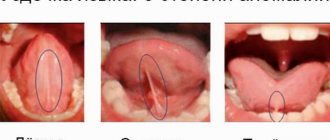
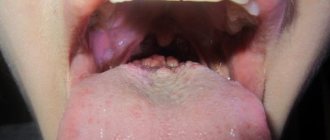
What is a blood blister on the tongue?
What does it look like?
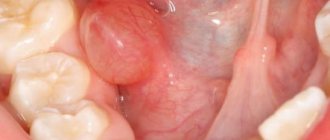
A blood blister is also called a hematoma, blood blister, or lump.
It is an accumulation of coagulated blood in an organic cavity under the mucous membrane.
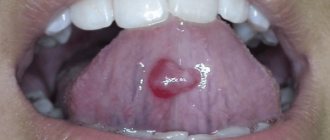
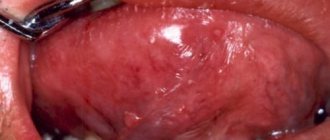
On the tongue, a hematoma looks like a swelling, the color of the tongue changes and becomes bluish, and swelling appears.
The patient feels pain and discomfort while eating and talking.
In addition, pinpoint hemorrhages are often observed on the mucous membrane.
The appearance of bloody bumps is a kind of hemorrhage that occurs as a result of injury to the capillaries and thin vessels of the oral mucosa.
Inside the bladder there may be a clear serous fluid without blood impurities, which indicates that the vessels are not intact and have not been damaged. Such hematomas are superficial in nature and the healing process occurs very quickly.
If a hematoma on the tongue contains blood inside, then the injury is deep and its healing period will be much longer until the blood resolves.
How does a blood blister form?
Bloody blisters in the mouth often do not pose a serious threat to human health.
They arise as a result of mechanical damage to the mucosa.
At the moment of microtrauma, harmful microorganisms begin to attack the damaged area.
To destroy them in the body, immune forces begin to activate.
Leukocytes and monocytes, macrophages are immediately sent to the injured area, which suppress the vital activity of microbes and eliminate them.
The level of health of the body is assessed according to the general condition and integrity of the oral mucosa, and only upon examination can a final diagnosis be made.
Since the clinical manifestations of many pathological conditions, including infectious, chronic, bacterial, occur along with a change in the color and integrity of the oral mucosa (tongue, gums). Here it is important to identify the true cause of the blood ball.
Localization
Blood blisters are distinguished by their location. They can be on the surface of the tongue, under it and on the cheeks.
The appearance of hematomas indicates that microtrauma has occurred or the presence of a serious pathological condition.
A large number of blisters on the oral mucosa, filled with blood, can form due to diseases of the gastrointestinal canal, dental problems, and disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system.
So, with stomatitis, blisters and ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, on the gums, and on the palate, as well as on the tongue.
With syphilis, blood bumps are located on the tip, back of the tongue or on its lateral surfaces. With tuberculosis, hematomas are localized on the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, and palate.
Causes of varicose veins
- Congenital weakness of the venous walls.
- Disruption of the nervous and endocrine systems.
- Hereditary predisposition to the occurrence of the disease.
- Insufficiency of venous valves.
- Impaired blood flow associated with the presence of mechanical obstacles.
- Pregnancy can provoke the development of the disease, since weight gain is added to hormonal changes.
Risk factors for varicose veins:
Latest information: Ointments for rosacea on the face. What is rosacea and why does it appear?
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Long and frequent standing in one place.
- Prolonged sitting in one position, including cross-legged.
- Lifting and carrying heavy objects.
- Age over 40 years.
- Regular overheating (sun, solarium, sauna).
- Limb injuries.
- Overweight. Increase in body weight more than 27 kg/cm2. increases the risk of developing varicose veins by 33%.
- Consumption of highly processed foods. Reduction in the diet of fiber (raw vegetables and fruits), necessary to restore the vein wall.
- Chronic constipation leading to increased intra-abdominal pressure.
- Hormone therapy or the use of hormonal contraceptives that affect hormonal metabolism in the body and cause complications of an already established disease.
Causes
Among the factors that provoke various external damage to the oral mucosa are:
Mechanical
Injury to the surface of the tongue is caused by all piercing and cutting objects that cause direct and instantly noticeable harm.
For example, dishes with bones cause damage to the oral mucosa during consumption. It is not the amount of food eaten that matters here, but the receipt of microtraumas that violate the integrity of the surface of the tongue.
Blood blisters that form due to mechanical action do not pose any threat to human health. To speed up the process of resorption of seals on the tongue, under it, it is recommended to rinse the mouth more often after eating.
Chemical
When eating salty or sour food in the mouth, small lesions in the form of ulcers appear almost instantly on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
This reaction is observed among most fans of oriental cuisine, where hot seasonings are used.
Thermal
Such damage includes microtraumas resulting from drinking too hot tea or coffee.
The duration of wound healing from thermal exposure directly depends on the depth of the lesion; they take quite a long time to heal.
Depending on the degree of damage, sensations change:
- In the first degree, the burn occurs only on the outer layer of the tongue. A person experiences pain, the color of the tongue changes to red and after some time begins to swell. Rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions will help speed up the healing process.
- In the second degree , the sensations become more painful, since not only the outer but also the inner layer of the tongue is affected. The formation of blood blisters, swelling of the tongue and its redness are also observed. In this case, it is recommended to seek medical help as soon as possible so that the doctor removes the lump, washes the affected area and treats it with an antiseptic.
- In the third degree, the burn penetrates deep into the tongue, the burned surface becomes black. The patient complains of a feeling of numbness of the tongue and severe pain. The help of a doctor is mandatory here, otherwise there is a high probability of death.
How to treat a blood bladder?
General therapy
Depending on the type of pathological condition that caused the appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth, treatment can be carried out with the following medications:
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents
For candidal stomatitis, antifungal drugs such as Levorin and Nystanin are effective.
- For diseases of viral etiology, the treatment regimen includes Viferon, Amoxicillin, Tsiprolet, Azithromycin.
- To combat gingivostomatitis, where it is expected to remove areas affected by necrosis, antiallergic medications, antibacterial agents, and vitamin complexes are used.
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents. If there is pain, the doctor may prescribe Cholisal, Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Lornoxicam, Kamistad.
- To eliminate tuberculosis, appropriate chemotherapy is prescribed, which includes Rifampicin, Ioniazid, Pyrazinamide.
Local therapy
To speed up the healing process, regularly rinse with antiseptic agents. Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Stomatidine, Betadine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide solution, Iodoform, Chlorophyllipt show good results.
Treatment of the affected tongue with disinfectant solutions should be performed twice a day, at a minimum, but before that you must brush your teeth and remove any remaining food.
What not to do?
If you have blood blisters, you should not:
Malignant processes in the oral cavity, including the tongue, are most often caused by obligate precancerous pathologies, poor environmental conditions and, in 50% of cases, bad habits.
What is cancer under the tongue?
A tumor of the floor of the mouth is also called cancer under the tongue. It accounts for 15% of all cases of malignant tumors in this area. The floor of the mouth is, so to speak, a collection of different structures that are located between the hyoid bone and the tongue. The main support of the floor of the mouth is the mylohyoid muscle.
It is this zone that is most often affected by malignant growth under the influence of carcinogenic factors such as:
- smoking;
- salts of heavy metals;
- thermal or mechanical injury;
- HIV – papilloma;
- leukopenia and other precancerous diseases.
Most often the tumor is localized near the frenulum of the tongue and less often at the mouth of the salivary duct. Cancer under the tongue often affects the strong side of humanity, that is, men. According to statistics, for every 4 men with oral cancer who are over 55 years old, one woman of the same age is sick.
In the initial stages of the disease, cancer is asymptomatic and there are no signs of alarm. Often, patients turn to doctors for help when they experience severe pain, when the stage of cancer has grown significantly and has begun to metastasize to other organs and tissues of the body. This is stage 3 or 4 of the malignant process. When metastases enter bone tissue, the metastases are often localized in the lower jaw, causing a significant limitation in the mobility of the tongue and its root. The tumor covers the salivary glands, which is accompanied by their inflammation, and salivation is impaired.
How to treat
Modern methods of treating varicose veins can be divided into medicinal and surgical. The former are used to slow down and stop the course of the disease in the initial stages, from initial manifestations to stage 2 disease.
Surgery is a panacea for advanced disease. However, it is the latter that has the most pronounced result and allows you to get rid of not only the cosmetic problem, but also the possible development of complications caused by this pathology.
The choice of the necessary treatment method is the prerogative of the attending physician alone, who can correctly assess the patient’s condition.
Conservative therapy involves taking medications with various pharmacological effects, namely venotonics, anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs . Some of them come in various forms and are used both internally and topically.
Blue swollen veins that appear under the tongue, photos of which can often be seen on the Internet, can be treated surgically or by injecting a sclerosing substance into the venous cavity, causing it to stick together.
Veins are removed by microphlebectomy or laser coagulation. Any of these techniques is aimed at restoring proper blood circulation. We described in our material how varicocele manifests itself and is treated in adolescents.
Diagnosis of cancer under the tongue
Diagnostic methods for tongue cancer are as follows:
- visual examination of the oral cavity;
- palpation of the submandibular zone is performed;
- digital examination of the oral cavity, including the tongue, tonsils and floor;
- Ultrasound is an integral part of diagnosis;
- X-ray of the neck area and lower jaw;
- orthopantomography;
- biopsy;
- a swab is taken from the throat and sent for cytological examination;
- for certain indications, CT and MRI are performed;
- general blood analysis;
- Determination of Rh factor.
Stages of development of cancer under the tongue:
- at the first stage of development, the tumor has the same dimensions as during the initial onset. Ulcers or papillomas have clear outlines and are small in size. In most cases, a tumor on the tongue measuring up to one centimeter is diagnosed. Such tumors are located in the mucous or submucosal membranes and do not metastasize to the surrounding tissue;
- the second stage of neoplasm development: the tumor increases in size and reaches 2 cm. When it spreads, it affects the muscles, degenerating them into malignant cells;
- At the third stage of the malignant process, the tumor grows in all directions and already occupies almost the entire mucous membrane of the organ. Affects the bottom of the tongue. The tongue is motionless at this stage. Metastasizes in all directions;
- fourth stage : almost the entire tongue is affected by the tumor, so to speak, one large compaction that has even grown into the depths of the bone. The spread of metastases increases. Cancer treatment at this stage does not produce any positive results. Death occurs in 75% of patients in the first two years.
The prognosis for treatment of cancer under the tongue is often unfavorable. Five-year remission is possible in 85% of patients, provided that the tumor is detected at an early stage of development. Unfortunately, the remaining patients live no more than one and a half years.
How useful was the article for you?
If you find an error, simply highlight it and press Shift + Enter or click here . Thank you very much!
Thank you for your message. We will fix the error soon
Many patients, having accidentally discovered blue vessels under their tongue, wonder: is this dangerous? Why are there blue veins under the tongue? Let's figure it out together.
Why blue veins may appear under the tongue and how to deal with it
Many patients, having accidentally discovered blue vessels under their tongue, wonder: is this dangerous?
Why are there blue veins under the tongue? Let's figure it out together. Since ancient times, changes in structure, color, and the formation of plaque on the surface of the tongue have been considered evidence of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs. That is, it acted as a kind of identifier of a person’s health status.
Bluish vessels, as already noted, are not always a pathological sign, but in some cases they, like a litmus test, make it possible to promptly suspect any disorders in individual organs and systems.
It’s worth noting right away that the presence of any disease is not limited to just increased coloration of the tongue; it should be considered, rather, as an additional sign. Let's consider a number of reasons that provoke such a clinical manifestation.
A lack of B vitamins can affect the appearance of not only blood vessels, but the entire oral cavity. In particular, when there is insufficient intake of vitamin B2, known as riboflavin, similar symptoms appear in the body.
In addition, a person becomes susceptible to a number of diseases of the oral cavity and throat, such as stomatitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, he regularly develops cracks on the lips that do not heal for a long time, the color of the tongue surface also changes, darkens and acquires a purple tint.
This condition is corrected by additional intake of vitamins in tablet form and selection of an appropriate diet.
Insufficient saturation of the circulatory system with oxygen due to various pathologies of the respiratory system leads to increased coloration of the lingual vessels, even black. For any of the diseases of the lungs and bronchi, the main symptoms are characterized by lack of air, coughing with or without sputum, and the presence of wheezing, which can be heard when listening to the chest with a phonendoscope.
Disturbed lipid metabolism and the appearance of fatty plaques significantly disrupt the natural blood flow and nutrition of organs. For this reason, the sublingual space may have an excessively dark color.
In most cases, it is problems with the circulatory system that provoke visual darkening of the vascular pattern. In particular, varicose veins in the sublingual area can appear as a result of:
- increased intravascular pressure as a result of heart failure due to atrial fibrillation and flutter and valve defects;
- hereditary predisposition, characterized by some thinning of individual walls, as a result of which nodes and bloating appear;
- hemorrhoids - a pathological condition accompanied by a violation of the outflow of blood with the formation of nodes localized in the rectal area. You can learn more about varicose veins of the rectum from our article;
- decrease in the elasticity of vascular walls due to age-related changes.
First of all, you should see a dentist.
You can use mouth rinses on your own:
- Stomatophyte.
- Hexoral.
- Iodinol.
If inflammation is present, the doctor will prescribe antibacterial therapy, drugs for salivation, and a course of physical therapy.
- Damage to the frenulum. This is a common cause of the problem. The mucous membrane is very vulnerable. There is a very delicate structure here that can be damaged during hygiene procedures or eating. If you have a shortened frenulum, then it can be injured while talking or eating. In childhood, stomatitis often occurs, which is accompanied by erosion throughout the entire oral cavity. This can also cause swelling in the mouth;
- Acute sore throat can cause inflammation of the area under the tongue;
- Teeth with caries are a source of infections. As a result, the mucous membrane may be affected; the area under the tongue is no exception;
- Formation of phlegmon or abscess. Swelling under the tongue is associated with purulent inflammation. This is a very dangerous disease that requires immediate specialist intervention. Cellulitis develops due to untreated periodontitis or periostitis;
- Inflammatory process of the salivary gland;
- Anomalies in the development of the hyoid bone or mechanical trauma that made its shape asymmetrical;
- Allergic reaction to irritants;
- Mechanical injury to muscle fibers, nerve endings, and blood vessels located in the oral cavity.
During treatment, you cannot do without consulting a doctor, as self-medication can lead to unpleasant consequences. It is necessary to choose medications taking into account the cause of the problem. Otherwise, it will be possible to remove only the consequence, which means that after a while it will make itself felt again.
At the first manifestations of negative sensations, you can independently check the oral cavity for the presence of ulcers, plaque, abscesses, pus and rashes. This way you will roughly understand what the problem is and how to solve it.
Briefly about the structure of language
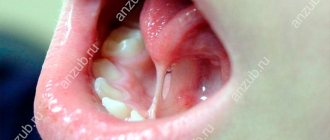
The tongue is an organ consisting of muscles and covered with a mucous membrane. It consists of apex, body and root. The top surface is called the back. The lower surface is much smaller than the upper and is called the inferior fascia of the tongue. The upper and lower surfaces are connected by the side edges. The mucous membrane of the lower surface of the tongue in the form of a thin fold passes along the midline to the floor of the oral cavity. This fold is called the frenulum of the tongue. On each side of it, fringed folds are visible, which converge towards the tip of the tongue and diverge towards the root of the tongue. Between the frenulum and these folds, the bluish veins coming from the apex of the tongue are clearly visible through the mucous membrane. This is the norm. Through them, blood saturated with carbon dioxide flows into the internal jugular vein. Blood, depleted of oxygen, is darker in color, so the veins visible through the mucous membrane are blue, sometimes even black. The closer they are to the surface of the mucous membrane, the more clearly they are visible and the richer their color.
Anatomical structure of the tongue
To better understand the reasons for the appearance of blue veins, one should turn to the anatomical features of the structure and functioning of the human tongue.
It is a muscular organ covered with a mucous membrane. The tongue has many nerve endings, thanks to which the necessary signals are sent to the central nervous system.
The tongue consists of two main parts - the body, which can be easily seen with the help of a mirror, and the root, located near the pharynx. They are separated from each other by a V-shaped terminal groove. The surface of the body is rough due to the presence of multiple papillae on it, which are responsible for taste, temperature and pain perception.
In the middle of the lower part of the organ, the mucous membrane forms a frenulum , which connects it to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. On the sides there are fringed folds, converging to the tip. It is between them and the frenulum that the elements of the circulatory system are visible.
The lingual artery is responsible for the blood supply to the lingual tissues; with its help, oxygen-enriched blood is supplied to the organ. This is how the tongue is nourished. Venous outflow is provided by a complex of lingual vessels connecting to the internal jugular vein. It is the change in their color that most often causes concern among people.
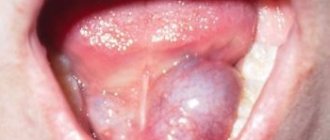
Blue veins under the tongue
If you notice blue veins under your tongue that bulge and may hurt, you should consult a doctor, as sometimes this indicates the presence of a number of health problems.
In rare cases, they are a reflection of the condition of the coronary vessels of the heart. The darker and more pronounced the vessels, the weaker they will be. In particular, such manifestations can be observed with superior vena cava syndrome or congenital heart disease, when pressure in the right side of the heart increases.
Most often, enlarged vessels under the tongue may indicate varicose veins. As a rule, dilated veins are observed under the mucous membrane of the lower surface of the tongue and in the sublingual area. At the same time, they swell, bend, and eventually become knotty. They may also have a bluish-red or purple color. When pressed, there is no pain and they smooth out. If there are a lot of them, then the surface of the mucous membrane becomes lumpy, reminiscent of caviar. This phenomenon has nothing to do with varicose veins and heart failure. It is explained by obstructed outflow due to pressure on the vessel from some pathological formation or loss of elasticity of the walls due to aging. The disease can be either hereditary or acquired. Occurs with equal frequency in females and males. In such a situation, treatment is not necessary.
Painful sensations
Swollen blue veins that appear under the tongue indicate the development of varicose veins. Due to anatomical features, the vessels themselves cannot hurt due to the absence of nerves in them.
Due to the course of varicose veins , they expand and put pressure on the nerve endings located in the immediate vicinity, causing pain in the sublingual area. It is these sensations that non-medically savvy people confuse with pain in the vessel.
In addition, late stages of the development of the disease provoke violations of the integrity of the integument due to the formation of ulcers, which will definitely cause discomfort.
promptly seeking qualified help , you can get complications from varicose veins in the form of thrombophlebitis. Blockage of the lumen of the sublingual vessel by a thrombus will inevitably make itself felt not only by visual changes, but also by physical pain.
If, during dental surgery, when a tooth was pulled out, blue veins with characteristic swelling were noticed under the tongue, you should consult the doctor who performed the extraction. He will be able to examine the picture in detail, draw appropriate conclusions and, if necessary, refer you to a specialized specialist.
Read more about massage for varicose veins in our material.
Varicose veins of the sublingual veins
Varicose sublingual veins occur in the following conditions:
- High pressure in large vessels, which occurs when the heart muscle is insufficient and is associated with atrial fibrillation and valve damage, in asthma with increased central venous pressure.
- A hereditary factor when some areas of the blood vessels are thinned and as a result they protrude in various parts of the human body.
- Hemorrhoids are when the hemorrhoidal veins become inflamed, dilated, tortuous, and blocked by blood clots.
- Reduced elasticity of the walls and difficult blood flow due to aging in older people.
If you have varicose veins under the tongue, you should consult a doctor, who will identify the cause of this condition and give recommendations on further actions.
Blue sublingual veins: normal or abnormal
The tongue helps push food, suck, detect the temperature and taste of food, and is also responsible for speech.
In a healthy person, this muscle has a clean pink and shiny surface, which may be covered with a faint, thin whitish coating.
Changes in the color consistency and structure of plaque, the relief of the tongue surface, as well as when pronounced black or blue veins appear under the tongue and pain can indicate the development of serious diseases.
Venous nodules on the lower part of the tongue
The appearance of blue veins under the tongue
Oxygen-depleted blood flows through the veins, which is darker in color than arterial blood (saturated with oxygen). Therefore, it is visible through the walls of blood vessels and the veins become blue. The closer the vessel is to the surface, the darker and clearer the vein will be. Therefore, when answering the question why there are blue veins under the tongue, they often say that this is the norm.
But if the sublingual veins swell and become knotty, then this is a clear sign of varicose veins.
Varicose veins of the sublingual veins are usually called a disease in which the vessels become inflamed and curved. This condition may manifest itself:
- when venous pressure is increased (in large veins);
- when heart failure associated with atrial fibrillation or valve damage progresses;
- when there is a hereditary predisposition to varicose veins, in which some fragments of blood vessels become thinner, where blood nodes form;
- when a person suffers from hemorrhoids - a disease in which there is inflammation, tortuosity of the veins, due to which nodules form in the rectal area.
Varicose veins often affect older people, but are not affected by peripheral enlargement or congestive heart failure.
The initial stage of varicose veins of the sublingual veins
The cause of age-related varicose veins lies:
- In the obstructed outflow of venous blood, which can occur as a result of compression of the vein, which occurs during the formation of a pathological formation (plaque or blood clot).
- When the walls of blood vessels lose elasticity, this is a physiological process of wear and tear that progresses with increasing age.
- A common location for varicose veins of the sublingual veins is the underside of the body of the tongue and its sides, as well as the sublingual space.
- The vessels located under the mucous membrane become bent, swollen and overgrown with nodes. This disease can affect people of different sexes with the same frequency.
The second stage of varicose veins - numerous nodes
Dilated sublingual veins look like blue or black fluctuating nodules of different sizes. If you press on them, they can come together and the patient does not experience pain. When diagnosed by diascopy, the nodules become white.
With multiple accumulations of varicose veins, the surface acquires a granular texture, similar to caviar.
Also, as the body ages, veins may appear on the tongue that were not there before. Upon careful examination, you can notice that these are pronounced vessels in the sublingual area. If the vessels are smooth and clear, then there is no need to worry - these are natural manifestations of aging, and not a disease.
But if bleeding begins, you should visit a doctor to identify the causes of this condition: dental trauma or a decrease in blood clotting, which can be caused by taking blood thinning drugs.
Hemorrhages in tissue with varicose veins
Sublingual veins hurt
Often, when visiting a doctor, a person complains that the veins under the tongue hurt. But there are no nerve endings in the vessels and therefore they cannot physically hurt, so such complaints are fundamentally wrong.
Painful sensations can come from nerves located in close proximity to the veins due to their pinching.
Pain can also occur in the skin covering the vessels, which may be swollen, have minor injuries or ulcers.
With varicose veins of the sublingual veins, pain occurs due to pressure on the nerve endings from the walls of swollen vessels or the development of varicose ulcers.
The cause of pain can be thrombophlebitis - an inflammatory process in the walls of the veins themselves and its partial blockage with a blood clot.
Thrombophlebitis on the tongue is a dangerous condition
Statistical data
According to statistics, everyone is susceptible to varicose veins, but the risk group includes:
- Patients with a hereditary predisposition, when both parents are sick, the percentage of development of the disease tends to 90. If only one parent suffers from the disease, then the percentage to inherit it is distributed between a man and a woman in a ratio of 25:60.
- Women are more likely to suffer from varicose veins, but the manifestation of the disease under the tongue occurs in both sexes with the same frequency.
- The disease progresses in older people.
- People who are overweight and lead a sedentary lifestyle are predisposed to early manifestations and a rapid progression of the disease.
Inflammation of the hypoglossal vein - top view
Although varicose veins are not a fatal disease, treatment should not be neglected, because the disease can cause concomitant diseases and significantly worsen the quality of life.
Pain in the veins under the tongue
Sometimes patients come to dentists with complaints that their veins hurt and the veins under the tongue are swollen. But the vessels themselves cannot hurt, since they lack nerve endings. It can get sore under the tongue as a result of pinched nerves located nearby. Dilated vessels can put pressure on nerve endings. Pain may also be associated with ulceration. Thrombophlebitis of the sublingual veins can be a serious problem. This is an extremely rare but dangerous condition caused by inflammation of their walls, the formation of a blood clot that partially clogs the vessel. A timely identified problem helps prevent possible complications.
Diagnosis of the disease
Only a doctor can make a diagnosis of varicose veins after all the necessary diagnostic procedures. An important place in the diagnosis of varicose veins is given to ultrasound examination, which will show the state of blood flow in the vessels. Another diagnostic method is angiography. With this method, a contrast agent is injected into the vessel and then an x-ray is taken. This method allows you to clearly determine how the vessels function. The specialist will also refer you for a special blood test to identify a tendency to thrombosis and, if necessary, prescribe medications to thin the blood and prevent this complication of the disease. Therefore, at the first symptoms of the disease, you must immediately consult a doctor. This will help to start treatment on time, if necessary, and prevent unwanted consequences of the disease.
How to diagnose
If you suspect the development of varicose veins, the only correct decision would be to consult a specialized doctor - a phlebologist. He will conduct a visual examination and collect anamnesis, after which he will prescribe additional studies to obtain comprehensive information on a particular case.
Ultrasound examination of the affected areas is an accessible and informative method of diagnosis for varicose veins. With its help, qualitative indicators of blood outflow are checked , allowing one to determine the presence or absence of blood clots that pose a real threat to health. Sometimes radiography is prescribed using a special contrast agent.
Despite the fact that women are more susceptible to developing varicose veins, its manifestations in the sublingual area occur equally often in both sexes.
We wrote in detail about the methods of diagnosis and treatment of varicocele on the left testicle in our article.
Treatment
If the disease is associated with weakness of the walls of blood vessels and occurs during pregnancy, overweight, in old age and does not cause inconvenience, then no special treatment is required. Pregnant women need to visit a specialist - a phlebologist, who will give the necessary recommendations for prevention and select compression garments. It is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, monitor your weight, and carry out general strengthening activities. Locally, for skin manifestations of the disease, ointments are recommended, which can be purchased freely in pharmacies or with a doctor’s prescription. There are now a wide variety of them. The phlebologist will also prescribe a drug depending on the stage of the disease that is right for you.
If the disease is caused by more serious problems and dilated vessels appear in other parts of the body, then complex treatment is necessary. It includes treatment of the underlying pathology by a specialized specialist and local treatment, including surgery, for the manifestation of varicose veins of the lower extremities, hemorrhoidal, inguinal veins, and scrotal veins.
A phlebologist treats the affected vessels. Today there are modern and very effective techniques. The most popular of them are sclerotherapy (injection of a special drug into a vessel that causes sclerosis), laser treatment of varicose veins, and phlebectomy surgery (removal of the damaged part of the vessel through incisions in the skin).