental prosthetics;
- use of medications;
- micronutrient deficiency.
Insufficient hygiene. Anyone who regularly neglects the basic rules of oral care should think about this fact: not even two hours after brushing your teeth, plaque begins to appear on them again.
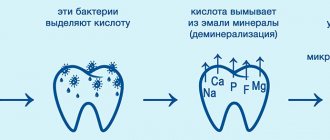
Reference. At first, the harmful waste product of bacteria - acid - is neutralized by saliva. But after a couple of hours, the plaque becomes very dense and the amount is no longer enough to cope with all the microorganisms.
Then the acid begins to destroy the enamel, the upper layers of dentin and sooner or later becomes the cause of the appearance of carious lesions in the cervical part of the tooth. Without timely treatment, it develops into root caries.
Inflammation of periodontal tissues. Any gum disease, be it gingivitis, periodontal disease or periodontitis, at its advanced stage provokes the formation of pockets in the gum area. Naturally, when eating, small particles of food can get there and accumulate. Over time, such “reserves” begin to rot, which will inevitably provoke the destruction of the root.
Error in dental prosthetics. An incorrectly installed metal-ceramic crown, an inappropriate size or poor-quality prosthesis material - all this will sooner or later cause premature atrophy of periodontal tissue. Having receded, the gums expose the tooth roots, on which millions of bacteria immediately settle.
Use of medications. There are certain groups of drugs that can inhibit the function of saliva production. Dry mouth is the best condition for the development of pathogenic microflora.
Severe deficiency of beneficial microelements in the body. Without enough fluoride and calcium, the enamel will become brittle and unable to withstand the constant attack of bacteria.
Features of tooth root caries
Based on the part of the tooth where the carious lesion is located, the disease is divided into dental crown, cervical, basal and root caries. The main difference between root caries and all others is its localization deep under the gum.
And if a lesion in the cervical and root parts of the tooth can be detected during a visual examination, then caries of the root cement is invisible and therefore the most dangerous of all. In addition, such caries develops noticeably faster than on a crown, since tooth cement is more sensitive to the effects of bacteria. Regarding the depth of penetration, tooth root caries can be without cavity formation or with cavity formation.
Factors that lead to the development of the disease are divided into groups:
- Affecting periodontal disease: insufficient oral hygiene, neglect of professional cleaning in the dentist's office, periodontal disease, anatomical features of the oral cavity.
- Factors that provoke the development of caries: poor nutrition, fluoride deficiency, improper salivation.
- In addition, the disease can be triggered by complications after treatment of cervical caries and incorrectly installed dentures.
The risk group for the development of root caries includes people with problems such as periodontal disease, infectious diseases, low immunity and chronic stress.
Elderly patients have a risk of developing caries in permanent teeth of up to 80%. This is dictated by receding gums and exposure of the root part of the tooth, characteristic of old age.
Those at risk include smokers and people who abuse alcohol and caffeinated drinks.
Prevention and treatment of root caries
A timely diagnosed onset of the development of the carious process can be stopped without the use of a drill. In general, dentists adhere to the following principles to prevent the development of tooth root caries:
- Elimination of factors that increase the risk of developing caries, such as plaque accumulation under crowns and in defects of old fillings, crowded teeth, damaged dentures. It is necessary to carry out refilling, treatment of gum diseases and replacement of prosthetic elements in a timely manner in order to minimize the risk of developing carious lesions.
- Carrying out a professional cleaning procedure. Hygiene at home is sometimes insufficient even if all the rules are followed. Various factors can lead to the appearance of deposits on teeth that cannot be removed with a regular brush. Hygienic teeth cleaning at the dentist allows you to effectively get rid of plaque and tartar, which helps to identify the pathological processes hidden behind them.
- Timely detection of pre-carious condition, as well as the initial stage of caries. Treatment at this stage is carried out using fluoride-containing gels and varnishes, which makes it possible to stop the development of caries without filling the dental tissues.
Tooth root caries often develops under crowns, bridges, old fillings, in hard-to-reach places (in places where teeth are twisted), where the accumulation of carious bacteria that destroys enamel is most likely.
Attention! The initial stage of tooth root caries requires deep fluoridation to avoid relapse of the disease.
Most often, a solution of sodium fluoride (concentration 0.05–2.0%), titanium fluoride (4%), tin fluoride (0.4%), and amino fluoride is used. Fluorides are often combined with solutions containing calcium at a concentration of 10%. If caries requires filling, the dentist faces some difficulties. The process is localized under the gum tissue, and placing a filling requires maintaining complete sterility of the surface, isolating it from saliva and other liquids. Therefore, in parallel with filling, gum treatment is often required, which involves removing excess tissue. The procedure can be carried out using special threads (retraction) or using an instrument heated to a certain temperature (diathermocoagulation). High-quality anesthesia allows you to avoid discomfort during the procedure. Treatment of dental tissue with a dental drill is carried out using a cooling liquid, which increases patient comfort. The cleaned surface is treated with an antiseptic and a seal is installed. Currently, the most common filling material is light-curing composites. However, they are extremely sensitive to moisture, and it is not always possible to ensure ideal dryness when treating root caries. Therefore, other filling substances are sometimes used:
- Glass ionomers. They are considered one of the best options, since the adhesion of such a filling is not impaired in a humid environment. An additional advantage is the content of fluoride compounds in this material, which have a long-lasting therapeutic effect.
- Compomers. A relatively new material that combines the durability of composites and the positive properties of glass ionomers. However, installing such a filling requires a drier surface, which is more difficult to provide.
- Amalgam. Mercury-based compounds make it possible to form a filling with the longest service life. However, due to their toxicity and unaesthetic appearance, such fillings are now rarely used in our country.
Classification
There are several ways to qualify a disease; they are usually named after the doctors who introduced them. Rikota Yu.N. According to the depth of damage to root tissue:
- Initial caries - partial destruction while maintaining the cemento-dentin boundary.
- Superficial caries is a defect with a depth of no more than 0.5 mm.
- Deep caries is a defect more than 0.5 mm deep.
By localization:
- Class 1 – caries on the contact surfaces of the root;
- Class 2 – caries on the vestibular (oral) surface of the root.
Ovrutsky G.D. According to the depth of damage to root tissue:
- Degree (initial caries) – the surface is soft, there is no tissue defect.
- Degree (superficial caries) – defect depth up to 0.5 mm.
- Degree (cavity caries) – defect depth is more than 0.5 mm.
- Degree (pulp caries) - a defect involving the tooth cavity.
Symptoms
The pathological process in the initial stages is characterized by an asymptomatic course, but the patient may experience pain while brushing teeth, eating sour, salty or sweet foods, which quickly passes after the irritant is eliminated. Sometimes hot or cold foods can cause discomfort.
If the pathological focus in the form of local darkening of the cement is located on the labial surface of the front teeth, the patient complains of unsatisfactory aesthetics. Sometimes the stain practically merges with the surface of the root or is hidden under plaque or tartar.
After the carious process reaches the cemento-dentin junction, it penetrates the surface layers of dentin, the cavity becomes deeper, fills with dead tissue, and food or dental floss gets stuck in it. Short-term pain can also be caused by chemical, temperature and mechanical factors.
When caries affects the dentin bordering the tooth cavity, pain often occurs when eating hot or cold food. Otherwise, the symptoms of deep caries are practically no different from those at its previous stages.
If no attempt is made to treat root caries, the process can reach the tooth cavity and provoke the development of pulpitis. At this stage, the pain is quite pronounced that the patient has to literally run to a specialist.
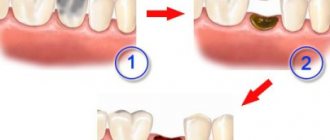
Removal of root caries is carried out in several stages: stripping, installation of the base, building up.
Diagnostics
Only a doctor can conduct a full diagnosis. If caries of the tooth crown can be detected independently, then if the root is affected, this is impossible. When examining the oral cavity, the dentist can detect indirect signs of the disease: inflammation of the gums, pockets, damage to the neck of the tooth. All these signs suggest that the root is also involved in the development of the disease.
Probing in many cases allows you to detect a cavity hidden from view. This technique is especially informative if there are cervical lesions. Using electroodontometry, you can determine the condition of the nerve and whether the pulp is viable.
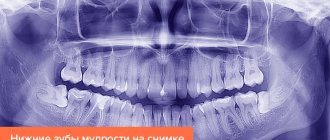
The final diagnosis can be made by X-ray examination - this diagnosis is more accurate. In the picture you can see the cavity, determine its topic and size. Radiography allows you to choose a treatment regimen and make a prognosis.
Timely detection of the disease helps prevent the spread of caries.
Diagnostics in the doctor's office
In modern dentistry, there are several methods for recognizing tooth root caries. Probing with a sharp probe is considered widespread. Before such a procedure, it is important to remove plaque and stone from the entire surface of the diseased tooth, because the foci of the disease are hidden behind these deposits.
A sharp probe is a safe tool for healthy dental tissue. Its use involves carefully inserting the instrument into a hidden lesion in order to identify enamel roughness, chips and other defects.
In order to identify root caries, X-ray examination methods are also used - orthopantomogram, bite-wing radiograph, parallel beam radiography. With their help, it is easy to determine the initial stage of root caries, even in the absence of a cavity.
If your doctor has prescribed additional diagnostics for you, it is important to undergo it. In time, a certain disease will be cured much easier, faster and without consequences. Whereas, advanced stages can threaten tooth loss.
Treatment
There is no single tactic for treating root caries. It all depends on the size and depth of the lesion, as well as the general clinical picture of the oral cavity. But in any case, the first step will be professional cleaning.
Without completely eliminating tartar, any action will not make sense, because this is the only way to get to the carious lesion and eliminate the possibility of its re-infection. After this, you can begin treatment directly, and here the options are therapeutic and surgical.
Anesthesia for the treatment of caries
The need to go to the dentist causes panic in some people because it is associated with painful sensations. A visit to the dental clinic is postponed until the moment when the symptoms become so severe that the patient can no longer tolerate it. Several decades ago, old-style drills that were not equipped with water cooling were used to treat caries. Pain relief was not practiced at all. Doctors used anesthesia only for complex tooth extractions. Therefore, older patients still have persistent fear and confidence that dental treatment is necessarily associated with pain. Currently, the picture has changed dramatically. One of the principles of work of modern dentists is patient comfort. For this purpose, there are modern methods of pain relief, which are used when there is a likelihood of unpleasant sensations. The most widespread in dental practice is local anesthesia by injection.
Important! The drugs used for anesthesia are selected taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient and the presence of concomitant diseases (hypertension, diabetes, consequences of stroke, etc.). The likelihood of an allergy to the anesthetic is also taken into account.
Many patients also experience fear before the injection itself. Fear of injections is associated with the painful sensations caused by the syringe needle when administering the drug. To minimize patient discomfort, the injection site is pre-treated with an anesthetic in the form of a gel or solution.
Application anesthesia is a method of pain relief, which consists of applying a gel to the surface of the area that needs to be anesthetized, without introducing it into deep tissues.
After some time, a gradual injection is carried out: first into the upper tissues of the mucosa, and then into deeper ones and under the periosteum. One of the most optimal drugs used for pain relief is ultracaine. It contains the smallest amount of elements that cause vasoconstriction. This injection can be given even to pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children over 4 years old. Sometimes the patient’s fear of the dentist is so great that it turns into a panic attack, making treatment impossible, despite high-quality pain relief. There are also patients with allergies to local anesthetics, and some people have an increased gag reflex, which also makes access to the oral cavity difficult. Treatment is also difficult to carry out in young children, who are rarely affected by tooth root caries, but still not excluded. In such situations, there are indications for dental treatment under general anesthesia.
Cure or remove?
If the damage is severe, when more than half of the tooth is destroyed, it is possible that it will be recommended to remove it. The degree of destruction and the prognosis for further treatment are determined by the doctor, based on the results of x-rays and examination using instruments.
But after this type of prosthetics, it is important to carefully practice oral hygiene to protect yourself from inflammation and re-infection. If caries is detected, it must be treated urgently. So, you will protect yourself from illnesses such as sepsis or purulent lymphadenitis of the submandibular lymph nodes, and avoid.
Tooth root caries is a serious problem that is easier to prevent than to treat. The best prevention is thorough brushing of teeth from plaque, regular use of dental floss and timely removal of tartar. Also remember that germs are afraid of saliva, so drink enough fluids and chew sugar-free gum from time to time.
Is it possible to cure dental root caries?
Previously, it was believed that carious root lesions were a direct indication for tooth extraction due to the high risk of infection of the gums and bone structures. Now there are many medications and treatment methods that allow not only to save the tooth, but also to prevent possible complications. Pathology therapy is always carried out in three stages.
At the initial stage of treatment, the patient is recommended to undergo professional oral cleaning to remove tartar. This is due to the fact that in most cases, foci of infection are located under a layer of plaque, and if it is not removed, insufficient sanitation of carious surfaces can lead to re-infection and inflammatory processes.
Polishing teeth after removing tartar
The second stage is the main treatment using medications and antiseptics, which can be carried out with or without filling. At the final stage, the patient is recommended to undergo restorative therapy aimed at eliminating factors contributing to the development of caries.
It could be:
- alignment of teeth;
- replacement of a prosthesis or crowns at the end of their service life;
- therapeutic treatment to strengthen the enamel and mucous membranes of the gums.
Prevention of caries:
| Photo | Way | Description |
| Brush your teeth morning and evening | Regular brushing is key to keeping teeth in good condition and preventing further decay. | |
| Floss your teeth once a day | Flossing your teeth is important. A toothbrush cannot clean the cavity between teeth, where bacteria that causes tooth decay usually hides. | |
| Rinse your mouth with mouthwash | Mouthwash is an excellent addition to dental hygiene. It slows down tooth decay by killing bacteria in the mouth | |
| Eat more vitamin D and calcium | Vitamin D and calcium are important for dental health, so getting enough of these two key nutrients will help fight tooth decay. | |
| Eat unprocessed foods | Highly processed foods contain a lot of sugar and starch, which can get stuck in the mouth (making them difficult to remove) and promote bacterial growth |
If the gum surrounding the affected tooth is damaged, the doctor may cauterize the pathological tissue using a special device or perform retraction of the gum tissue. The procedure involves the correction of gum edges that hang over the tooth and interfere with high-quality treatment of caries, using dental threads impregnated with hemostatic compounds and solutions. After this, the carious cavity is cleaned, antiseptically treated and a filling is installed.
Treatment of dental root caries
The material from which the filling will be made depends on the individual characteristics of the patient, the localization of the pathological process and financial capabilities. Three types of materials are most often used.
Table. Common materials for making fillings.
| Material for making a filling | Characteristic |
| Glass ionomer cement | One of the best materials for filling areas located under the gums, as it has maximum adhesive properties in conditions of high humidity. Fluorides are often added to glass ionomer cement to ensure the normal mineral structure of the tooth. |
| Amalgams | A very durable material that is prepared using mercury compounds. Rarely used in clinics due to complex mixing technology and the need for individual protection of medical personnel due to mercury vapor. |
| Compomer material | A combined material that in some cases may have poor adhesion to surfaces, resulting in the filling falling out and becoming damaged and requiring replacement. |
Important! Treatment without the use of a drill (by fluoridation method) is possible only for superficial caries with a minimal area of damage. If the tooth root is affected, this method of therapy will not be suitable.
Dental office