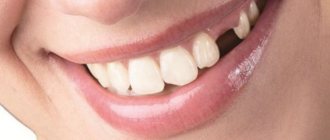
Why do they fall out?
The replacement of milk elements with permanent ones is provided by nature so that the baby can eat new food. A child grows 20 of them. In an adult, from 28 to 32. During the shift period, gradual resorption of the roots of baby teeth occurs. Then they become loose and fall out. In the free space, indigenous ones appear.
Baby teeth are formed in the mother's womb. But a permanent bite begins to develop after birth. The first elements appear at 6-9 months, when the baby eats milk (or formula), as well as vegetable, meat, and fruit purees. The maxillofacial apparatus is still small, like the first teeth, which gradually cease to cope with the chewing load. As the jaw grows, it can accommodate a permanent set.
The changing process begins with the lower jaw. The loss ends by the age of 14. But all deadlines are individual. The timing may vary depending on genetic predisposition, general development, as well as body growth, diet, the presence of diseases and pathologies.
The sequence of drops is the same. Sixes grow first. Then the lower and upper incisors become loose. After the first and second premolars. The fangs are the last to change. And after them the permanent second molars appear. After a few years, wisdom teeth grow in. By the age of 14, children have formed a permanent bite.
Sometimes teeth may not grow quite straight, and a gap appears between them. With large elements and a small jaw, pathologies are possible. However, with proper prevention of jaw abnormalities, bite defects are easy to avoid.
Factors that influence the shift order:
- Baby's genotype.
- Duration of breastfeeding.
- The presence of toxicosis in the mother during pregnancy.
- Infectious, inflammatory diseases.
When is medical help needed?
When accompanied by the following manifestations of the replacement process:
- Pain.
- Itching.
- Severe swelling of the gums.
- Increased sensitivity of enamel.
Milk teeth are removed in the dentist's office if they interfere with the eruption of molars. Removal is also carried out if inflammation occurs, there is looseness, pain, or other discomfort.
When should we expect the first losses? Baby teeth in children - loss pattern
Why do babies lose their baby teeth?
The answer is very simple - they give way to permanent ones. By about six years of age, in the depths of the gums - directly under the roots of temporary teeth - the rudiments of permanent teeth are formed. And after they enter the stage of active growth, the root of the temporary tooth simply dissolves. The field of this falls out, and a permanent one appears in its place.
The replacement process itself has some nuances.
When falling out, symmetry is maintained. This means that paired teeth become loose at the same time.
There is no exact dropout pattern. Every child is different. Which baby teeth fall out first? Most often, the lower jaw is released first. The order of drops is approximately as follows:
- the first are the lower central incisors;
- the second – the central incisors of the top;
- third – lateral incisors of the top and bottom;
- fourth – first molars;
- fifth - fangs;
- sixth - second molars of the top and bottom.
The milk kit must be changed without fail. Although in some cases, of course, not in full force, it persists throughout life.
The average age when a child begins to change teeth is five to six years. In some cases, the process may be slightly ahead of schedule or slightly behind. This is a physiological norm, but if loosening began much earlier, then the child should be shown to the dentist.
Dr. E. O. Komarovsky believes that a slight delay in the loss of breast milk is not a pathology. And if the baby lost his first tooth at 4.5 years old, then there is no reason for any concern.
The age pattern for the appearance of the indigenous set is as follows:
- 6…7 years – appearance of the first molars;
- 6…8 years – central incisors erupt;
- 7….9 years – time of lateral incisors;
- 10…12 years – first and second premolars;
- 9…12 years – appearance of fangs;
- 11…13 years – second molars are being cut.
A complete change of temporary set, as a rule, is completed at the age of fourteen.
The following factors may influence the delay:
- gender of the child;
- genotype;
- duration of breastfeeding;
- the duration of the period of toxicosis in the mother during pregnancy;
- infectious diseases suffered by the baby in infancy.
A long delay in changing a temporary set can be caused by:
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system;
- deviations in general development;
- the formation of rickets;
- the presence of hidden infections.
Possible problems
Sometimes changing a temporary set is accompanied by the following problems:
- "shark teeth";
- pain at the site of prolapse;
- a new tooth does not grow in the vacant space;
- crooked teeth.
Shark teeth
It is relatively uncommon, but the molar pair begins to grow before the corresponding milk pair falls out. And then both temporary and molar teeth are placed in the baby’s mouth at the same time.
This is not considered a particular problem, since after the loss of the milk one, its permanent brother will take its rightful place. Sometimes a temporary tooth – if it remains in place for a long time – will need to be removed.
Severe pain
In some cases, the child complains of pain at the site of the prolapse. Sometimes swelling may even develop and the temperature may rise. These are signs of gum inflammation and it is recommended to use special medications. One of these can be called Dentokind, which is both an anesthetic and anti-inflammatory agent.
There may be two reasons here:
- Delayed germination. Here two types of pathology are distinguished. In case of partial delay, only part of the tooth appears above the gum, but in case of complete delay, the formed tooth remains inside the gum.
- Complete absence. The reason is the death of the embryo.
We suggest you read What and how long after brushing your teeth you can eat: advice from dentists
In any case, the child needs an orthodontist consultation.
Crooked teeth
There are also two causes of pathology:
- The child’s habit of sucking fingers and chewing on hands. All this affects the formation of the bite. Most likely, your child will need braces.
- Slow jaw development.
If the molars grow crooked, the child should be shown to the dentist.
If the child’s jaws began to loosen before the age of four, then we can talk about accelerating the process. The reasons here may be:
- root injury;
- formation of caries;
- deliberate rocking.
Representatives of the milk kit that fall out prematurely free up a lot of free space. As a result of this, those neighboring them take over this space, and during the period of molar eruption there is simply not enough space for it. The result is his incorrect growth.
To prevent such a defect, the baby needs to be shown to an orthodontist. Most often, the child is fitted with a special prosthesis that does not allow neighboring teeth to move from their bed.
There are several reasons for this deviation:
- The rudiments of the permanent set are somewhat behind in development (physiological factor).
- Edentia. The concept hides the complete absence or partial death of the rudiments. The cause of the pathology is intrauterine infection.
- Retention. The diagnosis is typically indicated by the incorrect location of the formed rudiments.
To make a diagnosis, the child is given an X-ray of the jaw. If adentia or retention is confirmed, the child is fitted with a prosthesis. As you grow older, it needs to be changed.
Summary
The tooth replacement period is a very important time for a child. The gums are very vulnerable at this time. Any injury received by the baby can negatively affect the eruption of the molar set.
Our specialist comments:
- During tooth loss, in addition to brushing your teeth, you should also use special rinses. Additionally, you need to clean your mouth after every meal.
- Chewing gum is not recommended for children.
- It is necessary to treat caries even in baby teeth, since the infection can spread to permanent teeth.
During the period of replacement of baby teeth, it is necessary to reconsider the child’s diet. The menu should include foods containing calcium, vitamins and minerals.
Only in this case will the enamel of the primary set be strong and healthy.
Changing baby teeth to permanent ones
The first baby teeth begin to emerge in infants after they reach six months of age. Over time, permanent teeth replace baby teeth, which is a natural process that every growing child faces.
To minimize unnecessary worries, parents should familiarize themselves with the timing of the appearance and loss of baby teeth, the sequence, and the features of proper care for the child’s oral cavity.
Baby teeth
Milk teeth differ from permanent teeth not only in their fragility, but also in their quantity. So, in the oral cavity of an adult there should be 32 teeth, but the number of primary incisors in children does not exceed twenty.
This set is present in the oral cavity of every child closer to 3 years, which is considered the norm. Milk teeth are placed on the lower and upper jaws symmetrically and in equal numbers.
Milk claws are placed on both the upper and lower jaws in the following order (starting from the extreme point of the jaw):
- molars – 2 pcs.;
- fang;
- side bite;
- central incisors – 2 pcs.;
- side bite;
- fang;
- molars – 2 pcs.
Deviations from the specified number of baby teeth are extremely rare and, as a rule, are associated with the absence of their rudiments in the child. The pathology can be diagnosed by a dentist only after the baby reaches one and a half years of age.
Many parents look forward to the loss of the first baby tooth, which acts as a kind of starting point in the process when children's baby teeth are replaced with permanent ones (the change pattern is shown in the table below). In fact, changes in a child’s oral cavity begin to occur two years before the loss of the first baby tooth.
Attention! We are talking about the resorption of the root structures of baby teeth, which takes from one to two years. The dissolution of the roots leads to a gradual loosening of the teeth, which subsequently begin to fall out.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the timing of the eruption of baby teeth in children - table
It is also rare for third molars to appear after a child reaches four years of age. Many people do not lose these teeth and are permanent.
The age at which children's baby teeth change depends on several factors, but most often they fall out at the age of six or seven. It can take 6 to 8 years for teeth to be replaced, so by the age of 14, many people most often do not have a single baby tooth left in their mouth.
Timing of baby teeth loss
The specified time intervals are conditional in nature and are inextricably linked with the individual characteristics of each individual child. In addition, practicing dentists claim that such changes begin earlier in girls than in boys.
As a rule, the process of changing teeth is “led” by the incisors, which fall out first. Behind them comes the turn of canines and molars. How do they change, at what age, in what order do baby teeth fall out in children, which baby teeth fall out first?
For convenience, the answer to this question can be presented in the form of a table.
| Order number | Child's age | Changes in the dentition |
| 1 | 6-7 years | One of the incisors falls out first. Then the remaining central incisors on the upper and lower jaws |
| 2 | 7-8 years | Loss of lateral incisors on the upper and lower jaws |
| 3 | 8-10 years | Loss of first molars on the upper and lower jaws (small) |
| 4 | 9-11 years | Loss of fangs on the upper and lower jaw |
| 5 | 11-13 years old | Loss of second molars on the upper and lower jaws (large) |
From the table above you can see when the first baby teeth fall out.
As already noted, at the age of 4 years, many children may have permanent molars erupting. The norm is the loss of all twenty baby teeth as they are replaced by permanent ones, but deviations are not excluded. We have already found out which baby teeth fall out in children (the diagram is shown above), but how can we determine which tooth is changing?
Important! So, if by the age of fourteen a child still has 1-2 milk dumplings that differ in strength, most likely there will be no replacement.
Only a specialist can determine the nature of the remaining teeth. Such deviations from the norm are associated with the absence of the rudiments of permanent teeth as a result of injuries, various pathologies or banal heredity.
Nutritional Features
During the eruption of molars, their enamel is still being formed. The child needs to eat well. The diet should saturate the growing body with microelements and vitamins that are necessary for formation and growth. The baby should adhere to the following diet:
- Consume cottage cheese, hard cheeses, milk, and other calcium-rich foods.
- Eat fish dishes as often as possible: hake, pike perch, pollock.
- Fresh vegetables, fruits, most of them should be in solid form.
- Avoid white pastries, sweets, and sweet carbonated water.
- If you have a calcium deficiency, you need to take multivitamin complexes with calcium.
- Avoid hard and sticky foods: nuts, candies, toffees.
- The products should not contain active dyes that spoil the color of the enamel.
What can help keep baby teeth healthy?
- Regular oral hygiene at home and mandatory professional hygiene in a dental office (from 3 years of age).
- Limit consumption of candy and sugary drinks.
- Regular consumption of hard vegetables and fruits such as carrots, apples. They further clean plaque and also help the jaw muscles develop.
- Consumption of foods containing calcium and fluoride (dairy products, almonds, walnuts, fish, seafood).
- Regular preventive examinations at the dentist with a break of 4-5 months.
All this will significantly reduce the risk of caries and early loss of baby teeth in your baby!
Features of care
Good oral hygiene and caries prevention play a vital role during the eruption of permanent teeth.
The child should brush them twice a day with a brush with soft bristles that will not injure the gums. The paste should contain the optimal amount of fluoride and calcium. Parents should monitor the process and its duration.
Also, after eating, you should rinse your mouth with baby mouthwash, chamomile infusion or plain water. Plaque will not accumulate, and the risk of gum inflammation in the teething area will be reduced.
Your child should be taken to the dentist for an examination twice a year.
Consequences.
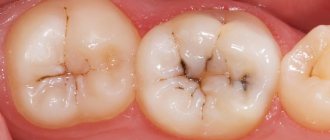
Groups of teeth are subject to carious destruction, but more often temporary
molars and first permanent molars. Defects of their crowns from the side
chewing surface contributes
decrease in bite height,
advancement of opposing teeth
deviation of the front teeth,
changes in occlusion and periodontium.
Such disorders are most pronounced during the period of tooth change, when the height
The first permanent molars hold the bite. Destruction of proximal
surfaces of the crowns of primary and permanent molars leads to
mesial shift of posterior teeth,
shortening of the dental arch,
incorrect position of individual teeth, their retention,
bite disorders.
As a result of carious destruction of the anterior teeth, morphological
changes. Functional disorders in the destruction of lateral teeth
are expressed in sluggish and insufficient chewing, displacement of the lower jaw. At
When the front teeth are destroyed, biting food, speaking, and swallowing are impaired.
After early loss of primary molars, myodynamic
balance between the tongue and cheeks, specific
bad habits, such as putting your tongue between your teeth
rows into the defect area, tongue sucking. Interocclusal
the position of the soft tissues delays the eruption of permanent teeth
and may promote the development of a deep bite.
Deformation of the dental alveolar arches, displacement of the lower jaw and
dysfunction of the dental system that occurs after
early loss of primary teeth is reflected in the formation of features
faces.
Early and late loss
If teeth fall out when the baby is not yet 6 years old, this period is considered early. Early loss is possible due to trauma, caries, intentional loosening, endocrine disorders, chronic infections. If such a process occurs long before the eruption of the fundamental elements, free space will remain. The rest of the teeth will gradually move onto it, which will lead to a lack of space for the molars. Crooked eruption is also possible.
In case of early loss, you should contact an orthodontist. In modern pediatric dentistry, prosthetic techniques are used to replace dental defects. The method prevents the displacement of other elements and helps to avoid problems with bite and cosmetic defects.
Sometimes the molars may erupt, but the baby teeth will not fall out. There is a risk of improper growth of primary elements and the formation of row defects. You will have to register your child for a baby tooth extraction procedure.
Late eruption may be associated with the following situations:
- Physiological delay. The rudiments grow more slowly due to the individual characteristics of the organism.
- If the baby did not have proper rudiments during intrauterine development, or they died due to inflammatory diseases. Partial primary adentia is possible.
- Incorrect location of the root element inside the jaw bone tissue.
- Past infection.
- Chronic dyspepsia.
- Rickets.
- Hereditary predisposition.
If loosening and loss have not begun by the age of eight, it may be due to the absence of molar rudiments.
Interesting: Adentia is a congenital or acquired absence of teeth. With primary partial edentia, one or more primary or permanent elements are missing. The absence of rudiments is shown by an x-ray. Gaps appear between the erupted ones. Due to the absence of most of them, the jaw will be underdeveloped. Hence, consequences such as speech impairment, slurred pronunciation of sounds, difficulties with chewing and biting off solid food are possible. An inadequate diet leads to gastrointestinal diseases and a deficiency of vitamins and microelements. The temporomandibular joint may not function properly.
The dentist will help identify the causes of untimely loss after an X-ray examination, which will determine the presence or absence of defects. When malformations of the dental system are identified, children are given temporary prosthetics. Over time, temporary dentures will be replaced with permanent ones.
What should parents do after baby teeth fall out?
Prevention of early absence of primary teeth
Measures to ensure the prevention of dental anomalies
clinical examination of children (identify and diagnose
dental anomalies, eliminate their predisposing factors
development;
identifying groups for clinical observation and drawing up a plan
preventive and therapeutic measures (for pediatricians of all
specialized service profiles);
timely referral of children with developed anomalies to
doctor for treatment;
control over the elimination of identified causative factors in children
occurrence of anomalies;
organizing and conducting children's training in children's groups, their
parents, teaching and medical staff methods
hygiene measures.
Timely sanitation of the oral cavity in children is important
an event that prevents the emergence and development
premature loss of baby teeth.
The dentition in children consists of a certain number of teeth, and if it is disrupted ahead of time, this can disrupt the formation of a correct bite. This happens because nearby milk teeth can shift to the place of the missing one, which means that permanent teeth will begin to grow unevenly.
The absence of baby teeth complicates the process of chewing and biting food, and also makes it difficult for a child to develop correct sound production and diction.
In addition, the absence of a tooth does not look aesthetically pleasing and can lead to psychological problems for the child and low self-esteem.
Even knowing that missing baby teeth can be replaced today, parents should teach their children to take care of their oral health and follow some rules to keep primary teeth healthy until they are naturally replaced.
We suggest you read: Do baby teeth need to be treated: advice from a dentist
Recommendations for parents
In most cases, the process of shedding and eruption is painless and does not cause concern. For pain, use the following remedies:
- Kalgel. Can be used from five months of age. It has a pleasant smell and taste. The drug contains: lidocaine, cetylpyridinium chloride. The product has an antiseptic effect.
- Dentinox. Suitable for children over one year old. Thanks to chamomile extract, the product acts as an antiseptic. Lidocaine anesthetizes, but is contained in the drug in small quantities, so the risk of allergic reactions is minimal. Polidocanol 600 has local anesthetic properties.
Gels relieve pain, relieve inflammation and swelling. The effect may last for several hours. Sometimes the process of loss is accompanied not only by pain and swelling, but also by an increase in temperature, which indicates the presence of inflammation. All this can put stress on the nervous system. Most drugs only relieve pain and relieve inflammation. Dentokind will not only relieve pain and inflammation. It will calm the nervous system and stabilize sleep.
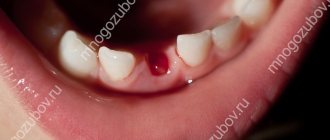
If there is a bleeding wound that has formed after the prolapse, apply a cotton ball to it. You need to bite it and squeeze it tightly for a few minutes. If the bleeding is prolonged, parents should contact their pediatrician. The cause may be poor blood clotting.
You cannot eat for two hours after the loss. On this day, salty, spicy, sour, too cold and too hot foods are excluded from the diet.
Under no circumstances should you:
- Try to loosen the tooth yourself and pull it out.
- Picking your mouth with sharp or metal objects.
- If you have a loss, chew nuts and hard candies.
- Use strong antiseptics (alcohol, concentrated hydrogen peroxide) for wounds.
The beginning and end of replacing baby teeth with permanent teeth is individual for each child. The number of simultaneously dropped elements and the duration of loss depend on the characteristics of the organism. Attempts to force events will not lead to a positive result. If, after the loss of baby teeth or during the process itself, deviations from the norm are observed, you should consult a doctor.