Reasons for development
Candidiasis develops when the fungus penetrates the mucous membrane of the throat. Microorganisms produce enzymes that damage the cells of the nasopharynx and surrounding tissues. There are several reasons for the development of the disease:
- weak immunity
- poor condition of the oral cavity (presence of caries, adenoids, etc.)
- burns of the oral cavity (thermal, chemical)
- autoimmune processes in the body
- avitaminosis
- diabetes
- obstructive respiratory diseases
- improper treatment of nasopharyngeal diseases (laryngitis, pharyngitis, sore throat)
- long-term use of certain medications (antibiotics, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, hormonal agents)
- chronic exhaustion of the body due to stress, fasting, heavy physical activity
Factors contributing to the development of candidiasis:
- severe infections
- taking alcohol or drugs for a long time
- chemotherapy, radiation therapy
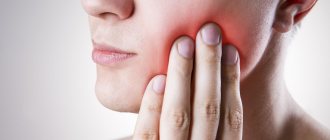
Symptoms of candidiasis
The initial stage of candidiasis is often not accompanied by clinical symptoms. When candida in the throat begins to actively multiply, a characteristic sign of the disease appears - a cheesy-white coating in the mouth. This is why candidiasis is sometimes called thrush. Other symptoms:
- redness
- pain
- appearance of dryness
- edema
- soreness, itching, burning
- increase in the size of the tonsils
In addition to the throat, the fungus often affects the oral cavity and larynx. The intensity of symptoms increases after taking sour, spicy, hot foods. If fungi cause a sore throat or pharyngitis in an adult, the temperature rises, weakness and malaise appear.
In children, candidiasis manifests itself more clearly, accompanied by symptoms of pharyngitis and high fever. If purulent processes occur, the plaque in the mouth may turn yellow. When you try to remove it, erosions remain and a little blood is released.
What is the candidiasis diet and how does it work?
The candida diet requires people to avoid foods and drinks that may increase the risk of candida overgrowth. These include gluten, sugar, alcoholic beverages and some types of dairy products.
Instead, the diet focuses on consuming lean proteins, healthy fats, non-starchy vegetables and probiotics. The purpose of using these foods is to help minimize inflammation and balance bacteria in the gut.
Higher glucose concentrations may promote Candida growth, according to a 2020 laboratory study. Researchers have also found that foods containing fructose may inhibit the growth of Candida in the mouth.
Theoretically, people may have a lower risk of developing a Candida infection if they eliminate foods that promote yeast growth. However, available scientific evidence does not yet support the effectiveness of this diet.
Complications
If there is no adequate treatment, inflammation continues to develop. The mucous membrane of the oropharynx is significantly damaged and erosions form. Under the influence of bacteria, secondary inflammation develops, accompanied by the appearance of abscesses.
Candida from the throat spreads to other parts of the respiratory organs. The disease can be complicated by the following pathologies:
- cheilitis (candidal lesions of the lip border)
- stomatitis (infection with oral fungi)
- laryngitis (inflammation of the larynx)
- glossitis (tongue damage)
- pharyngitis (inflammation of the pharynx)
- tonsillitis (inflammation of the tonsils)
If the immune system is very weak, a generalized infection develops. This is a very serious condition that is life-threatening and requires hospital treatment.
Where do Candida fungi live, routes of infection
Depending on the location of the foci of inflammation, the following types of oropharyngeal candidiasis differ:
- Cheilitis . Characterized by fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the lips, external manifestations: microcracks, peeling scales, uneven seals over the entire surface of the epithelium. With angular cheilitis, erosions (jams) occur in the corners of the mouth.
- Gingivitis . The area where fungus grows is the gums. They become covered with a white-gray coating of a cheesy consistency, become inflamed, and begin to bleed.
- Glossitis . The tongue suffers from an infectious lesion: microcracks and ulcers are formed, covered with a thin grainy white film.
- Stomatitis . Obvious manifestations of thrush are observed on the mucous membranes of the internal oral cavity. A white, yellowish or gray plaque is easily separated with a spatula, exposing the epithelium affected by many small ulcerations.
- Throat candidiasis , which is manifested by the following diseases: pharyngitis (infection invades the pharynx), tonsillitis (thrush invades the tonsils) and laryngitis (fungus settles in the larynx).
Fungal diseases of the throat of a focal nature are rare; usually there is a diffuse spread of pathogenic microorganisms throughout the entire area of the mouth and nasopharynx.
Depending on the degree of damage, a distinction is made between superficial throat candidiasis (fungi progress on the mucous membranes) and deep mycosis (with the formation of internal necrotic ulcers and tumors).
Treatment
Treatment of throat candidiasis must begin as quickly as possible, otherwise the disease will become chronic. Therapy is combined. It includes the following therapeutic measures:
- Taking systemic antifungal drugs and antibiotics
- Removal of plaque followed by treatment of the oral cavity
- Strengthening the immune system
- Following a special diet
Drug therapy
The following drugs are used in treatment:
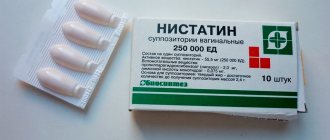
- Nystatin in a daily amount of 1500 thousand-2000 thousand units (for adults), 500 thousand-1 500 thousand units (for a child). The indicated dose is divided into 3-4 doses. The tablets are kept in the mouth until dissolved or swallowed
- Decamine is dissolved in 1-2 pieces. at intervals of 3-4 hours. After this, you should not drink or eat for 30-40 minutes.
- Ketoconazole is prescribed to adults and children over 2 years of age. The daily dosage can be 0.05-0.4 g. Duration of treatment – 4-6 weeks
- Fluconazole is used to treat candidiasis in adults. The daily amount is 50-100 mg. Fluconazole therapy is carried out from 7 to 30 days. Its duration depends on the severity of the fungal infection
At elevated temperatures, take antipyretics. To strengthen the immune system you need to take:
- immunostimulants
- restorative medications
- adaptogens (based on ginseng, echinacea, eleutherococcus)
- vitamins (especially group B, ascorbic acid)
Children can be given immunoflazid. Since oral candidiasis is usually accompanied by intestinal dysbiosis, probiotics (Linex, bactistatin, normobact) are needed.
Local therapy
The following is used as local therapy:
- Rinse with miramistin or chlorhexidine. You can use an infusion of oak bark, a solution of soda, boric acid, as well as a solution prepared from propolis tincture
- The throat should be treated with Lugol's solution or sea buckthorn or rosehip oil
- Lubricate the oral cavity with aniline dyes (for example, 2% fucorcin)
- Cracks that appear on the skin near the mouth are treated with amphotericin, nizoral 3-4 times a day
Physiotherapy treatments are effective:
- Ural Federal District
- laser therapy
- electrophoresis with potassium iodide solution
If you have dentures, you need to clean them regularly. Treatment of candidiasis is carried out under medical supervision; during this period it is necessary to regularly take blood tests.
Diet
During the treatment of candidiasis, a special antifungal diet is necessary. Its basis is:
- whole grain porridge with water
- buckwheat
- fish
- eggs
- vegetables
- lean meat
Healthy vegetables include: tomatoes, cabbage, onions, bell peppers, garlic, herbs.
Excluded:
- products containing sugar, fructose, vinegar
- products containing yeast
- products containing barley, wheat
- rice
- milk, fermented milk drinks and products
- pickles
- sauerkraut
- dried fruits
- baking
- mushrooms
- sweet soda
- alcohol
- coffee Tea
You need to eat 5-6 rubles/day, in small portions. Following such a diet will quickly get rid of candidiasis.
Traditional methods of treatment
For candidiasis, traditional methods are good only as a complement to the main treatment. The disease is fought by gargling and treating the oropharyngeal mucosa. This will speed up your recovery.
- Recipe No. 1. Extract the juice from a plant called golden mustache. Pour 1 tablespoon into 200 ml of water. l. juice, 1 tsp. l. lemon juice. You need to gargle 3 times a day
- Recipe No. 2. Squeeze the juice out of the cranberries. Add water in a 1:1 ratio. Gargle immediately after eating. Duration of treatment - 3-4 days
- Recipe No. 3. Pour 50 g of St. John's wort with olive oil (200 ml). Leave for 2 days (at room temperature). Treat your throat 3 times a day
- Recipe No. 4. Pour 1 tbsp. boiling water flax seeds in the amount of 2 tablespoons. l. Leave for an hour. Moisten a cotton swab or gauze, then lubricate the throat, mouth
- Recipe No. 5. Boil 1 liter of water. Add 1 table. l. salt and white of 1 egg. Gargle if you experience pain or irritation.
- Recipe No. 6. Make a solution of tea tree oil by adding 1 tbsp. water 2 drops of the product. Gargle several times a day
Consult your doctor before using these recipes.
How to treat throat candidiasis in a child
Pharyngitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis - the root cause of all these insidious ENT diseases is often massive damage to the mucous cells of the pharynx and larynx by Candida fungi.
If a person’s immune defense is strong enough, leukocytes and macrophages quickly destroy pathogenic flora, but if the body’s resistance is reduced, an acute inflammatory process provoked by a fungal infection - throat candidiasis - inevitably develops. Signs of thrush are often mild: no high fever, no severe pain in the larynx, no general weakness. It is for this reason that people go to the doctor untimely, only after a dangerous bacterial infection with life-threatening symptoms is added to the fungal infection.
Meanwhile, delaying the start of treatment for throat candidiasis leads to dire consequences: the fungal infection gradually affects the mucous membranes of the bronchi and respiratory tract, lungs, genitourinary and other organs, causing irreversible obstruction and severe toxicosis.
How to identify a fungus in the throat in time, what are the causes of infection and symptoms of candidiasis, how to treat thrush?
Depending on the location of the foci of inflammation, the following types of oropharyngeal candidiasis differ:
- Cheilitis . Characterized by fungal infection of the mucous membranes of the lips, external manifestations: microcracks, peeling scales, uneven seals over the entire surface of the epithelium. With angular cheilitis, erosions (jams) occur in the corners of the mouth.
- Gingivitis . The area where fungus grows is the gums. They become covered with a white-gray coating of a cheesy consistency, become inflamed, and begin to bleed.
- Glossitis . The tongue suffers from an infectious lesion: microcracks and ulcers are formed, covered with a thin grainy white film.
- Stomatitis . Obvious manifestations of thrush are observed on the mucous membranes of the internal oral cavity. A white, yellowish or gray plaque is easily separated with a spatula, exposing the epithelium affected by many small ulcerations.
- Throat candidiasis , which is manifested by the following diseases: pharyngitis (infection invades the pharynx), tonsillitis (thrush invades the tonsils) and laryngitis (fungus settles in the larynx).
Fungal diseases of the throat of a focal nature are rare; diffuse spread of pathogenic microorganisms throughout the entire area of the mouth and nasopharynx is usually observed.
Depending on the degree of damage, a distinction is made between superficial throat candidiasis (fungi progress on the mucous membranes) and deep mycosis (with the formation of internal necrotic ulcers and tumors).
Ways of infection with an infection that provokes candidiasis: endogenous, caused by the pathological proliferation of fungi that constantly live in the cavity of the oropharynx when factors unfavorable for the body occur, and exogenous (contact) with a sick person - household, sexual.
Babies can become infected with thrush during childbirth from a mother who is sick with vaginal candidiasis, or pick up a fungus while breastfeeding.
The risk group also includes:
- older children who may develop throat candidiasis due to dysbacteriosis, as well as incorrect use of antibiotics;
- children with a lack of vaccinated hygiene rules are also an important factor provoking oropharyngeal candidiasis;
- Children with high blood sugar levels (diabetics) are at risk of fungal infection of the mucous membranes;
- The development of thrush is promoted by viral and bacterial infections;
- Often the cause of the disease in children is improper metabolism - due to vitamin deficiency (or hypervitaminosis), as well as a deficiency of minerals;
- diabetic children are susceptible to fungal sore throat due to high blood sugar levels (a particularly favorable environment for fungi);
- A fungus in a child’s throat often forms as a result of autoimmune diseases.
Thrush can be provoked by dental diseases (caries, periodontal disease), as well as fungal diseases of the respiratory and digestive organs (along the ascending path).
Candidiasis in children often develops due to mechanical damage to the mucous membranes from an overly hot drink, swallowed hot cracker, or excessively spicy (sour) food.
In the photo, a whitish coating on the tonsils is a characteristic symptom indicating Candida fungus that has settled in the throat
To the above natural factors for the development of throat candidiasis, which are typical for children, are added age-related artificial causes of the development of fungal infection:
- long-term use of antibiotics, corticosteroids;
- constant use of antiseptics;
- the presence of caries, periodontal disease, gingivitis, stomatitis in advanced stages;
- poor-quality means for cleaning teeth and the oral cavity (pastes, rinses);
- infectious diseases;
- abuse of diets (resulting in a lack of vitamins);
- professional activity in hazardous industries (dust, chemicals);
- chronic internal diseases that weaken the immune system;
- smoking;
- strong alcoholic drinks;
- damage to mucous membranes from hot spices;
- stress loads;
- oncological diseases;
- HIV immunodeficiency.
With candidiasis of the throat, all neighboring areas are gradually affected: the posterior wall of the larynx, palatine tonsils, arch, uvula, mucous membrane of the surface and underside of the tongue, internal epithelium of the cheeks.
Characteristic symptoms that indicate that a fungus has settled in the throat and the infection is spreading to nearby tissues:
- redness of the throat;
- absence or subfebrile temperature values (37 – 37.5);
- slight pain when swallowing;
- itchy throat, sore throat;
- loss of sonority of voice, hoarseness;
- cough;
- presence of bad breath;
- a curd-like coating on areas affected by infection; when it is removed, numerous small hemorrhages, aphthae, single or merging ulcers are found on the mucous membranes;
- the progression of the disease is aggravated by hoarseness, increased pain during swallowing, the appearance of shortness of breath, and spasmodic cough;
- plugs appear in the folds of the tonsils and larynx.
Treatment must be started immediately, otherwise the affected tissues will become infected with other pathogenic microorganisms.
The addition of a bacterial infection is characterized by a sharp increase in temperature (39 - 40.5), pronounced hyperemia of the glands, severe swelling of the larynx, as well as increased bleeding, an increase in the affected area, and the appearance of purulent mucus on the surface of the epithelium.
If a fungal infection is suspected, the patient is referred for clinical blood and urine tests. If necessary, the biochemical composition of the blood is checked and pharyngoscopy is performed. If suspicions remain, specific tests of a throat smear are prescribed:
It is necessary to differentiate candidiasis from allergic, infectious diseases of bacterial and viral etiology, which helps to avoid errors when prescribing medications.
In order for the treatment of candidiasis of the throat and entire oropharynx to be successful, it is imperative to exclude factors that activate
Candida fungus, which causes a fungal infection:
- discontinuation of antibiotic and corticosteroid treatment;
- establishing a proper diet with the exclusion of sweet, sour, spicy, sour, fatty foods from the diet;
- elimination of bad habits: smoking, drinking alcohol.
High-quality and regular oral hygiene is the main condition for preventing the further development of Candida fungi.
To destroy a fungal infection and restore immune defense, the following systemic antimycotic agents are prescribed:
- Fluconazole . To destroy newly formed candidiasis in the throat, you need to drink 1 capsule (150 mg) in the morning for 1 - 2 days (as recommended by a doctor). If the fungal disease is chronic, take Fluconazole twice a day for a 10-14 day course.
- Nystatin . Before starting to take the medication, you need to find out your individual sensitivity to the active substance, for which you should take 1 tablet. In the absence of allergies, treatment of thrush follows a regimen determined by the doctor. The usual dosage is: every 3 hours, 500,000 units. within 10 – 12 days.
- Orungal . 1 capsule in the morning for 15 days.
- Itraconazole . 100 mg tablet once a day for 15 days.
- Ketoconazole . 10 days, dose per day from 200 to 400 mg.
- Diflucan from 10 to 12 days, single dose from 50 to 150 mg.
Local antifungal drugs:
- Nystatin - an aqueous suspension or ointment is used in the form of applications (4 procedures per day), or for gargling (10 ml);
- Amphotericin for rinsing, 1 ml of solution per time, 4 procedures per day;
- Clotrimazole or Candide 1% solution.
In the absence of allergies, it is allowed to gargle with folk antifungal remedies: a decoction of chamomile, calendula, sage, willow bark, oak, and soda.
Treatment of oropharyngeal thrush is unrealistic without the use of antiseptics:
- Tantum Verde . Spray day is used to irrigate the throat 4 to 6 times a day. Absorbable tablet up to 4 pcs. per day.
- Lugol's solution . Spray mucous membranes up to 4 times a day.
- Novosept . Dissolve 1 lozenge after 3 hours or apply throat spray.
- Chlorhexidine . One rinse with 10 ml of solution for a minute. In total, from 6 to 8 procedures per day.
- Oralcept . It is sprayed 4 times a day onto the oropharynx area.
- Fukortsin, Methylene blue for the treatment of aphthae and ulcers.
- Inhalation through a nebulizer to disinfect throat tissue with Miramistin, saline solution. In the morning and in the evening.
Be sure to take medications to strengthen the body’s immune system along with antifungal therapy:
- antipyretic drugs are prescribed only at temperatures above 38.6: Paracetamol, Nurofen;
- complex vitamin and mineral products : Complivit, Alphabet – 2 tablets in the morning;
- probiotics to restore the number of beneficial bacteria: Linex, Acipol;
- immunomodulators : Immunal - 3 times a day, 20 drops, Wobenzym - 3 tablets three times a day.
Untimely or incorrect treatment of throat thrush can lead to serious complications:
- fungal infection of the genitourinary organs and skin;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- dysfunction of the muscular and skeletal system;
- damage to the heart muscle;
- metabolic disorders;
- critical decrease in immune defense;
- development of allergies to medications.
The most common consequence of throat candidiasis is that the fungus settles in the respiratory tract, which leads to bronchial obstruction and pulmonary failure.
The primary preventive task is to exclude the above listed causes and factors for the activation of Candida fungus.
In addition, it is important to comply with the following rules:
- if someone in the family is sick with thrush, you need to limit close contacts: separate out individual household and personal hygiene items, wash them often, rinse them with antiseptics;
- during the treatment process, it is necessary to reduce to a minimum the consumption of fatty and carbohydrate foods, yeast buns, pies, and add protein and vegetable dishes to the diet; You should not eat ice cream and other cold foods; you should also limit hot foods;
- The room should be ventilated regularly; in winter, open only distant windows;
- if it’s not cold, you need to walk outside more often, away from traffic;
- Positive emotions and life without stressful situations are very important;
- One of the best ways to prevent thrush is systematic hardening of the body: sports activities, including swimming.
Throat candidiasis is a very dangerous infectious disease; at the first symptoms, you should immediately consult a doctor, otherwise fungal infection of the respiratory system, liver, and muscle tissue of the heart may develop. The sooner treatment begins, the more successful the removal of fungi will be, and the less threatening the consequences will be.
Based on materials from dentazone.ru
The inflammatory fungal disease candidiasis of the throat develops due to a sharp increase in pathogenic microflora on the oral mucosa and its downward penetration into the tonsils and larynx.
Treatment of the disease involves destroying the pathogen throughout the body and restoring the patient’s immunity.
The causative agent of pharyngomycosis is
the yeast-like fungus Candida albicans , which lives in the environment and the human body and does not cause harm to it.
But only if beneficial microorganisms in the human body control the amount of opportunistic fungus.
When the body weakens, the fungus begins to attack beneficial bacteria, gradually displacing them.
With candidiasis of the throat, the main amount of fungus is concentrated in the tonsils and upper respiratory tract, especially in the larynx.
The condition is quite dangerous, since it threatens the widespread spread of spores and mycelium of the fungus, complete damage to the bronchopulmonary and digestive systems.
The impetus for the proliferation of the fungus are conditions that weaken the human immune system:
- Contact with an infected person or objects. Babies become infected with the fungus when passing through the birth canal.
- Antibiotic therapy. Medicines used to kill bacteria also destroy beneficial microflora, developing dysbacteriosis. As a result, the place of beneficial bacteria in the body is taken by pathogenic microorganisms.
- Periods of hormonal changes in the body: adolescence, pregnancy, menopause.
- Infectious and inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity: caries, stomatitis, tonsillitis.
- Stressful situations and chronic fatigue.
- Injuries to the mouth and throat.
- Lack of hygiene.
- Alcohol and smoking abuse.
- Immunodeficiency states: HIV, postoperative and post-traumatic periods.
- Avitaminosis.
Additional reasons for thrush affecting a child’s throat:
- periods of teething;
- incorrect selection of formulas for artificial feeding;
- unfavorable microclimate in the children's room: dry air, infrequent wet cleaning, lack of ventilation.
Symptoms of pharyngomycosis affect not only the throat, but also the entire oral cavity. Often the fungus affects the larynx, palate, tongue, cheeks, and gums.
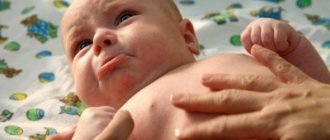
Signs of throat candidiasis in a child manifest themselves most intensely:
- redness of the mucous membranes;
- increased body temperature;
- painful swallowing;
- burning sensation, dry mouth;
- enlargement of the tonsils, formation of white plaque on them;
- hoarseness of voice;
- cheesy coating in the mouth;
- lack of appetite.
The symptoms of the disease in adults differ little from those in children . Additional signs of the disease may be a feeling of discomfort and burning sensation in the mouth when eating cold, hot or spicy foods.
An increase in temperature in adult patients is observed at a late stage of the disease. At the same time, a strong cough begins with the release of sputum mixed with cheesy masses.
In the early stages, patients feel aching joints, general malaise, and fatigue.
At first, throat thrush is similar to other inflammatory diseases.
Therefore, patients undertake conventional treatment methods, which only worsen the situation.
Experts warn about the need to visit a doctor for any symptoms of diseases of the mouth and throat, since only a specialist can evaluate the characteristic symptoms.
The doctor examines the oral cavity and refers the patient for tests:
- blood and urine;
- swabs for microflora from the oral cavity;
- bacterial seeding of materials.
Therapy for throat thrush begins with general strengthening of the body by taking immunostimulating drugs and replenishing the lack of vitamins in the body.
One of the methods of restoring the body’s defenses is to relieve allergic symptoms: swelling of the throat, soreness, hyperemia.
The main stage of treatment is taking antifungal drugs and treating the throat with special antifungal solutions.
The set of drugs for the treatment of throat candidiasis is as follows:
- Antifungal oral drugs:
- "Flucosist";
- "Mycostatin";
- "Futsis";
- "Fluconazole";
- Antihistamines:
- "Loratadine";
- "Zyrtec";
- "Zodak";
- Vitamins and immunostimulants:
- vitamins B, C;
- "Immunal";
- "Immudon";
- "Echinacea";
- a nicotinic acid;
- Throat treatment products:
- "Chlorhexidine";
- Lugol's solution;
- "Hexidine";
- "Miramistin";
- "Levorin";
- "Natamycin";
- Preparations for restoring intestinal microflora:
- "Linex";
- "Maxilak";
- "Acipol";
- "Bifidumbacterin";
- Drugs for secondary infection:
- "Acyclovir";
- "Zovirax";
- "Sumamed."
The restoration of healthy microflora of the mouth and throat occurs faster if drug therapy is supported by physiotherapeutic procedures:
- UV irradiation;
- laser irradiation;
- electrophoresis with solutions of potassium and iodine;
- quartzization of the oral cavity.
Candidiasis of the throat and oral cavity often develops in children under one year of age.
It is not easy to rid a baby of an illness, so parents will have to be patient. The most important condition is a strict diet for a nursing mother.
You cannot interrupt breastfeeding , despite the fact that the baby refuses to suckle due to inflammation.
Medications are not used to treat children under 6 months of age, so the only way to reduce the number of fungal spores on the mucous membranes is to treat the baby’s mouth with antiseptic solutions:
Your pediatrician will help you select the correct solution.
From the age of 6, antifungal drugs are prescribed . Doses and recommendations on how to take medications are determined by the doctor.
The following drugs are approved for the treatment of children:
The course of medication is enhanced with vitamins, immunomodulators, and probiotics. If throat thrush cannot be cured within a few months, you will need to consult an immunologist.
Most experts recommend combining treatment of the throat with remedies prepared according to folk recipes with drug therapy.
Preparations from traditional healers effectively free the oral cavity from fungus and relieve inflammation.
According to many patients, the greatest effect can be achieved by using the following means:
- gargling with infusions of sage, chamomile, calendula;
- treatment of the oral cavity with tea tree oil;
- rinsing with soda solutions;
- inhalations with eucalyptus and fir oils.
A selection of traditional medicine recipes for the treatment of candidiasis
Antifungal therapy will not bring the desired result if fungal spores are regularly fed from the products consumed by patients. Therefore, during treatment it is necessary to adhere to a special diet.
The following products are prohibited for patients with throat candidiasis:
- sweets and confectionery;
- fatty, spicy, smoked, salty dishes;
- carbonated drinks;
- foods with a lot of starch.
The patient's menu should consist of steamed or boiled dishes consisting of the following components:
- cereals: buckwheat, rice, oatmeal;
- vegetables: cabbage, zucchini;
- fermented milk products;
- lean meats.
Throat candidiasis is dangerous due to possible complications:
- deep damage to the respiratory system;
- pulmonary candidiasis;
- penetration of the fungus into the gastrointestinal tract;
- cachexia.
A difficult consequence of pharyngomycosis in children without treatment is candidal tonsillitis.
Most often, inflammation is localized on two tonsils at once.
Candida attaches to the baby's tonsils, and they become covered with a whitish-gray coating.
Photos of the tonsils for follicular and candidal tonsillitis are absolutely identical , so parents, assuming a sore throat, begin to independently treat the baby with traditional antibiotics, which worsens the situation, and the fungus multiplies even more.
Treatment of candidal tonsillitis requires the use of antifungal drugs as prescribed by a doctor.
To protect your throat from the proliferation of pathogenic fungi in it, it is enough to follow simple rules:
- avoid contact with infected people;
- maintain oral hygiene;
- strengthen immunity;
- regularly spend time in the fresh air;
- maintain an optimal indoor microclimate;
- avoid stress.
Throat candidiasis is a complex and dangerous disease for the general condition of the body that requires immediate treatment.
Penetration of the fungus from the throat cavity into the internal organs can cause the development of generalized candidiasis, which is almost impossible to completely cure.
Based on materials from gribok.guru
Throat candidiasis (also known as pharyngomycosis) is a fungal infection in which opportunistic fungi of the genus Candida begin to multiply and affect the mucous membrane of the throat (larynx or nasopharynx). As a rule, the disease develops against the background of severe oral thrush, when colonies of harmful microorganisms begin to migrate. With candidiasis of the throat, the tonsils, posterior wall of the larynx, arches, uvula and palate are primarily affected.
Candidiasis develops due to a sharp increase in the number of yeast fungi in a child’s body. They enter it through the amnion or from the birth canal if the mother is ill. Under a number of conditions, fungi begin to multiply and create pathogenic flora, due to which the disease develops. Conditions that favorably influence the growth of fungal colonies in a child’s body:
- lack of proper oral hygiene for the child (daily brushing of teeth, rinsing the mouth and throat);
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (washing hands after walking and contacting animals, eating dirty vegetables and fruits);
- bad habits (keeping your hands in your mouth, putting dirty toys in your mouth;
- the presence of other inflammations of the nasopharynx and esophagus (ARVI, acute respiratory infections, allergic rhinitis and cough);
- non-compliance with the microclimate of the room (high humidity, high temperature and stuffiness);
- mechanical damage to the throat (burns, cuts due to foreign bodies).
A large number of yeast-like fungi can enter the body of a small person from an unwashed pacifier, dirty toys and utensils, and when using public baths and swimming pools.
If a pregnant woman was sick with candidiasis of any type before conception or during pregnancy, then immediately after birth the baby is tested to detect this disease. As a rule, the results in this case are positive.
If throat candidiasis in a child is acquired, then as the disease develops, the following symptoms are possible:
- increase in the size of the tonsils,
- swelling and redness of the throat,
- pain when eating and drinking,
- loss of appetite,
- bad breath,
- feeling of sour milk in the mouth,
- increase in body temperature,
- the appearance of plaque on the tonsils, arches, and upper palate.
The plaque can be seen with the naked eye. It is a curdled mass of gray, yellow or whitish color. It is difficult to scrape off; there are sores underneath.
In children, due to an undeveloped immune system, the disease progresses very quickly, so if diagnosis and treatment are delayed, within a few days the baby may develop candidiasis of the oral cavity, intestines, genitals and skin.
To make an accurate diagnosis and identify the causes of the pathology, the doctor will need to carry out a number of diagnostic procedures:
- collecting an anamnesis of thrush among close relatives and primarily the mother,
- examination of the baby’s throat, skin and external genitalia,
- taking a scraping from the affected area of the mucosa for culture,
- blood tests, urine tests, stool tests, ultrasound of the throat.
If necessary, other tests may be required, such as a biopsy, ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
Throat candidiasis is very dangerous for children. Their immunity is not yet formed and is not ready to fight harmful microorganisms. The most common complication of the disease is the transition to an intractable chronic form, which is dangerous due to the following manifestations:
- bleeding ulcers on the mucous membrane of the larynx and nasopharynx,
- sepsis.
Other consequences of childhood throat candidiasis:
- damage to the genital organs, skin, intestines and oral cavity,
- problems with digestion and stool,
- loss of appetite,
- lack of body weight,
- general decrease in immunity,
- infection with other viral and fungal diseases,
- development of dangerous diseases of the respiratory system and esophagus,
- allergies to medications.
If a mother’s illness is detected during pregnancy, it must be treated in a timely manner. During childbirth, inform your obstetrician-gynecologist and neonatologist about this. This is necessary for prompt testing of the baby and, if necessary, immediate initiation of treatment.
If the disease appeared much later, then it is important for all family members to be tested to detect thrush of any form. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate. It is important to carefully follow all medical prescriptions and recommendations.
It is prohibited to treat a child with folk remedies. They can negatively affect children's health.
For treatment to be effective, parents should:
- maintain the child’s personal hygiene,
- isolate from unnecessary contacts,
- maintain the microclimate in the apartment or children's room,
- all family members undergo treatment if necessary.
After receiving the test results, the doctor makes an accurate diagnosis and identifies its causes. After this, an individual treatment regimen is developed. It consists of several stages:
- treatment of the underlying disease (the choice of means is determined by the disease, its form and severity),
- getting rid of pathogenic fungi (oral or anal antifungal drugs, antifungal solutions for irrigating the mouth and throat are prescribed, in severe cases injections are indicated),
- restoration of intestinal microflora after taking antibiotics (the doctor prescribes special probiotics),
- strengthening children's immunity (with the help of immunomodulators and vitamin therapy).
When treating candidiasis in a child, all family members are given a referral to undergo tests to identify the disease in them. If infected people are detected, they must be isolated from the small patient.
If a nursing mother is infected and is being treated with general medications, then she should switch to artificial feeding for the period of therapy.
To prevent childhood candidiasis, it is important to maintain the health of the mother during pregnancy and after childbirth. Transfer of pathogenic fungi from mother to baby is the most common route of infection.
Of course, it is important that all relatives are confident in their health. If they have symptoms of the disease, it is worth protecting the baby from contact.
To prevent throat candidiasis in a baby, parents should follow the following tips:
- maintain optimal temperature (not higher than 20C) and humidity (not higher than 70%),
- carry out hygiene procedures daily or teach your baby to perform them independently,
- feed breast milk for as long as possible, brush your teeth or rinse your mouth with special solutions after each meal,
- regularly visit a pediatrician and specialized doctors,
- complete all studies in a timely manner,
- follow all instructions of children's doctors.
Based on materials from detstrana.ru
Features of the treatment of candidal pharyngitis
Candidiasis of the throat and larynx is sometimes complicated by pharyngitis. Antifungal agents (antimycotics) and antiseptics are also used to treat it. The goal of therapy is to suppress the reproduction processes of the pathogen.
To treat pharyngitis caused by candida, systemic antimycotics are used only as prescribed by a doctor. Some of these drugs have serious side effects. Antifungal agents for topical use are produced in the form of sprays, aerosols, dragees, solutions, and caramels. To increase the effectiveness of treatment of pharyngitis, it is important to observe one condition: the medicine should remain in the oral cavity for as long as possible.
Antiseptics are used for rinsing and lubricating mucous membranes. Factors that provoke pharyngitis should be eliminated. For this purpose, the oral cavity is sanitized, endocrine changes are corrected, and the immune system is strengthened and stimulated.
Treatment of pharyngitis in a small child is quite difficult, since it seems impossible to use local drugs. As therapy, use plenty of warm drinks and warm the neck with dry heat. It is necessary to take mild restoratives.
Medicines for throat fungus
A systemic antifungal drug should be prescribed by a doctor, since drugs of synthetic origin can cause side effects on the kidneys.
Remember
Long-term use of medications leads to complications, so candidal tonsillitis is treated with antimycotics for no longer than 10-14 days.
For this purpose, the following groups of means are used:
- polyenes - Nystatin, Amphotericin B. They destroy the cell membranes of fungi, causing their death;
- allylamines – Naftitin, Terbinofine. They have a powerful antifungal effect and allow you to quickly cope with the signs of thrush in the throat;
- azoles – Bifonazole, Mycospor. They stop the active reproduction of yeast and mold spores, preventing their further spread throughout the mucous membrane of the larynx, respiratory tract and nasopharynx.
The drug Fluconazole is effective in the treatment of yeast infections; it belongs to the group of triazoles. A similar substance contains tablets Flucostat, Mycoflucan, Fucis, Flucoside, Fungolon and others.
The drugs are well tolerated and rarely provoke allergic reactions. The dosage and duration of the course are determined by the attending physician.
Prevention
Measures to prevent candidiasis include sanitation of the oral cavity. It is necessary to promptly treat ENT diseases, as well as existing chronic ailments. It is important to strengthen the immune system: harden yourself, play sports, drink vitamins. Long stays in the fresh air are beneficial.
You need to eat right and give up bad habits. If there are systemic diseases that weaken the immune system, spa treatment is indicated. For children, it is necessary to disinfect pacifiers, toys, household items, and dishes.
Causes of oropharyngeal candidiasis
The disease is caused by increased growth and reproduction of fungal flora. This occurs against the background of a decrease in general and local immunity, and an increase in the factors of aggression of the fungal flora.
The following factors contribute to this:
- prolonged and uncontrolled use of medications - antibiotics, hormones;
- chronic diseases of the oropharynx - tonsillitis, tonsillitis;
- diseases that suppress the immune system - diabetes, cancer, HIV infection;
- bad habits – smoking, drug use, alcohol abuse;
- pregnancy;
- In children, a predisposing factor is poor personal hygiene.
Against the background of suppression of the protective properties of the body, rapid growth and reproduction of fungal flora occurs, as a result of which the disease develops. A person can become infected with a fungus due to insufficient personal hygiene, sharing utensils, or kissing a sick person.