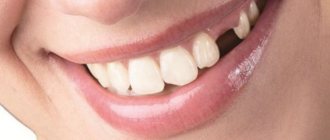
Do baby teeth have roots or not, what do they look like, how does resorption occur?
Milk teeth begin to erupt at 6-8 months of a child’s life.
Typically, the process of dental formation is completely completed before the baby turns 3 years old. The timing of teething can vary greatly among different children. Molars begin to grow at the age of 6 years, and the last teeth (“eights” or wisdom teeth) can grow only by 18-25 years. It is not always possible to preserve a baby's baby teeth until the molars take their place. Inflammatory processes and injuries can cause their premature removal, which can further affect the timing of the eruption of permanent dentition.
Do adults have
Baby teeth completely fall out by the age of 14-16, but it happens that they can last up to 50 years. What are the features of this manifestation:
- genetic disorders;
- metabolic disorders;
- osteomyelitis or jaw injury;
- chronic damage to tooth enamel and tissue;
- deep placement of permanent tooth buds.
There is a possibility that the rudiments may be completely absent, which may be due to their formation at the fetal stage.
In this case, milk teeth in adults are preserved for a long time.
What to do? Baby teeth can create serious problems - their lifespan is short, they are susceptible to caries and other dental disorders.
They also create discomfort for the eruption of molars and prevent them from growing, as a result of which the permanent dentition may be crooked. However, there is no need to rush to remove a temporary tooth, because the molar may not grow in its place.
If the roots of a temporary tooth have not resolved and there is no molar rudiment, you can install lumineers, a veneer, or carry out restoration on the tooth. Temporary teeth can serve well for many years with proper care and regular visits to a specialized doctor.
Features of temporary (baby) teeth
How many baby teeth should a child have? There are 20 of them in total, each with its own characteristics. The first teeth are smaller in size, the width of their crown is greater than the height. In addition, the layer of enamel covering temporary dental units is much thinner than the one covering permanent ones. The color of the teeth is also different: at first they are bluish-white, and after changing they acquire a yellowish tint. In primary teeth, unlike molars, the roots are smaller and have a rounded shape.
Deciduous incisors are more convex. They have no grooves on the palate. The central incisors are distinguished by a pronounced enamel ridge and a less rounded distal angle. The upper central incisors have an extended basal part with a curved apex. The lower incisors have a flat root.
A sharp marginal ridge stands out on the cutting surface of the fangs, and on the teeth of the lower jaw it wears off much more slowly than on the upper jaw. The crowns are convex, the roots of baby teeth are long, have a rounded shape with a curved apex.
The first molars of the upper dentition have three roots, but in 90% of cases there are 4 root canals, with wide apical foramina. A crown with two grooves has a convex palatal surface. The lower first molar has two widely spaced roots, the mesial one being longer and wider than the distal one. A temporary crown is very similar in appearance to a permanent one. It is slightly elongated in the vestibulo-oral direction and has 4 tubercles on the occlusal surface.
A distinctive feature of the 2 upper molars is their oblique shape of the coronal part, on which the enamel fold is clearly visible. There are 5 tubercles on the occlusal plane. Two of them are located closer to the lingual surface, and 3 - to the buccal edge. The lower 2 primary molars are similar in shape and structure to the molars of the lower jaw.
Structure of baby teeth
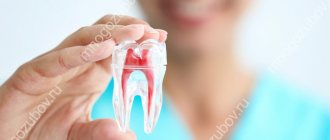
Each dental unit consists of hard and soft tissues. The crown, the visible part of the tooth, is covered by enamel. It is the hardest tissue of the human body. Beneath the enamel is dentin, which has a porous structure but is harder than bone tissue. The root part of the dentin, hidden under the gums, is covered with cement.
A tooth consists of several elements (the diagram can be seen in the photo):
Inside each baby tooth there is a cavity in which there is a pulp, consisting of connective tissue penetrated by blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerve endings. The pulp saturates the tooth with nutrients.
Do they have roots and nerves?
Teeth begin to form long before the eruption process begins. The embryo begins to develop teeth at 7 weeks of gestation. From this moment, the mineralization of enamel and the formation of dental nerves begin; these processes continue after the birth of the child.
In general, milk and molar teeth are very similar in internal structure - they have a pulp. Thanks to the nerve endings in the tooth, the child feels touch and distinguishes between hot and cold food. With increased tooth sensitivity, the development of pulpitis or caries, toothache causes children with baby teeth the same discomfort as adults. The roots of temporary teeth are also developed, but over time they are reabsorbed, so the teeth fall out almost painlessly.
Eruption of permanent teeth and loss of temporary teeth
- During the eruption of permanent teeth,
- destruction and loss of temporary ones.
- As the permanent tooth begins to move,
- it puts pressure on the root of a temporary tooth, resulting in destruction of its tissues (cementum and dentin).
- Localization of the initial sites of root resorption
temporary teeth are different. Thus, in incisors and canine teeth it begins in the apical region, in umolars - on the interradicular surface.
- The pulp of the tooth (temporary teeth) during its resorption is not
- only retains vitality, but also takes part in the processes of tooth destruction.
- Periodontal destruction of primary teeth occurs in
We suggest you read why sodium tetraborate is used in medicine
for a very short time and occurs without inflammatory phenomena. The ongoing processes of resorption of the root of a temporary tooth lead to the loss of connection between the tooth and the alveolar wall and the pushing out of the tooth crown in the oral cavity. The tooth usually falls out due to chewing forces. In this case, bleeding (usually weak) from damaged small vessels may occur.
- Loss of primary teeth usually occurs symmetrically
- on the right and left sides
- each jaw; girls are faster than boys.
- Sometimes parts of the tooth roots are outside the path of movement
- rudiments of permanent teeth and can avoid resorption.
- Such remains, consisting of dentin and cementum, are capable of
- persist inside the jaw for a long time.
What problems can there be with the roots of baby teeth, what should I do?
Since the roots of baby teeth are characterized by resorption, for a number of reasons this process can be accelerated or delayed. A tooth should only be removed if the molars are about to emerge. Due to injury and inflammation, complications often develop; to prevent them, the doctor must perform an operation to extract the tooth. If there is no new tooth yet, a temporary crown can be installed in its place to form a correct bite.
Inflammatory processes
Quite often, toothache is associated with an inflamed nerve. Soreness that is felt under the influence of external factors is indeed often caused by inflammation in the pulp. However, if it is removed, the tooth will “die.” Tissue nutrition will stop, the enamel will change shade, and the baby tooth will begin to wobble.
Typically, the depulpation procedure is resorted to when there is a threat of pulp inflammation or the development of pulpitis. Patients with advanced caries who complain of severe toothache often find themselves in this situation. Also, indications for the removal of a baby tooth may be:
- cyst on the root of a temporary tooth;
- gingival fistula;
- periodontitis.
Mechanical damage
Mechanical damage rarely leads to fracture; most often, teeth are displaced relative to the dentition. If a child has a horizontal or transverse fracture of the root part of a tooth, no therapeutic measures are taken. Treatment is required if the pulp is damaged as a result of multiple fractures - the tooth is removed.
A fracture is not always noticeable immediately after injury. Usually the first unpleasant symptoms appear within a few days. A polyp may form on the pulp, which pushes the fragments apart. If tissue necrosis occurs, the tooth is removed.
Preparing the child for the procedure
After making the injection, the specialist will open the crown using a drill and begin cleaning the dental canals. In this case, the main task will be not to harm the primary processes of the molar tooth. First, the nerve ending is removed, then disinfection is carried out to avoid re-infection.
If the upper part of the tooth tissue is not completely destroyed, the dentist will restore it. To do this, install a filling, if necessary a temporary one, under which the medicine is placed. It will subsequently be replaced with a permanent crown. To understand whether all dental procedures were done efficiently, an x-ray is taken.
Today, special modern mummifying compounds are used for filling. Their main advantage is that they have excellent disinfecting properties and are able to protect dental tissue from all kinds of infections. However, there is also a minus - they are extremely short-lived, so they will last approximately the period during which a baby tooth will be replaced by a permanent one.
At what age do the roots reabsorb?
After the child’s first teeth erupt, their roots continue to grow deep into the gums for some time. When the baby turns 2 years old, teeth stop growing.
Gradually, the roots begin to decrease in size. Complete resorption of the roots of baby teeth occurs at 5-6 years. At this point, the nutrition of the teeth naturally stops, and they fall out on their own. When the rudiments of permanent teeth approach the roots of milk teeth, the process accelerates, so that dental units fall out almost synchronously, and then new ones erupt. The timing of root resorption may vary in each individual case.
Is it possible to tell by external signs whether a tooth is permanent or baby?
To find out which class a tooth belongs to, you do not need to be an experienced dentist and know everything about the structure of the jaw and what the root system and periodontal itself look like. External signs that can be seen even in the photo will help you distinguish a baby tooth from a molar tooth. They include:
- Size. Firstly, baby teeth are smaller than molars in general. Secondly, the permanent ones are more elongated, that is, they are smaller in width than the temporary ones.
- Form. The cusps that are present on baby teeth are smooth, while on molars they are jagged, called mamelon.
- Enamel color. As mentioned earlier, the thin and rich enamel of baby teeth is distinguished by its whiteness, while in primary teeth it is characterized by a yellowish color.
How to properly care for your child’s oral cavity to avoid complications?
To avoid dental problems, you need to follow the basic recommendations of dentists and personal hygiene rules. Experts recommend the following as basic preventive measures:
- brush your teeth twice a day (morning and evening 30 minutes after meals);
- brush your teeth for at least 3 minutes, performing circular movements with the toothbrush;
- for high-quality treatment of the oral cavity, use special mouth rinses;
- At the first sign of a carious lesion, immediately contact a dental clinic.
Roots of baby teeth
Milk teeth are bone formations that are designed for mechanical processing of food in order to prepare it for subsequent digestion. They also influence diction and make the child’s speech correct and clear. In terms of their anatomical structure, they are in many ways similar to permanent ones, but they all have some differences. Among them:
- the coronal part is smaller;
- the thickness of enamel and dentin is less (from 0.6 to 1 mm);
- reduced degree of mineralization;
- no immune zones;
- the pulp volume is large;
- dental canals are shorter;
- poorly developed tubercles in the closure zone.
As for the number of root canals, their number remains unchanged.
The roots of baby teeth are slightly inclined. This is explained by the fact that the rudiments of permanent units are located above them.
It is a mistake to believe that children's teeth do not have roots. But this is what many adults think when they look at their children’s fallen teeth. In fact, by the time of prolapse, the formations located in the alveoli are almost completely resolved.
Why do crooked teeth grow?
Replacing milk units with permanent ones is a natural, inevitable process.
The first teeth appear at 6-9 months, when the diet, consisting of mother's milk or formula, begins to expand. During this period, the jaw is small, as are the teeth themselves. With the transition to an adult diet, due to their fragility and insufficient number (there are 20 of them), they no longer cope with the load. In addition, the jaw grows and the interdental spaces increase. As a result, the roots of baby teeth dissolve, they become loose, and the process of falling out begins to make room for strong permanent teeth.
Initially, a child has 20 baby teeth. Their loss and replacement with permanent ones occurs due to jaw growth. The molar units are characterized by their large size, so before the onset of loss, the distance between the teeth begins to increase.
Root canal treatment in children
The roots of children's baby teeth are filled with a special paste. It has the ability to dissolve in parallel with the process of resorption of hard tissues. This is the only way to ensure that the order of changing teeth is not disrupted and that there are no obstacles to the resorption of milk roots.
Once the root canals are treated, they are closed with a filling. Sometimes the doctor decides to use temporary filling material. This measure is justified if the likelihood of complications is high and you need to make sure that the inflammation has subsided. Only when the dentist is sure that everything is in order will he install a permanent filling.
Why is it important to treat baby teeth?
Now that it is clear that the structure of baby teeth is very similar to permanent teeth, the question “To treat them or not to treat them” should not arise for parents at all. Advanced caries often leads to destruction and damage to the pulp. Then the roots become involved in the pathological process. Removing dental nerves is not a pleasant procedure. It is important to prevent its occurrence.
Moreover, refusal of dental treatment can result in a number of other problems. This means:
- Incorrect bite formation. If, due to the destruction of the crown, the doctor has to remove it ahead of time, voids appear in the row, which “neighbors” tend to occupy. Then, by the time the “adult” unit erupts, there may not be a place for it - it will begin to grow somewhere on the side and ruin the smile.
- Damage to future teeth even before they erupt. With deep caries and periodontitis, cysts often form. They affect the rudiments of permanent teeth. Then the child is faced with the fact that his new tooth turns out to be sick and requires urgent treatment. Needless to say, its service life will be significantly reduced because of this.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. If parents believe that it is better to remove baby teeth rather than treat them, then by the age of nine their child (especially if he is prone to developing dental diseases) may lose half of his teeth. Is it possible to fully chew food in such a situation? No. The child regularly swallows poorly chewed foods. Because of this, the load on the intestines increases, which can result in frequent abdominal pain, stool disorders, nausea, gastritis and more serious gastrointestinal diseases.
- Psychological complexes. At 9-10 years old, a child evaluates his appearance and sees that his smile is very different from the smiles of his peers - it does not have a large number of teeth or they are dark in color, half destroyed. Because of this, he begins to be embarrassed to smile, laugh, and tries to talk less. All this negatively affects his self-esteem and does not allow him to quickly adapt to new situations and successfully go through the process of socialization in elementary school.
Don't waste your children's teeth. Teach your child from childhood to undergo preventive examinations in the pediatric dentistry department. At the same time, choose a specialist for him who you can trust. Then the child will not perceive another visit to the dentist as something terrible. He will be happy to go to the appointment, knowing that he will not be hurt.
An important question is whether baby teeth have roots.
The eruption of the first baby tooth is an important event in the life of every baby and his parents, who express especially serious concerns. This period can be difficult for the baby. Before they have time to get used to the appearance of their first teeth, they begin to fall out.
There is also a lot of excitement associated with this stage. Do baby teeth have a root? Parents want to receive accurate information about when and how this period should proceed.
The appearance of baby teeth begins differently for all babies. The age of 6 months is considered the norm . Full formation ends at 3 years. Each baby has an individual time frame for teething and shedding. An exact schedule that would suit all children cannot be established.
Deviations may occur, and parents should understand that this is quite natural.
The term was also named by Hippocrates. He believed that teeth are formed when a child feeds on mother's milk.
According to doctors, Hippocrates' theory is correct. Dairy products consist of calcium, which is responsible for the health indicators of each of them.
They cannot boast of the same strength as permanent ones. They are directly dependent on the baby’s nutrition.
Baby teeth
IMPORTANT! At birth, the baby's anterior crowns are already formed. They are located in special bags on the jaw. When the baby is born, the formation of the root begins along with the formation of interalveolar septa. This leads to partial atrophy of the gums at the site where the crown emerges.
Hypophosphatasia.
Clinically, hypophosphatasia manifests itself in the premature, causeless loss of anterior temporary (baby) teeth. Loss of front teeth can occur either spontaneously or in the event of a minor injury. In this case, inflammatory changes in the gums are not observed. Bone loss, in most cases, occurs only in the frontal region of the jaw.
Hypophosphatasia is characterized by low bone mineralization resulting from decreased alkaline phosphatase activity in the serum, liver, bones, and kidneys. This is a genetically determined disease and has several varieties (types). Early loss of primary teeth usually occurs in juvenile type (II), but also occurs in the third, adult type of the disease.
Recently, a condition called pseudophosphatasia has been described. With pseudophosphatasia, the genotype of a small patient corresponds to juvenile hypophosphatasia, the content of phosphoethanolamine in the urine is increased, but the activity of alkaline phosphate is normal. Clinically, this pathology manifests itself as true juvenile phosphatasia.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Nise: instructions, composition, indications, action, reviews and prices
Do baby teeth have roots?
Some parents believe that they have no roots. This is wrong. Baby teeth have roots. If you do not find out accurate information in time, you can have serious consequences.
Due to the rapid destruction of nerves, the child is almost not affected by pain. When the milk prototype is destroyed, it will loosen on its own and fall out. This gave rise to the myth of the absence of roots.
After the milkweeds have formed, they begin a three-year dormant period. Although this time is individual for each child. It is then that you need to go with your baby to the dentist to cure the damaged ones. If you ignore this procedure, the permanent ones will not grow up as healthy as you would like .
When molars and incisors grow, the baby tooth is pushed out. As a result, it begins to wobble and falls out. If such breasts are sick and are not treated, then they may fall out with complications, leading to the need to remove the nerve using local anesthesia.
IMPORTANT! Primary teeth have a short lifespan. At the age of 13-14 they change to permanent ones. The characteristics of milk teeth are similar in structure and function to permanent teeth and fully correspond to them.
What problems occur with the roots of baby teeth?
Temporary ones are special in terms of structure. If a root remains after they fall out, it may not be aligned after it falls out or is removed by a dentist.
Sometimes, due to the presence of a root in the thickness of the gums, inflammatory processes can occur.
In order to contact a dentist about removing the root of a baby tooth in children , there may be a reason:
- Damage by caries to most of the crown;
- Loosening without subsequent loss, which causes pain in the child when chewing;
- Due to traumatic injury, when a sharp edge damages the mucous membrane of the cheeks (the mucous membrane of the cheeks and gums becomes inflamed);
- Caries has damaged the root, under which the permanent one begins to emerge (caries will spread to the surface of the new one);
- When loosened without further loss, the new tooth has to leave the jaw row;
- Due to the presence of a fistula;
- When diagnosing pulpitis, chronic periodontitis, phlegmon, cysts, or other inflammatory diseases.
Main indications for removal
The nerve in a human tooth is located deep in the tissue and is reliably protected by enamel. In this way, the body ensures the sterility of all elements connected to the bloodstream (lymphatic and blood vessels, nerves) and protects the nerve from external influences (temperature, acidic or alkaline).
The reason that the nerve is removed is often the destruction of the tooth pulp. Dentin depressurization occurs in the following situations:
- Deep caries. The thinness of the enamel of baby teeth sometimes leads to infection of the pulp by harmful organisms. Because of this, they especially suffer from carious destruction, which develops in a short time. In a couple of days, a hole may appear at the site of a small spot, and the infection can spread throughout the body.
- Pulpitis. This is inflammation of the pulp tissue, which is a consequence of advanced caries. Nerves and blood vessels become the environment in which viral microorganisms develop and multiply. The results of their vital activity negatively affect dental tissue, destroying them.
- Periodontitis. An acute inflammatory process, the affected area is the area where the tooth connects to the gum. With the development of periodontitis, there is a danger of the formation of the already mentioned pulpitis and additional problems with the health of the baby’s teeth.
- Injury. If a child hits their jaw during a fall or other unpleasant situation, they can damage the enamel of their teeth. If the fabric is cracked, or a whole piece breaks off from a tooth, then food residues fall into the resulting hole. They become food for harmful bacteria, which, in turn, will not hesitate to begin to destroy the baby tooth.
In some cases, the removal of baby teeth is contraindicated:
- acute stage of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity (gingivitis, candidiasis, stomatitis),
- many infectious diseases: sore throat, pneumonia, whooping cough,
- the tooth is located in the area of a malignant or vascular tumor (in this case, the tooth must be removed along with the tumor in a hospital setting).
Doctors recommend removing baby teeth after the end of the acute stage of dental diseases and special medicinal preparation.
The doctor must exercise caution if the child has problems with the central nervous system, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels, blood diseases, or kidney disease.
In some situations, requesting deletion is mandatory.
These are situations such as:
- The temporary tooth wobbles, causing pain when chewing food or talking.
- The teeth are destroyed, which can lead to gum inflammation.
- It was accidentally knocked out, which led to bleeding and the parents were unable to stop it on their own.
- Temporary teeth interfere with the growth of permanent teeth.
- A small piece was chipped off, which led (or could lead) to damage to the gums.
- Formation of caries, goon child in pain.
It is also important to pay attention to the existing contraindications to the removal of temporary teeth:
- Particular care should be taken when removing teeth from children with cardiovascular diseases.
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the oral mucosa.
- The course of an infectious disease.
- Diseases of the nervous system, such as Down's symptom, mental retardation, encephalitis.
- Diseases of the circulatory systems.
- Kidney problems.
- Radiation disease of the second or third stage.
- Removal of a temporary tooth in the hematoma zone is absolutely prohibited.
However, there are several cases when teeth definitely need to be helped to fall out. For example:
- Bottle caries or other caries has damaged more than half of the tooth.
- The tooth has been loose for a long time, but cannot fall out. This makes it uncomfortable for the baby to chew.
- The tooth is broken, the sharp edge scratches the cheek or tongue.
- The root is affected by caries (there is a danger that it will damage the permanent tooth underneath).
- Pulpitis.
- There is inflammation or a cyst on the mucous membrane next to the tooth.
Do not make the decision to remove it yourself: if you see the symptoms listed above, contact your pediatric dentist. He will tell you whether the baby tooth needs to be pulled out and what treatment is required.
Pulling out baby teeth at home is dangerous: their thin walls and long roots go too deep into the gums. If you pull out a tooth with a thread or other improvised methods, you can easily disrupt the growth of permanent teeth that are hidden under the milk teeth.
At what age do the roots of baby teeth dissolve?
The process of formation, filling it with minerals, the process of appearance and time of resorption of the root, the stage of appearance of the permanent root and its root have a certain time and timing. These processes are very dependent on how the baby develops and eats.
The time for a permanent tooth to develop stops during the following periods:
- Central and lateral incisors - at 10 years;
- Canines and small molars - from 12 to 14 years;
- First molars – at 10 years of age;
- Second molars – from 14 to 16 years.
To determine what stage of root development is at a given age, and to clarify when the formation of the upper part of the root will end, many radiographic observations were carried out on the lower jaw. We studied data provided by children and adolescents aged 4–18 years:
- At 3 – 7 years old – 600 children;
- At 8 – 18 years old – 1287.
It is important to clarify these terms in order to select a pulp treatment method. Its condition depends on the duration of growth of the final formation of the apex.
Baby teeth are designed in such a way that root resorption begins spontaneously at 3–6 years of age. Then the loosening begins.
Resorption of the roots of baby teeth is a matter of time. It will definitely dissolve.
Root growth and formation ends when the apical foramen narrows to the minimum acceptable size. The x-ray shows a fully formed root, but without the upper part.
There is no exact time frame for the final formation of a permanent tooth. This is an individual process that is subject to fluctuations in one direction or the other.
IMPORTANT! Quite often, the root completes its formation much later than indicated in the medical literature.
The sixth is fully formed at the age of 10 in only less than 70% of children. In less than 5% of children, root formation ends no earlier than 12 years. And the seventh is fully formed at the age of 16, sometimes even at the age of 17.
Bones 3, 4, 5 are formed later than at 12 years of age.
Stimulation
In case of late tooth eruption, specialists prescribe special stimulating therapy. Standard stimulation therapy includes the following methods:
- Applying applications. To do this, use a ready-made 0.05% solution of humic acid obtained by isolating low-mineralized type sulfide silt mud.
The solution is prepared on the basis of isotonic sodium chloride. A tampon is soaked in the drug and applied to problem areas for an average of 5 minutes. The procedure is carried out for 15 days and no more.This drug has a powerful biostimulating effect by improving tissue respiration, normalizing metabolic processes and sedimentation of minerals necessary for crown development.
In addition, the product leads to slight loosening of the bone area in the area where the rudiment is located, which facilitates its formation and eruption.
- Irritating removable dentures.
It is a structure that looks like a bridge. But, unlike it, in an irritating prosthesis the main supporting part is located not on the adjacent teeth, but on the gum. Due to constant pressure on the area of the jaw with an impacted rudiment, trophic processes are improved and its growth is stimulated. The period of wearing the prosthesis will depend on each specific case. - Gum tissue massage.
Aimed at regulating metabolic processes and saturating tissues with minerals. As a rule, massage is done 1-2 times a day until a positive result appears or for at least 8 months. A set of exercises is selected by the doctor depending on the patient’s age and the area of the tooth. - Physiotherapeutic procedures. The most effective in this case was electrophoresis performed using adrenaline or lidase. Both drugs have the same pronounced stimulating effect, but their therapeutic effects are completely different.
Adrenaline is a hormonal drug whose action is aimed at stimulating the natural process of teething.Unlike lidase, it gives a faster and more predictable result, but can cause a disorder in the hormonal balance of the child’s body, which will entail negative changes in terms of general health.
The main action of lidase is aimed at loosening the bone area in the area of the bud, which facilitates the process of its eruption.
This drug also has its disadvantages: such exposure can lead to disruption of the mineral balance of the dental tissue of the developing tooth and adjacent crowns.
- The drug Honsurid. Aimed at restoring the functions of the embryo and improving metabolism in bone and cartilage tissues. The drug is used externally, diluting it with novocaine or sodium chloride.
For a stimulating effect, the drug is used to treat the mucous membrane in the area of the supposed root of the problem area. The procedure can be carried out once every 2 days for 10 days.In some cases, the course can be extended to 1 month.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Clasp prosthesis for the upper and lower jaws
What to do if a baby tooth falls out but the root remains?
In what order do baby teeth fall out? Regarding the issue of loss, it should be clarified that the representatives of the central incisors begin to fall out first. Next, the lateral incisors fall out (at about 6-8 years of age). Then it’s the turn of the first molars or molars (at 9-11 years old). The last ones in line are the second molars and canines (at 10–12 years).
Consequently, at the age of 12–14 years, all 12 teeth of the child become permanent. To these are added 8 molars.
If a baby tooth falls out but the root remains, there is no reason to worry. But if this causes pain in your baby, you should consult a dentist. After diagnosis, the presence of an inflammatory process may be noted. Then there will be a reason to remove the root.
Baby tooth without root
How to keep your mouth in order
Should I go to the doctor? Is it worth causing stress in a child if the teeth are temporary? The time will come and they will fall out. Is it necessary to traumatize a child’s psyche with visits to the dental office? Dentists say that baby teeth require attention just as much as permanent teeth.
They contribute to the correct formation of the jaw. In case of chronic infection of a temporary tooth, it can infect a permanent tooth, the rudiments of which are located very close to the roots of the milk teeth. Consequently, transmission of infection is possible even before the appearance of a permanent tooth.
Parents should teach their child to perform hygiene procedures from the age of 3 . The jaw and bite may be compromised due to sucking on lollipops. Then you will need to consult an orthodontist.
At the age of 12, the formation of a permanent bite ends.
In order for the child not to be afraid of the dentist, it is necessary to have a conversation with him first. Explain the importance of such a visit. It is impossible to accurately describe the stages of treatment, which can only frighten the baby more. Trust the doctor who can find a common language with the little patient. Through indirect suggestion, parents try to persuade the child not to be afraid, but they can only aggravate the situation.
The first visit to the dentist should be at 1 year of age . The doctor will advise parents on actions that will help ensure and maintain the baby’s health. Visiting the dentist will become addictive, and the child will no longer show fear. Treatment is carried out in a playful way.
Ages 3 and 12 years – time for consultation with an orthodontist. You should visit the dentist at least 2 times a year so that your baby can boast of a healthy smile.
It is important to teach your child to brush their teeth