What features are observed when teeth appear?
Up to a year, parents experience anxiety about the child’s health, especially strong if he is the first-born. In the absence of experience, even a slight runny nose in a baby causes panic in many mothers.
Parents need to know the following symptoms associated with a runny nose during teething in children:
- the gums swell in the area where the tooth emerges, a slight swelling and slight redness are visible;
- persistent pain in the mouth area, causing anxiety in the baby; toothaches tend to intensify at night;
- the temperature may rise during the day;
- discharge of mucus from the nasal passages;
- there is causeless anxiety, increased irritability, moodiness;
- nasal congestion bothers you;
- diarrhea;
- cough;
- refuses to eat.
It is unlikely that there are cases when a baby, when teething, does not have all the manifestations listed above.
Even the healthiest child may experience mild symptoms of discomfort on the days when his incisors erupt.
A common occurrence at this time is itching and inflamed gums. The child puts into his mouth everything that comes into his hands and gnaws on his fingers. The drool is flowing like a stream. A cough is provoked by mucus that gets into the throat, it sticks to the walls of the larynx, causing irritation. The presence of cough and snot, a stuffy nasopharynx at normal body temperature is a common occurrence when teeth appear.
Features associated with ARVI
If snot appears on the teeth, parents need to consult a pediatrician or understand that there are no reasons for concern. Komarovsky believes that a runny nose during teething cannot always be treated.
Viral runny nose can be characterized by the following reasons:
- the child, even before the causes of the disease appear, becomes lethargic, his appetite worsens, weakness and pain in the muscles may be observed;
- an increase in body temperature to high values. Although a temperature may be observed during teething, the fever is more pronounced with the virus. If the cause is teeth, then after a few days the temperature disappears without a trace;
- snot, dry or wet cough can be the cause of upper or lower respiratory tract disease. A dry or wet cough that does not go away within three days is possibly viral in nature. Komarovsky believes that teeth in combination with a cough can be the cause of the disease, and hard breathing without wheezing is a residual symptom of a viral disease;
- An infectious runny nose is accompanied by impaired nasal breathing and a large amount of mucus secreted. With a virus, the discharge can be mucopurulent, but when it erupts, it is usually transparent.
If a child, apart from snot, has no other signs of illness, he is cheerful and active, then is it worth contacting a pediatrician?
Can you have a runny nose when teething?
Doctors consider the appearance of a runny nose due to teeth to be a common event in the life of a child in the first years of life. There are two main causes of snot in infants: the first is physiological in nature, the second is associated with the immune system.
See also
How to rinse your nose with saline solution for a runny nose and sinusitis at home?
Read
Reasons in physiology
When babies in their first year of life begin to erupt their first teeth, gum inflammation begins. It is purely physiological in nature. Due to inflammation, blood circulation in nearby organs increases. This inflammatory process also affects the nasal mucosa. Therefore, when a child is teething, there is a thin discharge from the nose.
If it's about immunity
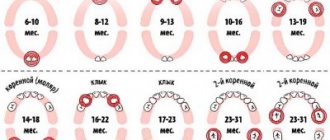
A baby's teeth most often begin to erupt around six months. It is at this time that mothers wean their infants from the breast and transfer them to a different diet. With mother's milk, the child received protective antibodies; mother's immunity protected him from aggressive bacteria and viruses.
When breastfeeding is stopped, a temporary decrease in the child’s immunity occurs. Therefore, the signs listed above may indicate a cold or infectious disease. The duration of the period when the protective forces are weakened is individual and depends on the characteristics of each individual infant.
Treatment of a runny nose in a baby
Doctors believe that rhinitis during teething does not require treatment if the child is no longer bothered by any symptoms. However, almost always the baby needs help to make it easier for him to endure this difficult but important stage of life. The main rule voiced by Dr. Komarovsky and other responsible specialists is: there is no need to rush to take medications.
We suggest you read: Severe pain after dental implantation
Even an inexperienced mother can most often independently determine whether the child is really teething in order to find out for herself whether it is necessary to begin treatment for rhinitis. If the gums are swollen, drooling is actively secreted, the little one is constantly gnawing on something - the process has begun. It is also important for parents to pay attention to how long a runny nose lasts and what the nature of the discharge is. If clear water flows from your nose and it lasts for weeks, you probably won’t need to take medication.
However, this does not mean that the baby does not need help. Dr. Komarovsky emphasizes the importance of providing a healthy environment. It is definitely worth creating a prosperous atmosphere in the house. This means that the room should not be hot, but the humidity must be maintained at 75%. Then the body, weakened by teething, will be able to fight well against attacks from viruses and bacteria. Crusts will not form in the nose, which interfere with breathing.
A prolonged runny nose in itself can irritate a child, and his delicate skin sometimes reacts with inflammation in the area around the nose. So mommy will have to make sure that the discharge is removed from her face in a timely manner. It is important to control that they do not stagnate. If this happens, the baby needs help. A solution of sea salt (or special drops) is injected into the spout, and then secretions and mucus are removed using an aspirator.
When teeth begin to emerge, the child is worried not only about rhinitis: severe pain is possible. If the baby cannot tolerate them, there is no need to torture the baby. It is worth using special topical anesthetic gels.
If the baby is healthy, but the nose is running, doctors do not recommend limiting the baby in its usual activities. Including, you shouldn’t give up going for walks. In normal weather, fresh air will only be beneficial. Experienced mothers note that it is much easier for babies to breathe outside.
As for nutrition, when teeth begin to erupt, you should not activate the process of introducing complementary foods. This can be explained very simply: the more the baby eats regular food, the less mother’s milk he consumes. At the same time, the level of immune defense decreases. And just during such a period, it is important to support the body so that it is not afraid of attacks from harmful microorganisms at the moment of weakening.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: How teeth cut in infants: when they erupt, teething pattern
If a toddler has discharge along with the eruption of his first teeth, the child can be considered healthy. It is important to provide him with support and monitor his health. But when other serious symptoms accompany a runny nose, a trip to the doctor cannot be postponed.
How long does a runny nose last during teething?
The doctor will decide whether snot during teething can be a sign of a cold. Given the general anxiety of the baby, it is difficult for parents to determine how serious the child’s runny nose is. A few tips can help parents better understand the condition of their children during this difficult period.
First of all, you need to pay attention to the appearance of the snot. It is normal if they are transparent and liquid. The appearance of thick green or yellow discharge is an alarm signal. A cause for concern may be copious discharge, causing persistent nasal congestion.
These manifestations may indicate that the child is developing rhinitis of a viral or bacterial nature. You need to sound the alarm and call a doctor if your runny nose lasts longer than 5 days. The separation of clear liquid from the nose within 3-5 days is considered normal.
How to treat
Only the doctor decides how to cure a child from snot when teething. Upon examination, the specialist determines the nature of the inflammation (immune, physiological) and determines the appropriate type of treatment.
How to treat a physiological runny nose
The child needs to create comfortable conditions that prevent the mucous membrane from drying out. The nose will be less stuffy if the air in the room is humid enough (45%). Maintain the room temperature no higher than 25 °C.
See also
How to treat a runny nose and cough during pregnancy?
Read
You will need pipettes to clean out your nasal passages. Pharmacy products are good for relieving inflammation of the mucous membrane:
- Dolphin;
- Aquamaris;
- Aqualor.
Use medications according to instructions, in consultation with your doctor. To clean the nasal cavity, it is better to have a baby aspirator; if you don’t have one, use a syringe bulb. When rinsing the nasal passages, remember that the baby does not need to pour in a lot of rinsing agent. 3-4 drops in each nostril are enough. Pharmacy rinsing preparations contain sea salt. It is harmless to children's health. To avoid dry mucous membranes, wash as often as possible.
How to treat a cold runny nose
What to do if your child has a cold, the main manifestations of which are:
- elevated temperature (39-40 °C);
- constant lethargy;
- poor appetite;
- yellow-green color of snot.
Already these manifestations are enough to urgently consult a doctor. If the condition is complicated by convulsions, cough, shortness of breath, it is all the more impossible to hesitate to call. You should not choose the treatment method on your own. A pediatrician, having diagnosed a runny nose during teething, knows how to treat it.
Runny nose and teeth - questions and answers - Dr. Komarovsky
Answered by Komarovsky E. O.
Teething is very often accompanied by a runny nose, and any practicing pediatrician can confirm this. The described phenomenon is usually explained by the fact that the process of teething is often accompanied by a decrease in local immunity, and this in turn significantly increases the likelihood of a viral infection.
Nevertheless, quite often a runny nose during teething cannot be explained by any viruses. The child’s condition is not disturbed, there is no increase in body temperature, an excellent appetite, and all that is there is, as you write, “transparent snot, not very much,” and plus teething. Again, such a runny nose can last for weeks, which is at least not typical for an acute viral infection. There is, apparently, another mechanism for runny nose during teething. The blood supply to the gums and nasal mucosa is closely related anatomically. When teething, blood circulation in the gums is activated, and this inevitably leads to increased blood supply to the nasal cavity. The consequence of the latter is more active work of the glands of the mucous membrane. Hence the additional mucus - transparent and in small quantities. As in your example. So a moderate runny nose during teething with normal body temperature and undisturbed general condition may well be considered as a variant of the physiological norm. Inflammatory processes affecting the airways, especially the bronchi, almost always change the volume of exhalation - it can be heard just as well as inhalation. Such breathing, in which the volume of inhalation and exhalation is the same, is called hard.
Thus, the doctor can hear hard breathing when the bronchial mucosa is inflamed (with bronchitis), as well as in a situation where there is dry mucus on the surface of the bronchi: this mucus makes the inner surface uneven, so breathing noise occurs both when inhaling and exhaling. If there was a lot of mucus, if it accumulated in the lumen of the bronchi, then the doctor would definitely hear wheezing. There is no wheezing - not a lot of mucus, “feels good” - serious inflammation in the bronchi is extremely unlikely. Most likely, both cough and hard breathing are residual manifestations of a previous acute respiratory viral infection, caused by the presence of dried mucus on the surface of the bronchi. It's not dangerous, time and fresh air heal it. Walk more, moisten and ventilate the children's room, do not be nervous and do not beg for medicine.
Read also: Plaque on the teeth of a 2-year-old child
Advice for parents from Dr. Komarovsky
First of all, remove inflammation from the gums. Children's anti-inflammatory gels make the child feel better: Kalgel, Kamistad. For prolonged runny nose, your doctor should prescribe an antiviral or antibacterial medicine. The type of medicine depends on the nature of the infection; it can be viral or bacterial.
Give your baby more fluids during teething. The daily norm is from 1 to 1.5 liters. Water helps the baby tolerate inflammation more easily and reduces the risk of complications. The drink must be warm.
For a short period of time (no more than 5 days), vasoconstrictor drops can be instilled. They are used only for persistent congestion that prevents full breathing.
Pay special attention to the sleep of a sick child. It is during this period that proper rest is important for him. Before going to bed at night, rinse the baby’s nose and clean it of dried crusts. To maintain immunity and improve the quality of night and daytime sleep, take short walks in the fresh air.