The effect of sweets on teeth
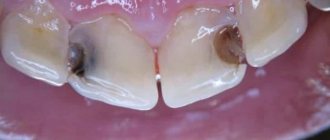
Cookies, candies, chocolate and other confectionery products contain large amounts of carbohydrates - in particular sucrose (sugar). Under the action of salivary enzymes, sucrose is converted into glucose, which immediately begins to oxidize. The process of glucose oxidation is a fermentation reaction, the determining role in which is played by microorganisms (bacteria) that live in the oral cavity. As a result of fermentation, organic acids are formed - lactic, butyric, formic, propionic, etc. The aggressive action of acids leads to the destruction of tooth enamel - it becomes loose and sensitive.
Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body. It is what protects our teeth from negative influences, irritants and diseases. Healthy enamel makes your teeth look attractive and shiny. The protective and aesthetic properties of enamel are due to the high level of mineralization. It mainly consists of hydroxyapatite, which contains calcium, as well as fluorine, magnesium and carbon. But the problem is that hydroxyapatite crystals are very susceptible to the aggressive effects of acids that are formed as a result of the oxidation of sucrose and fermentation of glucose. As acid levels in the mouth increase, the crystals break down and the enamel weakens.
To protect teeth from the negative influence of external and internal environmental factors, enamel covers their crowns completely. On the chewing apexes, the enamel layer reaches 2.3 - 3.5 mm, on the lateral surfaces it reaches 1.0 - 1.3 mm and completely thins out at the neck of the tooth - the place at the level of the gum edge where the crown meets the root. The crown of the tooth itself consists of dentin, inside of which there is a pulp, penetrated by a large number of small vessels and nerve endings. It is fibrous, loose and characterized by high pain sensitivity to external stimuli. The pulp provides trophism to the tooth tissue and is responsible for transmitting sensory information about its condition to the central nervous system. In case of damage to the enamel of the crown, cervical tissue or root, external irritants through the dentinal tubules affect the pulp, and we feel severe pain. This is a kind of signal indicating that there is something wrong with your teeth and it’s time to see a dentist.
Diseases of internal organs
Since the body is a single system in which all organs are interconnected, diseases of the internal organs affect the condition of the teeth and gums.
Teeth may break due to:
- gastrointestinal problems;
- nervous overexcitation, stress;
- frequent colds, ARVI;
- hormonal imbalance;
- angina pectoris;
- arthritis.
Gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract has a particularly strong effect on the condition of enamel and teeth. However, even with a healthy gastrointestinal tract, problems with teeth can also arise if the nervous system fails. With severe stress, the dental nerves through which nutrition enters the denta are damaged. Lack of adequate nutrition leads to serious dental problems, including the loss of an entire row of teeth.
Stress
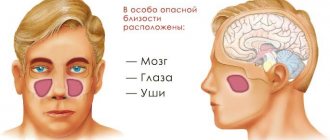
Due to stress and hypothermia of the body, the facial nerve can often become inflamed, which also has a negative effect on the dental nerves. Due to facial nerve pain, the teeth also suffer because they are located in close proximity to each other.
Note! In neurotic conditions, teeth may cramp during sleep.
ARVI
Laryngitis and sinusitis have a negative impact on the condition of the gums and teeth. With flu and sore throat, the infection can penetrate the dental nerves. Inflammation of the maxillary sinuses or tonsils causes a negative response in the dentofacial system. Conversely, problems with teeth and gums negatively affect the condition of the nasopharynx.
Hormonal disbalance
How can hormonal imbalance in the body affect dental health? Tooth pain is typical during the first months of pregnancy, as well as during menopause. The most unpleasant thing is that after such pain, teeth can be destroyed. Pregnant women need to have a temporary filling placed immediately and a permanent one installed after childbirth.
Note! Hormonal changes in the body also cause aching pain in the gums and teeth.
Angina pectoris
Angina attacks are also accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the dentofacial system, as well as drying out of the oral mucosa.
Also, the jaw can cramp for completely ordinary reasons not related to teeth and gums. Please note that this condition may occur when:
- sitting at a computer in an unventilated room for several hours in a row;
- regular migraine-type headaches;
- physical fatigue, lack of rest;
- increased nervous excitability;
- injury to the upper spine or jaw bones.
In this situation, there is no need to use medications or make an appointment with a therapist. Quality rest, relaxing massage and absolute peace are required. If you have been sitting at the computer for a long time in an unventilated room, take a 30-40 minute walk in the fresh air.
Arthritis
Arthritis affects not only the joints of the hands and feet, it can appear in the temporomandibular region. With age, the temporomandibular joint is subject to deformation and wear, so it can no longer fully perform its natural functions. With arthritis, the patient always feels pain: during a conversation, when yawning, when eating, even when laughing and coughing. Pain does not manifest itself only in a state of complete rest of the joint, when the patient’s face remains motionless.
Why do sweets make your teeth hurt?
Teeth hurt due to destruction, damage or thinning of tooth enamel. It loses its protective properties, and irritants reach the pulp, which reacts painfully to them. Problems with enamel can be caused by sugar consumption or a number of other reasons. The most likely of them is caries.
CARIES –
a pathological process accompanied by destruction of hard dental tissues. The trigger for its development is several unfavorable factors.
- Plaque accumulation.
- Poor oral hygiene.
- Foods rich in carbohydrates - sucrose.
- Low level of enamel mineralization.
- The buffering properties of saliva do not neutralize acids.
Dental plaque is a kind of mixture of bacteria and their metabolic products. Due to poor hygiene, it gradually accumulates, and the microorganisms living in it accelerate the fermentation process. Abuse of sucrose reduces the buffer capacity of saliva - it is not able to neutralize the resulting acids. They destroy hydroxyapatite crystals and the enamel is gradually destroyed. The combination of these factors significantly accelerates the carious process. After damage to the enamel, it spreads to dentin, and if left untreated, leads to inflammation of the pulp and periodontium - the connective tissue surrounding the roots of the tooth. On the contrary, eliminating cariogenic factors and timely treatment can stop the growth of caries and save the tooth. And the sooner you contact a dentist, the greater the chances of success. Therefore, experts recommend not to ignore regular preventive examinations, which can detect caries at the chalk spot stage - a demineralized area of enamel that indicates a problem. After its elimination, remineralization of the enamel and subject to the dentist’s recommendations, caries recedes.
It is not too late to seek help at the stage of superficial caries, when teeth react painfully to cold and hot, sour and sweet tastes. In this case, increased sensitivity indicates significant demineralization of the enamel and the progression of the carious process, which gradually spreads deep into the hard tissues of the tooth. But you can get rid of it quickly, easily and without complications.
Today, dentists successfully treat caries of any stage. But the later the patient seeks help, the more difficult, longer and more expensive the treatment will be. However, it also happens that teeth hurt from sweets, but there is no caries. In this case, non-carious causes are considered, which also lead to enamel damage.
INCREASED TEETH WEAR –
a pathology of non-carious origin, which is characterized by intensive loss of hard tooth tissues. They are literally erased - first the enamel, and then the dentin, which is accompanied by painful sensations after eating sweets and other irritants - sour, salty, cold, hot. In this case, pathological abrasion can be due to a number of reasons.
- Inappropriate distribution of load on the dentition due to tooth loss.
- Bite pathologies.
- Bruxism is teeth grinding.
- Wearing an incorrectly fitted denture.
- Hypoplasia is a congenital defect of underdevelopment of hard dental tissues.
- Fluorosis is damage to the enamel due to consumption of food and water with a high fluoride content.
- Harmful environmental or working conditions.
These reasons lead to pathological abrasion of teeth and serious damage to the enamel.
WEDGE DEFECT –
a pathology of non-carious origin, which is characterized by the formation of enamel defects in the area of the tooth neck.
Specific “steps” (depressions) resembling a wedge are formed on the surface of the enamel. Their appearance may be due to poor oral hygiene, plaque accumulation on the neck of the tooth, or inflammation of the periodontal tissues - the tissues surrounding the tooth that hold it in the alveolus. The formation of a wedge-shaped defect thins the tooth enamel. Its depth can reach dentin, which facilitates the penetration of the irritant to the pulp.
HYPOPLASIA –
underdevelopment of hard dental tissues or the entire tooth as a whole. The pathology develops as a result of disturbances in the metabolic process in the tissues of the tooth buds, which leads to abnormal formation of enamel and dentin. Often, hypoplasia is formed during the period of intrauterine development. The appearance of disorders can be provoked by a Rh conflict between the baby and mother, or diseases the woman suffered during pregnancy - toxoplasmosis, rubella, etc. The impetus for the appearance of hypoplasia of permanent teeth can be infectious diseases suffered at an early age, brain disorders, gastrointestinal diseases, rickets or dystrophy. Regardless of the causes, hypoplasia involves a partial or complete absence of enamel, and sometimes underdevelopment of dentin, which poses a threat to the pulp and tooth as a whole.
EROSION OF TOOTH ENAMEL –
non-carious lesions of hard tissues. Erosion is characterized by the appearance of small defects or stains on the enamel, which appear under the influence of a combination of internal and external environmental factors. The exact cause of the pathology has not yet been established by specialists. As a trigger for its development, they tend to consider mechanical effects on the enamel during oral hygiene, as well as abuse of foods high in acids. Erosion may not be noticeable externally, but it involves thinning and damage to the enamel, which makes it easier for irritants to penetrate the dental pulp.
NECROSIS OF HARD TISSUE OF THE TOOTH –
necrosis and destruction of enamel and dentin. The death of hard dental tissues can be caused by intoxication of the body, hormonal disorders, diseases of the central nervous system, exposure to acids, alkalis, radiation therapy and a number of other negative factors. If the enamel is weakened, then it cannot withstand their effects, which leads to pain and destruction of the hard tissues of the tooth.
MECHANICAL DAMAGE TO ENAMEL –
various chips and cracks facilitate the penetration of irritants through dentin to the pulp, and it responds with pain. Mechanical damage can occur under the influence of a number of external factors.
- Tooth injuries from impact or fall.
- Eating solid foods – nuts, seeds.
- Bad habits, for example, opening a bottle with a cork with your teeth.
- Improper oral hygiene - using a brush with excessively hard bristles, using abrasive products to remove plaque, increased pressure on the enamel while brushing your teeth.
To a greater extent, they are affected by weakened enamel, covered with dental plaque, plaque, and deficient in calcium and fluoride.
Description of the disease
Aches in the gums and teeth appear closer to night, when dental clinics are closed. There are dentists on duty, but they help with severe toothache or acute inflammation in the gums. When the jaw aches, this process occurs with completely healthy teeth and gums.
Common causes of pain:
- drinks too cold/hot;
- walking in cold weather;
- sweet/sour food;
- mechanical damage.
The body's reaction to irritants is different for everyone. Some people's teeth react to cold, others to sweet/sour. In others, they are hypersensitive to mechanical influences: the touch of a toothbrush, a visit to the dentist. There are patients who experience prolonged pain after dental treatment.
A reaction to cold can occur even with absolutely healthy teeth: a person’s cheekbones cramp or their teeth ache very much. This is a very unpleasant feeling that is impossible to get used to.
Note! Sensitivity of teeth to increases or decreases in food temperature indicates a thinning of the enamel layer.
Thinning enamel is an alarming symptom that leads to dental problems. After a reaction to cold or heat, a reaction to sour/sweet will follow, and your teeth will cramp after eating.
Aches in the gums and teeth can be caused by many reasons:
- hormonal changes;
- diseases of internal organs;
- periodic stressful circumstances;
- incorrect bite;
- heredity.
Dental problems can also cause pain:
- exposure of the neck of the tooth;
- gum problems;
- cracks in enamel;
- thinning of the enamel coating;
- deletion;
- bleaching.
Where is the pain located? They can be isolated or generalized (the entire lower jaw hurts). Pain in a single molar is always caused by either caries or a tissue reaction to the implant. But generalized pain, covering the entire jaw or all teeth, is a symptom of more serious diseases than caries.
What to do if your teeth hurt from sweets, hot and cold?
It is important to understand that pain is a signal indicating damage to the hard tissues of the tooth and the development of a pathological process. She cannot be ignored! You should not avoid pain by taking medications or limiting your intake of sweet, hot, cold or sour foods. It is necessary to identify and eliminate the cause of the pain - seek help from a dentist and undergo adequate treatment.
Tooth hurts from eating sweets after filling
Pain after filling is not uncommon. After all, the procedure involves preparation (removal) of a damaged area of enamel, which involves a mechanical effect on the hard tissues of the tooth. To ensure that the installed filling holds better, specialists etch the area to be filled with acids that improve the adhesive properties of the enamel. The combination of mechanical and chemical effects can cause weakening of the enamel and a decrease in its protective characteristics.
Ideally, the treated tooth should not hurt or bother you after filling. The filling reliably protects its internal tissues from the influence of irritants and infection. But if the procedure protocol was violated, low-quality material was used for filling, or the dentist made another mistake, then the appearance of pain is a signal indicating the existence of a problem. In this case, a repeat visit to the clinic cannot be avoided.
Don't be afraid of re-treatment. Most likely, remineralization therapy or fluoridation will be carried out, which will strengthen the tooth enamel. If a gross mistake was made during the placement of the filling, then repeated treatment and filling of the tooth will be required.
What to do if your teeth start to hurt from eating sweets?
If, after eating sweets, your teeth are cramping from pain, then it is necessary to determine the cause of the discomfort as quickly as possible. But the problem is that doing this yourself is not always possible. As a rule, the initial stage of caries, increased tooth wear, erosion or minor mechanical damage to the enamel is extremely difficult to detect using a visual examination at home. Not to mention the fact that it will not be possible to eliminate these invisible and visible causes using available means. They need to be treated, which means you need to seek help from a dentist.
15% discount on emergency care for acute pain!
Moscow
Solutions to the problem
If a reaction to sweets often occurs, qualified treatment is necessary. Its type depends on the reason:
- In case of caries, it is necessary to remove the affected tissue, seal the cavity and restore the coronal part with a filling.
- If hyperesthesia or microcracks are a factor, procedures are carried out aimed at strengthening the enamel: fluoridation, remineralization, fluoride varnish coating, and physiotherapy.
- To eliminate the consequences of incorrect treatment, you need to visit the dentist again.
- In each case, gels, pastes and rinses are additionally prescribed to reduce sensitivity.
Only a doctor can determine the cause of the teeth’s reaction to sweets.
Important! It is impossible to independently determine the cause of a reaction to sweets. Only a specialist can determine what exactly caused the problem and prescribe the correct treatment.
The reaction of teeth to sweets is just a symptom of one of the diseases of the enamel or gums. As a preventive measure, general hygiene recommendations are used: clean and rinse the mouth after each meal, replace confectionery products with fruits, undergo regular dental checkups and promptly eliminate emerging problems.
Treatment in dentistry
After diagnosing the condition of the oral cavity and studying the patient’s medical history, the dentist will determine the exact cause of the pain. Depending on the diagnosis, conservative therapy or surgical intervention will be prescribed. In modern dentistry, the following methods for eliminating pain after sweets have proven themselves well.
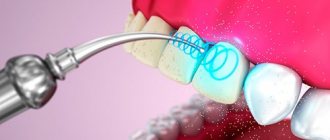
- Fluoridation of enamel.
- Remineralizing therapy.
- Sealing of fissures.
- Correction of bite pathologies.
- Preparation of damaged tissues and placement of fillings.
- Installation of crowns, veneers, lumineers.
- Dental implantation.
Treatment at home
The specificity of pain from sweets is that you can get rid of it at home only if it is caused by weakening of the enamel. For example, the patient ate an unbalanced diet for some time or suffered from a disease that reduced the level of mineralization of the enamel, which led to its thinning and pain. In this case, it is possible to locally use various drugs, the composition and action of which will help restore the level of mineralization and protective properties of the enamel.
- Varnish "Bifluoride 12".
- "Fluorovarnish".
- Cream "MI Paste Plus".
- Gel "Fluocal".
- Gel "Tooth Mousse".
These drugs are available in pharmacies without a prescription, are used according to the manufacturer's instructions and have a number of contraindications. In order to determine the appropriateness of their use and choose the right drug, you need to consult a dentist. Therefore, it is still impossible to avoid visiting the clinic.
If there are no serious dental problems that lead to pain, you can resort to a less effective home method - using a special toothpaste.
- "Oral-B Sensitive Original".
- Sensodyne-F.
- "MEXIDOL dent sensitive".
- "Rembrandt Sensitive".
Toothpastes should be used 2 times a day - morning and evening. If the problem with the enamel is trivial, then they can really help. But you shouldn’t expect a “super effect” from them, since manufacturers’ claims that hygiene products are capable of sealing microholes in dentin are greatly exaggerated. The active component capable of penetrating a hole 1-4 microns wide and sealing it is not yet known to science.
As for traditional medicine, in this case there is no significant benefit from them. The exception is propolis and fresh, unpasteurized milk - the products are rich in microelements beneficial for enamel. To absorb them, you can apply lotions to problem teeth. To do this, moisten a piece of cotton wool (bandage, cotton pad) in warm milk or propolis solution and apply to the enamel for 30 - 60 minutes. Lotions can be replaced by regular rinsing of the mouth with warm milk and propolis solution.
The rest of the “potions” of traditional medicine do not in any way affect the level of mineralization of the enamel, do not restore its protective functions and are only suitable for relieving symptoms, for example, if the gums hurt or the teeth ache unpleasantly. In this case, you can use decoctions of calendula, sage or oak bark to rinse the mouth.
Prevention
Is it possible to avoid problems with gums and jaw? If there is no genetic predisposition to thinning enamel, the pathology can be prevented. Doctors recommend paying attention to good nutrition and eating foods high in vitamin A. It is especially beneficial for the health of gums and teeth. This vitamin is found in yellow/orange/red foods:
- citrus;
- egg yolk;
- carrot;
- liver.
However, citrus fruits are not always useful for problems with enamel and teeth, so it is better to replace them with carrots, pumpkin or liver. In summer you should eat fresh apricots; in winter they can be replaced with dried ones.
In addition to vitamin A, calcium is necessary for healthy teeth and enamel. This microelement is found in large quantities in hard cheeses and fish. There is a lot of calcium in dairy products, cabbage (fresh, pickled), and leafy greens.
Fluoride is found in seaweed, seafood and nuts. A small amount of fluoride is found in freshwater fish, so to compensate for the deficiency of this microelement, it is better to consume seafood.
It is necessary to exclude from the diet:
- carbonated drinks;
- sour fruits, juices;
- chocolate candies.
You can’t chew seeds in their skins; it’s better to buy already peeled ones. The hard skin of the seeds damages weak enamel, forming cracks and chips on it.
Note! If your jaw constantly cramps, you should exclude solid foods from your diet.
To avoid damaging the thin enamel of your teeth, it is recommended to use a soft toothbrush and toothpaste for sensitive teeth.
If your gums are constantly bleeding, they should be strengthened with massage. To do this, use a brush with the softest bristles or massage using a soft cloth wrapped around the index finger. Movements should be light and circular. Do not press hard on the gums, as this may cause bleeding. If the problem of bleeding gums is acute, you need to massage with sea buckthorn oil. There will be a double effect: massage and healing. In addition to sea buckthorn oil, you can use special gels for bleeding gums.
What complications may arise?
If your teeth hurt from sweets, then at a minimum, we are talking about the II degree of hyperesthesia - increased sensitivity of the hard tissues of the tooth to chemical and temperature irritants. Without treatment, it will go into the third degree of hyperesthesia, in which the tissues will begin to react to all irritants without exception - it will be painful to chew, brush your teeth, speak, and even breathe in cold air through your mouth. Not to mention that the cause of the pain will progress and ultimately lead to necrosis of hard tissues and tooth loss.