Dental luxation is a traumatic change in the position of a tooth, in which its displacement is observed, as well as injury to the gum tissue. It can be partial, complete or impacted. The damage is accompanied by severe pain, hyperemia and profuse bleeding of the gums, and emotional shock. Requires immediate medical attention, otherwise the injury may cause complications. In this material we will analyze what kind of damage it is, what its causes are, what symptoms can be used to determine it, what complications it threatens, and also how to properly treat dental luxation.
Definition of disease
Luxation is a traumatic displacement of a tooth in the dentition, accompanied by damage to soft tissues in the oral cavity. Such an injury is usually isolated, but in some cases it may be accompanied by soft tissue rupture and even a fracture or dislocation of the lower jaw. More often, such damage is recorded on the frontal areas of the anterior jaw, less often they are noted on the lower jaw, since it is better protected from impacts and other damage. Patients of all ages, including children, are prone to dislocations.
There are three main types of dislocations:
- incomplete. With it, the root is only partially displaced from the alveolus, a change in the position of the tooth and a partial rupture of the periodontal ligament are observed;
- full. With such damage, the tooth emerges from the socket. In this case, a blood clot may form in the hole itself;
- hammered. With such damage, the tooth deepens relative to its neighbors, and it has increased stability. The damage is accompanied by rupture of periodontal tissue and increased bleeding.
The causes of such injury may be:
- Blows or bruises received from a fall or in shingles.
- Incorrect removal of adjacent teeth by the dentist. Damage is accompanied by pain and bleeding is possible. Read more about how to stop bleeding after tooth extraction here.
- Bad habits. Often such dislocations are recorded in patients who chew nuts with their teeth or open beer bottles with them.
- The presence of microtraumas of the gums or cracks in the tooth. In such pathologies, dislocation can be caused by eating solid food.
- Getting solid foreign objects into food: pebbles, glass, fragments of metal or plastic.
- Changing the trajectory of jaw movement when chewing food.
Most often, a dislocation affects only one tooth in a row. Less commonly, usually as a result of impacts from a fall or during a fight, several teeth are damaged at the same time. Such an injury requires longer treatment and complex diagnostics. Often, part of the dentition cannot be saved due to severe damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity.
What is tooth luxation
Tooth luxation is the displacement of a dental unit as a result of mechanical damage, which leads to displacement of the tooth from the alveolar socket and damage to the connective tissue. This type of violation of the integrity of the dentition cannot occur due to internal pathological processes: the main cause is only external damage.
The clinical picture of such damage is quite specific - there is no asymptomatic course. Treatment of an impacted tooth dislocation is carried out only comprehensively and is selected individually, depending on the severity of the damage and the condition of the tooth.
According to the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, such a violation falls under the section “Injuries, poisoning and some other consequences of external causes.” Thus, the ICD-10 code for tooth dislocation is S03.2.
Symptoms
The symptoms accompanying a dislocation directly depend on the type of injury:
- With incomplete dislocation, the symptoms are usually mild. The damage is accompanied by pain, which usually intensifies when chewing, tooth mobility, inflammation, and bleeding of the gums.
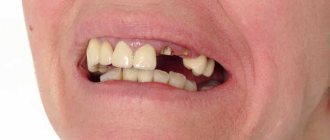
- With complete dislocation, the tooth falls out of the socket, severe bleeding of the gums and pain. Patients often experience emotional as well as pain shock.
- With an impacted dislocation, there is a displacement of several teeth in the dentition at once. The injury is accompanied by severe bleeding of the gums, swelling, pain that worsens while eating, as well as a decrease in the height of damaged molars or incisors.
Also, a patient with such pathologies experiences an increase in temperature, deterioration in sleep quality, decreased ability to work, and increased fatigue. As a rule, these symptoms disappear completely after full treatment of this disorder.
Classification
Classification of tooth dislocations.
The following types of injuries are distinguished:
- complete tooth dislocation - loss of a dental unit from the socket is often accompanied by trauma to nearby tissue;
- impacted tooth dislocation - complete or partial displacement of the dental unit towards the body of the jaw, which leads to significant destruction of bone tissue;
- incomplete tooth luxation - displacement of the root from the alveolus occurs only partially, and is accompanied by periodontal rupture.
Each form of damage has its own clinical picture.
Treatment
The treatment strategy is also selected depending on the type of damage. If the patient has an incomplete dislocation, therapy in his case will include:
- moving the tooth into place. It is fixed with plaster or a wire splint. The fixation is maintained for one and a half months, after which the doctor can remove the splint;
- limiting the chewing load on the damaged area after removing the splint. It is followed for a month;
- taking medications. These include rinses, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory drugs that help restore the mucous membrane. The timing of taking medications, as well as their dosage, are selected for each patient individually.
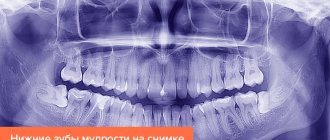
Before the start of treatment and after completion, the patient must undergo an x-ray. It allows you to determine whether the tooth is in the correct position after treatment, as well as determine the presence of complications after such damage.
For complete dislocation, the doctor may use the following treatment strategies:
- Removal followed by canal filling. It is recommended in cases where the patient has ruptures of the neurovascular bundle. Canal filling is carried out in several stages. Initially, temporary fillings are placed, after the inflammatory process is removed - permanent ones. A few months after filling the canals, the patient can apply for an implant.
- Replantation. It can be carried out in cases where the blood supply to the root is not damaged. It involves treating the wound with antiseptic agents, installing the tooth in its original place, and then fixing it with a splint.
After tooth replantation, the patient must undergo several control x-rays with a gap in time. If they show that the tooth has returned to its old place in the socket, the splint may be removed. If not, the doctor will have to re-set the dislocation or prescribe removal of the damaged tooth.
To increase the chances of successful tooth healing, the patient needs to ensure that it is properly stored before going to the doctor. So, if a molar, premolar, incisor or canine has fallen out completely, it should be washed with clean water (without using sponges or brushes) and try to return it to its original place in the mouth.
If this cannot be done due to pain shock, the tooth must be placed in a biocompatible environment. Containers with it can be purchased at the pharmacy. If there are no points of sale of medications nearby, the tooth can be placed in a container with milk. If there are no such substances at hand, it can be put in the mouth without inserting it into the damaged area of the mucous membrane. It is also not recommended for the victim to rinse his mouth before contacting a doctor. This can lead to the loss of a blood clot in the socket, which is why it will subsequently be impossible to implant the tooth there. Moreover, if an infection gets into the hole, alveolitis may begin to develop. Read more about how to treat alveolitis here.
Impacted dislocation in most cases does not require special treatment. Damaged over time
an incisor, canine, premolar or molar independently takes its place in the socket.
The patient only needs to be observed by a doctor during the recovery period to avoid possible complications.
The effectiveness of treatment in all of these cases directly depends on how quickly a person consulted a doctor and received full treatment. If he managed to do this in the first hours after the dislocation, the dentist will be able to save even a tooth that has completely fallen out of its socket.
If the patient came only a few days later, he will most likely be offered treatment of the gum tissue and subsequent installation of an implant, since in many cases it will be impossible to save the natural tooth.
How to treat
To begin with, they carry out diagnostics, but there is nothing complicated here. Sometimes the problem is noticeable even in the photo.
The doctor will immediately detect a dislocation based on the following signs:
- the tooth is movable;
- gums bleed;
- the dentition is changed.
Then the main question arises: Is it worth saving or is it better to delete? And the answer depends on the bone tissue at the root. If it has been preserved for half the length of the root, it is preserved (unless the patient has already decided to place an implant in this place for some reason).
In a situation where it is decided to restore an incomplete version of the injury, the treatment is as follows:
- Anesthesia is given.
- They put the tooth back.
- It is immobilized by splinting.
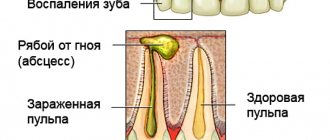
- Determine the condition of the pulp.
To understand what’s wrong with the pulp, they look at its reaction to electricity. To check, a current with a characteristic of 2-3 μA is applied. If the pulp reacts to this, then the condition is normal.
But here it is important not to draw premature conclusions, because in the first three to five days after a dislocation, a decrease in sensitivity is possible as a reaction to aggressive influence. The pulp is sometimes damaged due to rupture of the neurovascular bundle. If this happens, the pulp is removed and the canal is filled.
In case of a complete injury, replantation is carried out provided that the condition of the periodontal tissue is tolerable.
They do this:
- Trepanned.
- The pulp is removed.
- The canal is filled.
- Treat the hole and root with antiseptics (solutions).
- The tooth is inserted into the socket, fixing it in its original position. Fixation is achieved by splinting, but sometimes this will be unnecessary.
An important point: it is advisable to carry out replantation on time. Half an hour is the maximum that should pass from the moment of injury. It is clear that this is not easy, but it is worth trying.
At the same time, of course, we must not forget that only a doctor can do this. If you are late, the root will begin to dissolve within a month. Unfortunately, there are almost no exceptions. If everything is done on time, it will last for years.
If the injury is impacted, then:
- They make a fixation.
- The pulp is removed immediately so that the crown does not have time to stain.
- The tooth is pulled back to its original position using special forceps.
- Fixed.
Sometimes a professional will not treat a problem because it will go away on its own. This is only possible with a light version of the hammered variety.
When the procedure is completed, an x-ray is taken and a second examination is performed. After treating any injury, avoid solid foods. The diet creates the best conditions for the smooth recovery of the diseased area.
Possible complications
This pathology can lead to a number of complications. Among these are:
- formation of granuloma in the damaged dental canal;
- curvature of the tooth root, change in its length;
- stopping the growth of the tooth root (observed when a tooth dislocates in children);
- chronic granulomatous periodontitis;
- formation of a root cyst;
- pulp necrosis.
When such complications occur, the doctor often has to change the patient's treatment strategy. So, he may prescribe the removal of a damaged tooth for subsequent treatment of soft tissues and prosthetics. In the vast majority of cases, it is impossible to preserve a natural tooth during the development of such pathological processes.
How trouble happens
There are several situations where this is possible. They have one thing in common - in all cases the injury is caused mechanically, otherwise it is impossible in principle. That’s why the problem is much less common than caries.
Bad habits
This, of course, is not about smoking or alcohol, but about opening something with your teeth, for example, bottles. It is generally not recommended to put foreign objects in your mouth. Film footage of someone holding a flashlight in their mouth does not at all indicate the safety and harmlessness of such a thing.
Careless cleaning
Oddly enough, even with such a normal process, sometimes such a nuisance happens. This is a common traumatic factor.
People who are prone to thoughtfulness at the wrong moment, and even on exciting topics, can bite the brush in their hearts so that this is a sign of trouble. This is especially true for those who have powerful jaws with developed muscles.
Fall, hit, etc.
Mechanical injury received in this way is a common occurrence. With a strong blow to the jaw with a fist, such a nuisance is far from the worst consequence.
Even an accidental impact with the jaw, for example on a table, can lead to a problem. An accidental fall of a child is a common cause of impacted dislocation of a baby tooth. Irina Sevostyanova, a pediatric dentist, says: “Acute trauma is a common cause of tooth decay or loss in children.”
Foreign object in food
The safest thing is to eat your own food at home. When eating in public catering establishments, you should be careful, because there may be solid objects in the dish that can lead to such trouble.
For example, in a regular salad from a package there is sometimes a small part of a plastic container. And if a person bites sharply like this, then a problem cannot be avoided (if not this one, then some other one).
Solid food
This can also cause a problem. This is especially true for those who love:
- crackers;
- drying;
- oat cookies;
- nuts.
For example, crackers are usually not so hard that they cannot be bitten. However, for many quite tolerably chewy crackers, there may be a few very hard ones.
As for large nuts, there is an opinion among some dentists that they are, in principle, harmful in their whole form, and can also lead to such trouble. And what you definitely shouldn’t do is eat such food in a hurry.
Therefore, it is better not to chew something like this on the street, otherwise you might accidentally bite too hard from an unexpected sound. This is a common cause of tooth dislocation in children and adults with an increased pace of life.
In catering establishments, sometimes they are faced with the fact that food is too hard, and food that should not be so. Therefore, you should not chew quickly in such establishments in order to have time to react in time and not put too much pressure on the piece. Otherwise, injury may occur.
Incorrect deletion
This is the case when a dislocation occurs due to the fault of the dentist. Ignorant removal sometimes causes problems for “neighbors.”
Therefore, before agreeing to the procedure, it is worth asking whether the doctor has done this before and how many times. This will show that the doctor knows what to do.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing this type of injury, as a rule, does not cause difficulties due to the specificity of the clinical picture and obvious external signs of damage.
First of all, the dentist examines the oral cavity.
During the inspection the following is noted:
- the periodontal gap increases along the entire circumference;
- there is a pronounced pain syndrome during percussion.
In order to determine the severity of the pathological process and select effective treatment, additional instrumental tests are carried out, such as:
- three-dimensional computed tomography;
- X-ray of the jaw;
- electroodontodiagnosis - this examination method is used to assess the condition of the pulp, bone tissue and periodontal tissue.
Panoramic photo of teeth.
Standard laboratory tests are not performed as they do not provide diagnostic value. In some cases, a general blood test may be performed.
The treatment method is determined based on the results of diagnostic measures.
Dislocations and mechanism of occurrence
Tooth dislocation should be understood as a violation of its correct location in the jaw row against the background of pronounced changes in the position of the root system relative to the alveolar septa.
In the process of external mechanical influence on the organ (at the moment of an impact, an accidental fall), a displacement of the tooth fragment relative to the socket in an arbitrary direction is observed, that is, its reposition.
At the same time, it changes its localization trajectory and the root. Periodontal fibers are fragmented, and those that have managed to maintain their structural integrity are stretched.
The position of the tooth displacement can be different - with a slope towards the neighboring organ, backward or forward relative to the jaw row, falling into the occlusal plane.
In some cases, even its complete rotation relative to its own axis is possible.
In some cases, the only solution is to remove the tooth
If a patient goes to the dentist with a dislocated tooth, the doctor decides to remove it if the following predisposing factors are present:
- A serious inflammatory process is detected. To eliminate the problem, implants are used; if it concerns a child, they will be temporary, but for adults they choose permanent ones.
- Severe damage to bone tissue is observed after injury.
- If there is a dislocation of a baby tooth. But here, too, there is disagreement among doctors; some believe that there is no need to save the tooth, while others are confident that the opposite is necessary.
In any case, only a doctor will decide to remove a tooth after carefully studying the situation, determining the degree of complexity of the injury and the condition of the dental system.
Is it possible to prevent such an injury?
Of course, you cannot completely insure yourself against a dislocated tooth, because boys who prove their case in a fight cannot guarantee that they will not receive a strong blow to the jaw. But there are other measures you can take to reduce the risk of injury:
- Be more careful when choosing the foods you eat.
- Go to the store and buy a bottle opener, don't test your teeth.
- It is also not necessary to crack nuts with your teeth; you can use available tools.
- Personal oral hygiene has never harmed anyone, and its absence leads to weakening of bone formations. Plaque leads to the gradual destruction and weakening of tooth enamel.
- Eat more fresh vegetables and fruits; they not only cleanse your teeth of plaque well, but also strengthen them.
Beautiful teeth are not only health, but also beauty. Damaged or crooked teeth make us feel self-conscious about our smile. To prevent this from happening, you must maintain oral hygiene and take care of your teeth. At first glance, it seems that they are so strong and nothing is scary for them, but it turns out that just opening a bottle can end in disaster. It is important to teach children from early childhood to take care of their teeth, then, as adults, they will not sit in line for hours at the dentist’s office. Protect your teeth from dislocation and let your smile shine!