Dental plaque: what is it and is it so dangerous?
Plaque on baby teeth in children and permanent teeth in adults is a completely common and daily occurrence. True, only plaque that has a soft consistency, small thickness, white or slightly yellowish color and is easily removed with a regular toothbrush and paste can be considered normal.
Soft deposits appear on teeth almost around the clock, which is explained by the physiology and characteristics of the functioning of the oral cavity. They consist of food debris, bacteria and saliva components. However, such deposits need to be removed every morning and evening using hygienic procedures.
If you skip cleaning, soft deposits turn into hard ones under the influence of saliva and mineralization processes. And they are already dangerous for our health and, especially, for children.
Important! If a child’s plaque on his teeth is not cleared because it has hardened, then this is a prerequisite for the development of caries, pulpitis, stomatitis, gingivitis, as well as ENT diseases and gastrointestinal pathologies, because Bacteria from solid deposits can easily travel down the throat, onto the tonsils and into the stomach.
Against the background of weak immunity, insufficient mineralization of milk enamel and inadequate protective function of saliva, hard deposits, or more precisely, the bacteria that multiply in them, lead to destructive and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity in children.
Diagnosis of Priestley plaque on teeth
If darkening is detected on the enamel of a child’s teeth, you must contact a dental clinic.
The specialist will:
✔
inspection;
✔
laser diagnostics to determine the depth and size of the lesion;
✔
anamnesis collection.
After a conversation with the parent and child and collecting an anamnesis, the pediatric dentist will immediately prescribe treatment or conduct an additional examination. You should not neglect it - it is important for a specialist to find out why the child has black plaque on his teeth. Only after this will he be able to provide quality treatment.
Causes of increased accumulation of soft and hard plaque on teeth
We have previously learned that soft bacterial deposits are a normal physiological phenomenon and do not pose a particular threat if they are removed promptly. But hard plaque on the teeth of a child (as well as an adult) poses the greatest danger. And the reasons for its appearance are primarily related to lack of oral hygiene. For example, when the procedure is carried out “for show.”
However, severe plaque may also develop due to other factors. The main ones are presented in the table.
| Cause | Explanatory information |
| Non-compliance with diet | Plaque on the upper front teeth of a small child after 1 year can accumulate because he continues to be fed breast milk, juices and formulas, and sweet drinks at night. In the absence of oral hygiene, bacteria develop more actively after sweet foods - plaque appears |
| The predominance of soft foods in the diet | The growing jaw does not receive proper load, and the enamel does not have the opportunity to cleanse itself naturally with the help of hard vegetables and fruits (carrots, apples, cucumbers). It is impossible to delay the introduction of solid food for the youngest children, as this will also contribute to the development of pathology |
| Abuse of sweets | Babies and harmful bacteria are united by a love for everything sweet. Candies and chocolate without measure provoke the active reproduction of oral pathogens |
| Malocclusion | In this case, the baby predominantly chews on one side of the jaw, where there is a noticeable increased accumulation of deposits |
| Internal diseases of the body | If a child has a dense plaque on his teeth or it grows almost immediately after brushing, then pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and respiratory system, biliary tract, endocrine disorders, nasal congestion due to acute respiratory viral infections or acute respiratory infections, and metabolic disorders may be to blame. In this case, a coating on the tongue and bad breath are added to the alarming sign. |
| Indoor air is too dry or hot | Low humidity levels disrupt the natural process of salivation, causing the mouth to become dry, making it difficult to remove microorganisms and the smallest food debris. |
Description of the problem
Contrary to popular belief, tartar occurs not only in adults, but also in very young children. Of course, plaque formation on children’s teeth does not occur in one day, but 3-4 weeks is enough for visible deposits to appear.
In one-year-old babies
At one year of age, the baby almost completely switches from breastfeeding to adult food.
However, the saliva of a small child does not yet have the properties of the saliva of an adult - too little time has passed since the baby fed only mother’s milk or formula.
In addition, not all parents by this age begin to pay close attention to the child’s oral hygiene, teaching him to brush his teeth.
Often, a mother, fearing that her one-year-old baby might swallow toothpaste and harm himself, postpones teaching hygiene skills to a later date.
At the age of 2 years
By the age of two, the baby’s diet expands even more, however, it is often at this age that the child learns what sweets are. Constant and sometimes uncontrolled consumption of sweets disrupts the acid-base balance of the oral cavity. In addition, at this age, children are not yet able to fully care for their teeth, even if they already have the skill of brushing them.
Important! Almost all cases of tartar in children are associated with metabolic disorders.
If a child takes proper care of his mouth and eats sweets only occasionally, under the supervision of his parents, he will not be at risk of developing tartar. The only exceptions may be rare, genetically determined cases, or cases of exposure to negative factors on the fetus during intrauterine development.
At the age of 3 years
At the age of three, most children begin to attend kindergarten and oral hygiene, at best, comes down to morning and evening brushing of teeth.
During a daily stay in a kindergarten group, a child eats at least three times, without carrying out any hygiene procedures afterwards - not even basic rinsing of the mouth.
Food served in children's establishments typically has an extremely soft, mushy or puree-like consistency. Lack of solid foods in the diet is one of the reasons for the formation of plaque, especially in hard-to-reach areas of the oral cavity.
On baby teeth: causes of appearance
- In most cases, the front teeth and canines are the first to be affected in young children, due to bottle feeding. The sweet mixture gets on the teeth, and the resulting plaque hardens over time and turns into tartar.
- A particular problem is posed by night feedings , after which the child immediately falls asleep without any hygiene procedures or at least rinsing the mouth. The formation of deposits over time can lead to bottleneck caries.
- In older children, the main factor provoking the formation of plaque, and subsequently tartar, is the abundance of carbohydrate foods , which disrupt the acid balance and insufficient oral hygiene.
On permanent teeth
The main reasons for the appearance of tartar on permanent teeth are the same as on milk teeth – carbohydrates and insufficient hygiene. An additional factor may be the incorrect selection of a toothbrush.
The enamel of permanent teeth is stronger, which means that stiffer bristles are required. And the area of the cleaning surface of the toothbrush should correspond to the age of the child. It is advisable to use a brush with artificial rather than natural bristles, since bacteria multiply faster in natural bristles.
Why pigmented plaque may appear on the enamel
The deposits can be soft (usually whitish or yellowish in color) or hard (usually brown). But it also happens that the teeth suddenly become covered with pigment spots, and a pronounced yellow, black or dark coating appears on them. This may be due to several factors:
- treatment with certain medications: this phenomenon often occurs in children after taking antibiotics (especially against the background of dysbacteriosis), iron-containing drugs for anemia, tetracycline-based drugs,
- fungal infections: with them, the color of the enamel may generally turn green,
- addiction to coloring products and carbonated drinks: the enamel of milk units is very thin, sensitive and susceptible, it can change color from chemicals, darken from strong tea and cocoa without milk,
- Priestley's plaque: this is a non-carious pathology caused by the activity of specific bacteria. It appears as many small black spots or specks on the enamel, most often along the gum line. It does not pose a potential threat to the child’s health, but causes concern among parents, as it looks very unaesthetic. It can appear on the enamel literally overnight, or it can develop gradually. It occurs only in primary occlusion, but in any case, if a defect is detected, you should consult a dentist.
Removal
- The procedure for removing dental plaque in children is most often carried out using a special brush. Sometimes sandblasting or ultrasonic cleaning may be used. However, in most cases, experts prefer the first method, especially in cases with children, since incomprehensible equipment and noise frighten many children.
- After removing tartar, the dentist polishes the surface of the tooth enamel using special devices and abrasive paste.
- At the third stage, the surface is treated with a special fluoride-containing varnish, which covers the tooth with a smooth film, which helps to minimize the re-adhesion of bacterial plaque.
Video about removing tartar:
When plaque can be confused with dental diseases
Soft and hard bacterial plaque on a child’s baby or permanent teeth is one thing. And it’s completely different when the enamel is covered with stains, which in appearance can be mistaken for plaque. What could it be?
For example, white or brown plaque may be evidence of initial or advanced caries. Thus, white matte spots on the enamel signal the process of its demineralization. Brown - that cariogenic bacteria have already “corroded” the enamel and, possibly, dentinal layer. Naturally, it will not be possible to remove such stains by brushing your teeth. To eliminate them, you need to consult a doctor.
If you see dark or even black plaque or spots on your child's teeth, this may be fluorosis, indicating an excess of fluoride. A risk factor for the development of this disease is the oversaturation of the body with fluoridated pastes and drinking water with this element - these are the main sources of its production.
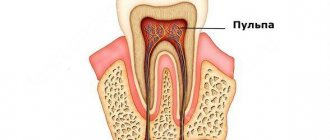
“My son was riding a scooter and fell, as a result he hit himself and chipped one of his front teeth. At first, of course, I cried and was naughty, but then I calmed down. And we didn’t make a tragedy out of it. Two weeks later, the enamel at the site of the chip turned black, and the son began to complain of pain - then we went to the doctor. The dentist looked and scolded me very much for not coming right away. It turns out that the impact exposed the pulp, it became inflamed, so the enamel turned black. We were treated with big scandals. I even wanted, a sinful thing, to ask the doctor to remove it, but he said that the growth of a permanent root is still far away, my son is only 3 years old, and it needs to be preserved.”
Sevostyanova Natalya, review from babyblog.ru
White or gray spots that cannot be removed by daily brushing and oral hygiene may be a sign of enamel hypoplasia. This disease often occurs against the background of impaired phosphorus-calcium metabolism in the body.
Main types of tartar
Currently, dentists distinguish two main types of tartar - supra- and subgingival. The first one can be seen independently; it usually has a grayish or yellowish tint. As a rule, such a stone is successfully removed by scraping. More often it forms in the area of the lower front teeth, as well as on the surface of the molars of the upper jaw.
Subgingival calculus can only be identified by a professional dentist. Its formation is associated with the process of accumulation of minerals, the main source of which is gingival fluid. This stone is usually dark brown in color with a slight greenish tint. Its localization occurs on the neck of the tooth, that is, deposits do not extend beyond the boundaries of the gingival margin, as well as on periodontal pockets1. The stone literally encircles the neck of the tooth, as shown in the photo below.
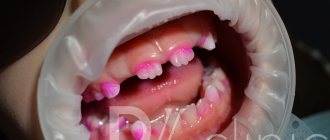
This is what dental plaque looks like on a child
What can the color of the deposits tell us?
- white: most likely, these are soft bacterial deposits and food debris, and the baby simply did not brush or brushed his teeth poorly,
- yellow: may again indicate poor oral hygiene, malocclusion, abuse of “colored” and sweet foods, treatment with various medications, including antibiotics,
- brown: caries, the presence of hard mineralized deposits, taking iron-containing medications,
- green: according to experts, a fungal infection or hormonal imbalance is to blame,
- grey: vitamin deficiency,
- black: the most common reasons for its appearance are dysbacteriosis, various internal diseases of the body (gastritis, diabetes mellitus, thyroid pathologies), fluorosis.
Tartar removal: how the procedure is performed
Professional oral hygiene cannot be performed if your baby has stomatitis or an acute infectious disease. Also, the procedure is contraindicated in case of enamel hypoplasia and if the baby is prone to allergic reactions to the components of the drugs.
How to remove tartar from a one-year-old child? The first thing you should do is visit your pediatric dentist. During the first visit, the doctor will conduct a thorough visual examination of the little patient’s oral cavity and prescribe professional cleaning.
This procedure involves removing plaque, as well as removing supra- and subgingival deposits using a special paste and brush. If the enamel and gums are hypersensitive, children will numb the affected area with local anesthetics such as sprays. If we are talking about a child 5-7 years old, then additional pain relief may not be needed at all.
“My daughter is only 4.5 years old, but she already has tartar! Not a plaque, but a stone! At the same time, I personally brush her teeth twice every day - in the morning and in the evening. No one gave me a clear reason; they associated it with taking antibiotics, which we had to take when our daughter was still an infant. As a result, cleaning had to be done. I was very worried how the child would react, but she didn’t even squeak once. They gave her some light freezing, and everything went great. Just in case, I added more solid fruits and vegetables to my diet - this is the best natural teeth cleaning.”
Galina, Moscow, from correspondence on a thematic forum
The photo shows a professional cleaning of a child's teeth.
After removing plaque, the doctor coats the enamel with a special fluoride-containing compound and gives recommendations to parents on how to properly brush their child's teeth and monitor oral care. You will have to visit the specialist again a few weeks after the procedure. At the appointment, the doctor will be able to assess the quality and effectiveness of the previously performed procedure.
Pay attention to the fact that professional hygiene has some differences between adults and children. An ultrasonic scaler is used for adults, while for children under 14 years of age its use is not entirely justified and is even contraindicated. This can cause harm, such as damage to the growth zone of the teeth or damage to the structure of the child’s fragile enamel, which subsequently negatively affects both the primary and permanent dentition.
How to deal with soft and hard deposits
If you notice that your child’s teeth are covered with whitish deposits, then you can deal with them yourself, since they consist of food debris and bacteria and are easily removed. The main thing is to teach your child how to properly and timely perform oral hygiene. Try to control this process, clearly demonstrate cleaning by your own example, and carry out morning and evening procedures together.
If soft yellowish deposits are localized on the enamel, then you can also remove them yourself by increasing hygiene using an irrigator, floss, a suitable brush and paste, as well as including more solid vegetables and fruits in your diet. However, it must be remembered that a change in shade from white to yellow indicates the occurrence of oxidation processes in the mouth, and parents need to keep this process under control.
When you find an uncleanable dark or brown plaque, which is predominantly located on the inside of the dentition, this indicates that the mineralization of soft deposits has already occurred and the so-called tartar has appeared. Only a dentist can remove it. How? Read more about this.
How to prevent it?
The main task of parents is not to cure the disease, but to prevent it! Therefore, certain measures should be taken to prevent mineral deposits on teeth:
- As soon as the first teeth appear, you need to teach the child to eat solid food, do not follow the lead of the little lazy person - do not chop carrots and apples;
- You should brush your teeth with a children’s brush, which is better to buy on the recommendation of a dentist;
- You need to change the brush every 2-3 months;
- Teach your child to brush their teeth correctly. The doctor will give you all the necessary recommendations at your appointment.
- purchase pastes with pyrophosphate (but strictly in accordance with the age of the baby).
But the most important rule is to bring your child once every six months for a dental examination. This will not only help get rid of tartar, but also prevent serious diseases in the future that are caused by mineral deposits: periodontitis, gingivitis, stomatitis.
Getting rid of the problem - how a dentist can help
The doctor will remove the deposits using professional oral hygiene. It is carried out differently for children of different ages:
- up to 3 years: this is a gentle method using a special brush, paste and floss. The procedure is carried out mechanically, i.e. manually,
- when changing a milk bite to a permanent one: for children aged 10 years and older, ultrasonic cleaning and Air Flow are already applicable.
In both cases, after the procedure, the teeth are coated with a fluoridated compound, which makes them stronger and protects them from bacterial attack.
What to do if deposits are not removed by cleaning or quickly build up again
Perhaps the reason for the appearance of such deposits is associated with the presence of pathologies of internal organs or fungal infection. In this case, the baby will need complex treatment, but first you need to contact a pediatrician who will conduct an examination. Perhaps in the future the help of highly specialized specialists - an endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, infectious disease specialist - will be needed. At home, it is important to review the nutritional system, follow a special diet, and strengthen oral hygiene.
Important! If you find green, black, gray or bright yellow stains on your child's enamel that cannot be removed by brushing, you should consult a doctor. You cannot self-medicate without establishing the true cause of the pathology.
If black or white dots on the enamel are associated with dental diseases, for example, caries, then it is also necessary to undergo treatment, but by a dentist. You can read about all the methods of treating caries in baby teeth by following the link.
Prevention of yellow plaque
Prevention should begin at the stage of bearing a child. During this period, any illness or metabolic disorders can lead to negative consequences. In infancy, the child is extremely susceptible to external conditions. For example, if the air in the room where he spends most of his time is too dry, his oral mucosa dries out. This leads to the fact that bacteria begin to actively multiply. By morning, a thick film forms on the teeth. Within a few months, it turns into a noticeable yellow plaque, which can no longer be removed with soft baby brushes for cleaning teeth. At the same time, abrasive pastes and brushes with stiff bristles are contraindicated for children.
Silicone children's toothbrush
Therefore, you need to either spray the room with water from a spray bottle, or use an electric humidifier. It is often built into an ozonizer, ionizer, and some models of household and semi-industrial air conditioners.
As early as two years old, children may experience a dense layer of plaque that cannot be removed with daily brushing. This is a direct indication for going to the dentist. In the office, the doctor will carefully remove the yellowing. If necessary, additional medical assistance will be provided to strengthen the enamel and restore healthy flora in the mouth.
Tartar removal
Every child needs to come for a routine check-up. Then there is a much lower chance of ending up in the same chair, but for the treatment of caries.
Whether the situation does not develop into a real problem depends on the attention of parents to this issue. After all, old plaque leads to caries. Early destroyed and fallen out or extracted milk teeth are a big disaster. The dentition shifts, and when a permanent tooth appears, there may no longer be room for it. It grows at the wrong angle.
Caries of baby teeth
Monitor your child's dental health. Then you won’t have to waste time, money and nerves on expensive treatment and orthodontic services. I look forward to your feedback and comments on the article. Be sure to subscribe to the news!
Is it possible to remove contaminants using traditional methods?
Some parents try to get rid of the problem with the help of folk and very affordable remedies. For example, activated carbon, soda or lemon, horsetail. Essentially, these products are designed to lighten the enamel by aggressively removing deposits; they have a powerful abrasive effect, so they are contraindicated for children. Babies have thin, sensitive enamel (and mucous membrane, too, by the way), with these products you can damage it, scratch it and make it even more brittle and susceptible to bacterial attack.
What are the reasons for a child's teeth to turn black?
Most often, dark spots and plaque on tooth enamel in children occur for the following reasons:
- violation of hygiene standards and rules, as well as neglect of brushing teeth in children;
- plaque formation;
- uncontrolled consumption of sweets and sour foods;
- weak immunity and lack of vitamins;
- phosphorus deficiency - the problem can be determined after passing the necessary tests;
- mechanical injuries to tooth enamel - in this case, injury can occur both during the child’s play and during careless dental intervention;
- salivary dysfunction - as a result of the problem, the child produces insufficient saliva during the process of chewing food. In this case, the enamel is not wetted sufficiently, and pathogenic microorganisms begin to multiply much faster.
Important! Children whose parents suffer from a similar problem are at increased risk of developing black spots and plaque on their teeth. In addition, children whose mothers took tetracycline antibiotics during pregnancy are especially prone to darkening of teeth.
Products that naturally remove deposits
We have already talked about fresh and hard vegetables - they should be present in the diet. Eating strawberries, strawberries, broccoli, pears and apples also helps to naturally lighten enamel and remove soft stains. These gifts of nature contain fruit acids and a lot of water; they also suppress the growth of pathogenic bacteria and help strengthen the mucous membrane. In addition, they contain many vitamins that are useful for strengthening the immune system in general.
On a note! Introduce fish into your diet; it doesn’t have to be expensive red varieties. Budget-friendly pollock, herring, saury, and cod are suitable. Almost every type contains fluoride, calcium, phosphorus and selenium, which are necessary to strengthen enamel and gums.
How to improve teeth color at home
Despite the fact that dentists categorically do not recommend carrying out any rough cleaning of children’s teeth on their own, nevertheless, a number of products that have a beneficial effect on the color of tooth enamel can be included in a child’s diet. These include:
- seeds and nuts - in addition to the fact that their coarse fibers are able to clean off plaque and deposits, in addition, these products are rich in vitamins and microelements that strengthen the child’s body;
- apples, carrots, pears - it is best to give them to children as dessert. Firstly, roughage strengthens teeth and gums. Secondly, a large amount of juice in fruits “washes away” plaque and pathogenic microflora;
- strawberries are a natural and healthy whitener for tooth enamel, which in some cases allows you to effectively fight dark plaque;
- broccoli - just like strawberries, cabbage fights dark plaque and gently whitens the delicate enamel of children's teeth.
What will be the consequences if the problem is not solved?
It all starts small, so if you don't remove soft deposits, they will become hard. Mineralized plaque, in turn, will contribute to the appearance of bad breath, the development of caries, bleeding gums, increased sensitivity, pain, and partial or complete destruction of the enamel.
The danger of long-term presence of bacterial deposits in the oral cavity lies in the fact that the bacteria multiplying in them provoke inflammation of periodontal tissues (gingivitis and periodontitis). Untimely treatment of these diseases can lead to early loss of primary and then permanent teeth, malocclusion and serious health problems.
How does petrification form?
Tartar in a 5-year-old child is formed due to excessive accumulation of bacterial deposits in the interdental and root spaces. The soft plaque begins to harden over time, mineralizing within the pathogenic microflora of the deposits.
Each subsequent layer of plaque undergoes a similar course of calcification. The result of this process is a hard mineralized layer (most often observed at the base of the lower anterior incisors). It can only be removed with professional medical instruments.
Since the layer is the result of the vital activity of bacteria that form dyes or pigments, most often in children, tartar is colored green. The microflora that forms the solid deposit contains chlorophyll, which has a corresponding shade.
Treatment methods
The specialist determines the treatment methods for blackened teeth . Only eliminating the causes of plaque will ensure that the darkening of the enamel disappears and does not form again:
- In case of intestinal microflora disorders, treatment is carried out; A review of the food system is recommended.
- Calcium deficiency or excess iron can be normalized by choosing the right diet or taking special medications.
- The development of early caries can be stopped using techniques such as silver plating or fluoridation. The enamel is treated with special solutions that preserve the condition of tooth enamel. This allows children to wait until their baby teeth are replaced by molars without deep, painful damage.
- Priestley's plaque can be removed with professional cleaning by a dentist.
Although there is no guarantee that deposits will not appear again. To avoid damaging the enamel, do not try to remove black stains. It’s better to wait until the baby grows up - Priestley’s plaque will disappear on its own.
Here you will learn how important it is to timely and accurately diagnose kidney pyelonephritis in children. It is necessary to quickly begin comprehensive treatment.
In this article, we propose to learn about the symptoms of herpetic sore throat.
How does asthma manifest in a child and how to determine its occurrence? Details here.
What to do if a child has tartar?
If you discover tartar in your child, first be sure to make an appointment with a pediatric dentist. At the first visit, the little patient undergoes professional teeth cleaning: dental plaque and soft plaque are removed. Subgingival stone is removed under local anesthesia using ultrasound. After the procedure, the dentist tells parents about the need to monitor whether the child is brushing their teeth correctly. Before and after the procedure, the hygiene index is checked and the oral care rules are repeated in the presence of parents. After 1-2 weeks, an appointment is made to monitor the thoroughness of dental plaque removal
Treatment options for black teeth
Treatments for black plaque and stains on teeth depend on the root cause of the problem. In general, specialists can prescribe the following therapeutic techniques:
- if the functioning of the stomach and intestines is disrupted - in this case it is necessary to carry out a full diagnosis, based on the results of which special drugs will be prescribed that restore the microflora;
- if there is a lack of calcium and iron , the problem is eliminated by prescribing an appropriate therapeutic course;
- with the development of caries - in this case, dentists recommend resorting to the procedure of silvering teeth, if we are talking about baby teeth. In the case of permanent teeth, the main prevention of caries is timely treatment and visiting a dentist;
- for Priestley plaque - treatment consists of timely cleaning and removal of plaque in the dental office.
Important! If plaque does not disappear after brushing with toothpaste and brushing, you should not try to get rid of it yourself. This way, you can damage the enamel of children's teeth and cause even more serious complications.