The symptom causes panic.
But in fact, it is not always a signal of concern and does not hint at health problems , since it can appear after feeding or become a harbinger of the first teeth .
Plaque can warn of the presence of a disease only in some cases.
Remember! New mothers definitely need to know about them in order to start treatment on time without harming the growing body.
Reasons for appearance
A white coating on a baby's tongue often appears as a result of breastfeeding.
However, the occurrence of this symptom can also be caused by various diseases and non-pathological factors . Among them:
- Candidiasis or thrush . It occurs when the bactericidal properties of saliva are lost and is diagnosed when active activity of yeast-like fungi is detected. The pathological process develops as a result of insufficient oral hygiene and without proper treatment can lead to damage to the larynx and internal organs.
- Disruption of the gastrointestinal tract . In the first months of life, the child’s gastrointestinal tract is not sufficiently formed. Because of this, the intestinal microflora can be disrupted due to poor nutrition. Babies who are bottle-fed or mixed-fed are especially susceptible to the problem.
- Gastritis with high acidity. The disease is extremely rarely diagnosed in infants and becomes one of the reasons for the appearance of white plaque. Acidity disorders in early childhood are associated with parasitic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract or congenital amino acid deficiency. This negatively affects the child's well-being.
- Viral stomatitis. Inflammatory infectious disease of the soft tissues of the oral cavity. It is characterized by a deterioration in the child’s general well-being, the appearance of mouth ulcers and an increase in body temperature. The occurrence of stomatitis is caused by acute and chronic diseases that can weaken the baby’s immunity.
- Allergic reaction. Appears as a result of long-term use of certain medications, consumption of infant formula, or contact with an allergen.
- Decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood. The problem is related to iron deficiency and often leads to oxygen starvation because cells and tissues do not receive enough oxygen. In this case, the blood circulation process is disrupted, and the microelements necessary for the body are poorly absorbed.
Keep in mind! Plaque that appears on a baby after feeding or regurgitation is not a sign of the development of a serious disease.
If it is a milky coating on the tongue of a baby
Milky deposits on a baby’s tongue can be easily removed by cleaning with a gauze cloth soaked in warm boiled water.
In most cases, the white coating on the child’s tongue disappears on its own some time after eating.
After regurgitation, white food particles may also remain on the tongue, forming a film that can and should be easily cleaned.
The occurrence of plaque is promoted by high humidity and high air temperature in the apartment where the child lives.
Also, such plaque may appear due to allergic reactions to mixtures, complementary foods, and medications.
This etiology of milk plaque is a normal physiological reaction of the child’s body.
It is easy to remove if you clean it with a gauze cloth soaked in warm boiled water. Such plaque does not pose any danger to the health of the baby.
White coating on the tongue can also be regarded as a symptom of various pathologies:
- Diseases of the respiratory system: with bronchial asthma, in the first stages of the development of the disease, plaque appears on the tip of the tongue, then covers the entire tongue.
- In case of influenza, ARVI, sore throat, the tongue is completely covered.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract: with gastritis, plaque is located in the middle of the tongue. A white dense layer covers the entire surface of the tongue during dysbacteriosis.
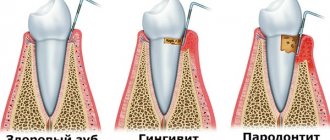
- Dental problems: stomatitis and caries.
Important! When the first small areas of milky plaque appear on your child’s tongue, you should consult your pediatrician. He will accurately differentiate milk plaque from candidiasis and select the appropriate treatment.
Features of consistency and thickness of plaque
By paying attention to the thickness and consistency of the plaque covering the tongue, you can identify the reason why it appeared:
- a thin layer of wet plaque - occurs after feeding or regurgitation;
- a thin layer of dry deposits – an allergic reaction;
- thick whitish coating – indicates dysbacteriosis;
- viscous dense formations of white color - gastritis with high acidity;
- dense cheesy – viral stomatitis;
- thick, loose plaque – thrush or candidiasis.
Associated symptoms
Stay up to date! Depending on the cause of the appearance of a white coating on the tongue, the newborn may also be bothered by additional symptomatic manifestations.
By monitoring the child’s condition, parents can identify the following symptoms :
- increased body temperature;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- pale skin;
- abdominal pain;
- constipation or diarrhea for more than three days;
- green mucus in stool, foam, or blood;
- intestinal colic;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- frequent excessive regurgitation or vomiting;
- bad breath;
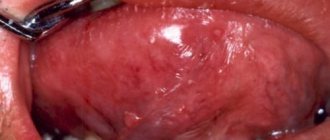
- redness on the oral mucosa;
- manifestations of allergic dermatitis in the form of a rash;
- formation of blisters, wounds and ulcers in the mouth;
- loss of appetite;
- dry mouth or excessive salivation;
- bright red color of the tongue in areas without plaque;
- swelling of the gums and tongue;
- jams and cracks in the corners of the lips;
- lethargy;
- poor weight gain;
- breast refusal;
- irritability.
Why does a whitish coating appear?
A dense white coating on a child’s tongue occurs due to functional disorders in the body. The horny cells of the filiform papillae become compacted, thickened, and it becomes difficult or impossible to clean them.
Why this happens is impossible to say based on one symptom – the appearance of white spots on the child’s tongue.
The reasons for the appearance of a layer of plaque can be different:
- violation of oral hygiene measures;
- taking certain medications;
- introduction of pathogenic flora of various types;
- diseases of the digestive organs of various etiologies.
If this symptom appears, you should first contact your dentist to rule out oral infections. It is enough to show a small child to a pediatrician. It is imperative to find out the reasons for the appearance of a white tongue in a child.
With inflammatory diseases, the baby refuses to eat, and this has a direct impact on the child’s health. Weight loss in children causes physiological lag.
How to assess a child's language
It is not recommended to evaluate the baby’s health solely by the appearance of the tongue.
Inflammation of the oral cavity causes the following additional symptoms:
- swelling of the oral mucosa;
- the appearance of dry mouth;
- when food gets into the mouth, painful sensations occur - the child even refuses sweets;
- there was a smell from the mouth.
When wondering why a white coating has formed on the tongue of an infant, parents first of all assume thrush.
What diseases are hidden under plaque?
- Candida fungus is considered a conditionally pathogenic flora and is constantly present on the skin and mucous membranes of a person of any age. The baby has no immunity against these microorganisms, and any violation of hygiene - and babies of a tender age constantly drag foreign objects into their mouths - causes the activity of the mycelium.
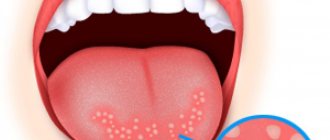
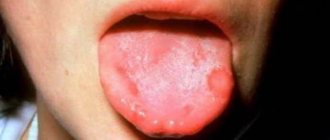
First, small white pimples appear, then they merge into a continuous spot. The mucous membranes become bright red; they appear “dry” and thinned out. At first glance, you might think that lumps of curdled milk are stuck to the tongue, but when you try to remove them, small hemorrhages remain. Large plaques appear when the inflammatory process worsens. The child's breath smells of sour cottage cheese. Submandibular lymph nodes may become enlarged.
- Geographical or desquamative glossitis can provoke the appearance of white plaque.
Clinical picture: white and red spots appear on the surface of the tongue. Unlike the “geographical” form of the disease, which is a harmless hereditary pathology, desquamative is a sign of the development of systemic diseases of the baby’s body or intestinal dysbiosis.
- White dots on a child's tongue appear due to stomatitis.
At first they are small, then they become larger. If you try to remove these points, bleeding ulcers also appear, which are subsequently covered with a white or grayish coating. Additional signs of the disease: moodiness; lack of appetite, lethargy, fever may rise. If the disease is not treated, the ulcers merge into continuous spots, and purulent discharge appears.
- Infection of the oral cavity also causes tooth decay. The localization of plaque in this case is near the inflamed area. An experienced dentist can even tell which tooth hurts by changes in the mucous membrane. White dots and large spots on the child’s tongue can be seen with diseases of the respiratory system.
By their location, you can determine the nature of the disease:
- A thick layer of plaque is concentrated near the root of the tongue - this is how tonsillitis, pharyngitis, tracheitis manifest themselves;
- The surface of the tongue is white – influenza, parainfluenza;
- Plaque on the front edge of the tongue is a symptom of bronchitis;
- This plaque takes on the appearance of foam - the condition worsens, the risk of pneumonia increases;
- A viscous coating on the very tip of the tongue is bronchial asthma.
- Thick, dense plaque in the oral cavity, a general increase in temperature, fever, enlarged lymph nodes, tearfulness, photophobia - all these symptoms are inherent in infections: measles, scarlet fever, diphtheria and other diseases.
- A translucent whitish coating occurs with gastritis. It is located on the edge of the tongue.
- A thick layer on the root of this organ is a symptom of enterocolitis. Additional symptoms: bloating, increased gas formation, stool disorders. In severe cases, the presence of blood in the stool and an increase in temperature.
- White pimples on a child's tongue can form as a result of allergic reactions. This is especially true when allergies to medications manifest themselves. The clinical picture is bright swollen mucous membrane with white vesicles that have serous contents. Allergies can also cause additional symptoms: dizziness, lack of urine, dry mucous membranes, general weakness, vomiting and nausea.
When should you consult a doctor?
You should know! You need to show your child to a pediatrician and undergo an examination if:
- the baby is suffering from diseases of viral etiology - the symptom may be a sign of infectious stomatitis;
- the white coating has a cheesy consistency and is difficult to remove by regular wiping - this indicates the appearance of thrush;
- plaque forms not only on the tongue, but also on the gums, inner lips, tonsils;
- the child has become restless and irritable, refuses to feed and cries constantly.
If the plaque disappears a few hours after its appearance, and the baby’s general condition is normal, there is no need to see a doctor.
Reference! This is explained by the fact that in this case the symptom does not warn of the development of pathology and is not considered dangerous.
What causes white plaque to appear?
Why does my child have a white coating on his tongue? Minor deposits are present and normal. They are formed by bacteria, epithelial cells and food debris. More noticeable in the morning after sleep. By the end of the day, the plaque almost completely disappears.
If you compare the layers on the tongue of a one-year-old child and a newborn, there is a difference. This is related to nutrition. When the baby begins to eat vegetables and fruits, the tongue becomes cleansed and whitish deposits can only be detected in the morning. But infants' diet is narrow: breast milk or formula. In this regard, the white coating on the tongue of a newborn is more noticeable and is present throughout the day.
But in order to understand where is the norm and where is a sign of pathology, you need to answer the following questions.
- Is the pale pink mucous membrane visible from under the layers?
- What is the consistency of the white coating on a baby’s tongue?
- Does it cover the back of the tongue evenly?
- Is it easy to remove?
- What is the condition of the mucous membrane in the baby’s mouth after removing the layers?
- How long does it take for plaque to appear again?
- Do you have bad breath?
- Are there any other lesions on the surface of the mucous membranes?
- Are the regional lymph nodes enlarged?
- Is the child’s general condition impaired?
The questions above were chosen for a reason. Since these aspects are key when making a diagnosis. White plaque in the mouth of a child who does not need treatment will look like this:
- a thin layer evenly covering the back; the towering mushroom-shaped papillae can be clearly seen;
- plaque of soft, uniform consistency;
- easily removed, mucous membrane without pathological changes.
If the tongue is coated, the layers cannot be removed, or they immediately reappear after removal, there is bad breath, the child is capricious and refuses to eat, consult a doctor. Most likely, your baby needs treatment.
Carrying out diagnostics
Some young parents believe that they can diagnose the disease themselves.
However, only an experienced doctor can establish the exact cause of the symptom and make a diagnosis.
During the examination, the pediatrician will assess the baby’s general condition, check the lymph nodes and, if necessary, refer to specialists :
- dentist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- neurologist;
- gastroenterologist;
- endocrinologist;
- nephrologist;
- immunologist.
For your information! To determine the cause that caused the appearance of an unpleasant symptom in a newborn, the small patient is prescribed a series of examinations and tests.
Possible diagnostic methods include:
- biochemical blood test - performed to assess the condition of the gallbladder, liver and pancreas;
- general blood test – necessary for diagnosing infectious and inflammatory processes in the body;
- bacteriological culture for microflora from the oral mucosa - prescribed for suspected candidiasis or viral stomatitis to identify the pathogen;
- Abdominal ultrasound, gastroscopy or fluoroscopy – performed if gastritis is suspected;
- coprogram – carried out to diagnose intestinal microflora.
Treatment
Need to know! A white coating on the tongue of a newborn is not an independent disease.
Therefore, therapy consists of careful oral hygiene and treatment of the underlying pathology .
Medicines and their dosage regimen are prescribed by the attending physician after consultation and diagnostics .
In the treatment of infants the following are used :
- Enterosgel . Destroys pathogenic bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract, fights dysbiosis and various pathologies in the gastrointestinal tract. The drug does not contain dangerous or harmful components, therefore it is absolutely safe for newborns.
- Espumisan. A remedy that has a carminative effect. Espumisan helps eliminate intestinal colic, bloating, normalize intestinal microflora and improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Viferon. An immunomodulatory drug with antiviral action in the form of an ointment for external and local use. The medication is indicated for damage to the oral mucosa due to infections or viruses.
- Candide. An effective antifungal agent for the treatment of thrush in young children. The drug quickly eliminates white plaque and other symptomatic manifestations caused by a fungal infection, and also improves the child’s well-being.
Important! Alternative medicine recipes are not used to treat various diseases and eliminate white plaque on the tongue of an infant.
Since herbal decoctions and infusions can worsen the general condition of the child and lead to a severe allergic reaction.
Can plaque be yellow?
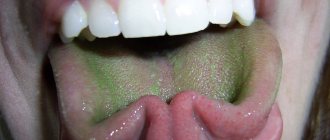
A yellow coating on the tongue after taking antibiotics may appear as a result of a disturbance in the intestinal microflora .
This contributes to the deterioration of its peristalsis and the occurrence of constipation.
For your information! Feces accumulate in the intestines, and toxins begin to be absorbed back into the blood. As a result, a yellow coating appears on the tongue.
Moreover, the more coated the tongue is, the greater the amount of toxins absorbed into the blood and distributed throughout the body.
Also, yellow plaque can be a signal of liver dysfunction and problems with the outflow of bile .
How to clean your tongue?
To cleanse the child's tongue of white plaque, parents can use a soda solution.
This is an affordable and budget-friendly product that can be easily prepared at home.
The procedure is carried out in several stages:
- Dissolve one teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of warm filtered water.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and prepare a small piece of sterile bandage.
- Wrap a bandage around your finger and dip it in a glass of medicinal solution, thoroughly saturating the fabric.
- Gently wipe your baby's tongue, inner cheeks and palate, removing all plaque. There is no need to apply force or pressure; just walk over the affected areas with light movements so as not to cause discomfort to the child.
- Repeat the procedure 5-6 times a day until the oral cavity is completely clean.
Important information! Baking soda has bactericidal properties and neutralizes the effects of inflammation in the oral cavity.
However, self-cleaning of the tongue with soda solution can only be done after consultation with the pediatrician . You also need to make sure that the child does not have allergies.