Every expectant mother, when registering for pregnancy, must undergo a commission of several medical specialists. Among them is a dentist who checks the condition of the oral cavity, gives recommendations to the pregnant woman, etc. And if there are problems, the dentist warns that there is no need to wait for the birth of the child - treatment can be carried out during the period of bearing the baby.
But for many pregnant women this seems almost unnatural - a rare treatment, it seems to a woman, takes place without local anesthesia, but it is contraindicated for pregnant women. Is it so? Of course, this is a myth, and a dangerous one at that. This can lead to loss of dental health.
Anesthesia in dentistry during pregnancy
Why is oral hygiene important during pregnancy?
Usually, on the same sheet that a pregnant woman takes before registering, the dentist writes: “The oral cavity has been sanitized” or “Needs sanitization.” Indeed, healthy teeth are not just a formality, indicating that the expectant mother has no problems in this regard. Carious dental cavities and decayed teeth are potential sources of infection that directly threaten the health of the fetus.
During pregnancy it is necessary to treat teeth
Dental treatment, procedures during pregnancy
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Treat teeth with and without local special anesthesia | Implant teeth |
| Remove teeth | Take x-rays of individual teeth and jaws |
| Remove dental plaque | Use dental gels without a doctor’s permission (only a doctor can recommend a particular gel, knowing its composition and effect on the health of the pregnant woman and fetus) |
| Do medicinal rinses to improve gum health (as recommended by a doctor) | Unauthorizedly take medications to relieve toothache, antibiotics, etc. |
As for prosthetics, if possible, postpone this issue until after childbirth, try to do so. There are no direct contraindications to prosthetics, but in the process of preparing teeth for prosthetics, a whole list of problems may arise. In addition, according to statistics, every third pregnant woman suffers from gingivitis - inflammation of the gums. With this complication, dental prosthetics are prohibited.
It is better for pregnant women to avoid dental prosthetics.
Similarly, installing braces during pregnancy is of questionable reliability. If you can wait with this, then don't rush. Still, this is a stressful moment for the body, some people tolerate it easily, but for others it will cause certain difficulties. The possibility of an inflammatory process cannot be ruled out, which is especially dangerous for the expectant mother.
It is better to get braces after pregnancy
The drug is intended for use in the oral cavity.
To prevent infection (including with the hepatitis virus), it is necessary to ensure that new sterile syringes and needles are always used when taking the drug from ampoules. Opened cartridges must not be reused for other patients (risk of hepatitis infection)! Damaged cartridges must not be used.
The drug should not be used if it has changed color or becomes cloudy. Dosage regimen
For anesthesia during uncomplicated extraction of teeth of the upper jaw in the absence of inflammation, it is usually sufficient to create a depot of the drug Articaine with adrenaline forte in the area
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=upload
transitional fold by introducing it into the submucosa from the vestibular side (1.7 ml of the drug per tooth). In some cases, it may be necessary to achieve complete anesthesia.
additional administration from 1 ml to 1.7 ml. In most cases, this eliminates the need for a painful palatal injection.
For anesthesia for incisions and sutures in the palate in order to create a palatal depot, about 0.1 ml of the drug per injection is required.
We suggest you read How to remove the smell of alcohol from your mouth quickly at home
When removing several adjacent teeth, the number of injections can usually be limited.
In the case of removal of mandibular premolars in the absence of inflammation, as a rule, it is sufficient to administer 1.7 ml of the drug per tooth. If in this way it was not possible to achieve the desired
effect, an additional injection of 1 - 1.7 ml of anesthetic should be performed into the submucosa in the area of the transitional fold of the mandible on the vestibular side.
If in this case it was not possible to achieve complete anesthesia, it is necessary to conduct a conduction block of the mandibular nerve.
During surgical interventions, depending on their severity and duration, the drug Articaine with adrenaline forte is dosed individually.
When performing one treatment procedure, adults can be administered up to 7 mg of articaine per 1 kg of body weight. It was noted that patients tolerated doses up to 500 mg well (corresponding to 12.5 ml of the drug).
Elderly patients and patients with severe renal and hepatic impairment
In elderly patients and all patients with severe renal and hepatic insufficiency, increased plasma concentrations of articaine may occur. For these
Patients should be treated with the minimum dose necessary to achieve a sufficient depth of anesthesia.
- For pediatric patients (over 4 years of age), the minimum doses necessary to achieve adequate anesthesia should be used. The dose of Articaine with adrenaline forte is selected depending on the age and body weight of the child, but it should not exceed 7 mg of articaine per 1 kg of body weight (0.175 ml/kg). The use of the drug in children under 1 year of age has not been studied. Side effect
- The incidence of side effects is presented in accordance with the classification recommended by the World Health Organization: very often (2 1/10); often (2 1/100, {amp}lt; 1/10); infrequently (2 1/1000, {amp}lt; 1/100); rarely (2 1/10000, {amp}lt; 1/1000); very rarely ({amp}lt; 1/10000), including individual messages; frequency unknown (cannot be determined from available data). Immune system disorders Not known
- Allergic or allergy-like reactions. They can be expressed in the form of swelling and (or) inflammation at the injection site, but can also occur regardless of the injection site and manifest themselves in the form of redness, itching, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, angioedema of the face with swelling of the upper and (or) lower lip, cheeks, swelling of the larynx with a feeling of a “lump in the throat” and difficulty swallowing, urticaria and difficulty breathing, which can lead to anaphylactic shock.
- From the central nervous system / Often
Paresthesia, hypoesthesia, headache (due to the presence of epinephrine in the drug).
Infrequently
Dizziness.
Frequency unknown
– dose-dependent reactions from the central nervous system (including at excessively high doses or after accidental intravascular injection): anxiety, nervousness, stupor, confusion to the point of loss of consciousness, coma, respiratory failure to the point of respiratory arrest, muscle tremors and twitching muscles up to generalized convulsions;
– if the correct technique for administering the drug is violated or due to anatomical features in the injection area, damage to the facial nerve is possible, which can lead to paralysis of the facial nerve and a decrease in taste sensations.
Visual disorders
Frequency unknown
Visual disturbances (blurred vision, mydriasis, blindness, double vision), usually reversible and occurring during or shortly after injection of a local anesthetic.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpressru
Articaine with adrenaline forte, solution for injection (40 mg 0.01 mg)/ml, ampoules 2 ml No. 10 price: 870.00 rub. (to order)
Articaine with adrenaline forte 40 0.01 mg/ml cartridges (1: 100,000) 1.7 ml No. 50 price: RUB 1,430.00
When can pregnant women have their teeth treated?
If a tooth hurts, it doesn’t matter what week of pregnancy a woman is in. You need to go to the doctor, warn the doctor about your situation, and solve the problem in the most gentle way possible. You cannot endure pain, much less take painkillers. The doctor, of course, will not leave the woman alone with pain and will carry out all the necessary procedures. But this should be a dentist, and not the advice of a friend or even a remedy from a pharmacist friend.
If your tooth hurts, you shouldn’t put off visiting a doctor.
The preferred period for sanitation of the oral cavity is the second trimester. This is a conditionally calm period of pregnancy, when the formation of the main organs and systems of the baby has already taken place, the general condition of the woman has normalized - there is no toxicosis and its most unpleasant manifestations. On the other hand, the period is still short, and it will not be difficult for a woman to go to the doctor or sit motionless in a dental chair for some time due to her increased weight.
The second trimester is the best period to visit the dentist
Even if nothing worries you, your teeth are healthy, you need to see a doctor in the second trimester. The fact is that, as already mentioned, very often expectant mothers encounter such a nuisance as gingivitis. There is even such a concept as “gingivitis during pregnancy.”
Gingivitis in pregnant women
Signs of gingivitis:
- gums become larger and hypertrophy;
- bleeding gums becomes noticeable;
- severe gum sensitivity, unpleasant odor.
If this disease is not treated and the process is started, then the probability of premature birth increases 6 times! That is, this is not just a temporary inconvenience and an aesthetic problem, but a risk to the fetus. Gingivitis can be successfully treated; there are remedies that will not threaten the normal course of pregnancy. No anesthesia is required for this treatment.
Treatment of gingivitis in pregnant women
Video: Dental treatment during pregnancy
What anesthesia is possible during pregnancy?
Of course, we are not talking about general anesthesia at all. Such a medical procedure, even for a non-pregnant woman, is not considered simple and harmless. During pregnancy, it can be used only in cases of urgent need, when without surgical intervention the health and life of the pregnant woman is at risk.
Local anesthesia is relatively harmless. But doctors still recommend using anesthesia for dental treatment in the second trimester. As mentioned above, the child’s organs and systems are already mature, all the most important processes are behind us, so treatment is possible. The most important thing is to warn your doctor that you are pregnant. Anesthesia in this case will be different.
Modern anesthesia in dentistry
In dentistry, pain relief is based on adrenaline. Thanks to this substance, blood vessels narrow, the risk of bleeding decreases, and finally, pain is blocked. Some patients do not feel not only pain, but even the touch of a medical instrument to the tooth and gum. Anesthesia usually lasts 1-3 hours.
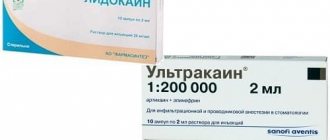
The use of epinephrine-based anesthetics during pregnancy is not recommended. This is fraught with an increase in pressure in a woman, which threatens uterine hypertonicity. Therefore, specifically for this category, anesthetics of a different line are used - articaine agents. These include primacaine and ultracaine. Adrenaline in these drugs is contained in minimal quantities, and these substances do not penetrate the placenta at all.
"Primakaine"
Ultracaine
Articaine preparations:
- excellent pain relief;
- have a calming effect on the inflamed area of the oral cavity;
- hypoallergenic.
Articainum
Once again, it is worth emphasizing: you need to warn the doctor about pregnancy, clarify the due date, and objectively assess your well-being. If you have high blood pressure, weakness, or poor health, anesthesia is not recommended. If you feel unwell after the administration of the anesthetic, you should immediately tell your doctor. If there is an individual intolerance to any component, this should also be reported to the doctor before treatment.
Video: Dental anesthesia during pregnancy
Interaction between Articaine with adrenaline and Lidocaine when taken simultaneously.
The toxicity of lidocaine increases when it is used simultaneously with cimetidine and propranolol due to an increase in the concentration of lidocaine; this requires a reduction in the dose of lidocaine. Both drugs reduce hepatic blood flow. In addition, cimetidine inhibits microsomal activity. Ranitidine slightly reduces the clearance of lidocaine, which leads to an increase in its concentration. Antiviral agents (eg, amprenavir, atazanavir, darunavir, lopinavir) can also cause increased serum concentrations of lidocaine. Hypokalemia caused by diuretics may reduce the effect of lidocaine when used simultaneously (see section "Special Instructions"). Lidocaine should be used with caution in patients receiving other local anesthetics or agents structurally similar to amide-type local anesthetics (eg, antiarrhythmics such as mexiletine, tocainide) since systemic toxic effects are additive. Separate drug interaction studies have not been conducted between lidocaine and class III antiarrhythmics (eg, amiodarone), but caution is advised. In patients concomitantly receiving antipsychotics that prolong or have the potential to prolong the QT interval (e.g., pimozide, sertindole, olanzapine, quetiapine, zotepine), prenylamine, epinephrine (with occasional intravenous administration), or 5-HT3-serotonin receptor antagonists (e.g., tropisetron, dolasetron), the risk of ventricular arrhythmias may increase. Concomitant use of quinupristin/dalfopristin may increase lidocaine concentrations and thus increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias; their simultaneous use should be avoided. Patients receiving concomitant muscle relaxants (eg, suxamethonium) may have an increased risk of enhanced and prolonged neuromuscular blockade. Cardiovascular insufficiency has been reported following the use of bupivacaine in patients receiving verapamil and timolol; lidocaine is similar in structure to bupivacaine. Dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine lower the seizure threshold to lidocaine. Opioids appear to have a convulsant effect, as supported by evidence that lidocaine lowers the seizure threshold to fentanyl in humans. Combinations of opioids and antiemetics, sometimes used for sedation in children, may lower the seizure threshold to lidocaine and increase its CNS depressant effects. The use of epinephrine with lidocaine may reduce systemic absorption, but with accidental intravenous administration the risk of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation increases sharply. Concomitant use of other antiarrhythmics, beta-blockers and slow calcium channel blockers may further reduce AV conduction, ventricular conduction and contractility. The simultaneous use of vasoconstrictors increases the duration of action of lidocaine. Concomitant use of lidocaine and ergot alkaloids (eg, ergotamine) can cause severe hypotension. Caution must be exercised when using sedatives as they may interfere with the action of local anesthetics on the central nervous system. Caution should be exercised with long-term use of antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin), barbiturates and other inhibitors of liver microsomal enzymes, as this may lead to decreased effectiveness and, as a result, an increased need for lidocaine. On the other hand, intravenous administration of phenytoin may enhance the depressant effect of lidocaine on the heart. The analgesic effect of local anesthetics can be enhanced by opioids and clonidine. Ethyl alcohol, especially with prolonged abuse, can reduce the effect of local anesthetics. Lidocaine is not compatible with amphotericin B, methohexitone and nitroglycerin. With the simultaneous use of lidocaine with narcotic analgesics, an additive effect develops, which is used during epidural anesthesia, but increases the depression of the central nervous system and respiration. Vasoconstrictors (epinephrine, methoxamine, phenylephrine) prolong the local anesthetic effect of lidocaine and can cause increased blood pressure and tachycardia. Use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (furazolidone, procarbazine, seleginine) probably enhances the local anesthetic effect of lidocaine and increases the risk of lowering blood pressure. Guanadrel, guanethidine, mecamylamine, trimethaphan camsylate increase the risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and bradycardia. Anticoagulants (including ardeparin sodium, dalteparin sodium, danaparoid sodium, enoxaparin sodium, heparin, warfarin, etc.) increase the risk of bleeding. Lidocaine reduces the cardiotonic effect of digitoxin. Lidocaine reduces the effect of antimyasthenic drugs, enhances and prolongs the effect of muscle relaxants. When treating the injection site with disinfectant solutions containing heavy metals, the risk of developing a local reaction in the form of pain and swelling increases. Mixing lidocaine with other medications is not recommended.
When is pain relief needed?
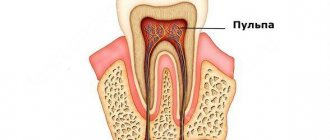
Should every visit to the dentist be accompanied by local anesthesia? Certainly not. Treatment of initial caries is, as a rule, painless; ultrasonic cleaning of teeth from plaque and deposits is also a completely tolerable event. Of course, it is almost impossible to remove a tooth without anesthesia, just like removing a nerve. Complicated caries requires pain relief.
Much depends on the individual sensitivity and general mood of the expectant mother. If she is mentally attuned to pain, then even the slightest discomfort will seem like severe pain to her. Today, a visit to the doctor does not take much time, and some inconvenience and minor pain can be tolerated.
Not every trip to the dentist involves anesthesia.
By the way, ultracaine and primacaine are also used as pain relief for patients who are breastfeeding. It does not pass into mother's milk, it is also safe for pregnant women - it is not transmitted through the placenta to the child. That is, even the most suspicious women need not worry; anesthesia for the treatment of pregnant women has long been established, and the safest regimens are used.