Causes of tooth sensitivity
Gum recession and enamel wear are the main causes of tooth hypersensitivity. As soon as the soft periodontal tissues begin to decrease in volume, areas unprotected from irritants are exposed. Unpleasant sensations appear when excessive pressure is applied while eating or performing oral hygiene measures.
Increased sensitivity can be acute, sharp, but passing after eliminating the causative factor. Such manifestations disrupt the normal way of life. But this is only the beginning of hyperesthesia. When a severe form of hypersensitivity develops, the pain slows down for a long time, even in the absence of an irritant.
Dental hyperesthesia according to ICD 10 has its code K03.8. and in the International Classification, increased sensitivity of enamel is considered as a separate pathology.
Systemic reasons
This is a group of negative factors of increased sensitivity of enamel caused by general changes in the body. These include:
- Viruses and infectious diseases. Pathologies associated with this cause disrupt the functioning of all organs and systems. By acting on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, irritation of the nerve endings occurs, which causes an increased reaction to irritants and even pain. Children often suffer from colds and unpleasant sensations may appear in the milk bite.
- Diseases of the digestive system. Completely related to changes in the oral cavity. First of all, there is a violation of the composition of saliva and a change in microflora. Low pH of the oral fluid leads to increased leaching of beneficial substances from the enamel. Accordingly, resistance to stimuli is impaired.
- Neuropsychiatric diseases. Helps reduce immunological status.
- Pregnancy. Increased sensitivity of tooth enamel during this period is not uncommon. Hyperesthesia is formed due to changes in hormonal levels.
- Lack of minerals. Substances such as phosphorus, calcium, magnesium and some others prevent the development of increased sensitivity of teeth. Their lack is often associated with dietary habits. Increased tooth sensitivity is the first signal of a lack of these substances.
Local reasons
Such factors include those that directly affect the tooth directly. Non-systemic causes of enamel hypersensitivity are:
- Tooth decay. Caries is the most common dental disease. Affected teeth have increased sensitivity in the area of enamel damage. The first unpleasant sensations appear already with the initial caries.
- Long-term use of enamel whitening agents. Increased sensitivity is caused by toothpastes and gels with abrasive inclusions. In this case, teeth whitening occurs mechanically and constant exposure to small particles during hygiene causes irritation of the nerve endings. Increased sensitivity usually decreases after stopping whitening pastes after 3-5 days.
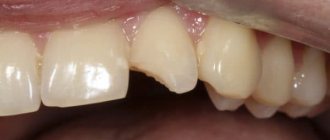
- Mechanical injury. Chips and cracks of enamel are a common occurrence. If such damage is not eliminated, pathogenic microflora begins to develop in this area. The process becomes similar to dental caries. If the chips are extensive, increased sensitivity manifests itself to any chemical and temperature irritants.
- Exposure to acids. It is observed as an occupational hazard, as well as with excessive consumption of sour vegetables and fruits. The most serious tooth decay and irritability occurs after prolonged consumption of sweet soda.
- Pathological abrasion. Due to various factors, horizontal loss of enamel is observed, sensitive areas of the tooth are exposed, and an increased reaction to irritants develops. This is facilitated by improper filling or poor-quality placement of orthopedic structures. In addition, pathological abrasion is a consequence of impaired development of hard dental tissues against the background of imperfect amelanogenesis or dentinogenesis.
- Incorrectly selected toothbrush. Increased tooth sensitivity develops with frequent use of a brush with hard bristles. Damage occurs not only to the enamel, but also to the edge of the gum. Bare areas of the anatomical neck of the tooth and roots begin to react to food irritants.
Attention! To completely eliminate the increased enamel reaction, it is necessary to accurately identify the cause of the pathology. Only a dentist can determine this. Early consultation with a doctor will help prevent the possible development of other oral diseases.
A variety of causal factors are associated with the activities of the person himself. But with a competent approach to the problem, the development of hyperesthesia can be prevented for a long time.
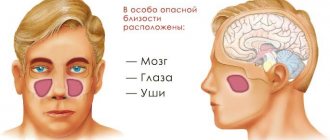
Causes of hypoesthesia
Hypoesthesia usually occurs due to pathological changes in the central and peripheral nervous system, provoked by such factors:
- Brain injury.
- A malignant formation, which, by limiting the volume of the skull, leads to numbness of the head. Moreover, as the tumor grows, the damage intensifies, vision is impaired, and headaches occur.
- Migraine.
- Circulatory disorders.
- Pinched nerve.
- Multiple sclerosis, as a result of which certain areas of nervous tissue are replaced by connective tissue cells. In this case, coordination of movements may be impaired.
- Diabetes mellitus, which contributes to nerve damage.
- Transient ischemic attacks, accompanied by damage to the arms and legs.
- Alcohol abuse.
- Deficiency of vitamins and microelements in the body, for example, lack of vitamin B. Associated symptoms may include excessive irritability, dizziness, fatigue and problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
- Rheumatoid arthritis, which affects the nerve and leads to joint deformation. Usually in the morning there is pain and stiffness at the site of the lesion.
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms and signs of tooth sensitivity
The main manifestation of hyperesthesia is an increased pain response to stimuli. Unpleasant sensations occur not only in the teeth, but also in the gums. The pain persists for 1–2 minutes, then subsides and does not appear spontaneously.
Over time, this reaction becomes persistent and pulsating, similar to deep caries or pulpitis. But unlike these diseases, the enamel retains its integrity with a pronounced pain reaction. The only exception is the increased sensitivity of baby teeth, before a change in bite, when there may be destruction. But this problem rarely occurs.
Hyperesthesia often goes into a period of remission. Increased sensitivity of the enamel is significantly reduced and does not arise from irritants, even with excessive exposure. Subsequent exacerbation manifests itself in severe pain.
Types of hyperesthesia
At the first stage of development of increased sensitivity of tooth enamel, discomfort appears only from cold and hot.
Further irritation is caused by spicy, sweet, salty or sour foods. The pain becomes more intense and lasts longer, even after the cause is eliminated. This is the second stage of development of hypersensitivity.
In severe cases, unpleasant sensations occur from any minor food irritant. Moreover, the pain reaction is pronounced and retains its intensity for a long time. The manifestation of discomfort is observed from air movement or light touch to the enamel.
But there are types of dental hyperesthesia depending on the cause.
Sometimes it is necessary to restore tooth sensitivity. This is no longer related to dental diseases, but to the neuropsychic status.
Increased tooth sensitivity during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the female body loses many beneficial vitamins and minerals. But this does not mean that tooth sensitivity is a sign of pregnancy. If discomfort occurs, you need to review your daily menu. Select all food products in such a way that they contain sufficient amounts of vitamin C, D, magnesium and calcium. Dietary restrictions should include all foods that are rich in acids.
During pregnancy, teeth are able to react to hot and cold, and temperature alternation always negatively affects the enamel.
To strengthen the enamel, even before planning a child, you need to undergo a procedure for remineralization of hard dental tissues. If tooth sensitivity occurs in the early stages of pregnancy, this indicates weakness of the enamel, which requires immediate intervention by a dentist.
Teeth sensitivity after whitening
Various methods are used today to whiten enamel. Most of them negatively affect tooth enamel. This is due to the use of abrasive materials and chemical components based on hydrogen peroxide. Such products thin the hard tissues of the tooth, causing increased sensitivity.
Discomfort appears after the first whitening procedure, does not go away on its own and requires restorative therapy. To reduce tooth sensitivity, you should use sensitive toothpastes after the procedure.
Sensitivity of teeth to cold and hot
An increased painful reaction of teeth to temperature stimuli is the first degree of hypersensitivity development. These problems are associated not only with thinning of the enamel, but can also result from general diseases of the body. The reaction to cold and hot also manifests itself in caries and non-carious lesions of hard dental tissues. When the first signs appear, you should contact your dentist to diagnose the disease.
Complaints about increased sensitivity in the oral cavity often appear after filling, especially when installing veneers, when the enamel layer has to be ground down. In half a percent of cases, restoration is associated with the use of phosphoric acid. When filling, the place where the material was introduced is treated with this liquid.
Another reason is an excessively deep carious cavity and irritation of the pulp during preparation. Such manifestations usually subside a week after restoration, subject to the dentist’s recommendations.
Prevention
Prevention of hyperesthesia is as follows:
- complete oral hygiene, which includes systematic brushing of teeth using appropriate pastes that do not contain abrasive particles and do not destroy tooth enamel;
- correct brushing technique, which involves using a medium-hard brush that does not injure the teeth and gums;
- minimal use of whitening paste, as it contains abrasive particles and chemical elements that can cause damage to the enamel and leaching of calcium from it;
- consumption of foods containing phosphorus and calcium;
- limiting the consumption of sour fruits, berries and juices;
- systematic visits to the dentist at least twice a year.
To prevent the disease, your dentist will help you choose an effective remedy for tooth sensitivity that will reliably protect your enamel from damage. If the patient has sensitivity to frost, cold, or hot, the doctor will also select a remedy for tooth sensitivity that seals the dentinal tubules, preventing changes in the speed of fluid movement inside them and preventing the occurrence of painful sensations.
If your teeth are sensitive, you can rinse your mouth with herbal decoctions. Rinsing is especially effective for inflammation of the gums and sensitivity of the cervical area of the tooth. Relieving the inflammatory process of the gums automatically reduces the patient's sensitivity. However, it should be remembered that traditional methods of treatment (such as rinsing and applications) are designed for long-term use, therefore, it is necessary to rinse the mouth constantly, and not from time to time. Only in this case will it be possible to achieve a long-term therapeutic effect.
Treatment of tooth sensitivity
If teeth begin to react to food irritants, then this is the first signal about the need to go to the dentist. When it is not possible to quickly see a doctor, dietary habits will help minimize the unpleasant sensation:
- eliminate the consumption of sour, sweet, spicy and salty foods;
- temporarily avoid citrus fruits, which contain high amounts of acids;
- consume food only warm and avoid temperature changes in the oral cavity;
- exclude solid foods such as nuts, seeds and crackers from the menu;
- Replenish your daily diet with food rich in beneficial microelements that will help relieve tooth sensitivity (fish, liver, cottage cheese, milk, cheese).
Treatment of dental hyperesthesia at the dentist
Unpleasant sensations are often caused by diseases of the oral cavity. Increased sensitivity is caused by caries and periodontal pathologies. With periodontal disease and periodontitis, the soft and hard tissues of the alveolar process are destroyed. Reducing the volume of the gum causes sensitivity of the tooth at the root.
Traditional methods of treatment and treatment at home cannot fully eliminate such problems. Treatment of periodontal diseases is a lengthy process and only a dentist can carry it out correctly. In addition, the doctor will help identify and eliminate systemic causes of increased tooth sensitivity.
Toothpastes and rinses
Systematic oral hygiene using targeted products will help you get rid of increased sensitivity of teeth. Effective toothpastes for relieving sensitivity are:
- Biorepair Sensitive Teeth Plus. The product is made in Italy and has a low abrasive content. The included hydroxyapatite helps form new enamel and dentin cells. Toothpaste is used classically 2 times a day. The technological form allows you to close microcracks in the hard tissues of teeth.
- Lacalut Extra Sensitive. Strontium acetate and potassium chloride, which is found in sufficient quantities in this paste, helps block dentinal tubules. It is recommended to use the product 2 times a day for 1.5–2 months. To consolidate the effect after a month's break, the use of the paste must be repeated.
- President Sensitive. Italian toothpaste, used for hypersensitive enamel, contains potassium nitrate. Mineralization is provided by hydroxyapatite and fluorine. In addition, the composition includes extracts of chamomile, linden and mint, which have a beneficial effect on periodontal tissue.
- Sensodyne Instant Effect. This is a specially developed paste to eliminate tooth sensitivity. The active ingredients are strontium acetate and sodium fluoride. Elimination of discomfort is observed not after days or weeks of using the paste, but directly during cleaning the oral cavity. If hyperesthesia manifests itself in the area of one tooth, then the product can be used to rub into the problem area as a medicinal gel.
- SPLAT Sensitive. The main active ingredient is hydroxyapatite. Thanks to the special formula, the component easily penetrates into enamel cracks, reliably sealing and protecting against tooth sensitivity from sweet, salty or sour foods. In addition, the paste has an antibacterial and antiseptic effect, reducing gum bleeding.
It is better to use the following brands of rinses for sensitive teeth:
- Listerine Total Care is a product that acts in 6 directions, including strengthening enamel.
- Splat Innova “Liquid enamel”. The product of a Russian company is based on the nanoHAP component.
- SPLAT Biocalcium. Contains the active substances hydroxyapatite and calcium as an extract from egg shells, which reduces the sensitivity of the enamel. The product can even inhibit inflammatory processes.
- Fluorodent (Avanta). Forms a protective film on the surface of the enamel, reducing hyperesthesia.
- Lacalut Aktiv strengthens enamel due to fluoride ions.
Attention! If rinses contain active antiseptics, then they cannot be used daily. This will lead to the development of oral dysbiosis.
Treatment at home
The cost of eliminating dental hyperesthesia depends on the cause of the problem, which only a dentist can eliminate. It is possible to use medications on your own, but only at the initial stage of the disease.
At home, it is allowed to use gels, varnishes and powders to restore dental protection. Depending on the purpose, the preparations are applied directly to the surface of the enamel or used to prepare solutions as a rinse. Effective remedies for relieving dental hypersensitivity at home are:
- drug Fluorlax;
- bifluoride varnish 12;
- fluocal gel;
- solution of 10% calcium gluconate;
- remodent powder;
- strontium chloride in the form of 75% paste;
- dental gel Touch Mouse;
- Mi paste Plus cream;
- 25% strontium chloride solution for rinsing.
These remedies will help eliminate increased tooth sensitivity at home with minor thinning of the enamel and general disorders of the body. Despite the safety of the drugs, they should be used only after the approval of the dentist.
Treatment of hyperesthesia with folk remedies
You can also use folk remedies at home. Natural products combined with traditional medications will help you quickly get rid of increased sensitivity of teeth and effectively strengthen the enamel. In addition, folk remedies and methods are publicly available and have a low price. To reduce hyperesthesia, the following are recommended:
- Tea tree oil. Dissolve 3 drops of the product in 150 ml of warm water and actively rinse the mouth. During the day, a solution of tea tree oil is applied 3-5 times. The desired effect occurs after a week of use. Teeth sensitivity when brushing will disappear within a couple of days.
- Decoction of burdock and chamomile. Provides elimination of increased sensitivity and inflammation of the oral cavity. To prepare the decoction you will need 1 teaspoon of chamomile and burdock, mixed in equal proportions. The herbs are poured into 200 ml of boiling water and left for 60 minutes. After cooling, use as a rinse.
- Oak bark decoction. Temporarily relieves hypersensitivity and irritation. The required solution is prepared from 1 tablespoon of crushed raw materials, which is poured with 250 ml of boiling water and left for 10 minutes. Afterwards, cool and rinse 2-3 times a day for 1-2 minutes.
Attention! Before using folk remedies to treat enamel hypersensitivity, be sure to consult a doctor. Some natural products are incompatible with medications.
Diagnostics
The difficulty in diagnosing hyperesthesia lies in separating it from other diseases. First of all, it is pulpitis. The fact is that with pulpitis there are also strong and sharp pain sensations, and there is also no way to accurately determine which tooth is their source.
To make a correct diagnosis, the duration of pain should be taken into account
. If with hyperesthesia the painful attacks are short-term, then pulpitis gives long-term pain. Moreover, it occurs mainly at night.
They also use the fact that with pulpitis, a reaction to electric current occurs at discharges of more than 20 μA.
Treatment of this disease is quite a complex process. The choice of technique usually depends on what exactly caused the disease.
- Remineralization and fluoridation. There are procedures that will help saturate the enamel with the necessary substances to strengthen it. First of all, it is calcium and fluorine.
- With severe thinning of the enamel (second and third degree of severity), it can be increased in volume using modern filling materials.
- If hyperesthesia was caused by caries, then it is necessary to completely remove all foci of its occurrence and close the resulting cavities.
- Exposed roots and cervical areas can be closed with surgery.
- If the enamel is subject to abrasion, then in most cases there is a need for preliminary orthodontic treatment, that is, correction of the bite.
- An extensive form of hyperesthesia, called generalized, is not subject to conventional dental treatment. In this case, it is necessary to take medications that can restore the metabolism of phosphorus and calcium. Basically, these are various mineral supplements and vitamin complexes.
- Most often, during treatment, experts recommend that the patient use special pastes and gels that will help restore enamel - containing fluorine and calcium.
- Electrophoresis is used in combination with special compounds (fluorine and calcium compounds), which serve to saturate the enamel with the necessary elements.
- Folk remedies should also not be overlooked. Usually these are rinses using tea tree oil, oak bark, burdock and chamomile.
All possible ways and means of caries prevention are outlined in our article.
We will tell you about the types of local anesthesia in dentistry.