The tongue is one of the most important organs of the human body. Therefore, when inflammation appears under the tongue, a person immediately feels discomfort in this area. The causes can be both infectious processes and injuries. Quick and accurate identification of the provoking factor will contribute to successful treatment.
Main reasons
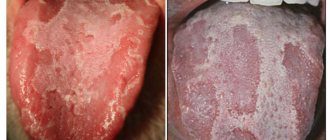
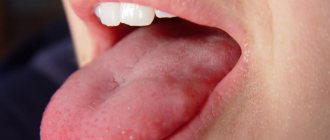
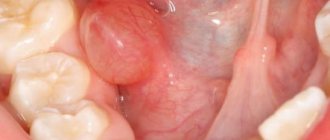
Discomfort, swelling, and the sensation of a foreign body in the sublingual area can occur suddenly in a person or increase gradually. It is not difficult to identify a pathological focus - just lift the tongue upward and carefully examine the tissue. In the case of an inflammatory process, various rashes can be observed on the red background of the mucous membrane .
The cause of swelling and pain under the tongue is most often due to infection of the salivary sublingual gland. The inflammatory process can be caused by other diseases, including: sore throat, pharyngitis, otitis media, sinusitis.
Among other provoking factors, experts indicate:
- previous viral pathologies of the oral cavity;
- formation of stones in the salivary glands;
- poorly performed dental services;
- malignant processes in the head area;
- avitaminosis – lack of vitamins and microelements in the diet;
- anemia – low concentration of iron in the bloodstream;
- allergic reactions.
Correct differential diagnosis of inflammation under the tongue is facilitated by timely implementation of instrumental and laboratory tests.
Diagnosis of sialadenitis
The list of diseases that can cause swelling under the tongue is very long, so it is almost impossible to identify the cause of the development of the pathology on your own. If something is swollen under the tongue, you need to urgently go to the doctor, especially if saliva is not produced, the gland is enlarged, and the general condition is worsening.
With such a symptom, you can contact a dentist or therapist (pediatrician), but to clarify the diagnosis, you may need to consult many other doctors, including a rheumatologist, surgeon, and phthisiatrician. For a complete diagnosis, the following examinations are necessary:
- Bacterial culture.
- ELISA.
- PCR tests.
- Ultrasound of the salivary glands.
- Cytological studies of the gland itself and its secretions.
- Sialography.
- Sialotomography.
It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own in this case. All three salivary glands are susceptible to inflammation. In addition, the disease can affect several glands at the same time. The examination should be carried out by a dentist or therapist. When examining a patient, a doctor can detect pus discharge and establish the exact location of the inflammatory process.
If the inflammation under the tongue is complicated by an abscess, an ultrasound or computed tomography may be needed. Most often, to make a diagnosis, a doctor only needs to examine the patient’s laboratory test results. Cytological examination of saliva allows you to accurately determine which pathogen caused the development of inflammation of the gland.
Symptoms and treatment of lesions of the submandibular salivary gland
Inflammation of the submandibular salivary gland can be recognized by symptoms such as significant swelling in this area and redness of the tissue. The mouth feels very dry. The patient is concerned about:
- stabbing pain in the sublingual area;
- foreign body sensation, swelling under the tongue;
- purulent discharge, as well as excessive viscosity of saliva;
- increased discomfort when eating and talking.
The above clinical manifestations can appear suddenly - literally in a few hours. This is an acute form of inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue. Less commonly, the process is chronic in nature - with episodic exacerbation and periods of subsidence of unpleasant sensations.
Treatment tactics will be determined by the doctor, taking into account the type of pathogen and the patient’s susceptibility to anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs. However, therapy must be comprehensive in order to suppress the activity of the causative agent of the disease and strengthen the patient’s immunity.
If the pain is associated with damage to the frenulum
According to experts, the most common cause of pain at the base of the tongue is inflammation of the tonsils, tissues that provide reliable protection against the penetration of viruses and infections. In our case, we are talking about the tonsils located directly in the larynx. As the disease progresses, they become inflamed and increase in size.
- the temperature rises,
- there is discomfort in the throat - soreness,
- the throat hurts when swallowing, it becomes painful to eat,
- the voice becomes hoarse
- cough and nasal congestion occurs,
- the soft tissues of the oral cavity swell,
- A plaque forms on the sides of the tongue.
Throat diseases can cause pain at the root of the tongue.
In such cases, specialists usually prescribe anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents. For advanced forms of the disease, antibiotics are prescribed. It is recommended to rinse with saline solutions.
If you have the slightest discomfort or pain in the space under the speech organ, you should visit a therapist. Consultation with an allergist may be required. Most often, dentists deal with problems of the floor of the mouth. It is important to regularly visit the hygienist. Professional oral cleaning prevents many dental and soft tissue problems.
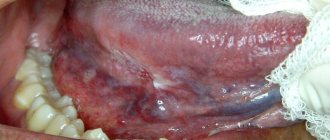
In case of frenulum injuries, rinsing with romazulan, chlorophyllipt, and stomatophyte is prescribed. The disease requires repeated rinsing: in the morning, after meals, in the evening. The affected area is treated with antiseptic drugs and agents to relieve the inflammatory process. If the salivary glands are affected, therapy should be started before an abscess appears. Medicines are injected into the pathological gland, antibiotics, drugs for salivation, and a course of physiotherapy are prescribed.
When an abscess forms, the patient needs a surgeon to clean out the gland cavity. As a preventive measure, dentists recommend proper oral care. It is necessary to take care of the gum tissue, prevent the accumulation of pathogenic microbes, treat caries in a timely manner, and clean the oral cavity twice a day.
In case of inflammation of the salivary gland, experts recommend not to self-medicate and seek medical help as soon as possible. This will allow timely initiation of adequate therapy and elimination of inflammation under the tongue without serious complications.
Forms of the disease that occur without complications can be successfully treated at home. However, in some cases it is impossible to do without a stationary regime.
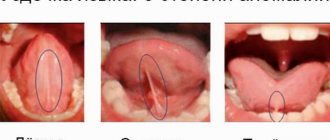
Symptoms and treatment of inflammation of the parotid gland
In some cases, inflammation under the tongue can be associated with infection of the parotid salivary glands. Viral agents are considered to be the main culprits of such pathological changes. For example, mumps affects children aged 10–12 years.
Main symptoms of damage:
- a sharp increase in temperature - up to 38.5–40 degrees;
- increasing weakness, increased fatigue;
- significant increase in size of the gland;
- constant dryness of the oral mucosa;
- difficulty eating;
- significant hearing loss.
When a bacterial infection occurs, a person can indicate to the doctor that, in addition to the symptoms of general intoxication, he has purulent discharge, and the pain will be not only under the tongue, but also in the area behind the ear.
Treatment tactics for mild forms of pathology are based on antiviral therapy and overcoming intoxication. Drugs are used to reduce fever, eliminate pain, and boost immunity. If the inflammation under the tongue is caused by bacterial microflora, the doctor will select and prescribe an effective antibacterial agent.
Other symptoms
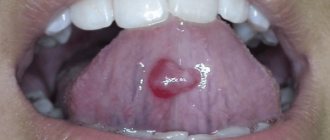
Ulcers or blisters in an adult are caused by many internal pathologies and external factors. There are a number of signs that may accompany the disease:
- enlargement of the tongue (allergic reaction),
- chronic cough (tuberculosis),
- change in voice timbre,
- inflammation of the lymph nodes,
- the presence of dense plaques under the tongue or on its root (lichen),
- headache, fever, weakness (chicken pox or scarlet fever),
- the appearance of pus in blisters, bleeding, increased salivation (ulcerative necrotizing gingivostomatitis), etc.
When the frenulum under the tongue hurts
The frenulum is a thin bridge located under the tongue. Its purpose is to connect the lower surface of the organ with the floor of the oral cavity. In the case of inflammation under the tongue, the cause may be injury to this particular part of the organ.
Provoking factors are:
- chemical burn of the mouth;
- thermal burn of the mucous membrane;
- course of stomatitis;
- inflammation of the gums involving the tissues of the floor of the mouth;
- using low-quality toothpaste;
- an allergic reaction – for example, to medications.
However, in most cases, the frenulum becomes inflamed due to injury - prolonged loud screaming, singing, or getting sharp objects into the mouth. Sometimes dentists determine that the frenulum of the tongue is too short from birth. Therefore, a person overexerts it every day when eating and talking. The solution to the problem is a cosmetic procedure - cutting the frenulum.
For inflammatory processes, treatment comes down to taking medications and performing physical procedures. If the patient follows all the specialist’s recommendations, improvement in well-being occurs in a short time.
Herpes
Herpes has a peculiarity - “sores” always appear in the same place. This means that if they appeared under the tongue, they will recur there. Relapses of herpes occur when the immune system is weakened, stress, hypothermia or overheating, after illness.
READ ALSO: pimples appeared on the tongue: causes, photos and treatment
The disease is characterized by a painful rash. It consists of transparent bubbles that are located almost on top of each other, forming a large blister.
READ ALSO: blisters appeared on the lips: symptoms, photos and treatment
Drug therapy
If any form of inflammation under the tongue appears, both mild and moderate, it is not recommended to take any therapeutic measures without first consulting a specialist. A swollen area in the sublingual area may hide the formation of a malignant tumor. Therefore, differential diagnosis is required.
As a rule, therapeutic tactics to combat symptoms of inflammation in the oral cavity begin with the use of rinsing solutions:
- antiseptic - Miramistin, Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt;
- anti-inflammatory - Iodinol, Rotokan, Potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine.
It is better to carry out procedures for rinsing the mouth 4-6 times a day to prevent further proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms.
If the tumor in the sublingual area is caused by damage to the salivary glands of bacterial etiology, the doctor will select antibacterial therapy. Injections directly into the swollen area have proven themselves to be excellent. Penicillin drugs are used in combination with novocaine. If the patient is intolerant to medications of the penicillin subgroup, inject streptomycin.
In severe cases of pathology, antibacterial drugs are recommended for parenteral administration - intramuscularly or intravenously. The total duration of therapy is determined by the doctor individually.
Symptomatic treatment:
- antipyretics – Paracetamol, Ibuprofen;
- analgesics - as needed;
- detoxification therapy for severe cases - intravenous drip administration of glucose solution, Ringer.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend physiotherapy - Sollux, electrophoresis, UHF.
Very effective remedy for tongue ulcers (for adults)
One of the reasons for the appearance of ulcers on the tongue may be any disease:
- stomatitis - acute or chronic inflammation of the oral cavity caused by a number of reasons;
- Setton's aphthosis - differs in the color of the ulcers (with this disease they have a whitish tint) and location (under the tongue);
- Bednar's aphtha - occurs in children; looks like small yellowish ulcers located on the side of the tongue;
- viral infection;
- syphilis;
- HIV and other diseases associated with immunodeficiency;
- gingivostomatitis;
- tongue cancer - most often women suffer from this disease; can only be cured by surgery.
Surgical treatment
The doctor will decide that the tumor under the tongue needs to be removed surgically if conservative treatment methods are ineffective. Indications for surgical excision of the lesion are:
- increase in pain syndrome;
- persistent increase in temperature;
- increase in tumor size;
- involvement of neighboring tissues and lymph nodes in the process;
- detection of stones in the salivary glands;
- lack of pronounced positive dynamics from the use of medications.
The tactics of surgical intervention are determined by the doctor, taking into account all the information from diagnostic measures. If a malignant process is detected, chemotherapy will be additionally prescribed - the introduction of special medications that suppress the growth of cancer cells, as well as radiation therapy - the effect of ionizing radiation on the tumor.
During the recovery period - after surgical excision of the pathological focus, the doctor will give detailed instructions on observing the rules of oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth 2–3 times a day with a gentle toothpaste;
- use rinses - for example, based on a decoction of chamomile, calendula;
- eat dishes at room temperature, with carefully crushed ingredients, so as not to further injure the oral mucosa;
- avoid long physical activity - talk less.
Early detection of inflammation in the sublingual area and timely implementation of treatment procedures is the key to a quick recovery and the absence of serious complications.
How to treat?
Depending on why the gland became inflamed and a tumor occurred, different treatment options are selected. In case of moderate condition, a novocaine blockade may be prescribed.
| Forms of sialadenitis | Treatment methods |
| Sialadenitis of infectious origin | Antiviral or antibacterial therapy: irrigation of the sublingual area with antiviral agents, administration of antibiotics inside the gland duct. Antipyretics, drugs to intensify salivation, physiotherapeutic procedures. |
| Sialadenitis as a complication of another disease | In addition to symptomatic therapy, the underlying disease is treated. |
| Purulent sialadenitis | In addition to drug treatment, an autopsy of the purulent focus may be performed. |
| Sialadenitis caused by a foreign body entering the duct | Surgical removal of a foreign body, anti-inflammatory drug therapy. |
With frequent inflammation of the parotid, sublingual or submandibular gland, a chronic form of sialadenitis may develop, which is difficult to treat. Sometimes it is not possible to completely cure the pathology. Therefore, you need to go to the doctor immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear; the course of treatment must be completed to the end.
Trying to relieve swelling under the tongue at home, without examination and doctor’s prescriptions, is dangerous. Self-selected methods of traditional medicine can be harmful or simply fail to have the desired effect, as a result of which the disease will continue to progress. In the presence of serious diseases of internal organs and neoplasms, delay in treatment can lead to dire consequences. Therefore, at home you need to perform only those procedures prescribed by the doctor.
If something is swollen and painful under the tongue, or pus comes out of the salivary ducts, you need to go to a therapist or dentist. A thorough examination is necessary to determine an accurate diagnosis, and then diligent treatment. It is necessary to try to cure the disease while it is in the acute phase, since the advanced chronic form of sialadenitis is not always completely curable.
The disease should be treated in the early stages of development. Chronic pathology is practically not amenable to medication and will periodically remind itself. To treat the disease, antiviral, anti-inflammatory medications, and sometimes antibiotics are usually prescribed. Particular attention is paid to local treatment.
During the therapeutic process, patients are recommended to take medications that will increase salivary secretion. Medicines such as Pilocarpine, Potassium Iodide and Galantamine are usually administered using physiotherapeutic methods (electrophoresis, galvanization). In cases of severe pain, novocaine blockades are used. Surgery is indicated only in severe cases, when inflammation under the tongue is accompanied by the formation of purulent accumulations.
Treatment of a chronic inflammatory process in the salivary glands takes a longer time. Doctors recommend that during exacerbations of the disease, taking antibacterial drugs and medications that will increase the secretion of salivary fluid. Patients suffering from a chronic type of sialadenitis need regular prevention of pathology.
Cancer
Tongue cancer is a malignant formation of squamous epithelial cells.
In men, the disease occurs 6–7 times more often than in women. Provoking factors of the disease are smoking, alcohol consumption, chronic mechanical trauma to the tongue, carriage of the herpes virus and human papillomavirus.
There are 3 clinical forms of tongue cancer:
- infiltrative;
- ulcerative;
- papillary.
In the infiltrative form, the pain syndrome comes first. A dense, tuberous infiltrate without clear boundaries is palpated on the tongue. The ulcerative form is characterized by the formation of an ulcer with uneven and bleeding edges.
Tongue cancer
In the papillary form of cancer, the formation protrudes above the surface of the mucosa.
Most often, cancer affects the lateral surfaces of the tongue. Less commonly, the root, lower surface and back are affected.
The first symptoms of a cancerous tumor are a feeling of discomfort in the mouth, the presence of an ulcer or formation. Then there is pain, itching, burning, swelling of the face, neck, and bad breath. In advanced stages, patients find it difficult to speak, swallow saliva and food, and bleeding occurs from the tongue.
Tongue cancer is characterized by rapid growth and metastasis.