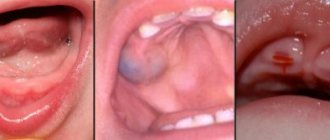
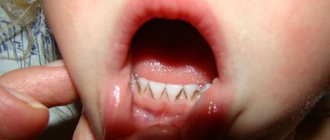
The term “throat” is usually used to refer to the visible part of the oropharynx - it is by its condition that experienced parents try to understand whether the child is sick or not. A red throat is an extremely common symptom that you need to be able to correctly identify. You can see in the photo what a healthy and sore throat should look like. Let's look at this issue in more detail.
What should a healthy throat look like?
Probably, most otolaryngologists will say: “I can only show the differences between a healthy and a sore throat in a photo or picture, because
Nowadays, the impeccable condition of the oropharynx is a rarity.” Most schoolchildren, despite their young age, have chronic signs of oropharyngeal diseases. Such pathologies include: tonsillitis, sore throat, pharyngitis, nasopharyngitis.
If inflammatory diseases of the throat are not treated, you can get not only local complications, but also become a victim of rheumatism, kidney and heart diseases. Moreover, an untreated acute infection in the throat often leads to surgical treatment, not to mention the fact that, for example, chronic pharyngitis remains a problem for life.
It should be noted that self-diagnosis is necessary. A patient with minimal knowledge of what a healthy throat should look like can already determine whether he has problems and whether he needs to see a doctor.
The textbooks on otolaryngology clearly highlight the signs of throat diseases, which can be used to determine whether everything is in order in the oropharynx. Among them are the following descriptions that define a healthy throat:
- the posterior wall of the pharynx has a smooth surface, there are no hypertrophic follicles, the network of vessels is not dilated, and no other pathologies are observed;
- there is no visible swelling on the entire surface of the throat and nearby tissues;
- there is no hyperemia in all its manifestations: the throat has a color from pale pink to pinkish tones without spots. All parts of the throat practically merge into one color;
- tonsils are small in size, not swollen, and do not contain various inclusions or plaque. Small tubercles may be present; sharp transitions and elevations in the tonsil area are not observed.
- A burning sensation in the throat - what it could be, what to do;
- Many of us have at least once in our lives encountered the phenomenon of a sore throat;
- – viral infection in the throat.
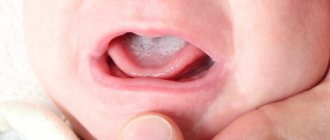
What a healthy and sore throat looks like in a child
A healthy child’s throat should be free of redness, rash or any other manifestations.
A clean pink mucous membrane is an indicator of the absence of nasopharyngeal diseases. Parents often encounter the phenomenon of redness of the throat in their baby. There are quite a few diseases that cause the throat to turn red. To understand what exactly happened to the baby, if the child has a red throat, look at the photos and descriptions of diseases that are accompanied by redness of the pharynx. Learn to look at your baby's neck correctly. It is not so difficult to independently understand what diagnosis will be made. But don’t limit yourself to self-diagnosis of your baby; be sure to visit a doctor.
Differences between a healthy throat and pathology
When examining a healthy throat, all the signs that we indicated above should be present, regardless of the patient’s age.
In most cases, a “beautiful throat” is rare. Some people have slight granularity, indicating pharyngitis, others have minor pathologies of the tonsils. And this is not to mention the obvious changes in the oropharynx.
When performing the diagnosis yourself, you should be alert to the following signs indicating a pathological process:
- mucus drips down the back of the throat. There may be several reasons for this condition: rhinitis, sinusitis, thinning of the pharyngeal mucosa, adenoiditis (more common in pediatric practice). Some patients refer to the mucus that drains as phlegm. It is not right. Sputum is released from the lower parts of the respiratory system and can appear in the mouth only when coughing (bronchitis, tuberculosis and other diseases);
- the appearance of redness of varying degrees of intensity, including individual spotting and granulation. The soft palate is often inflamed. The bright red walls of the pharynx stand out especially. This condition of the throat is accompanied by soreness, soreness, and itching. In principle, the presented picture indicates acute pharyngitis, starting with ARVI;
- The back wall of the throat is dotted with enlarged follicles, i.e. the pharynx has a loose surface. However, the throat does not have to be red. In most cases, this picture is observed in chronic forms of pharyngitis;
- uneven surface of the pharyngeal mucosa, all kinds of ulcers, blisters similar to herpetic rashes (possibly herpetic sore throat);
- inflamed and hyperemic tonsils, as if engorged with blood;
- the back wall of the pharynx seems thin, blood vessels appear on it, it is pale, as if covered with varnish. The presented description indicates atrophic pharyngitis;
- if the follicles have grown greatly and acquired enlarged forms, chronic pharyngitis with hypertrophy should be suspected;
- The oral cavity is literally completely affected by a white coating. The back of the throat, the tongue, the inside of the cheeks, the tonsils, literally everything is covered in plaque. This pathology has a name - candidiasis, or, as people say, thrush. Candidiasis is caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Untreated thrush often causes aphthous stomatitis;
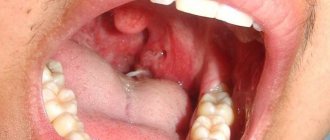
- yellow-gray or white plaque on the tonsils, accumulation of purulent contents in their lacunae, severe inflammation and swelling of the throat most likely signal lacunar tonsillitis. In this case, the patient also has the following symptoms: high body temperature, reaching 40 degrees or above, severe sore throat, general fatigue and weakness, fatigue. In some cases, angina may be less aggressive, i.e. There are plugs in the tonsils, causing inflammation and a slight sore throat. The tissue on the tonsils has scarring;
- an increase in the size of the tonsils, pinpoint purulent formations on them, hyperemia is visible in the area of the palatine arches - these are all signs of follicular tonsillitis. The patient's body temperature is elevated, there is a sore throat, and sometimes it radiates to the ears. There is also body aches and general malaise;
- long-term smoking and imbalance in the gastrointestinal tract become the culprits of a brownish-gray plaque on the oral mucosa. Against the background of such plaque, chronic pharyngitis of various forms is often observed. The patient feels a constant scratching in the throat, mucus flows down the back wall and tickles the throat. Sometimes, especially at night, when the head is thrown back, a coughing attack begins. This occurs due to drying of the pharyngeal mucosa.
Viral pharyngitis in children
This type of disease occurs quite often and can develop against the background of diseases of viral etiology, for example, ARVI or influenza.
Causes
The disease occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic viruses into the body. So viral pharyngitis can be provoked by:
- coronaviruses;
- parainfluenza pathogens;
- rhinoviruses;
- influenza pathogens;
- adenoviruses.
Much less often, this form of pharyngitis is provoked by the following pathogens:
- cytomegalovirus;
- respiratory syncytial virus;
- enteroviruses;
- pathogens of herpes simplex;
- Epstein-Barr virus;
- immunodeficiency virus;
- Coxsackie virus.
Main symptoms
A disease of viral etiology is characterized by the presence of the following symptoms:
- redness of the throat;
- painful sensations when swallowing;
- an increase in temperature up to 39 degrees, possibly up to 40, and low-grade fever may also be observed;
- a runny nose has been present since the onset of the disease;
- appetite decreases;
- a white-yellow coating forms on the mucous membrane, which is located on the tonsils and the back wall of the pharynx;
- dry and frequent cough, which after two days turns into a wet cough, sputum begins to be discharged.
Treatment
When considering methods of treating the viral form of the disease, you need to understand that the main emphasis is on destroying the causative agents of the disease.
- The child will be prescribed etiotropic treatment, which is aimed at destroying viruses inside the cells. These drugs include Arbidol, Tamiflu, Remantadine, Relenza or Cytovir.
- Parents should understand that antibiotic therapy is prescribed for the viral form of pharyngitis only when a secondary infection is attached, otherwise such treatment is ineffective.
- At elevated temperatures, antipyretics are prescribed, for example, Ibuprofen.
- Antiseptic preparations for rinsing, for example, Miramistin or Chlorophyllipt.
- A throat spray with anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, for example, Ingalipt.
- In order to mitigate the inflammatory process on the mucous membrane, lozenges are prescribed, for example, Faringosept.
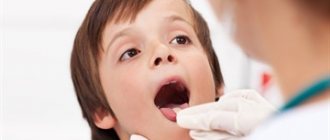
Throat examination
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to examine the throats of loved ones objectively.
For example, while looking down the child’s throat, a mother suddenly sees something “suspicious” and in a panic drags the baby to the pediatrician.
Of course, many people lack medical knowledge, but parents who have two or more children in the family are more likely to gain experience.
And yet, you need to be able to determine whether your throat is healthy or sore, i.e. not to make a diagnosis, but to understand whether the oropharynx is normal or pathological.
To assess the condition of the throat, it is necessary to conduct an examination:
- bring the patient closer to daylight, it is better to find a place near a window, or sit him on a chair and take a flashlight with a bright light bulb. We ask the patient to open his mouth wider and press his tongue so that the entire lumen of the throat is visible. If this maneuver does not work for the patient, it is necessary to use a spatula or a teaspoon to press the tongue. Next, we illuminate the pharynx well and examine all parts of the throat;
- You need to press on the spatula carefully, because... Some patients experience a gag reflex, so the examination procedure must be performed quickly. Do not press the spatula on the root of the tongue; it is enough to press the tongue in its middle part;
- when examining the tonsils, when we need to assess whether there is tonsillitis or tonsillitis, it is enough to stick your tongue forward; there is no need to press it. Using a flashlight, we examine the tonsils for plugs and purulent contents;
- During the examination, the patient must breathe deeply and evenly, this makes it possible to lower the tongue to the lower palate.
- Mucus in the throat with blood - causes and methods of treatment;
- Often, along with the appearance of minor tumors, patients may suffer from soreness;
- - It hurts my throat a lot.
Red throat - how can you notice it?
Redness in the throat is often accompanied by pain. If the child can already report feeling unwell, that’s already half the battle. And if the baby uses emotions rather than words, then the parent must learn to understand this and draw conclusions. For example, with a sore throat, a child may refuse to eat. Vomiting can also be an indicator of problems in the nasopharynx. Young children become capricious and restless.
What does a child's sore throat look like? Looking into the throat, you can see:
- Inflamed tonsils - they have a different appearance: red and swollen;
- The small tongue may be hyperemic;
- The back wall of the throat may be red, and vascular “twigs” may also appear on it;
- In this case, the tongue may be coated;
- The upper palate may also be covered in a rash or become red.
Note! Redness of the throat in children is almost always accompanied by fever. Moreover, a change in the child’s well-being may begin before the throat becomes inflamed.
Diagnostics
Whether the patient has a throat disease or not, only a specialist can answer this question. The first step to identifying all problems with the throat is a visit to the otolaryngologist's office, where a differential diagnosis will be carried out. If in doubt, the doctor will prescribe a further examination, which includes:
- survey (collecting anamnesis). The doctor questions the patient in detail, determining the main complaints and the duration of the disease, if any. The doctor is interested in literally everything, even stressful situations that can cause, for example, aphonia;
- performing rhinoscopy (standard examination). Upon examination, pathological processes in the nasopharynx are detected;
- endoscopic rhinoscopy – therapeutic and diagnostic manipulation (allows for minimally invasive surgical interventions);
- X-ray examination of the maxillary sinus and other sinuses. Thanks to x-rays, acute and chronic foci of infection are determined;
- general blood and urine analysis . Particular attention is paid to indicators such as ESR and leukocyte count. Their increase indicates an inflammatory process. If band neutrophils are also elevated in the analysis, we are talking about an acute infection;
- bacterial culture from the nasopharynx . The results of the study allow us to determine which infection causes inflammation in the throat. Staphylococci take the lead in sowing; they inseminate the nasopharynx and lead to various diseases of the nose and throat. In second place are streptococci, and they are not inferior in insidiousness. For example, streptococcal tonsillitis often causes complications in the heart (myocarditis) and joints.
What a healthy and sore throat looks like in a child
A healthy child’s throat should be free of redness, rash or any other manifestations. A clean pink mucous membrane is an indicator of the absence of nasopharyngeal diseases. Parents often encounter the phenomenon of redness of the throat in their baby. There are quite a few diseases that cause the throat to turn red.
To understand what exactly happened to the baby, if the child has a red throat, look at the photos and descriptions of diseases that are accompanied by redness of the pharynx. Learn to look at your baby's neck correctly. It is not so difficult to independently understand what diagnosis will be made. But don’t limit yourself to self-diagnosis of your baby; be sure to visit a doctor.
Treating a sore throat if necessary
Treatment for throat diseases depends on the diagnosis.
A viral throat (usually pharyngitis) does not require antibacterial drugs. It is enough to rinse with medicinal herbs and antiseptics.
Inhalations with alkaline solutions give good results.
The patient is also recommended tablet antiviral therapy.
Herpetic sore throat, like pharyngitis, is treated with antiviral drugs; antibiotics can only aggravate this disease. The treatment regimen includes antipyretics, antihistamines, vitamins and immunomodulators.
For sore throat and tonsillitis, antibacterial treatment cannot be avoided, and it must be carried out in a timely manner. Purulent plaque spreads very quickly, therefore, complications from other organs cannot be allowed. Typically, the treatment process begins with penicillins; if they are ineffective, they resort to macrolides or cephalosporins.
Fungal infections of the throat are often observed after long-term antibiotic therapy. To get rid of candidiasis, antimycotic and antiseptic agents are used. Irrigation, rinsing, dissolving tablets and lubricating with solutions are prescribed. It is possible to quickly cure a fungal infection, provided that all the specialist’s instructions are strictly followed.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to carry out independent antibacterial treatment. Unfortunately, many citizens attribute antibiotics to themselves without any justification, explaining their actions in order to prevent complications at all costs.
Causes of a red throat in a child
A child's red throat does not always look the same.
By the appearance of the problem, you can first orient yourself in the possible causes of its occurrence. If you look at a photo of a sore throat, it is not difficult to come to the conclusion who is the culprit of the baby’s illness. A sore throat occurs because the child is cold, drinks or eats something cold, in general terms – from hypothermia. In this case, a red throat will also be accompanied by a runny nose.
If it is painful for a child to swallow with an inflamed throat, then we are dealing with viral infections. Most likely, the diagnosis will sound like pharyngitis, tonsillitis, or tonsillitis. Treatment cannot be delayed. Sore throat is terrible for its complications.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammatory process localized at the back of the throat. Symptoms of pharyngitis are:
- Red throat wall and red dots on it.
- Sore throat when swallowing. The degree of pain depends on the person’s pain sensitivity threshold.
- There may be a lump in the throat, as if there is a dry foreign object there.
- The cough will be dry, since the purpose of the cough is to get rid of discomfort in the throat.
- Plaque of purulent film in the throat.
- There may be fever, headache and runny nose.
Read more about the disease pharyngitis and its treatment in the articles:
Chronic and acute pharyngitis in children and adults;
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is a classic sore throat, that is, inflammation of the tonsils of the palate.
- The child cannot swallow because it is accompanied by pain.
- The cough is suffocating and is caused by inflamed tonsils.
- Internal poisoning develops in the body.
- Tonsillitis is similar to pharyngitis in appearance; the difference can be seen by visual examination of the oral cavity.
- The tonsils are red. Although, tonsillitis does not always occur in its pure form.
Since sore throat is caused by coccal infections, as well as fungal parasites, treatment should be prescribed after examination.
Read more about tonsillitis in the article Acute tonsillitis - tonsillitis.
We also recommend that you find out what a sore throat looks like in our article What does a sore throat look like in adults and children.
Allergy
The neck may turn red due to an allergic reaction. Parents can find out what is causing the allergy by taking the appropriate test. The most popular allergens may be:
- Household chemicals;
- Dust;
- Down and feather pillows;
- Wool and fluff of pets;
- Some food products;
There are cases that babies suffer from redness of the throat for another reason - they are teething. The symptoms may be very similar to the above; the baby may suffer greatly during this period. A stressful situation for a small organism - teething - can weaken the immune functions of the body.
Weakened defenses of the oral mucosa can lead to infection. Care must be taken to ensure that the toddler does not become infected from unhealthy children.
Even if you are sure what caused the redness of the mucous membranes of your child’s pharynx, do not resort to self-prescribing medications! It is especially prohibited to take antibiotics unless there is a justified need. Leave this to more qualified specialists, such as your local doctor or the ENT specialist to whom your pediatrician will refer you.
Prevention - how to keep your throat healthy
How to avoid getting ARVI
Most often, a sore throat occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections.
To keep your throat healthy, it is necessary to take preventive measures to prevent respiratory infections.
First of all, this is to minimize contact with already sick people. If you get sick yourself, don’t infect others, go on sick leave. Of course, it is impossible to protect yourself 100% from viruses, therefore, the second stage of prevention is to increase immune defense.
Immunity can be increased in the following ways:
- air humidification, ventilation, wet cleaning of premises;
- hardening (swimming pool, contrast shower, walks in the fresh air);
- balanced diet;
- adequate drinking regime (drink at least 1.5 liters of water per day);
- elimination of chronic foci of infection in the mouth (carious teeth);
- maintain a normal body mass index.
Local prophylaxis is also necessary. To do this, use rinses with infusions of chamomile, eucalyptus, and sage. Rinsing with propolis has a good effect. Don't forget to change your toothbrush more often.
Hardening the throat is also useful. First, gargle with slightly warm water, then reduce the temperature to lower levels every day.
When you notice that the water has become cold enough, there is no need to lower the water temperature further.
You should not gargle with ice water, although some patients train their throat with ice cream. And it is worth noting that the method is very effective.
Don't forget to eat foods such as honey, garlic, onion, lemon. During periods of raging epidemics, drink rosehip infusion in two-week courses.
Prevention of sore throat
People with strong immunity do not know sore throats, and do not even imagine what a sharp sore throat and congestion are. As we said above, hardening and a healthy lifestyle help prevent illness. But the prevention of sore throat does not end there; it requires certain measures, especially if there is someone at home who is sick with this disease. To avoid getting a sore throat, try to adhere to the following rules:
- personal hygiene (individual toothbrush, towel, cup, plate, fork, spoon);
- If possible, transfer the patient to a separate room (in hospitals there are infectious diseases departments with boxes for this purpose);
- eliminate sources of chronic infection in the body (sinusitis, tonsillitis, caries, etc.). For this purpose, antibiotics and antiseptics are used, and in some cases surgical treatment is used.
Special medications are prescribed to stimulate the immune system. Currently, interferons, thymalin, and lycopid have become widely popular. These drugs stimulate cellular and humoral immunity. Also, such drugs as bronchomunal, imudon, and ribomunil showed good results. The drugs are prescribed strictly according to the instructions; if necessary, the doctor changes the treatment regimen.
Some patients suffer from recurrent sore throats; they are often triggered by hemolytic streptococcus. In such cases, prophylaxis is carried out with bicillin 3 or 5.
If preventive measures to prevent recurrent sore throats do not help, tonsillectomy is resorted to. This operation allows you to remove the purulent focus and prevent complications from other organs and systems.
Causes of a red throat in a child
A child's red throat does not always look the same.
By the appearance of the problem, you can first orient yourself in the possible causes of its occurrence. If you look at a photo of a sore throat, it is not difficult to come to the conclusion who is the culprit of the baby’s illness. A sore throat occurs because the child is cold, drinks or eats something cold, in general terms – from hypothermia. In this case, a red throat will also be accompanied by a runny nose.
If it is painful for a child to swallow with an inflamed throat, then we are dealing with viral infections. Most likely, the diagnosis will sound like pharyngitis, tonsillitis, or tonsillitis. Treatment cannot be delayed. Sore throat is terrible for its complications.
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammatory process localized at the back of the throat. Symptoms of pharyngitis are:
- Red throat wall and red dots on it.
- Sore throat when swallowing. The degree of pain depends on the person’s pain sensitivity threshold.
- There may be a lump in the throat, as if there is a dry foreign object there.
- The cough will be dry, since the purpose of the cough is to get rid of discomfort in the throat.
- Plaque of purulent film in the throat.
- There may be fever, headache and runny nose.
Functions of the tonsils and their location
The tonsils are a collection of lymphoid cells located in the nose and oropharynx. Their main functions are protective and hematopoietic . The tonsils prevent harmful microorganisms from entering the body. Lymphoid tissue produces antibodies that “fight” pathogenic microbes.
In addition, tonsils participate in the regulation of hematopoiesis, forming lymphocytes.
Humans have 2 paired and 2 unpaired tonsils. They are located at the junction of the nasopharynx and pharynx, forming a pharyngeal ring.
Tonsils are pink. They are the size of a walnut.