general information
Teething, along with colic and some other ailments of newborn babies, is perhaps one of the most popular and widely discussed topics among mothers who share their experiences and worries on various forums dedicated to pregnancy , childbirth and raising children.
According to statistics, a child’s first teeth appear no earlier than six months. There are many myths associated with the process of baby teeth emerging, for example, that girls cut their teeth faster than boys. This statement, firstly, is not supported by medical research. And secondly, infant development, which includes the growth of teeth, is a purely individual process.
This means that one child will experience early tooth development, while the second may develop his first incisors within a year or even later. It is important that in both cases we are not talking about a lag or deviation, this is just a variant of the norm.
Since the process of the appearance of baby teeth is most often associated with many inconveniences and worries for both parents and children, it is best to find out in advance how to determine that a baby’s teeth are growing, and most importantly, how to make this process easier for the child . After all, as they say, being aware means being armed.
What is the difference between baby and permanent teeth?
Approximately at the 20th week of intrauterine development, the rudiments of permanent teeth are formed - they are located deeper than the milk teeth, right below them.
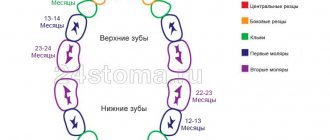
Table. Scheme of growth of baby teeth by serial numbers
| Tooth no. | Tooth name | Age of eruption |
| 1 | Frontal incisors (4 pcs.) | 6-10 months |
| 2 | Lateral incisors (4 pcs.) | 7-10 months |
| 3 | Fangs (4 pcs.) | 1.5-2 years |
| 4 | First molars (4 pcs.) | 1-1.5 years |
| 5 | Second molars (4 pcs.) | 1.5-2.5 years |
At about 5-6 years old, when the baby’s diet has completely changed - the child eats almost any solid food, the process of resorption of the roots of baby teeth begins. Yes, yes, baby teeth have roots, due to which the tooth is tightly located in the gum. True, the size of the root of a baby tooth is much smaller than that of a molar, and has a slightly different, more “airy” structure, with large and wide root canals.
Source: Fotolia
Symptoms of teething in children
How can you tell if your child is teething? This question worries all parents without exception. It often happens that mothers, having noticed a deterioration in their children’s health, do not associate this with the appearance of the first teeth, but think that their child has caught a cold or caught a virus. This is due to the fact that the first signs of teething in a child are very similar to the development of acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections .
In order not to waste your nerves, time and money, and not to stuff your baby with unnecessary and, in addition, ineffective medications, parents simply must know what symptoms of teething in infants occur and how to help the baby in such a situation. Let's first talk about how a baby behaves when teething.
It is noteworthy that although teething is an absolutely normal and natural physiological process for the human body, unfortunately, in most cases it brings a lot of inconvenience to the child, from which there is no escape.
When a child teethes, he changes before our eyes, becomes capricious and more irritable.
The baby really suffers and experiences discomfort, because this is the first time he has encountered such pain.
Therefore, during this difficult period, parents are simply obliged to support their child and do everything to alleviate his condition.
Children's doctors (for example, the famous Dr. Komarovsky) recommend showing as much care and affection as possible to the baby during this difficult period of time, hugging and kissing the child more often.
After all, the best medicine is parental love and the warmth of mother’s hands. And even though you may not be able to completely eliminate pain, your baby will feel your support and compassion. As mentioned above, the first teeth usually appear at six months. However, this does not mean at all that a child cannot have his first tooth, for example, at 3 months.
By the way, this age is considered the earliest, according to doctors, when babies can start cutting their first teeth. Modern pediatricians are increasingly saying that each child is unique, and it is not entirely correct to apply the same norms and rules to all children. An individual approach to diagnosis and treatment is the future of medicine.
It is important to understand that the presence and severity of certain symptoms of teething in children under one year of age depends solely on the health status of the particular baby. There are cases, and there are many of them, when a child endures this process almost painlessly and does not experience even half of the ailments associated with the appearance of his first teeth.
When a child is teething, the symptoms can be so invisible to others that parents, upon discovering their baby’s first incisor, may not only be delighted, but truly surprised.
So, if a child is teething, the symptoms may be:
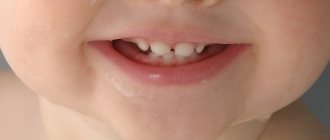
- swelling of the gums and swelling at the site of eruption is perhaps the surest sign that the baby will soon have his first tooth. You can see this symptom with the naked eye, you just have to look into the child’s mouth or feel the “bump” on the gum with your finger. hematoma (collection of blood ) may form at the site where the teeth erupt This is considered a variant of the norm, provided the child is generally feeling normal. As a rule, the hematoma goes away on its own immediately after the tooth erupts. When an infection an abscess or abscess may be present on the gum they also go away on their own over time. If this does not happen, and the baby’s condition worsens ( the temperature , this is how the body reacts to inflammatory processes ), then you should immediately consult a dentist;
- increased salivation can also be considered a sure sign of teething. A lot of saliva is actually released, both when the first incisors appear and then when the molars and canines develop;
- The baby’s desire to chew on everything is due to severe itching of the gums , another sure sign that the teething process is gaining momentum;
- decreased appetite , changes in taste preferences, or the child’s complete refusal to eat;
- Changes in the behavior of newborn children (increased irritability, causeless capriciousness) are caused, first of all, by the fact that the child experiences painful sensations at the moment when the teeth are actively “storming” the surface of the gums. In addition, due to increased salivation, irritation or rashes appear on the skin, which cause a lot of anxiety to the baby; sleep disturbance.
It is worth noting that the main symptoms listed above can provoke the occurrence of other associated ailments, for example, due to increased salivation, cough and runny nose, irritation and rash on the face, as well as diarrhea .
Cough during teething in children
Quite often, mothers ask pediatricians whether the cough due to teething, or whether this symptom indicates the development of other ailments. The child's body begins to prepare in advance for the appearance of the first teeth. Within just a few weeks, and sometimes even months, the salivary glands begin to produce many times more secretions .
However, the child has not yet learned to swallow saliva, as we adults do without thinking and reflexively.
As a result, saliva accumulates in the throat, especially when the child is in a lying position.
The baby begins to cough to clear the airways from the secretions accumulated there.
In addition, due to the large amount of saliva entering the nasopharynx, wheezing can be heard. When saliva gets into the middle ear, the child develops a runny nose .
Diarrhea (diarrhea) during teething
Not many parents know that diarrhea in a baby is not only a symptom of poisoning . The causes of diarrhea can be teeth, or more precisely, increased salivation. The thing is that an overly susceptible and not fully formed child’s stomach can react painfully to saliva entering with food.
A large amount of secretion dilutes the stool , and the bacteria contained in it provoke digestive upset . In addition, as baby teeth grow, the entire child’s body experiences enormous stress, which affects the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract . As a result, the child suffers from diarrhea or constipation , which can also be caused by an excess of saliva.
It is worth remembering that diarrhea lasting no more than 72 hours is considered normal when teething. If you notice any of the following symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor for treatment:
- change in the color of stool or the presence of foreign inclusions in it, namely the appearance of a black or greenish tint of stool and blood (blood streaks);
- too frequent bowel movements (more than five times a day);
- The duration of diarrhea is more than three days, and the number of bowel movements does not decrease, but rather increases.
Vomiting during teething
Can you vomit if you are teething? In rare cases, children may experience vomiting during the teething period. However, this is a rather rare phenomenon, also caused by strong salivation, in which part of the secretion gets into the child’s stomach with food. It is important to emphasize that if vomiting is associated with diarrhea and these ailments are often repeated, and the child’s body temperature has increased, then this indicates the development of a viral infection.
In this case, it is better to immediately consult a doctor for advice. Because without timely treatment , rotaviruses, adenoviruses, astroviruses, caliciviruses, noroviruses , collectively called stomach or intestinal flu , causing severe gastrointestinal disorders, can cause irreparable harm to the child’s health.
What temperature can it be during teething?
Elevated body temperature is a signal immune system , indicating those processes occurring in the body that can be caused by the harmful effects of various microorganisms, for example, bacteria or viruses . However, even when the first teeth erupt, the child may experience a high temperature .
True, as a rule, it will not exceed 38-38.5 C. This reaction of the body is due to the presence of inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity , because the teeth pass through the gum tissue, i.e. actually damage their integrity. In addition, during this period of time the baby begins to grab and chew everything that comes to his hand and can introduce infection into the wounds.
It is important to understand that the reaction to teeth may be a slight increase in temperature. Moreover, this condition usually lasts for several days.
If a child has a fever for a long period of time, it is not related to the teeth.
In such cases, you should immediately seek medical help.
It is also worth paying attention to the fact that not always when the child’s incisors, molars or fangs erupt, the body temperature rises.
This means that it would be incorrect to classify temperature as the main sign of teething. Rather, it is a possible symptom that may or may not exist.
How to distinguish teething from disease?
When a baby is teething, the risk of infection by various infectious agents increases. Often, during the period of teething, the baby may develop ARVI, stomatitis, intestinal infection or another disease. In order to respond to its appearance in time, parents should be vigilant and monitor the baby:
- If the baby refuses to eat, the child’s temperature has risen, he is capricious, and ulcers have formed in the mouth, these are signs of stomatitis and the baby should be shown to a doctor as quickly as possible.
- If parents look into the mouth of a toddler with a fever and runny nose, and notice a reddened throat, then, most likely, the symptoms are associated not with teething, but with ARVI or sore throat.
- If your baby has loose stools, a high temperature, a swollen stomach and pain, you should immediately call a doctor to rule out an intestinal infection.
Read also: When do children start teething?
Timing of teething
Most parents wonder what time their children’s first teeth appear. After all, on the one hand, everyone is looking forward to this exciting moment when the first beautiful tooth “settles” in the baby’s mouth. On the other hand, mothers understand that this period of time can be difficult due to possible ailments.
How babies teeth erupt, photo
When do babies' first teeth start to grow? Several decades ago, in the medical literature and reference books, the question of when a child’s first teeth appear was given an unequivocal answer - from 6 months of life.
Modern pediatricians are no longer so categorical, since there are increasingly cases where a baby’s first teeth come out much earlier than this time.
Therefore, there is no definite answer to the question of when the first teeth appear in babies; in all children, this process begins only when their body is ready for it.
However, parents should worry if their beloved child does not teethe at 6, 8 or 10 months, since the delay in teething is directly related to the delay in growth and development of the entire organism as a whole, which can be caused by such pathologies as:
- edentia , i.e. absence of the rudiments of future teeth themselves. Not many people know that the basis of baby teeth is formed in children in the womb, at about 6-7 weeks of pregnancy, which is why it is so important for women to receive all the necessary vitamins and nutrients for the correct and harmonious development of all vital systems of the fetus’s body. This disease can only be diagnosed with an x-ray;
- rickets , a disease that develops in infants due to a lack of vitamin D , which plays an important role in the absorption of calcium necessary for the development and growth of teeth.
The time at which infants start teething is influenced by factors such as:
- heredity;
- nutrition;
- climatic conditions;
- water quality and its composition;
- the presence of certain diseases, for example, ailments associated with the endocrine system;
- baby care.
Formation of molars
The source for the formation of permanent teeth is the epithelial dental plate.
The timing of their formation is somewhat behind those for baby teeth. Root rudiments begin to appear only by the fifth month of intrauterine development. Permanent teeth are divided into 2 groups:
- Substitutes that have analogues in the milk kit. These include incisors, canines and premolars.
- Additional ones that have no temporal predecessors. These teeth are represented by molars.
The rudiments of permanent replacement teeth begin to grow in the same alveolus with milk teeth, located behind their lingual surface. And only after some time they are completely isolated by bone tissue.
The formation of additional teeth begins even later, only after a year, which is associated with the need to increase the size of the jaw.
Molars in most cases complete their growth by 15-18 years
The order of teething in children
We talked about what time teeth come in, now we’ll figure out the order in which they erupt. So, when do canines, molars (molars) and incisors ?
Timing of baby teeth eruption in children, table
Let us consider the above table of dental growth in children in more detail. The table contains information not only about the timing, but also about the sequence of teething in children. It is important to emphasize that this information about the order of eruption of baby teeth is for reference only.
This means that parents should not panic or worry if their baby's teething order does not match the information presented in the table. The appearance of teeth, like other moments in childhood development, for example, the basic parameters of height and weight, are purely individual.
Therefore, there is no point in comparing the order in which your baby’s teeth or the neighbor’s toddler’s teeth grew. So, what is the order in which baby teeth erupt? And also which teeth erupt first and at what age? The diagram proposed above will help answer these questions and tell you how teeth grow in children.
However, first, let's understand the terminology. The table provides information about how baby teeth grow and which first appear. Milk teeth are the original “set of teeth” in humans and, interestingly, in other mammals too.
Yes, we are not mistaken, our pets cats and dogs and many other animals also lose their milk teeth, and in their place second, permanent ones grow. Based on the pattern of the appearance of the first teeth, it is clearly visible that the teeth on each half of the jaw, having the same name, for example, upper and lower incisors or canines, emerge simultaneously, i.e. in pairs.
Typically, the two central incisors of the mandible erupt first. We can consider these to be the first teeth that appear in babies at 3 months or later. Then, based on the schedule of teething in children proposed above and taking into account the principle of pairing, the central incisors in the upper part of the jaw emerge.
After them comes the time for the second incisors, only the lateral ones. They can appear either from above or from below, this is individual. It is considered normal for children under one year of age to have a full set of incisors, i.e. Both the upper and lower teeth come out.
The order of eruption of molars in children
Logically, the incisors should be followed canines or “eye” teeth. However, the process of teething in children begins only after the molars . In the meantime, so-called “tooth spaces” form in place of the fangs.
So, after all four incisors, molars appear - the first upper molars and the second lower molars. And only after all the molars take their places, the fangs emerge, which, by the way, are the strongest and most durable teeth.
How long does it take for upper and lower baby teeth to erupt?
It is considered normal that by the age of three, the number of canines and molars is equal, and their total number reaches 20 pieces. However, let us repeat once again, these are averaged data and in each specific case the process of eruption occurs at its own individual speed.
You shouldn’t even try to speed it up, since the body itself “controls” the situation, which means teeth will appear when needed.
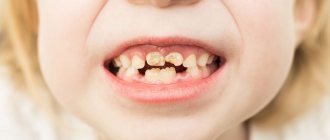
Teething of upper teeth, photo
The central incisors (lower, upper) appear first in the interval from 3-6 months to 10-12 months. Lateral upper and lower incisors - from 7-9 months to 16-13 months.
The first upper molars are cut from 12-13 months to 18-19 months, the second lower and upper molars - from 20-25 months to 31-33 months. And the last lower and upper canines - from 16 months to 22-23 months.
Changing teeth, i.e. The loss of milk and the appearance of permanent ones in their place also occurs purely individually.
However, on average, the first teeth begin to fall out at the age of 6-7 years, and permanent teeth are fully formed by 10-12 years. The incisors are the first to change, and the canines and molars appear last.
How do baby teeth change to permanent teeth?
By the age of 5-6 years, the child’s jaw has already increased significantly, but the size of the baby teeth remains the same, so distances appear between the teeth, as if they are moving apart. This is normal, because permanent teeth are larger than those in the place of which they will grow. By this age, the child’s first permanent teeth erupt, these are molars (6th teeth), which is a harbinger of the approaching change of baby teeth.
These teeth grow immediately as permanent teeth; they have no milk predecessors, so parents often believe that these are belated milk teeth.
Table. Diagram of baby teeth loss
| Age (years) | Teeth |
| 6 — 7 | Incisors in the center of the bottom row |
| 7 — 8 | Incisors in the center of the top row, lateral incisors at the bottom |
| 8 — 9 | Upper lateral incisors |
| 9 — 10 | Lower row canines |
| 10 — 12 | First order premolars upper and lower, then second order |
| 11 — 12 | Upper canines |
As the roots of primary teeth dissolve, the tooth loses support and begins to “lose.” As a rule, by this moment in the gum, under the loose tooth, there is already a fully formed permanent tooth that strives to come out.
The replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones occurs approximately in the same sequence in which the baby teeth came out, but violation of this order is not considered a pathology. However, it is worth showing the child to a specialist to be completely calm.
Source: Shutterstock
How to keep your child’s teeth healthy: advice from a dentist
Medicines for teething in children
How to help your baby teething? And what remedies for teething in babies will help effectively relieve pain and alleviate the child’s condition? We will try to answer these questions further. As mentioned above, it is impossible to predict in advance the reaction of the child’s body to the birth process.
However, even if your baby can withstand all the hardships of this period of time relatively easily, and his health remains good, it is still worth knowing how to help your child if any ailments associated with the eruption of baby teeth occur.
The main goal of parents is to make the process of teething as painless as possible for their child.
This can be achieved with the help of all kinds of medications that have an analgesic effect and also prevent the development of infections and inflammatory processes at the teething site.
So, what effective medications for pain relief exist:
- gels, for example, Baby Doctor “First Teeth” , Holisan, Kamistad Baby, Kalgel and others;
- drops, for example Dentinox , this drug is also produced in the form of an anesthetic gel;
- ointment for gums, for example, Traumeel S.
homeopathy can help eliminate painful symptoms of teething . True, you need to be extremely careful with medicinal herbs and plants, as well as with drugs made from them. Of course, natural herbal ingredients for the child’s body are the best alternative to synthetic drugs.
But if the child has allergies , homeopathic remedies can significantly worsen the baby’s health. Therefore, before starting to use them, you should definitely seek medical advice from a pediatrician. Let's talk about the most popular and well-proven drugs.
How to help your baby and reduce painful symptoms?
Children's eye teeth erupt very painfully. No parent can stand by and watch their child cry. How to help a baby and ease his suffering when fangs are cutting on top? There are such remedies; special teethers have been developed for children, as well as medications that anesthetize the gums, relieve swelling and relieve inflammation.
Read also: How much does a wisdom tooth hurt?
Special teethers and pacifiers
Pharmacies sell special teethers that are designed to relieve itching and relieve pain during teeth growth. They are painted in bright colors and have a regular, orthodontic shape, and inside are filled with liquid and cooling gel.
When a baby sees a new toy, he will definitely try to chew it. The hypoallergenic material is pleasant to the touch and children enjoy biting it. Thus, they eliminate itching from the eruption of baby teeth, and the anesthetic gel relieves pain. Teethers should be stored in the refrigerator, so they will have a greater effect, because cold relieves swelling well and reduces irritation.
Massaging the gums helps a lot. With clean hands, gently massage the gums, alternating pressing, circular and stroking movements. If the baby starts sucking his finger at the moment of teething, you should not scold him for this habit, it helps the baby get rid of pain. Gradually you need to replace your finger with a teether or pacifier.
Medications
If the growth of an eye tooth is accompanied by severe pain, it is impossible to get rid of it with the help of pacifiers and pacifiers. For this purpose, pharmacies sell dental gels and ointments designed to numb the inflamed area. You can buy medications to facilitate teething only after consulting a dentist.
The table provides a list of medications suitable for easing teething:
How long does it take to cut a tooth?
Today, medicine is not able to predict at how many months teeth will begin to appear in a particular child and in what sequence, and even more so, how long it will take for the first tooth to appear. These indicators are individual and depend on many factors. Doctors can give average figures. So, from the moment the gums become enlarged and red before parents see a white tooth, it can take from a week to two months. And it may take from three days to a week for a tooth to cut through the gums. The entire period while the tooth breaks through bone and mucous tissue may be accompanied by pain. The peak occurs at the moment when the tooth ruptures the inflamed gum. There may be a complication due to an infection. When a tooth is already sticking out of the mucous membrane, it does not cause discomfort for the baby.
Read also: How many baby teeth should there be?
Between six months and three years, a person develops 20 baby teeth in their mouth. This means that starting from six months of age and until the entire dentition is formed, some of the teeth will erupt. Of course, if they don’t go several at a time.
How long it takes for a tooth to grow depends not only on the individual characteristics of the child’s body, but also on what kind of tooth it is. So, the teeth of the upper jaw are the longest and hardest for the baby.
Negative consequences
If at least one tooth has grown behind the milk tooth, the bite must be corrected. This can lead to serious consequences in the future:
- Impaired diction.
- Inadequate chewing of food and, as a result, problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Displacement of adjacent healthy units, leading to a significant change in occlusion.
- Diastemas and tremas are gaps between the anterior and chewing units.
- Curvature of the roots of healthy teeth.
When milk units do not fall out in time and interfere with the growth of permanent ones, they must be removed.
What else is important to remember
Over time, the primary teeth will replace the baby teeth. But dairy products are also important in the formation of skills such as chewing and speech. When the first teeth appear, the use of pastes and brushes for the smallest ones is allowed. The main thing is to choose the right accessories, depending on age.
Read also: Malocclusion before and after
You need to make sure that your baby doesn’t fall asleep with a bottle. The liquid will act on the teeth for too long, which can cause them to break down later. This is especially true for mixtures containing sugar. Because of it, bacteria appear in the mouth, destroying the enamel. Then caries begins to appear.
It is better not to treat caries later, but to prevent its occurrence from the very beginning. A bottle as a pacifier is not the best solution for babies. He shouldn’t go to sleep with a bottle at all if there is not plain water inside it.
How many days does it take for children to erupt their first teeth?
The key to future dental health is not only the correct answer to the question of how long it takes for the first teeth to appear, but also regular oral hygiene.
The above figures are a general guideline. As already mentioned, this process is individual for everyone. And everyone is looking for their own answer to the question of how long it takes for a child’s first tooth to come in after erupting.
When do baby teeth start to emerge?
The timing of teething in infants is individual and depends on external and internal factors. Heredity, climatic conditions, and the child’s diet influence. It has been noticed that girls usually erupt teeth 1–1.5 months earlier than boys.
Most children start cutting teeth starting at the age of six months. However, if the child’s process began only at 10 months, then this is not a pathology.
Usually the lower incisors appear first, followed by the upper ones. Teeth come out in pairs: if you see the first tooth, then most likely the next one will appear within two days. It is also possible for four or more teeth to erupt at once. After the first tooth erupts, the next ones usually appear at intervals of two months.
A child celebrates his first birthday with eight teeth: four incisors per row. But this is not the rule. Some babies have only one tooth at this age and this is also a variant of the norm. But if by the age of one year there are no teeth and the swelling of the gums is not even visible, this is a reason to contact a pediatric dentist. Reasons for missing teeth in a one-year-old child:
- child growth retardation, for example, with rickets;
- the rudiments of the organ are absent (edentia);
- insufficient intake of calcium, phosphorus, vitamins D, A, C into the body;
- hypothyroidism (reduced activity of the thyroid gland).
It is possible for teeth to appear already during the period of embryogenesis, then the child is born with teeth. Doctors advise tearing them out from newborns so that the mother can breastfeed the baby painlessly. A tooth can grow early, at four months. This may be a symptom of a dysfunction of the endocrine system.