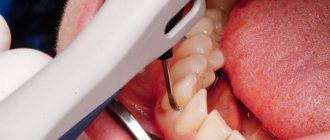
Application anesthesia (from the Latin applicatio - application) is a non-injection anesthesia in which an anesthetic is applied to the oral mucosa, hard dental tissues or pulp in the form of an ointment, gel or spray - without any injections.
Application anesthesia also has other synonyms - terminal or superficial. Allows painless treatment of teeth and gums, grinding of teeth for prosthetics. In pediatric dentistry, this procedure is simply irreplaceable for almost all manipulations - no needles and syringes, which frighten children so much.
Mechanism of action of surface anesthesia
Anesthesia occurs as follows: the anesthetic enters the tissue of the crown or gums, “seeps” 1–3 mm deep and affects the terminal nerve endings - the “end” parts of the nerve fibers. As a result, the fibers temporarily lose sensitivity. The effect occurs within a few minutes and lasts up to a maximum of half an hour.
The method allows you to temporarily relieve the sensitivity of the mucous membrane of the oral cavity and gums, dentin, that is, internal hard tissues, and pulp (neurovascular bundle).
Varieties
Application anesthesia agents can be classified according to their principle of action:
Cauterization
This is the first method of pain relief, which uses strong drugs, such as: silver nitrate; zinc chloride, etc. With their help, not only periodontal tissue, but also dental tissues can be frozen.
When such drugs penetrate into tissues, they narrow the pores and thereby prevent any effect on nerve cells. This method gave good results, but did not become very widespread due to the substances used. Since they belong to the group of toxic substances, when they enter the mucous membranes and tissues they have a destructive effect on tooth enamel.
Dehydration
In this case, the drugs have dehydration properties, which are aimed at reducing pain. In most cases, these are hydrocarbonates or carbonates, for example: potassium, sodium, etc. with a similar effect.
They reduce the sensitivity of tissues and teeth, as they remove moisture from enamel and dentin. This method is often used for minimal manipulation of the teeth and also for high-quality teeth cleaning.
Physiologically active compounds
Such preparations include strontium, aspirin and sulfidine pastes. Their action is aimed at dentin receptors, thereby stopping the transmission of impulses to nerve cells.
In addition, such pastes, or rather the substances contained in them, have a therapeutic effect, as a result of which they are used in the treatment of teeth with damaged enamel, etc. Periodic use of such compositions restores damaged tissue and helps strengthen teeth.
Local spectrum painkillers
The most famous drugs for surface anesthesia. With their help, you can quickly numb the area for a certain period of time. To do this, specialists use concentrated anesthetics : lidocaine, tetracanine, etc. Substances quickly block the sensitivity of nerve endings.
Indications for use in dentistry
- Treatment of simple caries. Tissues affected by caries are impregnated with an anesthetic that eliminates the sensitivity of dentin;
- hyperesthesia. In case of pathological sensitivity of teeth, an anesthetic drug is rubbed into the hard tissues;
- treatment of pulpitis. A swab moistened with medication is placed under a temporary filling at the bottom of the carious cavity, as a result of which the sensitivity of the pulp is reduced;
- grinding of “living” teeth before prosthetics;
- removal of milk and pathologically mobile molars;
- removal of tartar. The anesthetic is applied to the gums and enamel; opening of submucosal abscesses. When cleaning the tissues from pus, the gums must be numbed.
Superficial anesthesia is often used as additional pain relief before an injection. To administer the drug painlessly, an anesthetic is first applied to the injection site. After this, the patient does not feel discomfort or pain during the injection.
Technique
The drug is applied to tissues by lubrication (with ointments, gels and pastes) or irrigation with a spray. When anesthetizing the pulp and dentin affected by caries, cotton swabs are soaked in an anesthetic and placed in the drilled cavity.
For maximum effectiveness, teeth are sealed from saliva using a rubber dam, a thin sheet of latex that is placed over the tooth and secured with metal clips.
It is important to understand that you should not expect a powerful effect from application anesthesia of the tissues of molar teeth. In comparison with injection methods of local anesthesia, superficial, of course, loses. Nevertheless, the result is sufficiently evident.
Rubber dam for saliva isolation
How is the procedure done?
- scalp preparation;
- applying a medicinal composition to it using a special brush that stimulates blood flow and eliminates dead epithelial cells;
- the effect of a steam sauna, which opens pores, removes toxins, deep penetration of active ingredients and enhances their effectiveness;
- washing your hair, applying a special solution to the skin;
- drying with a warm hairdryer.
To enhance the effect, therapeutic massage of the cervical-collar area is also used, which allows you to activate local metabolism by stimulating blood circulation. In addition, it helps relieve muscle spasms, increase skin elasticity, and has a calming effect. Complements the complex of home care procedures in accordance with the recommendations of a trichologist.
The duration of treatment is usually at least six months. It is divided into two stages:
- main (about 4 months), during which the hair condition is normalized and the scalp is healed;
- supporting (its duration is determined by a specialist) - allows you to consolidate the result.
It is important to know!
The exclusive IHC procedure - Application Method - allows you to saturate the scalp with useful substances, ensuring an improvement in the external and structural characteristics of the hair.
This unique technique involves applying a therapeutic mask to a previously prepared scalp and ensures deep penetration of active ingredients through the effects of a steam sauna.
Types of anesthetics
Preparations for topical anesthesia differ in their principle of action:
- Anesthetic.
Ointments, gels, aerosols and solutions based on anesthetics that block nerve endings. Can be used in all cases where topical anesthesia is indicated.
- Dehydration.
Carbonic acid salts “take” fluid from the dentinal tubules. Relieves symptoms of hyperesthesia.
- Physiological.
Pastes based on fluorine, strontium and other minerals block the transmission of pain, clog dentinal tubules and prevent fluid from leaking out of them, which causes hyperesthesia. In addition to treating hypersensitivity, they are used for pain relief.
- Cauterizing.
Strong chemicals (nitric, carbolic acid, etc.). Seal the dentin tubules. Previously, they were used to treat hyperesthesia, but now they are practically not used due to their high toxicity.
Anesthetic drugs
Anesthesia
The problem of pain and anesthesia in dentistry is very important. Local anesthesia is one of the most significant for the general condition of the patient. The introduction of a local anesthetic into the internal environment of the body can cause allergic reactions, as well as general toxic effects in case of its overdose or insufficiency of its metabolism and excretion systems. The components of a local anesthetic drug can be especially dangerous in the so-called risk group patients (Zoryan E.V. et al., 1997; Stosh V.I. et al., 1998; Ivasenko P.I. et al., 2000). Patients at risk include the following categories:
- patients with concomitant general somatic pathology, - patients experiencing increased anxiety and fear of treatment, - pregnant and lactating women.
With local injection anesthesia, pain sensitivity is blocked at the site of injection of the anesthetic (infiltration anesthesia), as well as in the zone of innervation of a given nerve or part of it (conductor or regional anesthesia).
Having anesthetics of different chemical groups in our arsenal, we reduce the toxic effect of the anesthetic to a minimum. For example, patients who have:
1. IHD, heart failure, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, stroke, myocardial infarction:
We use anesthetics without VC or with adrenaline in a concentration of no more than 1:200,000. Carpuled preparations: Septanest 1:200000, Ultracain DS, Ubistesin (based on articaine), Scandonest 3% plain, Mepivastesin (based on mepivacaine without VC)
2. Allergic status, bronchial asthma:
We use anesthetics without preservatives (sulfites, parabens). The least allergenic carpules: Scandonest 3% plain, Mepivastesin (based on mepivacaine without VC, does not contain sulfites or parabens); preparations Septanest, Ultracain DS and DS – forte, Ubistesin, Ubistesin forte (based on articaine, do not contain parabens, but contain sulfites as a preservative).
3. Thyrotoxicosis (hyperthyroidism), diabetes mellitus:
We use anesthetics without VC. Adrenaline is contraindicated. Carpuled preparations: Scandonest 2% noradrenaline (based on mepivacaine with norepinephrine), Scandonest 3% plain, Mepivastesin (based on mepivacaine without VC)
4. Liver diseases:
We use articaine-based anesthetics (Ultracain DS and DS forte, Septanest, Ubistesin, Ubistesin forte).
5. Kidney diseases:
we use the least toxic drugs with rapid metabolism based on articaine (Ultracain DS and DS forte, Septanest, Ubistesin, Ubistesin forte
6. Glaucoma:
We use anesthetics without VC or with felypressin. Adrenaline and norepinephrine are contraindicated. Carpuled drugs: Scandonest 3% plain, Mepivastesin (based on mepivacaine without VC)
7. Pregnancy:
We use anesthetics without VC or with adrenaline in a concentration of no more than 1:200,000, felypressin is contraindicated! When carrying out pain relief, it is advisable to use the least toxic drugs with rapid metabolism based on articaine. Carpuled preparations: Septanest 1:200000, Ultracain DS, Ubistesin (based on articaine).
8. Lactation period:
When providing pain relief, we use the least toxic drugs with rapid metabolism (based on articaine): Septanest, Ultracain DS and DS – forte, Ubistesin, Ubistesin forte (based on articaine).
9. Age factor (over 60 years):
For pain relief, we use anesthetics without VC, with felypressin or with adrenaline in a concentration of no more than 1:200,000. Carpuled drugs: Septanest 1:200000, Ultracain DS, Ubistesin (based on articaine), Scandonest 3% plain, Mepivastesin (based on mepivacaine without VC), lidocaine without a vasoconstrictor (for short-term interventions).
When choosing a drug for pain relief, a thorough history is required. This approach will help prevent possible complications that may be associated with pain relief.
The procedure of sedation in combination with local anesthesia is a safe alternative to deep anesthesia. Sedation has a calming effect on the patient at the required level, while keeping him conscious and, importantly, the person retains all reflexes, breathes independently, and responds to the doctor’s questions and requests.
Previously, the patient undergoes a consultation, during which indications for the use of sedation are identified, drugs and their dosage are individually selected. All treatment is carried out under the constant supervision of an experienced anesthesiologist. During the entire procedure, monitoring is carried out (saturation, pulse oximetry, blood pressure measurement with appropriate entries in the medical documentation).
Drugs
The pain-relieving effect during topical anesthesia is provided by means that include:
- lidocaine;
- tetracaine;
- benzocaine.
Preparations with these substances are produced under such commercial names as Perylene ultra, Peril-spray, Xylonor, Kamistad, etc. Some lidocaine sprays are available in various fruit flavors and are indispensable in pediatric dentistry.
Along with the above remedies, the effective analgesic effect of propolis, a natural substance that is a product of the vital activity of bees, has been proven. It should be used with extreme caution, since propolis has strong allergenic properties.
Substances included in anesthetics
Side effects
Complications after superficial anesthesia occur extremely rarely. These include:
- allergic reactions - if you are allergic to an anesthetic, itching, redness and swelling of the mucous membranes are observed;
- difficulty breathing and hoarseness when using the aerosol and getting it into the respiratory tract.
The effect of topical anesthetics on pregnant women and children under 2 years of age has not been sufficiently studied. It is not advisable for these categories of patients to undergo the procedure unless absolutely necessary.
One of the guarantees of effective pain relief without unpleasant consequences is the experience and qualifications of the doctor. On our website you can find a list of clinics that successfully practice painless treatment using topical anesthesia.
Advantages and disadvantages of applications
The absence of pain during application is not the only advantage of topical anesthetics. Other positives include:
- there is no general toxic effect of the anesthetic on the entire body;
- there is no need to scrupulously calculate the dose of the drug;
- there is no long-term feeling of numbness characteristic of injection methods, which can be observed within 1-2 hours after the procedure;
- success does not depend on the experience and professionalism of the doctor - pain relief always works;
- speed of impact - the effect occurs within 30-60 minutes;
- minimal number of side effects.
Applications work best on mucous tissues - a more developed and thin network of blood vessels penetrating the surface ensures rapid absorption and almost instantaneous action of the drug.
Main disadvantages:
- pain relief acts very superficially - the drug covers only the upper 3-5 mm of tissue, without penetrating into the deeper layers; this greatly limits the scope of application, especially in adult patients;
- all main compounds have a vasodilating effect, which increases bleeding;
- difficulties with dosing the drug, especially in the form of sprays;
- excess applied substance is absorbed into the blood and can have a toxic effect on particularly sensitive patients.