What does it represent?
In medical terminology, a pip or callus is called glossitis. This is an inflammatory disease of the tissue fibers of the receptor organ (tongue), caused by the formation of cracks, mechanical damage, wounds or burns on the mucous tissues of the organ where the infection penetrates.
In other words, any cuts on the tongue facilitate the active penetration of bacteria into them, which instantly cause inflammation, redness and create great discomfort.
Glossitis is one of the most common oral pathologies. Children, especially young ones under 5 years of age, are at high risk. They are the ones who pull dirty toys and hands into their mouths, thereby allowing bacteria to penetrate and infect mucous tissues.
Stomatitis under the tongue
The oral cavity is one of the most vulnerable parts of the human body. She is constantly in contact with bacteria, exposed to irritation or minor injuries. Oral infections occur quickly and often unnoticed. What causes the infection? What symptoms may the patient exhibit? What to do if a blister pops up, and how to treat it correctly?
Main symptoms
A pathological rash may appear under the tongue, on the root of the tongue, on the palate, or cover the entire oral cavity. It depends on the causative agent of the disease, as well as its neglect. Main features:
- the presence of blisters, ulcers, hematomas, ulcers or abscesses in the mouth (we recommend reading: mouth ulcers: causes, symptoms with photos and treatment),
- discomfort and pain,
- inflammation of the mucous membranes,
- change in color of the mucous membrane (becomes red),
- raid,
- bad breath.
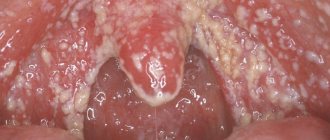
White sores under the tongue and in the mouth
White sores are usually a symptom of candidiasis. Fungal stomatitis under the tongue, near the frenulum, at its root and in the entire oral cavity is characterized by the formation of a characteristic white coating (film) (we recommend reading: why is there a white coating on the tongue of an adult and how to treat it?). In addition to white sores, stomatitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
READ ALSO: stomatitis on the tongue: symptoms with photos and treatment
- burning and itching
- formation of a dense white coating,
- feeling tired or lethargic
- loss of appetite,
- when pressed the bubble hurts,
- salivation is impaired,
- taste perception is impaired.
Blood blister on the root or center of the tongue
Typically, blisters on the base of the tongue are filled with clear fluid. A bloody wound indicates damage to the blood vessels. This means that the infection has penetrated deep into the tissue, and in the absence of treatment, serious problems (abscess or abscesses of the root of the tongue) are possible.
Watery “sores” or spots occur due to infectious diseases of the ENT organs. Against the background of reduced immunity, infection of the mucous membrane occurs.
In this case, the following symptoms will be present:
- heat,
- a sore throat,
- redness of the throat walls,
- dense coating of yellow or gray color,
- tonsillitis,
- cough.
Bloody sores or blisters may indicate a herpes virus. The blister will consist of many small bubbles. At the same time, itching and burning are felt. The tissues of the mouth swell, the color of the mucous membrane changes. Possible increase in body temperature. After a few days, the balls burst, forming painful erosion.
Blisters or sores under the tongue
Ulcers and blisters under the tongue near the frenulum may indicate disturbances in the functioning of the salivary glands, dental diseases, infection of scratches, and stomatitis. Symptoms will directly depend on the nature of the disease.
With stomatitis, spots or dots spread throughout the mouth, pain, redness, and swelling appear. Violation of the process of saliva production leads to the appearance of an unpleasant odor and plaque.
Pathologies of teeth or gums are characterized by pain and bleeding. The pain often radiates to the ears or temples.
Other symptoms
Ulcers or blisters in an adult are caused by many internal pathologies and external factors. There are a number of signs that may accompany the disease:
- enlargement of the tongue (allergic reaction),
- chronic cough (tuberculosis),
- change in voice timbre,
- inflammation of the lymph nodes,
- the presence of dense plaques under the tongue or on its root (lichen),
- headache, fever, weakness (chicken pox or scarlet fever),
- the appearance of pus in blisters, bleeding, increased salivation (ulcerative necrotizing gingivostomatitis), etc.
Causes of pain under the tongue
Pathologies that cause ulcers or hematomas under the tongue near the frenulum:
- stomatitis,
- herpes,
- ENT diseases (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis),
- fungal infections,
- allergy,
- dermatitis,
- scratches or wounds,
- chicken pox,
- scarlet fever,
- tuberculosis (in rare cases),
- thermal or chemical burns,
- malignant formations, etc.
Stomatitis
Most often, the disease is caused by fungal or viral infections. Canker sores or ulcers can spread throughout the mouth or be localized to a specific area.
Reasons for appearance:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules,
- unsatisfactory condition of teeth (tartar, caries),
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract,
- permanent injuries to the mucous membrane due to braces or crowns,
- abuse of bad habits,
- the presence of a fungus or virus in the body.
Herpes
Herpes has a peculiarity - “sores” always appear in the same place. This means that if they appeared under the tongue, they will recur there. Relapses of herpes occur when the immune system is weakened, stress, hypothermia or overheating, after illness.
READ ALSO: pimples appeared on the tongue: causes, photos and treatment
The disease is characterized by a painful rash. It consists of transparent bubbles that are located almost on top of each other, forming a large blister.
READ ALSO: blisters appeared on the lips: symptoms, photos and treatment
Sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis
Infectious diseases of the ENT organs often lead to pathologies of the oral cavity. Pathogenic microorganisms pass from the nasopharynx to the mouth, causing problems. READ ALSO: how to remove burning sensation in the mouth and tongue?
The base of the tongue is attacked first, as it is closest to the throat. Ulcers under the tongue form later when the bacteria have spread. That is why sore throat, pharyngitis or tonsillitis cause an abscess of the root of the tongue (purulent inflammation leading to tissue melting).
READ ALSO: inflammation under the tongue: what could it be?
Allergy
Allergic reactions in the mouth are called allergic stomatitis. At the same time, the tongue swells and enlarges. Itching and discomfort are felt. Allergies are mainly caused by food and medications. The reaction can develop after accidentally ingesting foreign chemicals into the mouth.
To relieve swelling, you must immediately eliminate the irritant and take an antihistamine. Afterwards, you should contact an allergist to prescribe therapy.
Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a common manifestation of allergies. The disease is difficult to tolerate and difficult to treat. The cause of dermatitis is chronic allergies and genetic predisposition.
In addition to the mucous membranes, painful bumps appear on the face or other parts of the body. The patient feels constant pain of varying degrees and severe itching.
READ ALSO: there is a lump on the gum above the tooth and it doesn’t hurt: what to do?
Why did sores form under the tongue?
Why do bubbles or hematomas appear in the mouth? “Sores” under the tongue cannot be called a separate disease; they are usually an external symptom of one of the ailments. Externally, blisters and ulcers differ from each other in each individual case. This is especially clear if you look at the photos of several patients.
Factors that influence the appearance of tumors under the tongue or on the tongue:
READ IN DETAIL: how to treat ulcers on the tongue?
- reduced immunity,
- exacerbation of chronic diseases,
- disturbance of the oral microflora or the amount of saliva produced,
- long-term use of medications, especially antibiotics,
- chronic gastrointestinal problems, etc.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you notice that a spot has appeared under the tongue or an abscess has appeared, you should immediately consult a doctor (we recommend reading: what are the reasons for spots on the tongue?). Depending on the accompanying symptoms, patients turn to a dentist, ENT specialist or therapist.
First of all, the doctor conducts a visual examination and determines the nature of the rash. To confirm the diagnosis, laboratory tests are prescribed: blood test, smear, ulcer biopsy. After a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and prescribes the correct and effective course of treatment.
Treatment of blisters under the tongue
The course of therapy should also be comprehensive. It is necessary to fight the cause and relieve unpleasant symptoms. Usually a course of medications, antiseptic and healing agents, and a gentle diet are prescribed.
Sometimes alternative treatment is used in parallel with drug therapy. It calms inflammation and speeds up the healing process.
Medicines
Medicines are prescribed to combat the causative agent of painful spots or abscesses. Depending on the nature of the infection, these may be:
- antibiotics (Amoxicillin, Cifran, Metronidazole, etc.),
- antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Riodoxol, Tebrofen),
- antifungal agents (Candide, Amphotericin, Levorin),
- To heal and reduce the inflammatory process, gels and ointments are used (Cholisal, Stomatidin, Holicet).
Rinse
Rinsing with disinfectant solutions plays an important role in the healing process. A number of drugs are suitable for these purposes:
- chlorhexidine,
- furatsilin,
- stomatidine,
- hexethidine,
- miramistin,
- iodoform,
- betadine,
- hydrogen peroxide,
- chlorophyllipt.
You need to rinse your mouth at least 2 times a day, after clearing it of food debris. After the procedure, you should refrain from eating and drinking for about 30-60 minutes. This will increase its effectiveness.
Other treatments
Folk recipes that have antiseptic, soothing and healing properties:
- Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt and soda in a glass of warm water, add 1-2 drops of iodine. Repeat rinsing 3 times a day.
- Aloe. Squeeze the juice from the plant leaf and rinse your mouth with it 3 times a day. Cut a piece of fleshy leaf lengthwise and apply it to the diseased area with the inside.
- Collection of medicinal herbs (oak bark, chamomile, calendula, thyme, celandine, sage St. John's wort). Take 4 tablespoons of dry ingredients for 0.5 liters of water, boil for 15 minutes, cool and strain. Use as a rinse or compress.
Prevention of oral diseases
Preventative measures are simple, everyone can follow them:
- maintaining hygiene,
- complete nutrition,
- drinking enough water
- taking vitamins,
- regular dental checkups,
- periodic general medical examinations,
- strengthening the immune system,
- limiting or completely abandoning bad habits,
- timely treatment of injuries in the mouth.
Loading…
Source: https://spacream.ru/stomatologiya/stomatit-voldyri-i-bolyachki-pod-yazykom-shema-lecheniya-v-zavisimosti-ot-prichiny-vozniknoveniya-yazv
Causes
As already mentioned, glossitis occurs as a result of damage to the integrity of the soft tissues of the receptor organ. But this is not the only reason.
Quite often, a callus on the tongue does not appear as a separate disease, but indicates the presence of more serious pathologies of the body.
There is a list of factors that, to some extent, can influence the development of glossitis. So, the main causes of calluses on the tongue are as follows:
- Injuries to the mucous tissue and fibers of the tongue. This can be cuts from cutlery, sharp edges of lollipops or sucking sweets, biting the tongue, piercing with a fish bone, damage to the shell from seeds, stale food (bagels, crackers, crispbread, etc.).
- Prolonged sucking of lollipops also leads to damage to the mucous membrane, because such products cause tissue irritation.
- Irritation of the mucous membranes as a result of eating hot, spicy and very salty foods.
- Any allergic reaction to any food can cause swelling of the tongue, which develops into an infectious inflammation.
- Carbonated drinks, concentrated juices, sweet water. All these products contain large amounts of citric acid, which in high concentrations can burn the mucous tissues of the oral cavity. You should be especially careful when drinking alkaline water.
- Drinking alcohol, as alcohol corrodes soft tissue.
- Smoking. Nicotine contained in tobacco consists of 30% heavy salts that burn mucous tissues.
- Very often, the cause of a callus on the tongue can be various types of dental diseases, such as periodontitis, stomatitis or gingivitis.
- Oxidative reactions in the mouth resulting from the installation of braces or plates made of low-quality metals.
- Lack of vitamins, in particular lack of protein and amino acids.
- Acute diseases of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas.
- Poor oral hygiene. Everyone brushes their teeth at least twice a day, but you shouldn’t forget about your tongue. The plaque that accumulates on it indicates that the pores are clogged with food debris.
- Ulcers on the tongue also occur as a concomitant symptom of diseases such as scarlet fever, measles, rubella, and syphilis.
- Infestation caused by worms and other intestinal parasites.
Quite often, small pimples on the tongue can appear during acute respiratory diseases, such as purulent tonsillitis.
It should be remembered that a pip on the tongue is the cause of a condition such as pain, nervousness, and it must be treated regardless of its origin.
Callus on the tongue and mucous membranes of the mouth in children and adults: how to treat
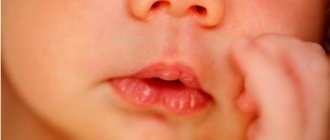
True calluses in the mouth occur only on the lips, and they are observed exclusively in newborns.
The fact is that their skin is very delicate and vulnerable, so even a soft rubber nipple or mother’s breast can rub it.
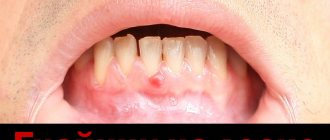
A callus on the tongue, on the gum, on the palate, on the inside of the cheeks is actually a blister that can appear at any age as a result of microtrauma.
Causes and symptoms
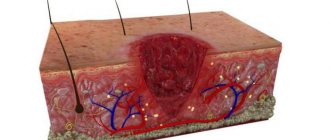
A callus is a keratinization of the skin as a result of a protective reaction to mechanical friction or pressure.
If the body feels a threat to the integrity of any area of the skin or mucous membrane due to heavy load, it forms an additional layer of dead epithelial cells in this place.
In newborns, a similar formation may appear on the lips - it is called a milk callus. At first it looks like a bubble filled with a colorless liquid - phlegm.
This bubble may then burst and turn into a white lump. The child does not feel any discomfort, since there are few nerve endings in these areas of the mucosa.
There is only one reason for the appearance of a milk callus - intense sucking.
Blisters due to microtrauma
Injury can occur anywhere on the mucous membrane of the mouth or lips as a result of accidental biting or other minor injuries, such as from seeds or chewing candy.
Often, a protective reaction in the form of local tissue necrosis can be a consequence of a burn due to too hot food, irritation from salty or spicy foods.
The blister formed in this area resembles a water callus and is of a similar nature.
People with braces are at risk: their oral cavity is injured very often.
The mucous membrane is less resistant to damage if the body lacks vitamins A or C. With a lack of vitamin A, it becomes dry, and therefore more vulnerable. A lack of vitamin C has a bad effect on the condition of blood vessels, which can cause blood blisters to appear in the mouth.
Diseases that are often mistaken for calluses
It is quite easy for a person to determine whether a blister in his mouth is actually the result of an injury: if he does not remember under what circumstances the injury occurred, it is probably a symptom of a disease, and not a slight damage to the mucous membrane. But people still often make the mistake of considering a callus to be a manifestation of pathology:
- Stomatitis. This disease can be caused by many reasons. In some cases, its symptoms are similar in appearance to the formation of a callus: rashes appear in the mouth that resemble blisters - one or a whole scattering. Stomatitis can be caused by viruses, bacteria (usually staphylococci), fungi (candidiasis), radiation and severe chemical burns.
- Pemphigus. An autoimmune disease that causes watery blisters to appear in the mouth. There are types of pemphigus that affect the skin.
- Oral vascular diseases. Abnormal growths or tumors of blood vessels can also at first be mistaken for blood-filled blisters formed as a result of injury.
Drug therapy
In infants, milk calluses appear often, but quickly pass and do not leave any traces. There is no need to treat them, but to avoid the risk of infection, a burst water callus on the baby’s lips should be treated with a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
Under no circumstances should you pierce a blister on the baby’s oral mucosa or lips!
Blisters due to microtrauma also go away easily. Usually no special measures need to be taken other than careful hygiene. For better disinfection, it is a good idea to rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine.
But if such a formation does not resolve within a week, you need to consult a doctor.
He may discover hemangioma (proliferation of vascular walls), vascular tumors, or other diseases that the patient mistook for traumatic blisters.
If blisters in the mouth appear frequently, this may be a sign of vitamin deficiency. In such cases, the missing vitamins are prescribed, usually A or C.
Traditional treatment
Folk remedies used in such cases are needed for better disinfection of the mouth in order to reduce the risk of infection of the lesions. The simplest and most accessible active ingredient is ordinary soda. You need to rinse your mouth with the solution after each meal, diluting a teaspoon of powder in a glass of water.
Herbal infusions are also widely used for the same purpose. They are usually prepared in a glass, pouring boiling water over a certain amount of medicinal herb and keeping it covered for 15-20 minutes, after which it is filtered and used for rinsing. To make such solutions, use one of the following plants (per glass of boiling water):
- chamomile - 2 teaspoons,
- sage - 3 teaspoons,
- St. John's wort - 1 tablespoon,
- calendula - 2 tablespoons,
- eucalyptus - 1 tablespoon.
One of the most powerful anti-inflammatory and regenerating agents is oak bark: pour 2 tablespoons with a glass of boiling water and then keep it in a water bath for fifteen minutes. The strained and cooled product is used for rinsing.
Calendula and eucalyptus are often used in the form of alcohol tinctures (20-30 drops per glass of water). It is also useful to rinse your mouth with propolis tincture - 1 teaspoon per glass of water.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely prevent the formation of calluses in infants or microtraumas of the oral mucosa in adults. However, you can reduce the risk of infection and complications. To do this, you just need to maintain good hygiene, brush your teeth twice a day and preferably rinse your mouth with a special liquid after eating.
It is better to peel seeds and nuts with your hands rather than chew them in your mouth.
Babies also have their own hygiene rules. It is necessary to wipe your mouth with a cotton swab moistened with warm water half an hour after eating. For the same purpose, you can use special wipes soaked in xylitol solution. The first teeth should be brushed with a very soft brush designed for infants. The paste can only be used after reaching one year.
Assess your chances against coronavirus. Take our test
Attention!
The site administration advises you not to self-medicate, and in any controversial situations, consult a doctor.
Source: https://fr-dc.ru/kozhnye-zabolevaniya/travmy-kozhi/mozoli-i-mikrotravmy-vo-rtu
Symptoms
The most important thing is to be able to distinguish ordinary glossitis from inflammation caused by various diseases. At the first signs of pathology, it is recommended to consult a doctor.
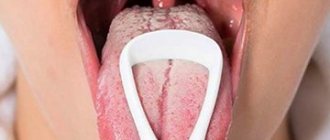
Among the main symptoms of calluses on the tongue are:
- changes in the color of the tongue, it can become brighter (rich red or crimson) or, conversely, fade, changing color to white-pink;
- the formation of a large amount of plaque, causing an unpleasant taste and sensation in the mouth;
- small spots that appear in a specific area or throughout the tongue;
- swelling of the tip of the tongue, in which the pores are clearly visible, the surface looks loose;
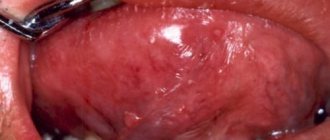
- tissue compaction, roughening, appearance of small blisters;
- callus can have different shapes - it can be in the form of a purulent abscess, plaque, small tissue compaction, inflammation;
- the tongue may dry out and crack;
- compacted tissues cause discomfort, especially when chewing food, causing sharp pain and burning.
Even the slightest changes in the mucous tissues and fibers of the tongue, which are hardly noticeable to the naked eye, are clearly noticeable, so violations will become known from the very beginning.
The difference between milk callus and pathologies
Most parents of infants do not have higher medical education, so they can easily confuse a harmless milk callus with a dangerous pathological rash.
To prevent this from happening, you need to know the main differences between them:
- The callus from sucking has a round shape, resembling a bead with a diameter of up to 5 mm. It is located in the middle of the upper lip (very rarely on the lower lip). The color of the safe callus matches the color of the child's lips. This is a single neoplasm that is not accompanied by other rashes;
- pathological inflammation has a white, gray or yellowish color, accompanied by the appearance of white ulcers, blisters or plaque both in the child’s mouth and in other areas (in the corners of the mouth - “zaids”, genitals, face, soles). First of all, it is recommended to examine the baby’s mouth: the inside of the cheeks, tongue, palate, neck. The presence of inflammation in the mouth can be a manifestation of herpes, infectious stomatitis or thrush.
Symptoms indicating the inflammatory nature of the neoplasm:
- increased body temperature;
- irritability and moodiness;
- loss of appetite;
- change in stool (constipation or diarrhea, sour odor, green color);
- severe regurgitation in infants and vomiting in one-year-old children;
- sweating;
- increased salivation;
- rash, redness of the skin.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Transparent pimple on the lip inside
Diagnostics
As mentioned earlier, at the first signs of inflammation of the mucous tissues of the oral cavity, you need to consult a therapist who can determine the severity of the disease and prescribe additional examinations from doctors of a more specialized profile.
As a rule, the diagnosis of glossitis consists of the following steps:
- General examination by a general practitioner.
- Examination of the oral cavity and ENT organs by an otolaryngologist.
- Saliva analysis.
- Analysis of scraping plaque and saliva from the site of inflammation.
- Analysis of pus in the presence of purulent inflammation.
- If necessary, general and extended (biochemistry) blood tests can be performed.
As a rule, all of the above diagnostic methods are quite sufficient to determine the root causes of glossitis formation. A study of saliva and scrapings with pus will help determine the etiology of the disease and determine whether it was caused by a virus or an ordinary infection.
If the problem lies deeper, blood tests will show deviations from the norm in certain indicators, which will become the basis for further, more detailed examination.
Feeding rules and prevention of occurrence
During the first months of life, a child’s desire to suck appears every 1 hour during the day, and 3-4 times at night. When breastfeeding, the mother gives breast at the baby's request. With the breast in his mouth, he relaxes, gets the right dose of milk, and falls asleep. Sucking gives him a feeling of peace. When feeding on demand, nipples and bottles are not used to avoid loss of breast milk.
Feeding by the hour when the mother does not have her own milk or there is a deficiency. The mixture is taken every 3 hours. With such feeding, there may be problems with lactation and lack of milk. Prevention of formations - apply natural olive and vegetable oil to the baby’s delicate skin. The products will help soften the callus and rough crust.
If there are difficulties with artificial feeding:
- the hole in the nipple should be made wider;
- change the nipple to a silicone nozzle. Latex is tactilely more pleasant.
Nutrition
The first step is to remove the load from the tongue so that the disease does not worsen. To do this, use a special diet that limits the consumption of salty, sweet, pepper and spicy foods, and excludes alcohol, carbonated drinks, juices, various sauces, ketchup and mayonnaise from the diet.
Food should be soft, easy to chew, without touching the inflamed areas. This could be mashed potatoes, soy pudding, chicken broth, fruit yoghurts.
If the cause of the callus is an infection, the consumption of fermented milk products is strictly prohibited. The bacteria it contains create a favorable environment for the development of pathogenic organisms, which can aggravate the situation and slow down the treatment process.
Drug treatment
To eliminate pain, discomfort and relieve inflammation, doctors recommend using painkillers, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen, Ledocaine, Drotaverine.
In case of severe damage, agents are prescribed that accelerate the processes of restoration of mucous tissues. For example, “Glutamine”, “Imudon”.
To eliminate the infection, you must regularly rinse your mouth every 2 hours. For this purpose, special solutions are used - “Furacilin”, “Chlorhexodine”, “Hexoral”.
Folk remedies
If the inflammation is minor, many recommend treating tongue tip at home using both traditional medicine and pharmacy analogues.
The best way to relieve inflammation and disinfect the oral cavity is chamomile infusion. An infusion of oak bark will help heal ulcers and cuts, if any.
In pharmacies you can also buy ready-made concentrates of celandine, calendula, nettle or St. John's wort for rinsing the mouth. It is recommended to lubricate small pustules with sea buckthorn oil or rosehip oil.
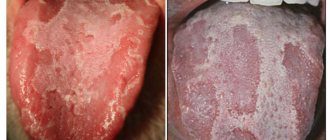
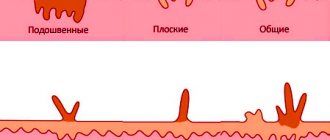
Types of mouth ulcers
And this is what this disease looks like in the photo.
Ulcers are very diverse, they differ in color and location.
Depending on the color, ulcers are distinguished:
- white (milky and light beige);
- red (light or bright red).
Types of white sores include:
- leukoplakia;
- candidiasis.
We suggest you read: Cheek swollen after tooth extraction
Leukoplakia is whitish in color and most often forms on the cheeks, gums and tongue. Appears as a result of excessive cell growth. People who abuse smoking are especially susceptible to their formation. Such ulcerations are dangerous because they can develop into cancer.
Candidiasis (oral thrush) occurs due to the proliferation of a fungal yeast infection.
Often such milky ulcers appear in people wearing dentures, people with weak immune systems, young children and after treatment with antibiotics.
White sores are usually painless and disappear in a short time.
Red types of ulcers include herpes ulcers, aphthous stomatitis and syphilis ulcers. They are characterized by pain and cause discomfort to the patient. These ulcers have a bright red base and may bleed upon contact with their surface.
Recovery may take from 1 to 3 weeks. The peculiarity of such ulcerations is that they can form on almost any part of the oral cavity.