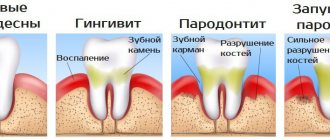
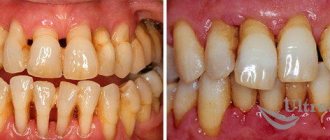
What is periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the soft and bone tissues of the supporting apparatus of the tooth. When periodontitis occurs, not only the gums are damaged, but also the bone tissue of the alveolar process of the jaw. The ligamentous apparatus of the tooth, which holds it in the socket, is destroyed. Looseness of the dental arch appears. Painful reaction of the gums occurs already in the first stages of the disease.
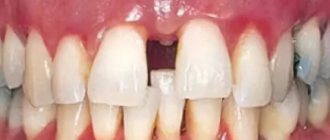
As the pathology progresses, complete loss of teeth is possible. Periodontitis is almost always preceded by gingivitis.
Diagnosis of generalized periodontitis
The initial stage of diagnosis is assessment of dental status:
- color and condition of the gums, frenulum of the tongue and lips;
- volume and nature of dental plaque;
- degree of root opening;
- depth of the vestibule of the mouth;
- presence of malocclusion.
The doctor necessarily sends the tissues for PCR analysis to identify the microbial flora (liquid from the periodontal pockets is examined by bacterial culture), conducts a Schiller-Pisarev test (applies a solution of iodine and potassium to the gums and, based on the degree of staining, determines the localization and depth of damage to the connective tissues), draws up a periodontogram – a table with data about each tooth.
Additionally, blood biochemistry, intraoral radiography or biopsy are prescribed. They help differentiate generalized periodontitis from gingivitis, periostitis, bone osteomyelitis, determine the boundaries of inflammation and understand how much the disease affects the general condition of the body.
Orthopantomogram for the diagnosis of generalized periodontitis
Causes of the disease
After eating food, pathogenic bacteria begin to actively multiply in the oral cavity. In the absence of proper care, soft plaque forms abundantly, which gradually turns into tartar. Decay products and toxins from microorganisms penetrate the gums, causing irritation and then inflammation.
Additional causes of periodontitis:
- anomalies in the structure of the dental system;
- weak general and local immunity;
- lack of microelements and vitamins;
- dry mouth due to general diseases of the body or associated with damage to the salivary glands;
- pathologies of internal organs and systems;
- poor oral care.
If periodontitis affects bone tissue, then folk remedies will no longer help. Surgical intervention in the form of curettage of periodontal pockets is required.
Forecast and preventive measures
If treatment is started in the early stages of the pathology, this leads to remission and the possibility of its extension. In restoration measures and in the process of preserving tissue functions, compliance with recommendations related to the implementation of preventive measures plays an important role. If the disease is advanced, the prognosis is unfavorable. This may be due not only to the loss of almost all teeth, but also to the fact that severe systemic complications will begin to develop, especially in the cardiovascular system.
The preventive complex involves compliance with a number of care and hygiene measures:
- timely brushing of teeth;
- a competent choice of cleaning products and tools - toothpastes, powders, brushes, threads;
- regular implementation of professional hygiene;
- timely treatment of emerging diseases;
- removal of deposits from the teeth;
- carrying out treatment of concomitant pathologies.
With these simple measures you can prevent illness and feel great.
Thus, generalized periodontitis is a serious disease that tends to constantly develop and progress. In this regard, it is necessary to diagnose it in a timely manner and take therapeutic measures. This approach will prevent complications and keep all teeth normal, eliminating unpleasant symptoms and improving the patient’s well-being.
Laser gingivectomy in the area of one tooth
Treatment of generalized moderate and severe periodontitis
Open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets
Splinting teeth for periodontitis with fiberglass and tape
Catarrhal and hypertrophic gingivitis symptoms and treatment in adults
Laser gingivotomy - surgical treatment of complex forms of periodontitis
Types and stages of periodontitis
It is customary to distinguish several forms of periodontitis. First of all, the division goes along the flow:
- Acute periodontitis. It occurs more often due to mechanical effects on the gums and is easily treatable.
- Chronic periodontitis. The inflammatory process in the gums is formed due to the influence of microflora, is accompanied by a severe course and requires long-term treatment using traditional and folk methods.
The photo below shows periodontitis in the frontal area of the jaw. Another classification divides the disease according to the extent of gum damage:
- Localized. Gum inflammation occurs within one or more teeth;
- Generalized. The process involves periodontal tissue of the entire jaw or one side.
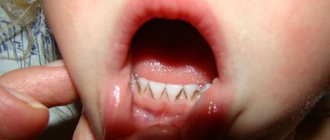
Generalized severe periodontitis
As periodontitis progresses, the degree of damage increases, which can be as follows:
- Easy. Bleeding gums appear, but there is no tooth mobility.
- Average. The formation of pockets no more than 0.5 mm deep is observed.
- Heavy. Tissue destruction is visible to the naked eye. The presence of plaque and tartar is determined.
Causes of periodontitis
The occurrence and development of periodontitis is associated with a whole complex of different causes, among which local and systemic (general) ones are distinguished.
Local reasons:
- insufficient or improper oral hygiene, which contributes to the growth of pathogenic microflora and injury to periodontal tissues, for example, with toothpicks, too hard a toothbrush and/or inept movements when brushing teeth; excessive hygiene can also cause microflora imbalance and chronic generalized periodontitis;
- incorrect bite, too crowded, closely spaced teeth, increased work of the masticatory muscles, unsuccessful dentures;
- the presence of tartar and smoking increase the risk of occurrence and aggravate the course of periodontitis.
Systemic reasons:
- vitamin deficiency C, which causes scurvy - a subtype of periodontitis;
- accumulation of heavy metal salts in the body (especially Hg, Pb, Bi);
- diseases of the blood system (leukemia), immune system, gastrointestinal tract (ulcers, enteritis, colitis), vascular disorders, diabetes mellitus, etc., as there is a deterioration in the supply of nutrients to periodontal and alveolar tissues due to their poor absorption in Gastrointestinal tract, vascular dysfunction or deterioration of blood quality gives rise to degenerative processes and leads to periodontitis;
- endocrine (hormonal) disorders lead to pathological mobility of teeth with the formation of gum pockets, which are filled with purulent contents. In this case, x-rays reveal the destruction of interdental septa and resorption (resorption) of bone tissue of the I–II degree. In the photographs, the jaw bones are characterized by increased transparency, which indicates the development of osteoporosis.
Symptoms of periodontitis
The clinical picture of the disease is determined already at the initial stage. Bleeding gums is the first sign. This symptom indicates gingivitis. If left untreated, superficial gum inflammation will quickly develop into periodontitis. Other manifestations will be:
- swelling and redness of the gums;
- pain from hot, cold and sour foods;
- bad breath;
- foreign discharge from the gums;
- increase in plaque and stone volume.
The presence of any symptom requires prompt medical attention. A timely visit to the dentist will help to quickly cure periodontitis, even using traditional methods.
Classification of periodontitis
There are several stages of development of periodontal inflammation:
- initial;
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
Periodontitis can be cured in just a few weeks if you consult a doctor at the initial or mild stage of its development. Getting rid of severe stages of the disease takes longer and is more difficult. Recession (decrease in level) of the gums persists.
By duration
Based on the duration and nature of the course, the following forms of periodontal disease are distinguished:
- Spicy. The inflammatory process begins quickly and leads to sharp deformation of the tissues surrounding the tooth. Accompanied by pain, the appearance of abscesses, and bleeding gums. It is more common in children due to their increased activity, often leading to jaw injuries.
- Chronic. Gradual and persistent periodontal infection occurs, which greatly complicates therapy. Against the background of stress, weakened immunity, and secondary inflammatory diseases, periods of exacerbation of the pathology occur. Treatment inhibits the destruction of periodontal disease during the remission stage, but only temporarily, since it is difficult to get rid of chronic periodontitis forever.
By prevalence
Based on the prevalence of lesions, there are two types of periodontitis:
- Localized. Covers a small area - periodontal tissues near several teeth. The development of a localized form of pathology is often caused by injuries.
- Generalized. Extensive inflammation of the periodontal tissues around the teeth on one or both jaws. The cause of the development of the disease may be associated with trauma or infection of the periodontium.
Treatment of periodontitis at home
Today, pharmacological companies offer consumers a large selection of ready-made drugs for the treatment of periodontitis. But even with such an assortment, you should not make your own appointment. Only a dentist can select the right medications after a thorough examination of the oral cavity.
A remedy for periodontitis, first of all, must be safe and highly effective so as not to delay treatment. For this, it is recommended to use special gels and ointments:
- Metrogil Denta. Gum applications are carried out for 2 weeks. The gel contains Chlorhexidine as a strong antiseptic and Metronidazole as an antimicrobial agent.
- Levomekol. The antibiotic Chloramphenicol destroys most of the harmful microbes that are so abundant in periodontitis. The second active component is Methyluracil. Provides acceleration of gum tissue regeneration. The ointment is applied 2 times a day until the symptoms of periodontitis disappear.
- Parodium. The course of treatment is about 3 weeks. Apply to affected gums 3 times a day, preferably after meals, after brushing your teeth or rinsing your mouth. It has a hemostatic effect and ensures periodontal regeneration. The gel contains Chlorhexidine, rhubarb root extract and formaldehyde. The drug is prescribed for all forms of periodontitis.
- Ortofen ointment. The concentration of the active substance is 2%, but this is enough for the desired effect. The ointment is applied to a gauze strip and applied to the problem area on the gum. The therapeutic course is 10 days, 2 applications per day.
- Chlorophyllipt. Provides complete destruction of all pathogenic microbes. Used as a rinse, 1% solution. Sometimes the drug is considered as an alternative treatment for periodontitis.
- Miramistin. The drug is active not only against bacteria, but also against fungi. The therapeutic effect is achieved even when the wound is suppurated. Treatment is carried out several times a day until severe symptoms subside.
Drug therapy
The tactics of drug treatment of periodontitis provides for an individual approach to the patient, taking into account the severity of the inflammatory process and the patient’s dental status.
If the infection in the oral cavity worsens and the pain increases, antibacterial drugs are prescribed. Antibiotics that have an effect on periodontitis pathogens include:
- "Tsiprolet";
- "Ecositrin";
- "Lincomycin";
- "Amoxicillin";
- "Wilprafen".
The dosage and duration of the course are prescribed by the attending physician. To maintain normal microflora of the oral cavity and intestines, probiotics are recommended for use: Lactobacterin, Acipol or Linex.
In patients with periodontitis, local and general immunity is reduced. To restore the body's protective factors, immunostimulants are used: Cycloferon, Isoprinosine and Polyoxidonium.
Ointments and gels
Dental topical agents have pronounced activity due to the ability to quickly be absorbed into the mucous membrane and destroy pathogens. Ointments and gels should not only eliminate the cause of inflammation, but also enhance tissue regeneration. The most popular drugs for the treatment of gum periodontitis are:
- "Periodonticide";
- "Metrogil denta";
- "Holisal";
- "Asepta";
- "Solcoseryl";
- "Kamistad".
Since many products contain lidocoine, before using the gels you should consult a doctor and rule out the possibility of allergic reactions.
Rinse aids
Mouth rinses have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. Solutions relieve unpleasant symptoms of the disease, cleanse plaque from enamel and freshen breath. Examples of therapeutic and prophylactic rinses for inflammatory gum diseases include:
- "Forest balm Limited edition";
- "Lacalut active";
- "Splat medicinal herbs";
- "Parodontax";
- "Mexidol dent".
In addition to ready-made medicinal solutions, herbal infusions are used as rinses. Chamomile, oak bark, calendula and sage reduce inflammation, destroy pathogenic microflora and promote rapid wound healing. It is recommended to do the procedures at least 3 times a day after brushing your teeth.
Vitamins
It will be much easier to cure periodontitis if you treat it not only locally and with traditional methods. Therefore, during the therapeutic course, taking vitamin complexes is mandatory.
To accelerate epithelization and strengthen local immunity, vitamins A and E are used in the form of applications. “Aekol” is used for this purpose. Clean gauze with a small amount of the drug is applied to the affected area of the gum for 1–2 minutes. Applications should be carried out 2 times a day after brushing your teeth.
To normalize metabolic processes and strengthen the body's overall resistance to infectious agents, vitamin C is prescribed in combination with rutin (vitamin P). Treatment is carried out in tablet form or by injection.
To prevent repeated exacerbations of periodontitis and improve overall health, it is recommended to take multivitamins 3 times a year. In addition, it is worth visiting a dentist for preventive examinations and treatment of concomitant oral diseases.
Oral hygiene
Good oral hygiene is the key to healthy teeth and gums. Since during periodontitis a large amount of pigmented plaque and tartar accumulate on the crowns, the dentist carries out professional oral hygiene. During the procedure, factors that provoke gum inflammation are removed, the enamel is polished with special brushes and pastes, and then strengthened with fluoride-containing agents.
It is very important to monitor your oral health at home. For periodontitis, the dentist selects individual products and personal hygiene items.
Rules for caring for the oral cavity during periodontitis include:
- Brushing your teeth 2 times a day with therapeutic and prophylactic toothpastes and soft brushes.
- Using dental floss to clean between teeth.
- Using an irrigator filled with antibacterial solutions and herbal infusions (chamomile, oak bark).
- Rinsing the mouth with rinses to treat gums (every time after meals).
- Massage the gums with your thumb and forefinger in a circular motion (while brushing your teeth).
Diet for periodontitis
During treatment of periodontitis, it is recommended to add fresh fruits and vegetables to the diet: apples, pears, cucumbers and carrots. To treat vitamin deficiency, the following are consumed: bell peppers, berries, citrus fruits, herbs and nuts. To strengthen the enamel, it is recommended to consume foods rich in calcium: milk, kefir, cheese, cottage cheese, broccoli, beans and dried apricots.
To prevent irritation of the mucous membrane of the gums, it is necessary to avoid fried, highly salted and spicy foods. Hot drinks also worsen the disease.
Alternative medicine recipes
The following recipes cannot be used as the primary treatment for periodontal disease. They can only be used as part of combination therapy to increase the effectiveness of the methods used. If visible improvements do not appear within 3-5 days, you should stop home treatment and consult a doctor.
Beetroot pulp
This is one of the easiest and fastest ways to cope with periodontal inflammation at home. Beetroot pulp contains natural anti-inflammatory and antibacterial substances and helps improve the patient's condition after 1-2 days of use.
Beetroot pulp contains natural anti-inflammatory and antibacterial substances
To get beet pulp, you need:
- Wash and peel medium beets;
- pass it through a meat grinder or grind it in a blender;
- Squeeze the resulting mass through cheesecloth (put the juice in the refrigerator).
What remains in the gauze after squeezing the juice is beet pulp. It is used for medicinal compresses: wrap a small amount of cake in gauze and apply to the inflamed gum for 12-15 minutes. The procedure needs to be carried out 3-4 times a day. Duration of therapy is two weeks.
Advice! The treatment will be more effective if, after removing the compress, you rinse your mouth with beetroot juice. Before use, you need to keep it at room temperature for a while.
Saffron lotions
Saffron is the stigma of the purple crocus, which in dried form is widely used in cooking and folk medicine. You can buy saffron at a pharmacy, and residents of Dagestan, Crimea or Azerbaijan can also use freshly harvested raw materials. The plant grows only in countries with a warm, sunny climate and normal humidity, so wild saffron is almost never found in Russia.
Saffron lotions are an effective remedy in the treatment of periodontitis.
To cure periodontitis with saffron, you must:
- mix a teaspoon of chopped saffron with a small amount of any vegetable oil (about a third of a spoon);
- Wrap a little mixture in gauze and apply to the site of inflammation for 15-20 minutes.
Such lotions should be done 2-3 times a day. The last procedure is recommended to be carried out after evening brushing. Seven days of daily treatment is usually enough to completely get rid of the problem.
Symptoms of periodontitis
Video: Folk remedy for periodontitis
Effective treatment of periodontitis with folk remedies
Treatment of gums for periodontitis with folk remedies is justified in the initial stages of the disease. It can be used in combination with traditional therapy for severe forms of the disease and as preventive measures.
They mainly use decoctions and infusions of medicinal herbs, extracts and freshly squeezed juice. All products are effective as rinses for periodontitis, oral baths or lotions.
Hydrogen peroxide and soda
Treatment of periodontitis with hydrogen peroxide and soda is the most popular method of traditional medicine. In the initial stages of periodontitis, the impact of these ingredients is great.
Hydrogen peroxide has antistatic activity. Therefore, after treating the problem area, up to 90% of bacteria die.
Attention!!! When hydrogen peroxide comes into contact with biological fluids, a specific chemical reaction occurs. As a result, water and oxygen are released. They actively saturate periodontal tissues, which has a stimulating effect and prevents suppuration of wounds.
Hydrogen peroxide as a folk remedy for the treatment of periodontitis is used in three ways:
- Wiping. A sterile cotton swab or ball is moistened in a 3% antiseptic solution and wiped on the inside and outside of the gums. After treatment, bleeding is reduced and the pain reaction is reduced. Rubbing is recommended 2-3 times a day.
- Rinsing. To prepare the solution, two tablets of hydroperite are required. 100 ml of boiled warm water is dissolved in them. Rinse with a solution at room temperature every 5–7 hours. If you have gum inflammation, you should not rinse your mouth for a long time with peroxide, as this will negatively affect the enamel.
- Cleansing. In this case, hydrogen peroxide is applied directly to the toothbrush. For brushing your teeth, it is better to choose medicinal pastes with an anti-inflammatory hemostatic effect. It is enough to apply 2-3 drops of solution to the bristles and thoroughly clean not only the surface of the teeth, but also carefully treat the gums. The manipulation should be done after breakfast and dinner before bedtime, until the symptoms of periodontitis subside.
Soda also has a pronounced antiseptic effect. This component is used as a folk method in combination with other substances. It is recommended to make a medicinal paste consisting of 0.5 teaspoon of soda, 20 drops of 3% hydrogen peroxide and 10 drops of fresh lemon juice. Use the resulting mixture to clean teeth and gums as with daily hygiene care.
Oak bark decoction
Oak bark will help get rid of periodontitis. A decoction is prepared from it, to which linden flowers are added. The combination of ingredients should be 2:1.
Brew a tablespoon of the mixture with a glass of boiling water and leave to brew for 15–20 minutes. After this, the broth is filtered and while warm, frequent rinsing or oral baths for the gums are carried out.
30 minutes after the procedure, rinse your mouth with running water. Eating is allowed one hour after the end of treatment.
Attention!!! Oak bark is a hypoallergenic product. It can be used by all categories of patients for the treatment of periodontitis and other dental diseases. If you experience any discomfort, you should abandon the technique and replace it with another remedy.
Treatment of periodontitis with salt
No less effective is rinsing the gums with a saturated saline solution for periodontitis. This is an affordable folk remedy to combat inflammation of the oral cavity. Table salt contains about 20 useful minerals. It helps not only to treat periodontitis, but also to strengthen the enamel and even the bone tissue of the alveolar process. The positive effect of alternative treatment also lies in the ability to draw out purulent exudate and drain pathological fluid released during periodontitis.
The product is used in three ways:
- rinsing with a saturated solution (1 tablespoon per glass of warm water);
- application of a mixture of salt and vegetable oil;
- oral baths on the affected area.
Honey and propolis
Beekeeping products differ from other folk remedies in that they not only have a pronounced therapeutic effect, but also contain a large amount of useful substances. When treating periodontitis, it is enough to chew bee glue or propolis several times during the day. Penetrating into the interdental spaces and pockets, it lingers there, having a positive effect on the gums.
Propolis tincture
An alcohol tincture of a folk remedy also helps fight periodontitis. You will need 50 g of propolis and 500 ml of vodka. Mix the ingredients in a glass container with a closing lid and shake thoroughly. Leave the mixture in a dark place for 2 weeks. Every day the container must be shaken without opening the lid. The result is a brown liquid, which is used to treat sore gums. A cotton swab soaked in alcohol tincture of propolis is placed in the periodontal pocket.
Medicines are often prepared from honey or used in pure form for applications. The sweet product is dissolved in decoctions of medicinal herbs for lotions and oral baths for periodontitis.
Fir oil
Essential oils are very popular in folk medicine. The most effective oils in the treatment of periodontitis are sea buckthorn and fir. They are often used together for a pronounced therapeutic result.
The oil is used for applications on sore gums. They also perform a finger massage with him. For periodontitis, each side of the jaw is treated for 10 minutes every day.
Rose petals
This folk remedy is little known. Although the following microelements were found in rose petals:
- zinc;
- manganese;
- molybdenum;
- phosphorus;
- chromium;
- B vitamins.
Folk tincture is prepared with alcohol. Place the petals tightly in a half-liter jar, fill with liquid and compact. Leave for about 10 days. To rinse teeth and gums during periodontal inflammation, you need to prepare a solution. Dilute 30 drops of tincture in 100 ml of water. Carry out the procedure up to 3 times a day.
Garlic
Another popular way to treat periodontitis is garlic. To prepare the tincture, you need 1 spoon of crushed product and the same amount of black tea. Pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture and leave for 20 minutes.
Strain the resulting tincture and rinse the gums after hygiene care for 10 minutes, up to 3 times a day. The procedure is carried out for at least 1 week. The product is recommended for use in adults, as during rinsing it will cause discomfort in the form of a burning sensation.
Beetroot pulp
How to treat periodontitis at home quickly and easily? Beetroot pulp is suitable for this. This folk remedy contains antibacterial and anti-inflammatory substances. A positive effect is observed within 3 days after using the cake.
To prepare the product, rinse, peel and chop medium-sized beets in a vegetable cutter. Squeeze the resulting mixture and place the juice in a cool place. Place the cake in a small amount in a single layer of gauze. Beetroot is applied to the sore gum 4 times a day and left for up to 15 minutes. The remaining juice can be used as a mouthwash.
Saffron lotions
Purple crocus or saffron helps eliminate signs of periodontitis and gum disease. Mix 1 teaspoon with a little olive oil. Place the mixture in gauze and apply to inflamed gums up to 3 times a day, for 20 minutes. After a week, periodontitis practically disappears.
The most effective ointments for periodontitis
Ointments, which are recommended by traditional healers for the treatment of periodontitis, can quickly relieve the inflammatory process, strengthen the gums and relieve pain. In addition, thanks to these remedies, you can remove bad breath.
Oils based on fir and sea buckthorn
Take fir and sea buckthorn oils in equal quantities. Mix them. Wrap gauze or bandage around your index finger. Dip it into the mixture and gently massage your gums. The duration of the procedure is 2-3 minutes. Frequency – 2 times a day.
Fir oil
Important! Instead of sea buckthorn oil, it is also useful to use peach oil. In addition, many healers recommend mixing fir oil and fish oil in equal quantities.
Banana peel and sea salt
The peel of a ripe banana is crushed using a blender and mixed with three teaspoons of sea salt. Add 1 tbsp to the mixture. l. any vegetable oil without flavorings. The ointment is rubbed into the gums for 2 minutes. Therapeutic manipulation is carried out 2 times a day.
Important! You can massage your gums with a clove of garlic. In addition, it is recommended to chew sauerkraut daily. These simple manipulations will relieve pain, strengthen the gums, and relieve inflammation.
Banana peel and sea salt
Honey and salt
A mixture of salt and honey is considered a good preventive and therapeutic remedy. To prepare it, you can take any liquid natural honey.
So, mix 2 tbsp. l. honey and 2 tsp. (without a slide) salt. Rub the mixture in for 2-3 minutes.
Honey and salt
Important! It is very useful to rub olive oil into the gums, and then rinse your mouth with a decoction based on chamomile or lemon balm.
Aloe vera
This plant cures many diseases - it:
- disinfects;
- soothes the inflamed area;
- heals tissue.
If you have periodontitis, you should rub aloe vera gel on your gums and teeth. The procedure is carried out 2 times a day. Tissues regenerate very quickly.
Aloe vera
Important! Don't forget to rinse your mouth with water after the procedure.
Turmeric, Indian melia
This remedy disinfects and eliminates inflammation, reduces pain, stops bleeding gums, and strengthens their tissue. It should be gently rubbed into the gums three times a day.
Take:
- turmeric powder;
- Indian melia leaves (powder);
- salt.
All products are taken in equal quantities and mixed thoroughly. The medicine is stored in a glass jar in a dark place. Use your finger to scoop a small amount of powder and gently rub it into your gums.
Turmeric
Burnt alum
Alum gets rid of plaque and even the oldest tartar. In addition, this miraculous powder can destroy bacteria, restore oral microflora and prevent the development of gum disease.
For treatment 1 tsp. alum should be mixed with ¼ tsp. iodized salt. 1 drop of mustard oil is also added to the mixture. The product is gently rubbed into the gums and teeth. The procedure is carried out after eating food. The manipulation is carried out for at least 5 minutes.
Burnt alum
Reasons for development
The main factor that causes periodontitis is considered to be tartar, which is the result of excessive accumulation of plaque. In some cases, the disease can be triggered by inflammatory processes in the body or serious pathologies in the performance of important systems. Rarely, periodontitis is inherited (it is not possible to avoid the disease even if you follow the rules of oral hygiene and regular visits to the dentist).
The following factors can cause the development of periodontitis:
- diabetes;
- excessive smoking;
- decreased saliva production;
- congenital or acquired malocclusion;
- deficiency of vitamins in the body;
- lack of complete self-cleaning of teeth;
- lack of calcium in the body;
- lack of oral hygiene;
- hormonal imbalances;
- side effects of certain medications;
- lack of timely treatment of dental diseases.
Periodontitis: treatment
For periodontitis, treatment begins immediately after the first symptoms of the disease appear. If this is not done, the disease will progress quickly and may ultimately lead to tooth loss.
Currently, acute periodontitis can be treated with both medications and surgery. In case of minor inflammation, the physician thoroughly cleans the teeth, polishes their surface and applies a therapeutic bandage to the affected area. Antibiotics for periodontitis are prescribed when inflammation is accompanied by severe pain.
General treatment of periodontitis involves the use of various types of stimulants that promote tissue regeneration. Very often this procedure is accompanied by the use of special means. Such drugs have an analgesic and antimicrobial effect.
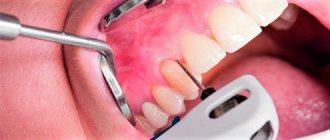
Surgical treatment of the disease is carried out in the later stages of its development, when deep periodontal pockets and severe tooth mobility are diagnosed. Doctors may perform the following surgical procedures:
- Curettage.
During this procedure, dental plaque is removed from under the gums using a curette or sclera. Curettage is always performed using anesthesia. If the periodontal pocket does not exceed 4 mm, then doctors perform closed curettage. In this case, there is no need to open the gums.
- Flap operations for periodontitis are often used.
In this case, doctors make a small incision on the gum (no more than 1.5 mm). After this, the deposits are removed and the remaining strip of tissue is further removed.
- Gingivectomy. Using this procedure, it is possible to reduce the size of the overgrown gingival papilla and clean out the gingival pocket.
Also, for periodontitis, splinting is also implied, i.e. strengthening loose teeth.
Many people are concerned about the question: “How to treat periodontitis with a laser?” It should be noted that this procedure is currently very popular. The thing is that the laser has antibacterial and cleansing properties. During the procedure, doctors use a laser to clean each periodontal pocket. Processing each pocket takes several minutes. Laser treatment is painless and virtually bloodless.
As mentioned above, if treatment for periodontitis is not started on time, the risk of tooth loss increases. In this case, doctors perform implantation. Implantation does not mean the treatment of periodontitis itself, but the elimination of its consequences. Before installing implants, doctors try to eliminate the main cause of the disease.