Causes
Hyplasia is most often congenital
Hypoplasia begins to develop after the birth of a child, but most often it is congenital.
The main factors provoking the development of Hutchinson's teeth:
- Different Rh factors in the blood of the mother and fetus, which come into conflict with each other
- Viral, infectious diseases suffered by a woman at the beginning of pregnancy
- Severe, prolonged late toxicosis
- Premature birth (before 40 weeks)
- Child dystrophy, rickets (poor appetite, lack of vitamins, other reasons)
- Gastrointestinal diseases
- Diseases of somatic nature
- Metabolic disorders
- Difficult childbirth, birth injuries
- Brain disorders from birth to one year
- Infections acquired in utero or in the first six months of life
- Mechanical damage to the jaws and face
Symptoms of disease development
Experts divide hypoplasia into two main types or types: systemic and local. Their reasons are common, but they manifest themselves in different ways.
Systemic hypoplasia
- All teeth are affected
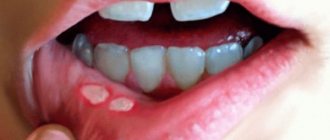
- Tooth enamel becomes covered with white or yellow-brown spots
- The enamel is thinned or absent at all
- The layers in the core of the tooth are underdeveloped
Local hypoplasia
- Pathology concerns only a few dental units
- Due to damage to the deep layers, foci of inflammation may appear
- The shape of the teeth changes, various defects develop
- On teeth affected by hypoplasia, there may be no enamel layer at all or it may be too thin
In addition to these two types of hypoplasia, there are several special forms of manifestation:
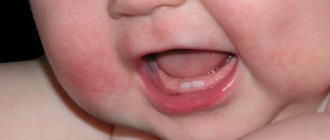
- Hutchinson's teeth. There is a change in the shape of all or several teeth. The cutting edges take on the shape of a sickle, and the teeth themselves are oval or barrel-shaped
- Pflueger's teeth. The appearance of the affected teeth is similar to those described by Hutchinson, but the cutting edge looks like healthy teeth, its shape is not changed
- Fournier's teeth. The “sixes” in the dentition of permanent teeth acquire a cone-shaped shape, which is wider towards the root and narrows towards the apex. The surface is covered with weakly defined tubercles. This type of lesion is associated with infection with syphilis inside the womb
There are several characteristic features of Hutchinson's triad:
- Due to the influence of the causative agent of syphilis (pallidum spirochete) on the rudiments, all or only some teeth are deformed
- Parenchymal keratitis occurs
- Hearing loss progresses
The hearing loss of such patients is associated with degradation of the vestibulocochlear nerve, which is located in the bone of the temporal lobe (in its petrous part).
This phenomenon is called the syphilitic labyrinth. The manifestation of the three listed signs indicates that congenital syphilis is at a late stage. But most often, patients exhibit 1-2 signs from the triad; all together are rare.
Degrees of the disease
The appearance of dark spots on the teeth is one of the signs of hypoplasia.
There are 3 degrees of development of Hutchinson’s teeth, which differ in shape and complexity:
- The initial stage of hypoplasia - small dark spots of pigmentation on the enamel layer of some or all teeth
- Moderate degree of the disease - the surface of the enamel layer is covered with convex or concave grooves and depressions. At the same time, Hutchinson's triad may begin to appear
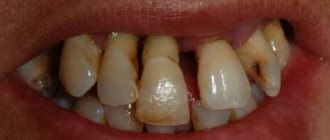
- A severe degree of hypoplasia is characterized by abrasion of enamel or visible deformation of dental units
Therapy is necessary for any of the degrees described, but its methods will vary at each stage.
Filling and prosthetics
Filling is used for pronounced erosive depressions, as well as mixed forms of hypoplasia, when the integrity of the dental units is compromised. Composite materials are used to restore teeth. In some cases, the vestibular surface is covered with veneers. This technique helps to give teeth an aesthetic appearance and prevent their destruction.
Prosthetics are used for severe damage to the enamel of primary or permanent teeth. Crowns help maintain the health and aesthetics of your teeth. Installing crowns for hypoplasia in childhood contributes to the formation of a correct bite and the development of normal diction.
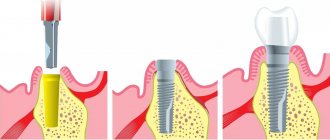
Depending on the extent of the damage, the condition of the soft and hard tissues, it may be necessary to remove the affected tooth followed by implantation.
Forms of the disease
Experts divided hypoplasia into 6 forms:
- Spotted. On the surface of the teeth (usually the incisors are the first to be affected), whitish or light brown spots become noticeable. In these places the structure of the enamel changes
- Erosive (cup-shaped). Round or oval defects of different sizes appear on the enamel, similar to a cup. Such erosion usually occurs in pairs and simultaneously affects symmetrically located teeth. In places of defects, the enamel becomes thinner in the direction of the depression or disappears completely. When the color of the spot is yellow, this means that dentin is already visible in this place
- Furrowed. The tooth is gradually covered with parallel grooves. Then the pathology spreads further to the teeth adjacent to the affected unit. The depth of the grooves depends on the severity of the disease, in the end, they appear on all teeth, the upper incisors are most damaged
- Linear and wavy shapes. Expressed by vertical grooves mainly on the vestibular part of the teeth. It seems that the enamel has become wavy
- Aplastic. Complete absence of enamel on the teeth or a very small amount of it. This is the most severe form of hypoplasia
- Mixed. With this form of the disease, all the manifestations described above are observed, which affect several teeth in the mouth. Cup-shaped and spotted forms are most often present.
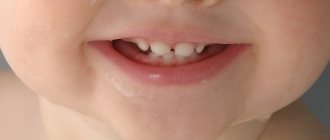
Hypoplasia of primary teeth
Hypoplasia of primary teeth in children is not so rare.
The disease is very common in children. This is associated with various disorders during intrauterine development. Sometimes it happens that when the shape of the bite changes, hypoplasia goes away on its own. But it’s not worth waiting to see whether this will happen or not without doing anything.
Violations in the enamel of baby teeth can cause caries, which will subsequently affect the health of permanent teeth. Hypoplasia weakens the child’s immunity, which is why he can get sick often.
If the disease is not treated in time, the child may develop symptoms of an advanced stage:
- Increased abrasion of the enamel layer
- Damage to tooth tissue
- Loss of diseased teeth
- Abnormal bite
Tips for parents
Many parents do not even suspect that dental hypoplasia is a very common disease among children. In order to alleviate the child’s condition, the following actions must be taken:
- Eliminate all sour and sweet foods from your diet.
- Use special toothpastes.
- For small children, purchase silicone finger brushes for oral hygiene.
- Carry out the procedure of silvering your teeth regularly.
- Monitor their condition and promptly fill teeth if necessary.
Diagnosis of hypoplasia
At a late stage, the symptoms of hypoplasia become pronounced, which makes the diagnosis easier. In the initial stage, its symptoms are very similar to the development of caries - its initial and superficial types.
| Symptom | Caries | Hypoplasia |
| Location of spots | A single white spot appears near the neck of the tooth. | Numerous spots ranging from white, yellow to light brown appear throughout the tooth. |
| Condition of tooth enamel | The surface of the enamel layer remains even and smooth. | Sometimes there may be no enamel layer at all or partially; grooves and depressions are spread over the entire surface. |
| Shape of teeth | Remains unchanged. | In some types of the disease, the shape of the teeth changes, becoming barrel-shaped, the cutting edge is bent in the shape of a crescent moon. |
When the first symptoms of hypoplasia appear, you need to contact a dentist, who will clarify the diagnosis, determine the stage and form of the disease, and prescribe adequate treatment.
Possible consequences
Without or incorrect treatment, serious complications can be expected to develop. Since the progressive disease significantly impairs the protective properties of the enamel, the following negative consequences arise:
It should be noted that diseases of the oral cavity affect the condition of the body as a whole. In particular, excessive destruction of enamel often leads to the formation of chronic diseases of the digestive system.
Hypoplasia is a common and quite serious dental disease, which, if not treated correctly, can lead to tooth loss and the development of diseases of internal organs.
In this regard, it is necessary to begin treatment at the first symptoms of this disease, and to prevent its development, follow preventive recommendations.
Treatment
If hypoplasia is at the very beginning of its development, and spots are already there, but are not yet visible to the naked eye, you can do without treatment. But if pigmentation has already appeared or the teeth begin to decay, it is no longer possible to do without consulting a doctor and adequate treatment.
In fact, hypoplasia cannot be completely cured. As a rule, cosmetic defects are eliminated. But in the future the patient will be forced to seek help again.
Most often, teeth whitening is prescribed to remove stains, but in the later stages it is not effective, so it is not performed. Lumps and other irregularities, including the cutting edge, are removed from the enamel surface by grinding.
In the early stages, remineralization is an effective method, so doctors often resort to this procedure. The mineral composition of the enamel is restored through the use of solutions of calcium gluconate, Remodent, and fluorides. If the teeth are already beginning to decay or have a too lumpy surface, the patient will be offered veneers, bridges or crowns. Pre-treatment of other diseases that exist in the oral cavity is carried out.
The destructive effect of hypoplasia slightly interrupts careful dental care. They may need to be cleaned more than 2 times a day. With the help of orthodontic treatment, it is necessary to eliminate caries.
Doctors insist that orthopedic treatment cannot be carried out on children whose dentoalveolar system is not fully formed. Otherwise, with age, periodontal pathologies and pulpitis may occur.
Remineralization
Remineralizing therapy involves saturating tooth enamel with fluoride and calcium. Artificial mineralization is carried out using dental gels, pastes, varnishes and other means. Treatment can be done in a clinic or at home.
Remineralization in a clinical setting consists of several stages:
- Professional oral hygiene.
- Application of restorative gel.
- Coating with a fluorine-containing compound using a tray or brush.
The dentist selects the frequency of procedures and the type of drug individually. In addition, your doctor will often prescribe oral vitamins and minerals as additional support for your body.
Prevention
To prevent enamel hypoplasia from developing in an adult, preventive measures are necessary. These are quite simple rules, following which you can completely avoid the disease. But you will have to pay attention to prevention in advance.
Nutrition
Proper diet and hygiene are the essence of preventing hypoplasia
A large role in the prevention of hypoplasia is given to proper, nutritious nutrition. A woman should pay close attention to her diet, starting from the planning stage of pregnancy. It is necessary to ensure that the child eats fully and correctly. After switching to complementary feeding, instead of breast milk or formula, the baby’s diet must include:
- Products containing fluorine and calcium (cottage cheese, milk, cheese and others);
- Vitamin D in the form of a ready-made preparation or exposure to the sun for a sufficient time;
- Products containing vitamin C (oranges, tangerines, broccoli, spinach, cranberries);
- Foods containing vitamins A and B - seafood, legumes, carrots, poultry.
Hygiene
From the age of one, your baby should begin to be taught daily oral hygiene. At first, it may just be a game, morning and evening, especially if the baby doesn’t like brushing his teeth at all. Here parents will need imagination, and, of course, they need to set a personal example. You need to teach your child to rinse his mouth after every meal. It is necessary to visit the dental office twice a year in order to identify problems at an early stage.