From the age of six months, children begin to bother their parents with frequent tears. And the cause of these tears is toothache. After all, it is at this age that babies begin to erupt their baby teeth. And only at the age of six these baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. Many parents who worry about their babies begin to wonder about various questions regarding the structure of teeth. After all, this is the key to unraveling why and under what circumstances pain occurs. In this article we will tell you whether there are nerves in a child’s baby teeth .
Is there a connection between the nerves of the molar and baby teeth?
According to statistics, every second parent wonders whether there are nerves in baby teeth? And at the same time, most are sure that baby teeth simply do not have nerves. However, such a statement is misleading. In reality, every tooth contains a nerve. It doesn’t matter at all whether we are talking about molars or baby teeth. It is worth noting that the nerve is the most important component of the tooth.
And although nerves are present in both teeth, there is no connection between them. That is why, if a disease such as pulpitis is detected in a baby tooth, there is no need to fear that it will necessarily be diagnosed in a permanent tooth. However, this does not mean at all that you can avoid treatment at all and not visit a dentist. Indeed, in cases where the children’s parents neglected treatment, the inflammatory process was guaranteed to penetrate the bone tissue. This has a negative impact on the process of permanent tooth formation.
When treating baby teeth, doctors must take into account the age of young patients. This need is due to the fact that closer to the age of 6, the roots of non-permanent teeth begin to dissolve. Consequently, at this age, during treatment, the risk that a molar tooth will be injured increases many times over. That is why, in cases where it is necessary to remove a nerve, the canals are processed exclusively at the mouth. In this case, the tooth that has been treated is covered with a solution. This solution helps it survive until the time when the molars are replaced.
Are there nerves in a child's baby teeth?
It is a medical fact that baby teeth have nerve endings. Their composition is completely similar to the molars and includes pulp, capillaries and nerve. The enamel surface may deteriorate, in which case the child will experience pain. This occurs with the development of caries and pulpitis.
The first teeth begin to form in children even before birth. At the same time, nerves are formed. After birth, the baby’s teeth are being cut, the crown located under the gum is actively growing, and the roots are growing deeper. When a child has acquired all his teeth by the age of two, they stop growing, and only by the age of five do their roots begin to become smaller. In this case, the tooth first becomes loose and then falls out painlessly.
How are permanent teeth different from molars?
The most obvious difference is the number of teeth. A person has 28-30 molars, but only 20 primary teeth. There is a difference in the size of the crowns and even the roots of the teeth. According to dentists, baby teeth are smaller than molars. This is explained by the fact that children have a much smaller jaw than any adult. Consequently, it is not able to accommodate teeth the size of molars.
The thickness of dentin and enamel also differs significantly. In baby teeth they are much thinner. But if the dentin and enamel of primary teeth are inferior in thickness to molars, then in the case of pulp volume, it is the non-permanent teeth that take precedence. An interesting fact is that it is not necessary to visit a dentist to remove a baby tooth. But if we are talking about removing a molar incisor, you cannot do without the help of a qualified dentist. After all, this process takes much longer and is characterized by pronounced pain, increased body temperature, and slight bleeding from the gums.
Relationship between the nerve endings of primary and molar teeth
There is an opinion that the nerve endings in children’s baby and molar teeth are somehow connected (we recommend reading: Do children’s baby teeth hurt?). Experts confidently refute these speculations. So if a child has a dental nerve removed, don’t worry: the molar will grow with a new one, and the removal will not affect its development in any way.
Problems with the previous one can affect the growth of a new nerve. Every tooth has them, be it milk or permanent. Carious decay and other dental diseases can cause it to develop incorrectly. Therefore, before the removal procedure, it is necessary to consult a dentist for the treatment of all other diseases in order to avoid the risk of infection. However, the best treatment is prevention, so it’s worth taking your child to the dentist from time to time.
Why do baby teeth sometimes have to be removed?
As was written above, most often such teeth can be removed without resorting to professional help. However, sometimes there is still a need to visit the dental office. Before we look at the reasons why you have to seek help from dentists, let's talk about the location of the dental nerve. It is located quite deep in the tissues. The enamel provides it with reliable protection from external influences.
Why does the body need to protect the dental nerves? This can be explained quite simply:
- nerve endings that are located in the pulp must always be sterile. After all, they have a connection with the general blood flow;
- Temperature changes, acids, alkalis negatively affect dental nerves. If they are exposed, the person begins to feel unbearable pain. Therefore, to relieve a person from pain, it is necessary to protect the nerves well;
- a tooth can perform its assigned functions only if the pulp is not affected by external factors.
From the above we can conclude that any violation of the integrity of dentin can lead to the removal of nerves. But is it possible to remove the nerve in a baby tooth? Will this have negative consequences? Removing the nerve is a safe and sometimes necessary procedure. The most common reasons for removing nerves from teeth are:
- pulpitis – is an inflammatory process that occurs in the pulp tissues;
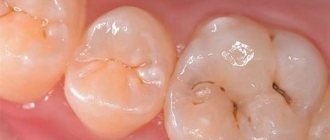
- caries (deep) – thin enamel is not able to fully protect the tooth from the negative effects of harmful microorganisms. This is why the carious process quickly affects the tooth and spreads almost instantly;
- periodontitis - quite often children, afraid of a visit to the hospital, hide from their parents that the tooth hurts. Gradually, such neglect turns into a disease. Periodontitis develops, which occurs at the junction of the tooth and gum;
- Tooth trauma – trauma can cause damage to the enamel. In the future, this becomes the reason for removing the nerve.
How does the condition of baby teeth affect permanent teeth?
Some parents think that if their child has dental problems, they will solve themselves when the teeth are changed. This is caused by understandable emotions: parents do not want to once again expose themselves and their child to unpleasant experiences associated with painful dental treatment.
But the fact is that already under the roots of the baby teeth there are the rudiments of the molars. Thus, oral diseases experienced in childhood can affect the health and development of permanent teeth.
.
Therefore, try not to postpone visits to the dentist unless absolutely necessary. Pathologies of the oral cavity that occur in children under eight years of age require mandatory treatment. Otherwise, the disease can spread to the permanent tooth or bone tissue, and sometimes even leads to the cessation of growth of the permanent tooth. As a rule, this happens if the disease develops at an early age.
When choosing treatment, the doctor will take into account the child’s age and the likelihood of damage to the molar rudiment. When pulpitis occurs in a baby tooth in a child over six years of age, a specialist usually performs root canal cleaning. He also carries out treatment with a special composition, which allows you to stop the development of the disease and protect the tooth from further destruction.
How to prevent diseases of baby teeth?
Inflammatory infections of the oral cavity that develop at an early age can cause a variety of unpleasant symptoms. Among them:
- heat;
- fever;
- fluxes;
- acute pain.
In this case, the disease in an advanced state can lead to very serious consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully care for your child’s oral cavity.
To keep your baby's teeth and gums healthy, follow these simple guidelines;
- teach your child to care for their teeth from early childhood;
- monitor his diet, try to reduce the amount of sugar in his diet;
- Get regular check-ups with your pediatric dentist.
Specialized Asepta toothpastes are suitable for dental and oral care for children of all ages. They fully comply with the requirements for children's hygiene products, carefully care for the oral cavity and reliably protect your child's teeth from any diseases. Our pastes consist of natural ingredients, have a pleasant taste and are safe to swallow. With Asepta your child's teeth will be healthy and beautiful!
Possible complications after nerve removal
Parents often associate complications that arise after removal with the low level of professionalism of the dentist who performed the procedure. They begin to ask another question: is the nerve always removed correctly? Perhaps this procedure is associated with certain risks? Indeed, this kind of thing happens. The need to seek re-treatment may arise in several cases:
- Re-infection, which became possible due to insufficient treatment with an antiseptic.
- Destruction of the installed filling, which was caused by a poorly performed filling procedure.
- Compression of the tooth root by an installed filling.
- A root fracture that can occur if the dentist works too hard with various instruments on the surface of the pulp.
Of course, this doesn't happen very often. However, if the child complains that the pain does not go away, but rather gets worse, you should visit the clinic again. Never ignore your child’s words that something hurts! Moreover, never resort to painkillers. After all, pain is a consequence. To get rid of it, you need to look for the cause. And only a qualified dentist with enough experience can do this.
Other indicators for the removal of baby teeth
- Caries, which can develop on the teeth of a two-year-old child. The resulting carious cavity can become a source for the spread of infection.
- Inflammation of the pulp, which occurs against the background of advanced caries.
- Periodonitis. Inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth.
- This disease occurs in 3-5% of children.
- Trauma, as a result of which the tooth became loose and part of the tooth broke off. When a tooth is injured, the nerve bundle often ruptures. The pulp becomes unviable and must be removed.
Teeth structure system
It’s worth noting right away that you can find a lot in common in the structure of molars and baby teeth. For example, milk teeth, like molars, differ from each other. After all, each tooth has a specific purpose. The shape of the incisors itself is also different.
We suggest you read why a person's tongue is brown
All teeth are covered with enamel, consisting of 96% salts (mineral, calcium). It is thanks to this composition that it is rightfully considered the strongest of fabrics. The enamel shell, which many people don’t even know about, is called the cuticle. Over time, the cuticle may gradually begin to thin out or simply wear off on the chewing surface of the tooth.
The basis of the tooth is dentin, it is located under the enamel. It is bone mineralized tissue and ranks second in strength among all tissues. Dentin covers not only the cavity of the tooth itself, but also the root canals.
The pulp is located in the inner cavity of the tooth. Pulp is a tissue penetrated through and through by a huge number of blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves, and has a loose and soft surface. It is located not only in the crown, but also in the root of the tooth.
Please note that the roots of baby teeth are never removed. After all, over time they simply dissolve. Thanks to this, the displacement of a baby tooth by a molar occurs quite quickly and painlessly.
Causes of depulpation in children
In some cases, dentists still remove the inflamed nerve in a baby tooth because it can no longer be cured. In dentistry, nerve removal is referred to as “depulpation.”
In case of inflammation, the doctor is forced to completely remove the pulp along with its nerves and blood vessels. As a result of this procedure, the tooth stops feeling pain and also no longer reacts painfully to cold and hot foods and drinks when eating. The situation is complicated by the fact that, left without blood vessels, the tooth is deprived of the opportunity to receive the necessary nutrition.
Carrying out timely pulp removal is very important, since this procedure helps prevent the spread of the inflammatory process into the deeper tissues where the rudiments of permanent teeth are located.
In the situation with baby teeth, it is very rare for them to become destroyed, since they only exist for a few years. The situation is much worse if the nerve endings of the root were inflamed. It is unlikely that a new one will grow in place of the last one. Therefore, it is very important to avoid inflammation of the nerves and pay attention to children’s complaints of pain in the mouth.
Pulp disorders, which most often cause removal, can appear for the following reasons:
- Pulpitis. This is an inflammatory process of the pulp, which can be caused by ordinary caries that was not cured in time.
- Periodontitis. Severe inflammation of the gum area. Inflammation is localized in the tissues surrounding the tooth root. The source of infection is located directly in the pulp. Therefore, the doctor begins periodontitis therapy by removing the inflamed pulp. If the development of this disease is not stopped in time, it can lead to pulpitis and other problems with the baby’s oral health.
- Caries. Today, the trends are such that caries develops even in 2-year-old children. The danger of caries in children is that it develops at lightning speed and can reach the pulp in a short period of time. As a result, the doctor can only remove the inflamed nerve. This can happen in just a few weeks. Therefore, you should never delay visiting a specialist. It is better to take control of the situation when the disease is only at the development stage, since untreated diseases are a constant source of infection in the oral cavity.
- Physical damage, injury. Since children are quite active by nature, there is a high probability of a situation that can lead to the separation of the nerve bundle, as a result of which the pulp becomes dead, so it is removed.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the gap between the front teeth: why it appears and how it can be removed
It is important to remember that in order to avoid undesirable consequences and in order to ensure the health of the child, including the oral cavity, mothers and fathers should teach their child to maintain personal hygiene from an early age.
The article was prepared under the editorship of doctors - dental implantation center ICDI ROOTT
A complete overview of the problem of pulpitis in primary teeth: how to determine and whether the tooth can be saved
Some parents still continue to believe that annual preventive examinations at the dentist are not at all necessary for their child - after all, the baby will soon grow up, and then the bite change is very close. It is as a result of such judgments and lost time that problems often “creep up,” of which, perhaps, the most negatively memorable for both the baby and his mom and dad is pulpitis of a baby tooth.
The article is a must-read for everyone who cares about the health and psychological state of their child. And also for those who want to understand whether there can be pulpitis of baby teeth in children, what it is, how it occurs and how to best solve the problem without consequences for permanent occlusion in adulthood.
Possible complications
Although the operation of removing a nerve by dentists is well practiced and is not classified as dangerous, if it is performed unprofessionally or if the doctor’s work is interfered with due to the child’s restlessness, complications sometimes subsequently arise. Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist? Yes No Most often they are caused by insufficient cleaning of the internal cavity of the dental unit, careless antiseptic treatment of root canals. Then inflammation of the gums may begin, accompanied by aching pain. Don't expect this to go away on its own. Immediately visit a doctor with your child so that he can correct the error: remove the filling, clean the tooth cavity, cure the inflammation and re-seal the tooth. If measures are taken urgently, there are many chances to save him.
It happens that the entire filling falls out of a baby tooth or is discolored in parts (if the cement is of poor quality). The child may not experience much discomfort. Due to the absence of the dental nerve, there is no pain either. However, it is necessary to go with him to the dentist and get a new filling. Otherwise, food will accumulate in the open dental cavity and putrefactive bacteria will parasitize, which will ultimately invariably cause inflammation of the gum tissue.
In rare cases, rough work by a dentist can lead to a fracture of the dental neck or root processes. Then the baby tooth falls out prematurely, and its particles remain in the gum. They are removed through surgery.
To avoid nerve removal and all the associated troubles, teach your child oral hygiene from an early age, do not give him a lot of sweets, and monitor the health of his baby teeth.
The primary bite in children is quickly replaced by a permanent one, for this reason some parents do not consider it necessary to take their child to the dentist. In addition, adults believe that baby teeth do not have nerve endings that provoke pain when the enamel and pulp are damaged by caries. Can this assumption be considered a myth or truth? The answer to the question will be discussed in the article.