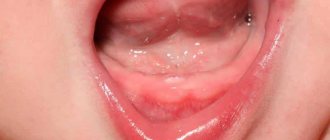
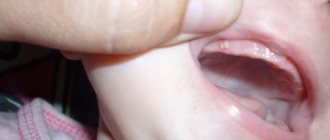
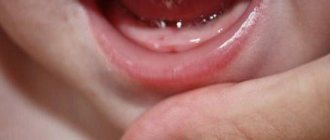
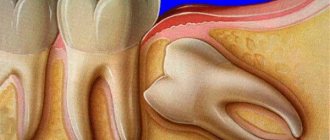
Perforation of the floor of the maxillary sinus
The paranasal sinuses are a system of cavities in the bones of the skull located around the nose.
The nasal cavity and accessory sinuses are connected by small canals. The maxillary, frontal, main sinuses and ethmoidal cells are distinguished. Thanks to them, certain parts of the skull bones are filled with air. The meaning of such formations is to increase the volume of the skull, which contributes to the growth of the volume of our brain without excessively increasing its mass. The accessory cavities are located in the bones of the skull and are practically not subject to tensile loads, so the bones in these parts degrade.
The sinuses have a special mucous membrane, which is formed by small processes - cilia, covered with mucus. With each pulsation of the cilia, mucus, along with dust particles that penetrate here during breathing, are directed to the nose. Thus, self-cleaning of the sinuses occurs.
This material will tell you what is the difference between sinusitis and sinusitis.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane can lead to disruption of the self-cleaning mechanism. The drains can become clogged, and then pus collects in the paranasal sinuses. This is an acute form of sinusitis.
The roots of the teeth of the upper jaw protrude into the maxillary cavity. If you count from the center to the side, then from the 4th to the 8th tooth from above are limited by the maxillary cavity. If the sinus is sclerotic - small, neat, then there are fewer problems with it. If the pneumatic sinus is wide, then its bottom goes around the tops of the dental roots. Hence the mutual relationship of inflammatory processes occurring in the sinuses or in the upper jaw.
Perforation of the bottom of the maxillary (maxillary) sinus is one of the complications that can happen to a patient in the dentist's chair.
And although the main classification of diseases ICD 10 does not separately identify such a disease, it still occurs quite often.
We will tell you about what it is - perforation of the maxillary sinus, why such a problem occurs, how it is treated, what such a complication is fraught with and what to do to avoid it.
The maxillary sinus (its other name is the maxillary sinus) is located in the thickness of the bone tissue of the upper jaw. It is separated from the oral cavity by the alveolar process of the upper jaw, which forms its bottom. The volume of such a sinus is quite large, and in adults it can reach 10 cubic centimeters.
Runny nose during teething - how to treat a runny nose during teething in children
Teething causes pain, so the baby may be constantly capricious. Sometimes parents doubt that their offspring has a stuffy nose due to teething. How to distinguish a regular runny nose from a “dental” one? Only a doctor can accurately determine the cause of snot, but an attentive mother can notice some symptoms:
- The baby is salivating profusely. This phenomenon sometimes becomes more noticeable, and sometimes disappears altogether. In the “hottest” moments, saliva can flow in a continuous stream and cause particular discomfort - the baby constantly has wet clothes on his chest and tummy. This leads to diaper rash and skin irritation. Some mothers even wear bibs, which have to be changed several times a day.
- The gums are swollen, they may hurt and change color. If the normal color of the gums is pale pink, then during this period it becomes bright pink, with a purple tint. Sometimes hematomas can be seen on the gums in places where the top of the tooth has approached the surface.
- The baby does not sleep well, crying out sharply in his sleep. He also sometimes refuses the pacifier or breast. If the baby cannot use his gums or suck milk at all, he should be given water from a plastic cup or spoon.
- The baby sometimes grabs himself by one or the other ear - this is how teeth can go. It is important not to miss the signs of otitis media. You need to slightly pull your ear down - if this action does not cause crying or screaming, then everything is in order.
- Diarrhea is also an indirect sign of teething.
If such symptoms occur against the background of rhinitis, there is a high probability that the child will soon please his mother with his first or subsequent tooth. Despite the fact that the cause of rhinitis is teeth, it is still necessary to treat it, since any runny nose in such a baby can lead to complications.
To determine whether a baby's incisors are cutting or his body is fighting an infection, you need to pay attention to body temperature. When teething, it should not exceed 37.5 °C, and according to Dr. Komarovsky, a temperature of 38 °C is also acceptable.
It is also important to determine how long the elevated temperature lasts. With the growth of dental units, it should not last more than 2–3 days; infectious diseases are characterized by an increase in temperature from 37 to 40 ° C and its duration over 3 days.
| Sign | Teething process | Infection |
| Consistency | “Tooth snot” is watery, does not make breathing difficult and does not cause discomfort to infants. | Watery discharge gradually becomes viscous. During the day, they dry out and form crusts, making breathing difficult. |
| Color | The mucus has an exceptionally transparent color. | The initial stage of rhinitis is characterized by the release of clear snot, which then becomes cloudy and turns yellow. When bacteria accumulate, the snot turns green. |
| Abundance | “Snot on teeth” occurs periodically throughout the day, not in abundance. | Discharge does not flow from the nose, congestion occurs. The snot needs to be blown out. |
| Duration | The nose may become blocked for 3 to 5 days. | Rhinitis lasts 10–14 days. |
Parents should focus on how long a runny nose lasts during teething, since the symptoms of infectious rhinitis in the initial stages are similar to the signs of inflammation of the nasal mucosa for physiological reasons.
A runny nose that occurs in children when teeth appear most often does not require drug treatment. To help babies survive the teething process more easily, you need to:
- Periodically clear the nasal cavity of mucus using an aspirator. This should be done as snot accumulates in the nose.
- Rinse the nose with herbal decoctions or saline solutions.
- Monitor the child's water balance - the baby should drink a lot of warm water.
- Humidify the air in the room. This can be done either with a humidifier or with improvised means (a bowl of water, damp laundry).
- Ventilate the room at least 4 times a day for 15 minutes.
- Make sure your baby stays in bed.
We suggest you read: Red spot on the palate of an adult The following folk remedies help get rid of nasal congestion:
- steam inhalations with medicinal herbs, salt or soda solution;
- instillation of diluted aloe juice into the nasal cavity;
- mustard foot baths.
If nasal congestion is severe and makes breathing difficult, and “tooth snot” is green in color, the use of nasal drops is acceptable.
Many parents try to cure such a runny nose with vasoconstrictors, but their use can result in the body getting used to them and constant swelling of the nose.
Therefore, only a doctor should decide how and with what to treat snot during teething.
Pediatricians, when examining a sick child, pay attention to the throat and oral cavity. If a 4-8 month old baby has noticeable swelling on the gums, the doctor concludes that the period of dentition has begun.
The gum tissue and nasal mucosa share a common blood supply. During the teething phase, the gums are actively supplied with oxygen through the capillaries, and this leads to increased blood supply to the walls of the nasal cavity.
The glands of the nasal mucosa begin to work more actively, which serves as an impetus for the production of mucus.
The second possible cause of a runny nose is a decrease in the body’s immune defense during dental procedures. The contact of viruses or pathogenic microorganisms on the baby’s nasal mucosa will almost certainly lead to the development of the disease. In this case, the period of teething will aggravate the course of the disease, reducing the body's resistance to infection.
Strengthening the baby's immunity
Timely vaccinations for the baby play an important role in this matter, since in this way it is possible not only to strengthen the baby’s immune system, but also to develop protection against various serious diseases.
The vaccination calendar in all countries is almost the same, since it is developed taking into account the state of the body of children at a certain age.
Parents who try to refuse vaccination or postpone it to a later date are often playing with fire and risking the health of their child.
Hardening gives excellent results, so it is better to start it as early as possible. For newborns, for hardening, it is enough to do contrast dousing procedures on the arms to the shoulders, using alternately cold (+20°) and hot (+35°) water, gradually increasing the area of the treated skin and the duration of the session.
The baby will not feel much difference in the temperature of the water, so it will not experience negative sensations, but this will be enough to stimulate the immune system.
It is also necessary to harden the mucous membranes; they must respond quickly to changes in ambient temperature, and this requires frequent training. It is important that the baby is often outdoors.
A balanced diet plays a significant role in strengthening the immune system of newborns, so it is very important to maintain breastfeeding. With mother's milk, the baby receives a sufficient amount of antibodies that protect his body from many infections and diseases.
After a child switches to a more varied diet, it is necessary to maintain the correct balance of microelements and vitamins in the body.
Vaganova Irina Stanislavovna, doctor
Causes of pus formation
Pus in the nasopharynx usually appears as a complication of a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. Rarely - as a consequence of injury, improper treatment of teeth and gums.
An independent disease is only tonsillitis caused by the proliferation of streptococcus.
Factors contributing to the appearance of pus in the nasopharynx:
- Sore throat, including viral and mycotic forms.
- Complications of acute respiratory infections - rhinosinusitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis.
- Periodontal disease.
- Overgrowth of adenoid tissue, constant inflammation in the nose.
- Retropharyngeal abscess is a complication of tonsillitis. It develops when treatment protocols are violated and there is no antibacterial therapy.
- Nose injuries accompanied by deviated septum and stenosis of the passages.
- Condition after surgery on the oral cavity, nasopharynx. Pus can be a complication due to improper treatment, neglect of antibiotics, and antibacterial agents.
- Stomatitis, candidiasis of the nasopharynx due to decreased immunity.
Possible causes of pus in the sinuses and throat include treatment with aggressive drugs, chemotherapy, and HIV.
Odontogenic sinusitis is a bacterial or viral disease caused by the penetration of infections into the paranasal maxillary sinuses as a result of damage to the upper molars.
If prompt, comprehensive treatment is not started by an otolaryngologist and dentist, odontogenic sinusitis quickly turns into purulent. This risks the treatment taking weeks or even months. During this time, the inflammatory process will take root in the sinuses, and the disease will be chronic.
The inflammatory process can occur in the absence of oral care. If you do not follow the dentist’s instructions in a timely manner, delay treatment, or brush your teeth irregularly, you may encounter unpleasant consequences.
The flow of mucous secretion (snot) from the nasal cavity is in itself an extremely unpleasant process. If they are purulent, then many people immediately panic.
Sometimes pus comes out of the nose in its pure form or mixed with the blood.
In addition, sometimes people complain of a rotten, unpleasant odor from the nose.
Any of the above situations requires increased attention and proper treatment. Do not try to diagnose yourself. Timely consultation with a doctor will help avoid adverse health consequences.
All existing causes are very dangerous. After all, the presence of pus in the snot indicates an inflammatory process in full swing. And if we remember that the location of inflammation is in close proximity to the brain, then without further explanation we will understand the degree of danger.
Treatment of advanced sinusitis will be complex. In almost 100% of cases it will require the use of antibiotic drug therapy.
Remember, if you have inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, you cannot choose your own antibiotic. This is due to the fact that there is no universal cure for all bacteria that can cause inflammation. Only a doctor can choose the right drug based on test results.
Also, in the treatment of sinusitis and frontal sinuses, a variety of physiotherapeutic techniques are used, based on rinsing the nasal passages and paranasal sinuses with medicinal solutions.
Purulent runny nose or rhinitis is an inflammatory disease of the nasal mucosa. Its main symptom is the discharge of snot with pus.
The inflammatory process occurring on the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity threatens the occurrence of serious complications.
Firstly, it can lead to the development of atrophy of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, in which case it begins to degrade and die. Many of the changes that this pathology brings with it are irreversible. For example, this is the ability to perceive smells.
In this regard, when purulent rhinitis appears, timely and correct treatment is required. If a bacterial infection develops severely, it will most likely not be possible to do without antibiotics. However, with timely consultation with a doctor, there are cases where successful drug therapy was carried out using less strong medications. For example, Protargola or Collargola.
Both of these drugs are solutions of colloidal silver that have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effects.
A boil in the nose appears due to a bacterial infection in the hair follicle - the sac from which hair grows.
With a boil, pus flows from the nasal cavity at once. This only happens after the boil has broken through.
If such a symptom occurs, go to the doctor. He will select the right therapy that will relieve pain and prevent complications.
All materials are for informational purposes only.
Before using the information received, consult your doctor.
Copying of materials is permitted only with an active link to the source.
Bacterial sinusitis very often leads to the accumulation of purulent contents in the paranasal cavities. The main line of therapy in this case is the fight against pathological bacteria with the help of antibiotics. Along with suppressing the bacterial flora in the inflamed sinuses, every doctor has a second task - restoring the drainage function of the maxillary sinuses. And if…
Ceftriaxone is a fairly strong antibiotic that is often used for sinusitis. In this case, you should understand how to properly carry out treatment and what precautions should be taken.
At the same time, it is prescribed to treat the following problems: infections of the lower and…
We suggest you read: Is tooth decay transmitted through a kiss? Is it possible to get infected with it?
A special effect can be obtained by using the drug furatsilin, which has a disinfecting effect.
Sinusitis is an inflammatory process localized in the maxillary sinus of the nasal cavity. The treatment of the disease is carried out not only by an ENT specialist, but also by a dental surgeon. Dentistry deals with the treatment of odontogenic sinusitis.
The infection can come from both the nasal passage and the oral cavity. If the source of infection is a diseased tooth, we are talking about an odontogenic disease, and if the infection comes from the nasal cavity, it is a rhinogenic disease.
The acute course of the inflammatory process usually begins with the serous stage. It is characterized by the following symptoms: swelling, blood vessels are dilated, cells are filled with fluid. If timely treatment is not started at this stage, sinusitis goes into the purulent stage.
The purulent stage is characterized by the following symptoms: a repulsive odor from the mouth, weakness and fatigue, pain in the head. Breathing through the nose is difficult, body temperature is higher than normal. Each of the listed stages has two options - to occur in acute or chronic form.
With purulent sinusitis, the symptoms are more pronounced. Additional symptoms occur (sharp pain when touching one part of the face or pain when tapping with a spoon on the teeth whose roots are located in the affected area)
X-ray diagnostics are used to identify affected teeth. But the most reliable diagnostic method is endoscopy. The procedure is carried out using a special device - an endoscope.
A wide viewing angle allows you to carefully examine the condition of the sinus and anastomosis.
Traditional methods are ineffective for odontogenic sinusitis. Treatment is possible only with the help of a specialist. The first thing therapy begins with is eliminating the source of infection. After this, the oral cavity is sanitized.
After removing the source of the disease, it is necessary to use drugs that promote vasoconstriction for several days. This is necessary so that the mucous membrane returns to its pre-inflammation state.
After the operation, the nasal cavity is washed with a solution every day for a time determined by the attending physician.
At his discretion, the doctor can prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, and if the patient is bothered by acute pain, prescribe painkillers.
How can I help my child?
If nasal discharge is a consequence of teething, then you should not resort to using special medications to treat a runny nose. To alleviate the child’s condition, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- Optimal humidity in the room will ensure normal breathing for the baby and prevent the mucous membrane from drying out.
- Rinsing can be used as an additional means to ease breathing. This can be done using a special solution that is sold at the pharmacy.
- If the baby does not know how to blow his nose, then special aspirators or nasal bulbs can be used to remove accumulations of mucus.
- Dried crusts that remain inside the nose should be removed using special cotton wool, pre-moistened in saline solution.
- During this period of time, it is necessary to give the baby as much fluid as possible. The extra fluid helps remove mucus from the body.
- If severe congestion is observed, then it is necessary to use special nasal drops.
- Special medications will help relieve symptoms.
Such symptoms do not require special treatment during this period. Even without using any special means, all symptoms will go away on their own as soon as the tooth appears on the surface of the gum.
In addition to traditional methods, you can use traditional medicine to help the baby alleviate the condition during a given period of time. Among the most common recipes are:
- instillation of aloe juice;
- inhalation with fir or eucalyptus oil;
- softening mucous membranes with honey.
Recipes containing honey should be used with caution, as many babies may have allergic reactions to this product.
Symptoms of toothache with sinusitis
Many of us are faced with various problems related to teeth, for example, odontogenic maxillary sinusitis or chronic odontogenic sinusitis, which will be discussed today.
These diseases are very similar and extremely unpleasant.
The worst thing is that diagnosis requires modern equipment, so it is worth understanding the symptoms in detail in order to be able to determine the development of the disease and take timely measures.
What kind of disease
Odontogenic sinusitis is a complex disease. Infections penetrate from the affected tooth, resulting in inflammation in the mucous membrane, as well as the submucosal layer of the maxillary sinuses.
The upper jaw has such a structure that the disease affects its back teeth. This is because the upper molars and premolars are very close to the maxillary sinuses and practically touch them.
Because of this, a diseased tooth can easily provoke infection of the paranasal sinuses.
Most often, acute odontogenic sinusitis of the maxillary sinus develops exclusively in one of the sinuses: right or left, it depends on which side the affected tooth is located. Then the other side becomes infected, after which bilateral sinusitis occurs.
In some cases, the infection can spread to other sinuses, especially if the immune system is weak.
The main reason for the development of the disease is infection from the affected tooth. This may happen in the following cases:
- Poor dental care, rare visits to the dentist. This leads to caries beginning to develop, and if everything is really bad, then nerve necrosis. The inflammation begins to gradually spread and ends up in the maxillary sinus.
- Seal. There are tooth roots that can be very close to the maxillary sinus, which is why when treating deep areas, the filling material can get into it.
- Is it possible to remove a tooth? After a tooth is removed, a channel is formed in its place, which allows infections to pass through. Provided that the root is not far from the sinus, inflammation is only a matter of time.
- Pathologies. It is not uncommon for this disease to form due to a cyst, especially if it suppurates.
That being said, there are several types of patients at risk of developing odontogenic sinusitis:
- Those who have undergone a large number of operations related to the upper jaw.
- People with weak immune systems.
Regardless of the causes of the disease, its symptoms are always the same:
- The sense of smell disappears, it can disappear completely.
- Migraines, feeling of weakness.
- Fever and chills.
- On teeth that have provoked inflammation, an aching sensation occurs; if you tap on them, a sharp, severe pain is felt.
When the disease worsens, the signs become more noticeable, and especially if it becomes purulent. When inflammation subsides, symptoms remain but become less intense, making them difficult to recognize.
If the cause of the infection is constantly located at the roots, as well as in the sinus in the teeth, then pain will be felt with sinusitis. Because of this, patients cannot eat solid food, although they feel absolutely healthy.
In addition to all this, a fistula may form. Its sign will be that liquid food consumed by a person will flow out of the nose along with pus. This only happens when you are in an upright position.
Odontogenic sinusitis is a disease that should be treated by an otolaryngologist, but in cases where it has developed due to dental problems, you should contact a good dental surgeon.
It is worth noting that odontogenic chronic sinusitis is easy to detect, but finding the cause is not so easy. To do this, you will need to take a good medical history.
If a patient has odontogenic sinusitis, its main symptom is pain in the teeth. To accurately determine the disease, an examination is required, after which the patient is prescribed:
- A thorough examination of the oral cavity using x-rays.
- Diaphanoscopy.
- Puncture of the affected sinus.
- Examination of the nasal cavity using a rhinoscope.
- MRI and CT.
If chronic odontogenic maxillary sinusitis is diagnosed, the doctor decides how odontogenic sinusitis will be treated, based on the patient’s condition.
In any case, antibiotics are necessarily prescribed, and their selection occurs individually, based on many factors. Caries and any other dental diseases are urgently eliminated. In most cases, the tooth has to be removed.
If the cause of dental sinusitis is any foreign body that is in the maxillary sinus, it must be surgically removed. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Through the gum, the surgeon approaches the area that has been affected by the disease. This allows you to prevent the formation of surgical marks on the patient’s face.
If the case turns out to be severe, then to eliminate the disease it is necessary not only to remove the foreign body, but also to perform a sinusotomy.
The essence of the operation is that its contents are sucked out of the sinus, the affected areas of the mucous membrane are eliminated, if there was a fistula, it is sutured, and its course is closed with a flap taken from the inside of the cheek.
All this is performed using endoscopic equipment, which is introduced through the nasal cavity. It doesn’t matter what the patient’s treatment was, in any case, after it the patient is prescribed:
- Antibiotic treatment of sinusitis and teeth.
- Rinsing the nose with special solutions.
- Use of drugs with vasoconstrictor effects.
- In order to soften dry crusts, sea buckthorn oil is used.
In cases where sinusitis occurs during pregnancy, treatment is temporarily delayed until after labor has passed. Before them, physiotherapy, UHF and local antibiotics are prescribed.
In some cases, for pregnant women with illness, a puncture is used, which causes relief for some time.
We invite you to read: Lump on the lip - what is it and which doctor should I contact?
Treatment with folk remedies is extremely dangerous; you can pay for it with your health, and sometimes even with your life. Often the disease develops and becomes purulent, which can cause severe complications, such as brain damage.
Skillfully assessing the patient’s condition, as well as the advanced state of the disease, the doctor prescribes the rehabilitation of odontogenic sinusitis using one of the methods. After a successful operation, doctors recommend the following:
- Rinsing the nasal cavity with medicinal herbs and infusions.
- Inhalation.
- Propolis infusion.
In general, it is impossible to cure the disease with home remedies.
It is very important to take care of your teeth, as well as the entire oral cavity in general, so as not to get sick. It is advisable to visit the dentist at least once every six months.
It is necessary to treat all diseased teeth, and you should only contact good specialists. It is highly recommended not to let diseased teeth get to the point where they need to be removed.
Such an operation contributes to the development of sinusitis due to a diseased tooth, and generally impairs a person’s ability to chew. It is also worth following the following recommendations:
- Try not to visit places where there are a lot of people during the period of ARVI and flu.
- If necessary, you should take vitamins and immunomodulators.
- It is advisable not to allow any chronic pathologies to develop.
Conclusion
So we looked at what odontogenic sinusitis is, its symptoms and treatment. The disease is complex, but if diagnosed in time, it can be successfully treated and complications avoided.
Yulia Kalashnik
With sinusitis, the patient either does not notice anything at all, or feels slight pressure under the eye. Some complain of nasal discharge containing pus and blood.
There are a number of symptoms that you should pay attention to:
- the whole side of the skull hurts;
- discomfort in the nasal and frontal sinuses;
- upper jaw ache;
- pain spreads to the area near the nose, under the eye, above the eyebrow, temple;
- unilateral headache with sinusitis;
- general malaise, temperature.
A special characteristic sign of sinusitis is a feeling of dull, pressing pain when bending the head forward. In this position, the pain is most acutely felt in the paranasal area. Thick purulent discharge is sure to appear.
An ordinary toothache does not produce such symptoms. It is felt only in the area of the diseased tooth. The feeling is more acute, aching.
Yellow nasal fluid or brown mucus
Clear, liquid snot usually appears when a virus is present. Such pathologies are not dangerous and can be easily treated if the doctor’s instructions are followed. However, the appearance of brown or yellow snot is a sign of a serious illness that can harm your health and cause other complications.
When the color of the mucus changes, suspicions fall on sinusitis. The fact is that the facial sinuses become inflamed, and small vessels in the nasal mucosa begin to burst. Because of this, the blood mixes with the liquid, and the result is a brown tint of snot. The mucus may turn green - this is a harbinger of a bacterial infection. At the same time, the patient often begins to sneeze. It is worth monitoring the characteristics of nasal discharge, as this information can be very useful when prescribing therapy.
Treatment of congestion in the nasopharynx
Treatment of plugs of pus depends on the patient’s diagnosis, age, and medical history. A prerequisite is massive antibiotic therapy with system-wide agents to suppress the bacterial flora in the nasopharynx. If the mycotic nature of the disease is proven, the prescription of antifungal drugs is indicated.
For diseases of the nasopharynx, local antiseptics are used: drops, spray, solution, tablets. Additionally, physiotherapy is indicated.
In difficult cases - sinusitis, retropharyngeal abscess - surgical treatment is performed. Puncture of the paranasal sinuses is performed with drainage of the source of pus formation.
Medicines are prescribed by a therapist, infectious disease specialist, ENT specialist, maxillofacial surgeon or dentist - the doctor’s choice depends on the cause of the nasopharynx disease.
Traditional methods for treating pus of such localization are ineffective.
Medication
Pus forming in the nasopharynx is a sign of a bacterial process. Candidiasis forms of diseases of the throat and oral cavity are rare.
At the beginning of treatment, tests are needed for bacteriological examination and determination of sensitivity to antibiotics. The results will be ready no earlier than in 5 days. To suppress pathogenic flora, drugs with a broad spectrum effect are used.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
The dosage form depends on the severity of the disease and the patient’s condition. Suspensions, tablets, intramuscular injections, and intravenous infusions are allowed.
Drugs used for pus inside the nasopharynx:
- Penicillins, including synthetic ones - mainly for purulent tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis. Augmentin, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav. Tablet forms and suspensions are taken 3 times a day.
- Cephalosporins - for any diseases of the nasopharynx and maxillary sinus system. Available in different dosage forms. The doctor will prescribe Ceftriasone, Cefutil, Zatsef, Cefix, Zinnat. The frequency of administration is 2 times a day with an interval of 12 hours.
- Macrolides are well accumulated by the respiratory system. Azithromycin, Clarithromycin of various forms. The frequency of taking medications for pus based on Azithromycin is 1 time per day, Clarithromycin is 2 times.
- Fluoroquinolones are rarely used to treat the respiratory system. The main indication for this group of drugs is diseases of the urinary system. They are prescribed for proven sensitivity of the pathogenic flora of the nasopharynx to fluoroquinolones, if cephalosporins or penicillins were ineffective.
- Aminoglycosides are reserve antibiotics, indicated for pus, if drugs from other groups are ineffective, for severe forms of the disease, pneumonia, sepsis.
- Sulfonamides are antibacterial agents on an inorganic basis, prescribed as auxiliaries to antibiotics.
- Local means for treating the throat - antibacterial sprays, tablets, solutions. The active ingredients suppress bacterial and fungal flora. Drugs - Tantum Verde, Forteza, Angilex, Heppilor, Hexoral, Lizak, Strepsils. Used for all diseases of the nasopharynx, including pathologies of the gums and teeth.
- Medicines for washing and removing masses of pus from the nasal passages - Dolphin, Aquamaris, systems based on saline solution, sea water. They have an antibacterial effect, remove exudate, and make breathing easier.
- Means for stimulating mucous secretion in the maxillary sinuses - accelerate the evacuation of contents from the nasopharynx and have an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Nasal drops - antibiotics, vasoconstrictors, allergy remedies.
- Antimycotics - if the fungal nature of the disease is confirmed. They use tablet preparations, means for local treatment of the oral cavity: Fluconazole, Itracon, Candide.
The course of treatment for nasopharynx pus is at least 7 days, usually 10-14.
At the first signs of improvement, it is forbidden to discontinue antibiotics and antibacterial agents.
Surgical
Surgical treatment for pus in the nasopharynx is carried out if drug therapy is ineffective. The list of indications is limited.
The operation will be prescribed in the following cases:
- Puncture of the maxillary or frontal sinuses - for sinusitis or frontal sinusitis. It is carried out on an outpatient basis or on a hospital basis. The puncture is made through the nasal wall, the cavity is drained and washed with antibacterial agents. The catheter remains for the entire duration of treatment and is used for forced lavage of the sinuses and removal of pus. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
- Sinusotomy - if the cause of the process is cysts, formations in the sinuses, or a chronic form of sinusitis. There are 2 methods of surgical intervention - classical, through an incision in the oral cavity, and endoscopic - through the nasal passages. Both procedures are performed in a hospital setting. With classical maxillary sinusotomy, general anesthesia is indicated, with endoscopic – local anesthesia.
- Purulent plugs in the nasopharynx and tonsils after tonsillitis. The minimally invasive procedure is often performed without pain relief. It is indicated for exudate in the lacunae of the tonsils that have not opened after the inflammatory process has stopped. No hospitalization required.
- A retropharyngeal abscess is a severe complication of inflammation; it can only be treated surgically, with access to the nasopharynx through the oral cavity or an incision in the neck. If the cause of pus is syphilis or tuberculosis, puncture is performed to remove the infiltrate. The operation is performed in a hospital setting. The method of pain relief depends on the severity of the condition and the age of the patient.
- Diseases of the teeth and gums – if conservative treatment is ineffective. Tooth root resection, procedures for periodontal disease. Usually does not require hospitalization.
- Restoration of nasal structures after injury or surgery.
- Removal of tonsils and adenoid tissue.
Traditional methods
In folk medicine, there are no recipes with proven effectiveness for diseases that cause the formation of pus inside the nasopharynx.
Gargles and lubricating the throat with Lugol's solution are used, but these methods cannot completely suppress germs.
Do not replace the prescriptions of traditional herbalists with the prescriptions of official medicine to get rid of pus.
Treatment
Treatment of perforations of the maxillary sinus floor depends on what changes are present in the sinus cavity itself.
Treatment without surgery is possible only in cases where perforation occurred during tooth extraction and was detected immediately, and according to radiography there are no signs of infection of the sinus cavity or the presence of even minor foreign bodies in it. With this option, the doctor’s tactics are to preserve the blood clot formed in the socket as carefully as possible, as well as to prevent its infection. To do this, a small gauze swab soaked in iodine solution is inserted into the lower part of the hole. Usually it is tightly fixed in the wound cavity on its own, but sometimes sutures are required on the gum. This treatment with iodine continues for at least 6-7 days until full granulations are formed and the defect is closed. In this case, the tampon is not removed from the hole so as not to damage the blood clot.
It is also possible to temporarily close the defect with a small plastic plate, which is fixed to adjacent teeth with clasps. It separates the oral cavity and sinuses, which promotes healing of the perforation.
At the same time, a course of preventive measures is prescribed, aimed at preventing the development of inflammatory complications. It includes taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, drops with a vasoconstrictor effect. This course is carried out on an outpatient basis or at home.
If, during perforation, foreign bodies penetrate into the sinus (implant, filling material, fragment of a tooth root), then treatment is carried out only in a hospital setting. In this case, an operation is indicated to open the cavity of the maxillary sinus, remove the foreign body and non-viable tissue, followed by plastic closure of the perforated defect.
Under what circumstances can a tooth hurt?
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinuses is caused by various reasons. The disease is most often caused by dental problems. This is why you may be referred to an ENT specialist and a dentist at the same time regarding sinusitis.
Odontogenic sinusitis is diagnosed when the cause of inflammation of the maxillary sinus is a diseased tooth. If the 4-8 tooth in the upper jaw becomes inflamed, then sinusitis is not far away. Inflammation of the roots easily spreads to the maxillary sinus.
Odontogenic sinusitis is difficult to treat. You can ideally wash the sinus and extinguish the inflammation, but since the real cause is not in the sinus itself, but in the oral cavity, an outbreak of odontogenic sinusitis will definitely return. That is why the ENT doctor must properly treat the maxillary sinus and then refer it to the dentist.
We suggest you find out how long after you can eat food after tooth extraction
If it is possible to save the tooth, then it is treated, carious areas are removed, filled, depulped, if necessary, and preserved. If he is completely bad, then you need to say goodbye to him.
A striking sign of odontogenic sinusitis is an extremely unpleasant putrid odor. If you smell a smell from the nasal cavity or, during puncture of the maxillary sinus, the doctor notes a sharp, unpleasant stench, then the diagnosis is unambiguous.
Because of wisdom teeth
The roots of wisdom teeth are located almost in the cavity of the maxillary sinus and this is very bad. If you have had a CT scan or a regular x-ray of the paranasal sinuses, the image will show how the roots go directly into the maxillary sinus. Periodically, wisdom teeth will provoke odontogenic sinusitis.
For most people, they deteriorate immediately after being cut. Some patients experience inflammation of the gums above the wisdom tooth as it erupts. If the gum cap is too thick, it cannot break through, so the gum has to be cut. In this case, it often turns out that the enamel under this cap is already affected by the carious process.
If you feel that you often experience symptoms of sinusitis, you need to contact your dentist and treat your wisdom teeth in the most thorough manner. Many people prefer to remove them immediately so as not to cause problems.
You will find all the information about the treatment of sinusitis without pus with swelling of the nasal sinuses in this article.
The roots of the teeth grow into the maxillary sinus, causing a chronic inflammatory process. In this case, the patient is indicated for an operation to remove the foreign body from the sinus cavity - microsinusrotomy. The operation is performed under local or general anesthesia. The doctor makes an incision above the gum in the area of the 4th upper tooth, opens the maxillary sinus and cleans or removes the root. Then the symptoms of sinusitis subside and the tooth can be saved.
Tooth root cyst
Often patients receive a diagnosis such as a maxillary sinus cyst. This is a small formation that is located on the roots of the upper teeth. People who live with this pathology are always in doubt whether to remove this cyst or not? If the cyst is in the sinus and tends to grow, then it is better not to postpone the operation. If the cyst does not increase every year, its size is small, then surgical intervention can be postponed.
A root cyst is like a time bomb. It can fester, especially in the hot season, or become inflamed due to injury or hypothermia. Suppuration occurs very quickly, the cyst causes sinusitis and severe pain. And during an airplane flight, a festering cyst may even burst. This can also happen on a high-speed train or with a jaw injury.
If the cyst ruptures, pus will pour out and the patient will suffer severe suppuration of the sinus itself. And simply prolonged contact of the cyst with the sinus will lead to chronic cystic sinusitis. Therefore, if there is a cyst, its size is more than half the size of the sinus, there is pain and cases of inflammation of the sinuses, it is better to remove the formation.
After tooth extraction
It happens that as a result of a medical error after tooth extraction, a patient develops an orantral fistula. This is the hole that connects the socket to the maxillary cavity. This happens when the root was inside the sinus, and the doctor looked at this moment on an x-ray. To prevent this from happening, the doctor must carefully examine the image.
How to recognize sinusitis in a photograph is described here.
If inflammation at the root of the tooth has led to bone atrophy and perforation of the bottom of the maxillary sinus, the doctor removes it and curettages the hole. This is followed by treatment with an antiseptic and drying the hole with a gauze swab. An osteoplastic material is applied to promote disinfection and healing of the socket. The gums are then carefully sutured to prevent bacteria from entering the wound.
From 1 to 3 weeks, the material swells and releases the antibiotic. After 3-9 months, new bone tissue will form at this site, which will close the fistula.
Sometimes patients complain that after puncture and rinsing of the sinus, the upper teeth hurt greatly. This is a normal situation; the roots of the teeth react to the antiseptic that is poured into the cavity for disinfection. Also, after the puncture, severe swelling forms, pressing on the trigeminal nerve.
Toothache may not be related to the piercing. It is necessary to check whether the sick zuyu is the cause of the sinusitis that has just been treated. In fact, it is the problem with carious teeth that becomes the primary source of problems with purulent sinusitis.
If a person visited the dentist, installed an implant and got sinusitis, it is not the dentist’s fault. The teeth in the upper jaw can grow with their roots into the maxillary sinus. Some roots are quite large, but the bone membrane is very thin and fragile.
During installation of the implant, the membrane may be damaged. The tip of the dental implant enters the maxillary cavity, causing inflammation. The problem is solved through a simple operation. Using a special instrument, the doctor cleans out polyps formed due to a foreign body, removes the implant from the sinus, and disinfects it.
It is unpleasant that the patient loses his implant. However, after completing the rehabilitation period, it can be returned to its place with one caveat. If the membrane is very thin, then it needs to be expanded before installing the implant.
Three secrets to a straight back and beautiful teeth
1. Shut your mouth!
If nasal breathing is impaired, the patient lives with his mouth open. The tongue is out of place, the jaw is pulled forward, the head is tilted. The cranial vault, neck muscles, and the spine itself are under improper load. The shoulders are at different levels. The man is hunched over. It is difficult for a chiropractor to correct posture. You need the help of a dentist and an ENT specialist to achieve free breathing.
If the trouble lay in a deviated nasal septum, then after the operation the patient feels that now he not only breathes better, but can also straighten his shoulders. This is understandable - the person had difficulty breathing through the deviated septum, and the lung muscles were under tension. When the situation was corrected, the patient immediately felt relief, his posture straightened. Then the dentist can easily build the correct occlusal plane.
2. Don't strain your jaw!
The muscles of the mouth should always be relaxed, the upper and lower teeth should not be clenched. Do not close them - there should be a distance of 1-3 mm between them. Remember this position? Have you noticed how straight your back has become? Try not to spontaneously clench your teeth whether you are watching TV, reading a book, or driving a car. The most difficult thing is to remember this rule when sorting out relationships with colleagues in the boss’s office.
It would be good to ask your spouse if you grind your teeth in your sleep. If the patient strains his jaw at night, you can purchase a mouth guard at the pharmacy, which you should put on before going to bed. And after just a few nights a person will feel comfortable in the morning. The muscles will release the jaw, and it will rest overnight.
If even after the mouth guard the patient feels stiffness and tension, you can relax tired muscles with the help of auto-training sessions. Choose the exercises that suit you best. For some, a minute of relaxation in between work is enough, while others will have to spend 10–15 minutes studying in the morning and evening. But in any case, when performing autogenic training, pay attention to proper breathing. When exercises become a habit, your posture will be better and your bite will be more correct.
3. Get examined by all doctors!
Of course, the occlusal surface changes over the years. If a tooth falls out, its violation is obvious. Fortunately, the continuity and integrity of the dentition can be restored by an experienced prosthetist.
But often a person does not notice the defect: the teeth are there and that’s enough. In fact, the canines and lower front teeth have worn down and changed the anterior bite, lateral occlusion on the left and right. The doctor offers the patient to build up the worn-out part with filling materials or crowns, but the patient does not understand why such “pampering”: they haven’t fallen out, they don’t wobble, there’s no caries... It seems that the doctor persuaded the patient and made the necessary restoration. But the dentist does not calm down - he sends the patient to a chiropractor, ENT specialist, or neurologist. And he does the right thing! Don’t be lazy – check out these doctors too.
Danger of exudate in the nasopharyngeal area and prognosis for recovery
The process of pus formation in the nasopharynx is dangerous due to its localization in the head close to the brain. Nasal congestion, exudate, heaviness in the bridge of the nose, pain may begin to be accompanied by other symptoms and cause serious consequences.
Possible complications:
- chronicity of the process;
- melting of the periosteum, bone structures;
- phlegmon;
- sepsis;
- pneumonia;
- meningitis;
- heart disease, joints;
- glomerulonephritis, chronic renal failure;
- death.
The prognosis for timely consultation with a doctor is usually favorable. After recovery, you need to follow the rules of hygiene.
It is possible to remove pus from the nasopharynx only by identifying the cause of its appearance. Do not look for the names of medications on your own, do not try to get rid of pathology with untested traditional medicine recipes, especially when treating a child. Consult a doctor to get the right treatment and avoid consequences.
The article has been reviewed
by the site editors
What Doctor Komarovsky says
Let's find out what the famous pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky thinks about a baby's runny nose during teething. The doctor considers the main causes of this runny nose to be:
- reduced immunity;
- close proximity of the mucous membranes of the mouth and nose.
Immunity
Komarovsky believes that the main cause of a runny nose during teething is a decrease in immunity. He connects this fact with the cessation of breastfeeding. To prevent a decrease in immunity during weaning, the pediatrician recommends making the baby’s complementary foods more fortified and including vitamins A, C and group B in the diet.
Proximity of mucous membranes
This is the so-called anatomical factor, a natural feature of the child’s body inherent in nature. The inflammatory process in the oral cavity, in the immediate proximity of the nasopharyngeal mucosa, easily penetrates there and causes a runny nose.
On video how to treat a runny nose during teething in children according to Komarovsky:
Komarovsky advises parents not to panic and not show strong concern with this type of runny nose. But only if this symptom is not accompanied by a high temperature. In the latter case, and if the discharge is excessively abundant, urgent treatment is necessary. These symptoms indicate the introduction of harmful viruses into the child’s body.
Attention: parents need to be on alert, and if the runny nose lasts for more than 5 days, and the discharge from clear becomes cloudy or greenish, a doctor’s help is necessary. Komarovsky considers the maximum permissible temperature during teething to be 39 degrees. If the temperature is higher or lasts longer than two days, it is already a viral infection.
This information will help you understand which nebulizer solutions for a runny nose are the most popular for children to use.
But what is the most popular medicine for an inhaler for cough and runny nose and its name is described in great detail in this article.
But how to use the Omron cough and runny nose inhaler and how to do it correctly is described in this article.
If the child is very small, then it will be interesting to know what inhalations a 3-year-old child should use for a runny nose.
Treatment of inflammation
If the root cause of your sinusitis is dental problems, then comprehensive treatment must be carried out. First you need to cure the diseased teeth, then begin treatment for sinusitis.
Antibiotics
For sinusitis, a course of antibiotics is prescribed in the form of drops, tablets and ointments. In severe cases, injectable drugs are prescribed.
What drops are prescribed:
- Isofra.
- Fluimucil.
- Polydexa.
Price – from 340 rub.
Find out which is better than Polydex or Isofra here.
List of ointments for sinusitis:
- Vishnevsky.
- Ichthyol.
- Levomekol.
- Syntomycin.
Symptoms
Let's look at exactly what external manifestations we can understand that the baby has a runny nose from teething.
- The child's appetite decreases.
- The baby becomes restless, capricious, and sleeps poorly.
- He is salivating profusely.
- The gums swell.
- Sometimes the temperature may rise.
- Often the child develops indigestion and diarrhea.
- Often, in addition to a runny nose, a cough also appears. But, as a rule, coughing attacks are infrequent and without clearing the throat. This is simply a way to get rid of microbes that irritate the nasopharynx, an attempt to “clear the throat.” A cough that appears does not require serious treatment. You certainly shouldn’t give your baby antibiotics for fear that he has a sore throat. If you suspect that the cough is not simple, it is better to consult a pediatrician for your own peace of mind.
Having seen all these symptoms (of course, if the child is at the right age: from 3 to 12 months), you can almost accurately diagnose that he is teething. In addition to the listed symptoms, the process of teething is often accompanied by the following signs:
- the child chews everything he can reach;
- constantly whines, sobs, cries;
- A characteristic gesture is to cover his ears with his hands. The child reaches for his ears because the pain echoes in them.
What is the best remedy for inhalation with a nebulizer for a runny nose can be seen in this article.
But this article will help you understand what cough occurs most often during teething in children.
It will also be interesting to learn about how to treat a runny nose with a nebulizer: https://lechim-gorlo.ru/n/lechenie-n/ingalyacii-nebulajzerom-pri-nasmorke.html
You may also be interested in learning about what to breathe through a nebulizer when you have a runny nose.