- Published by: Laima Jansons
This symptom is not a separate disease, but just one of the signs of dysfunction of one or another internal organ. The feeling of a “dry mouth”, which occurs as a result of a reduction or 100% cessation of salivation, is a pathology called xerostomia.
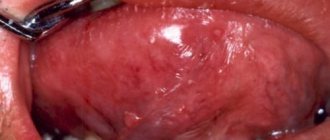
Photo 1: In order to find out why your mouth is dry, you need to visit a doctor who will prescribe the appropriate tests, and possibly a full medical examination of the body. Source: flickr (Laura).
Symptoms of xerostomia
- dry throat and mouth as a result of insufficient salivation;
- difficulty swallowing;
- slurred speech;
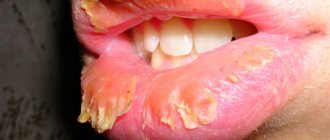
- the appearance of erosions, cracks, wounds in the corners of the lips, as well as on the mucous membrane (accompanied by severe discomfort, burning, pain);
- constant desire to drink;
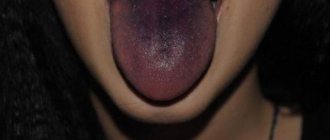
- dry tongue, turning bright red;
- distortion of taste, the feeling that some kind of foreign taste is always present;
- smell from the mouth;
- hoarse voice;
- sore throat.
Note! If dry mouth is observed for a long time, the risk of developing periodontal disease, damage to the oral cavity by fungi, and the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms increases. The body becomes more susceptible to viral diseases, including sore throat, tonsillitis and stomatitis.
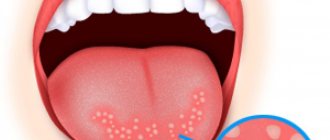
Types of plaque on the tongue
Doctors identify a large number of types of white plaque that forms in the human oral cavity. It may differ in shades, localization and accompanying symptoms. All these signs must be taken into account during diagnosis.
The localization of plaque almost always accurately indicates a specific pathology arising in the human body:
- Plaque in the center of the tongue - diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Plaque at the base of the organ is an intestinal pathology.
- Plaque on the tip of the tongue – diseases of the cardiovascular system.
- Formations along the edges of the organ are diseases of the spleen and liver.
- Plaque on the back of the tongue is a sign of problems with the pancreas.
- Formation in the palate is the beginning of candidiasis.
- Plaque on the tonsil - purulent sore throat.
According to the degree of saturation, there is the following classification of plaque types:
- Lightweight, easily removable, small.
- Thick and dense.
- Curdled, vaguely distributed.
The color of the plaque can be as follows:
- White-brown.
- White-green.
- White-yellow.
- White-gray.
Based on the color scheme, it is also possible to diagnose certain pathological conditions occurring in the body of a particular patient:
- Dense white plaque – gastrointestinal disease.
- Blue plaque and dry mouth indicate typhus and dysentery. In addition, they are often observed in people who smoke.
- A yellow formation, accompanied by a bitter taste, may indicate improper functioning of the pancreas and cholecystitis.
- Green plaque is provoked by liver pathologies or long-term treatment with antibacterial drugs.
- The black color occurs against the background of dangerous intoxication caused by diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver or Crohn's pathology.
Plaque formations in the mouth are most often signs of gastrointestinal diseases. This is explained by the fact that the digestive tract is similar to the structure of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
When organ walls are damaged, increased renewal of the epithelium occurs. Peeling areas of skin attract bacteria located in the mouth. It is precisely such phenomena that provoke plaque.
In addition to the symptom in question, swelling of the tongue is often observed, indicating chronic intestinal pathology.
Reasons Why Your Mouth and Throat Sometimes Dry
There are a lot of factors that provoke drying of the mucous membranes of the larynx and oral cavity. The exact cause of the disease can be determined by the nature of xerostomia. Each type can be triggered by various disorders in the body.
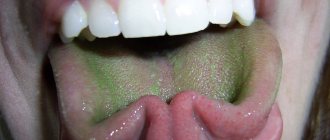
Photo 2: Dry mouth can occur periodically or be a constant problem, occurring at night or in the morning. Source: flickr (albori2003).
Dry mouth in the morning
A feeling of dry mouth in the morning can be caused by:
- taking certain medications,
- smoking;
- increased ambient air temperature;
- eating fatty, too spicy or salty foods;
- dry mouth in the morning as a result of alcohol withdrawal syndrome (hangover);
- poor-quality oral care products (toothpastes, rinses, etc.) or their improper use;
- insufficient amounts of group A vitamins in the body, which causes blockage of the salivary glands;
- lack of potassium;
- too much magnesium content.
Dry mouth at night
- forced mouth breathing (for allergies, colds, etc.);
- snoring, which leads to a dry throat;
- too dry air in the bedroom;
- diabetes mellitus, which almost always causes sleep disturbances;
- itchy skin rashes that prevent you from sleeping.
Dry mouth and thirst
- Often, the oral cavity dries out in females due to changes in the functioning of hormones, for example, during menopause or pregnancy.
- Diabetes. In this case, it dries out due to an increase in glucose levels, resulting in the need to drink more fluid.
- Dryness and severe thirst are provoked by severe vomiting, diarrhea, severe sweating, diuretics, and insufficient water consumption during the day.
Dry mouth and frequent urination
This is one of the symptoms of diabetic disease. In addition to thirst, the functioning of almost all body systems, including the salivary glands, is inhibited. Frequent urination also leads to dry mouth in the presence of chronic kidney disease.
Dry mouth, nausea, headache
The cause of nausea accompanied by dry mouth may be a consequence of a disease of the endocrine system. The likelihood is especially high if there is irritability, a feeling of unreasonable fear, the person sweats a lot and profusely, trembling and loss of appetite bother him.
If, in addition to dryness and nausea, there is heartburn, and the tongue is coated, this may be the cause of a gastrointestinal tract disease.
Headache and dryness can be caused by hypotension, when along with dryness there is weakness, increased drowsiness and frequent dizziness.
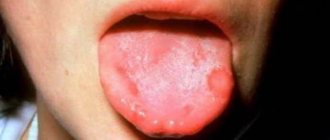
Coated tongue and feeling of dryness
Often dryness is accompanied by heartburn and nausea, and a thick coating appears on the tongue. The bitter taste may be disturbing. All this speaks of gastrointestinal diseases.
Other causes of dry mouth
- Systemic diseases (Parkinson's, Sjögren's, Alzheimer's, HIV, artiritis, scleroderma).
- Innervation. As a result of problems with the nerve endings in the cervical spine and head, the salivary glands begin to work incorrectly, which causes xerostomia.
- Stress, depression. With psychological and nervous disorders, a person is constantly tense, which can cause dry mouth. These symptoms do not disappear on their own and quickly, so observation by a doctor in this case is a prerequisite.
- Low blood pressure causes drying of the oral mucosa.
- Abnormal proliferation of lymph nodes. If the lymph nodes behind the ears or under the lower jaw are affected, salivation is often impaired. These are signs of cancer, so you need to visit a doctor urgently!
- Various infectious diseases, which may result in dehydration.
This is interesting! The daily rate of saliva production by the body is 1.5 liters. Its main purpose is to protect the mucous membranes from drying out, as well as from the appearance of caries on the teeth. With the help of saliva, food debris is washed away, acids are neutralized, chewing and swallowing of food is facilitated, and the risk of proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms is reduced. Saliva contains a special enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates during food consumption.
Dry tongue cause and treatment
Dry tongue is a drying out of the mucous layer of the oral cavity, which is a consequence of impaired functioning of the salivary glands.
Against this background, there is a partial or complete absence of saliva production. In the overwhelming majority of cases, such a symptom indicates the occurrence of a serious disease in the body, but in addition to pathological factors, its appearance is influenced by physiological causes.
This manifestation has many specific clinical signs, which include a feeling of extreme thirst, difficulty speaking and the appearance of an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
In order to determine the cause of such a disorder, patients need to undergo a large number of laboratory and instrumental examinations.
Treatment will vary depending on the etiological factor, but conservative methods are often sufficient.
Etiology
In medical practice, dryness of the tongue, lips and mouth is considered a serious signal indicating a dysfunction of the body, which requires immediate seeking qualified help.
The main etiological reasons that the tongue dries out:
- the course of diabetes mellitus;
- a wide range of gastrointestinal pathologies, in particular pancreatitis, IBS, atrophic gastritis and intestinal dysbiosis;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- lack of vitamins and nutrients in the body;
- kidney pathologies;
- improper functioning of the thyroid gland;
- the presence of an inflammatory process;
- damage by viruses to the salivary glands and circulatory system, for example, with mumps;
- anemia;
- Parkinson's or Alzheimer's disease;
- stroke;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- colds or ARVI;
- decreased blood tone;
- mumps;
- Sjögren's syndrome;
- the presence of stones in the salivary glands;
- oncological processes, namely their treatment with radiation or chemotherapy;
- Surgery or a wide range of head injuries - in some cases can interfere with saliva production;
- bacterial infection of the throat or mouth, which is expressed in pathologies such as pharyngitis, glossitis, stomatitis and tonsillitis;
- rotavirus infections;
- HIV;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system - in such cases, a dry tongue is observed with normal salivation.
In addition, the causes of a dry tongue can be:
- dental procedures;
- long-term addiction to smoking;
- the onset of menopause in females;
- prolonged exposure to stressful situations;
- dry climate conditions;
- dry air or a large amount of dust in the room;
- abuse of coffee or tea;
- not drinking enough water per day;
- poor nutrition, when the diet is based on fatty and spicy foods, sour and salty foods;
- abuse of certain groups of drugs. These include antidepressants, antibacterial substances, antispasmodics and anti-allergenic agents;
- night snoring caused by impaired nasal breathing. This can occur against the background of a runny nose, sinusitis or adenoiditis;
- severe dehydration of the body;
- excessive physical exercise;
- allergic reactions to foods or cosmetics.
Female representatives often complain about the presence of a similar symptom during the period of bearing a child. In this case, this may be a sign of the development of gestational diabetes.
In addition, the risk group includes elderly people who have a large number of chronic ailments, which is why dry tongue is a common phenomenon.
Symptoms
Dry tongue is never the only clinical manifestation; it is accompanied by those signs that are characteristic of a dysfunction of a particular internal organ or system.
The main symptoms are considered to be:
- a constant and strong feeling of thirst, even though the person drinks a large amount of liquid;
- dry lips – this leads to the appearance of cracks on them and in the corners of the mouth;
- increased urge to urinate;
- burning of tongue and mouth;
- sore and sore throat;
- discomfort in the nose;
- white coating on the tongue;
- redness of the tongue;
- hoarseness of voice;
- violation of the breathing process;
- change in the taste perception of food;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth, which is felt by strangers;
- redness of the cheeks;
- the presence of irritated areas in the oral cavity;
- difficulty speaking, as well as the processes of chewing and swallowing food.
The above symptoms constitute a list of the most common, but depending on what was the source of the main symptom, the clinical manifestations will differ.
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of dry mouth can be difficult because it is impossible to make a correct diagnosis based on symptoms alone. It follows from this that the search for an etiological factor requires an integrated approach.
To carry out initial diagnosis, you can contact:
- ENT;
- dentist;
- therapist;
- gastroenterologist.
First of all, the doctor needs:
- collect a life history and familiarize yourself with the patient’s medical history;
- perform a physical examination, which will be based on a study of the condition of the oral cavity;
- conduct a detailed survey of the patient, during which it is necessary to inform the doctor about all symptoms, their first time of appearance and intensity of expression.
Based on these data, the doctor may refer the patient for examination to another specialist.
The second step in identifying the cause is laboratory tests, including:
- clinical and biochemical blood test - this will make it possible to refute or confirm the presence of a pathological process in the body;
- general urine analysis;
- microscopic examination of feces.
Among the main instrumental methods it is worth highlighting:
- Ultrasound of the peritoneal organs;
- EGDS – to identify gastrointestinal pathologies;
- ECG - to monitor the work of the heart;
- CT and MRI.
In each individual case, additional diagnostic measures and consultation with other specialists may be necessary, for example, a pediatrician if the patient is a child or an obstetrician-gynecologist for pregnant women.
Treatment and prevention
In order to get rid of such an unpleasant symptom, you need to find out the exact etiological factor that caused the appearance of dry tongue. Based on the data from all diagnostic procedures, the clinician will prescribe an individual treatment strategy for a particular disease. The treatment regimen may include:
- prescription of medications;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- maintaining a gentle diet;
- surgical intervention.
However, there are several general recommendations that will reduce the discomfort of a dry tongue. Among them:
- drinking a large amount of liquid per day - more than two liters. It is best to drink purified water in small sips;
- minimizing the consumption of coffee drinks and strong tea;
- chewing gum, but only without sugar - this will lead to an increase in saliva production;
- exclusion of smoking and alcohol;
- complete rejection of fatty and spicy foods, as well as excessively salty, sweet and sour foods;
- use special saliva substitutes;
- use traditional medicine recipes, which involve preparing medicinal decoctions or infusions based on mint and cinnamon;
- monitor thorough humidification and supply of fresh air to the room where a person spends the most time;
- use ointments and gels for the oral cavity prescribed by your doctor.
In addition, regular adherence to oral hygiene rules, as well as taking medications only as prescribed by the attending physician and with strict adherence to the daily norm, serve as preventive measures.
It is also very important to undergo a full medical examination several times a year, visit the dentist once every three months, do not miss consultations, and consult a doctor at the slightest deterioration in your health.
Dry tongue has its own medical name - xerostomia. This may be a temporary condition, or it may be a manifestation of certain diseases. This symptom should not be ignored. It is provoked by a decrease or even a complete stop in the production of saliva. First, you should ask your therapist how serious your condition is. He will assess your situation and refer you to the right doctor.
Main reasons
If before the dryness there was a burning sensation, itching, cracks or dryness in the throat, this may be a sign of the development of a serious disease. In this case, it is important to consult a doctor and receive timely qualified assistance. Sometimes the lack of proper treatment can even lead to mucosal atrophy, partial or complete. This is extremely dangerous!
If before the dryness there was a burning sensation, itching, cracks, or dryness in the throat, this may be a sign of the development of a serious disease.
Which doctor is best to see? First, you should see a therapist. In some cases it can help. If the case is more complex, he will refer you to a specialist. Most often, such dryness is accompanied by other manifestations.
Mouth breathing or snoring
The most common of all reasons is dry mouth due to snoring or prolonged mouth breathing. If you wake up in the morning and feel that your tongue is dry, you should think about it. Prolonged snoring could lead to this. Ask your loved ones if they have heard that you snore.
Mouth breathing is often associated with a runny nose, polyps, allergies, hay fever, deviated septum, or advanced sinusitis. If it was snoring or mouth breathing that led to dryness, then this symptom will be observed only in the morning.
Taking certain medications
There are many remedies with this side effect. They must be taken as prescribed by a doctor, since not all drugs can be combined.
Infection
Often, dryness is the result of an active infection affecting the body. At the same time, a person’s temperature rises and intoxication of the whole body develops.
Dry mouth is a common symptom of diabetes.
Mumps occupies a special place among infectious diseases. People call it piggy. Mumps leads to damage to the salivary glands. Because of this, much less saliva is produced than necessary.
Source: https://agrosmac.ru/sohnet-yazyk-prichina-i-lechenie.html
Homeopathic treatment of dry mouth and its manifestations
Increasingly, many patients are resorting to homeopathic treatment for various ailments. The popularity is due to many justifiable factors.
Firstly, the principle of homeopathy is aimed at eliminating the root cause of any ailment, and not at temporarily eliminating symptoms.
Secondly, homeopathic medicines have virtually no side effects; they are even prescribed to infants.
If we talk about homeopathic treatment of xerostomia, then in most cases homeopaths prescribe the following medications:
- Akonitum (Aconitum) - prescribed for dryness, accompanied by a thick yellowish-white coating on the tongue;
- Aesculus (Esculus) – too sensitive mucous membrane, burning sensation, dries the mouth;
- Alumina – dryness in the morning, putrid odor in the mouth;
- Anacardium – bitterness, parched throat;
- Arnica – dry mouth, intense thirst;
- Arsenicum album – prescribed for “cooked” lips;
- Belladonna - indicated for a burning tongue, as well as a dry mouth, but without a feeling of thirst;
- Cannabis sativa – indicated for patients who experience a sensation of sticky lips;
- Carboneum sulphuratum – helps with unquenchable thirst;
- Hina (China) – saves from the formation of thick and viscous saliva and a thick grayish coating;
- Coca – morning dryness;
- Echinacea – dryness in the larynx, when taking medications the mucous membrane burns very much;
- Ferrum muriaticum - dries out the mouth, and there is no taste of food;
- Hyoscyamus – salty saliva, feeling of dryness .
It is worth noting that self-administration of homeopathy medicines is permissible only in isolated cases of symptoms of xerostomia as an emergency aid. If the disease occurs frequently or is a constant concern, you need to make an appointment with a homeopath, who will prescribe an appropriate examination, identify the cause of the disease and prescribe a course of therapy.
What measures need to be taken
If dryness appears on the tongue and mouth, you need to consult a general practitioner , then tell in detail about the additional symptoms that are bothering you, the therapist will give you a referral to a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist or other doctor. Dentist help may be needed.
- To alleviate the condition, you need to drink clean water instead of coffee, tea and other usual drinks.
- You also need to drink during meals, avoid salty, spicy, and sweet foods.
Photo 2: In case of unpleasant sensations of dryness during a conversation, in places where it is not possible to drink water in a timely manner, stock up on candies and sugar-free chewing gum in advance. Source: flickr (Sebastien Michel).