What happens to teeth during pregnancy?
According to many women, the child “sucks” all kinds of nutritional substrates from the mother, including calcium from dental tissue, causing its rapid destruction. This is not entirely true. Calcium in dental and bone tissue remains in its place. The baby has enough calcium contained in the mother’s blood, but it may not be enough to meet the needs of her own body.
The main causes of dental diseases in pregnant women:
- hormonal changes that reduce the protective properties of saliva, which causes an increased proliferation of bacteria in the oral cavity, as well as excessive formation of plaque and tartar;
- the destructive effect on enamel of high acidity of gastric contents during vomiting caused by toxicosis;
- unbalanced diet, excessive consumption of baked goods, sweet, carbohydrate foods that destroy enamel;
- insufficient attention to oral hygiene due to poor health or other distractions;
- reduced concentration of calcium and fluoride in the blood;
- rare visits to the dentist.
The most common dental problems that a pregnant woman may encounter are:
- caries that first appeared (on healthy dental units) or secondary (previously treated);
- gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) during pregnancy, caused by increased formation of tartar under the influence of estrogens and progesterone;
- gum tumor (pregnant supragingival tissue) – a benign neoplasm of unknown nature in the gum area, which spontaneously resolves after delivery;
- erosion of enamel under the influence of increased acidity, the upper front incisors in the cervical region are most often affected;
- diffuse toothache - painful sensations that do not have a clear localization, are not associated with the load on dental tissues, spontaneously appear and disappear; presumably associated with increased blood flow and stimulation of nerve endings in the pulp;
- increased sensitivity of dental tissues, which goes away after childbirth.
Calcium for teeth: a safe choice exists!
However, there are also counter-arguments. Today, a lot of scientific research has accumulated on the dangers of calcium for blood vessels, kidneys and other organs. In particular, one of them involving 23,980 people shows an 86% increase in the risk of heart attack when taking high-dose calcium supplements. A scientific article describing this experiment was published in the journal Heart in 2012.
This insidiousness of calcium is directly related to its capricious disposition. Taken in megadoses, this mineral prefers to settle in blood vessels and soft tissues, slowly integrating into the tissues of teeth and bones. This is why calcium is best taken in moderate dosage.
Additionally, different forms of calcium carry different degrees of risk. Thus, calcium citrate salt is recognized as safer than ordinary chalk - cheap calcium carbonate, which is included in most drugs. With better bioavailability - 2.5 times higher than that of carbonate - citrate does not stay in the blood for a long time. This reduces the likelihood of vascular calcification. And the alkalizing effect of citrate prevents the formation of kidney stones.
Calcium citrate has another advantage that is significant specifically for teeth. When the drug is absorbed, citrate is able to penetrate into the gum tissue, stimulating a number of biochemical reactions in them and improving local metabolism. This activation of metabolism in the tissues surrounding the tooth serves to prevent periodontitis.
So, if your teeth are crumbling after childbirth, calcium citrate in a small dosage is an effective and safe choice for strengthening them. However, calcium alone is not enough.
Is there an impact on the baby?
Maintaining dental health during pregnancy is important not only for the expectant mother, but also for the child. Any infectious foci in the body of a pregnant woman pose a potential danger to the fetus. Microbes and the toxic substances they release can be absorbed into the bloodstream and enter the placenta along with the blood, causing infection of the child.
The risks are especially high in the first trimester of pregnancy due to the formation of internal organs and systems. If infection occurs at this stage, there is a risk of fetal malformations. With later infection, premature birth, hypoxia and fetal malnutrition are possible. In addition, some microorganisms can cause an increase in uterine tone, opening of the cervical canal and damage to the membranes of the fetus, which greatly increases the likelihood of miscarriage.
Dental treatment during lactation
Currently, medicinal substances are used in dental practice, the toxic effect of which on the body of a young nursing mother is minimized. For anesthesia, drugs are used that practically do not penetrate into breast milk and do not contain vasoconstrictors - such drugs are safe for the baby’s health. However, before performing anesthesia, you must tell the doctor that you are feeding your baby. When using X-ray diagnostics, you should also be extremely careful: it is recommended to use the minimum dose. In this case, it is preferable to use a radiovisiograph: in modern radiovisiographs, the projection of X-rays occurs not on film, but on a more sensitive electrical sensor, as a result of which the radiation is reduced by 10 times.
Do I need to visit a dentist?
Many women ignore the need for dental treatment, believing that dental procedures can harm the child. This is not entirely true. There are procedures that do not pose any danger to the mother and baby; you just need to choose the right time to visit the doctor.
The optimal period for dental treatment during pregnancy is the second trimester: 14–26 weeks. At this stage, almost all therapeutic procedures are allowed, but it is advisable to limit the use of medications and x-rays.
If this is not possible, then the dentist will choose the safest agent for anesthesia (ultracaine, ubistezin, septanest), and photographs of the jaws can be taken using a dental computed tomograph: this is the safest (due to the low radiation dose) and informative option.
Manipulations allowed in the second trimester:
- treatment of caries;
- treatment of periodontal diseases;
- therapy of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- non-surgical tooth extraction;
- installation of braces.
In the first and third trimesters, only emergency procedures are usually performed (treatment of pulpitis, periodontitis), trying as much as possible to avoid anesthesia.
Dental procedures contraindicated for pregnant women:
- implantation;
- prosthetics;
- any surgical treatment options;
- removal of tartar.
How is oral treatment performed after childbirth?
In the postpartum period, the main complaints of young mothers are gum disease and destruction of tooth enamel. Both of these problems require appropriate treatment.
Treatment of periodontitis or periodontal disease in a nursing mother
Quite often, during breastfeeding, women go to the doctor with a complaint that their teeth are loose after childbirth. The sign usually indicates that the mother has problems with her gums or, as doctors call it, periodontitis. If teeth fall out after childbirth, then this is a sure symptom of such a pathology.
Typically, treatment of pathology will be complex. Most often, infectious disease specialists and endocrinologists come to the aid of dentists.
Basically, doctors adhere to the tactics of therapeutic treatment of this disease in nursing mothers, prescribing drugs that enhance metabolism in the mother’s body and stimulate blood flow in the affected area.
Considering that during breastfeeding, any medicine can become dangerous for the baby, treatment must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
In addition to medications, splints on problem areas, prosthetics made from special dental crowns, and complete removal of teeth that cannot be corrected are widely used to get rid of periodontal disease.
In rare cases, they resort to surgery: using a bone graft, the body of the jaw is restored. Such surgical intervention is used in 70% of cases for pathology of the lower jaw.
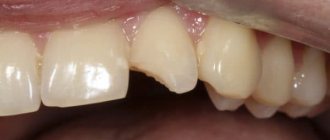
Caries after childbirth
This type of pathology of the oral cavity of a nursing mother usually completely depends on the process of changes in the woman’s hormonal levels. Estrogens and progesterone affect the resistance of enamel and contribute to the destruction of the teeth themselves.
Stages of caries development after childbirth
It should be noted that dentists adhere to some basic rules when treating nursing mothers:
- Modern drugs for local anesthesia usually last no more than 2-5 hours, which allows you to avoid interrupting the baby’s feeding.
- If there is an emergency operation, then a young mother should express breast milk so that 2-3 breastfeedings after surgery do not risk the baby’s health.
- Dental treatment after childbirth requires massive use of antibiotics. Such therapy in 90% of cases requires stopping breastfeeding. Before going to the dentist, a nursing mother should discuss the issue of feeding her baby with her pediatrician.
- When treating caries, you need to remember that fillings and dental implantation are completely prohibited during lactation. Any foreign elements are not recommended for young mothers. If there is an urgent need for a filling, it is recommended that you discuss with your pediatrician the issue of temporarily stopping breastfeeding.
Treatment of oral diseases in a nursing mother is a rather serious problem and does not always coincide with the baby’s feeding regimen. If there are no big problems, then it is best to follow certain prevention methods than to treat teeth during lactation.
Watch the video about dental treatment after childbirth:
How to take care of your teeth?
A number of simple hygiene rules will help you preserve your teeth during pregnancy:
- You should brush your teeth with fluoride toothpaste twice a day. For gum inflammation, it is recommended to use pastes with herbal ingredients (chamomile, sage). In case of increased tooth sensitivity, it is advisable to use special toothpastes of the “sensitive” category.
- Between meals, do not forget to use floss and mouth rinses.
- After episodes of vomiting, you can chew gum with xylitol without sugar or rinse your mouth with a soda solution to neutralize the acid - 1 teaspoon of soda dissolved in a glass of water.
- It is advisable to limit the consumption of sweets, carbonated drinks, and fruit juices as much as possible.
Video: dental health during pregnancy.
Complete nutrition and vitamin complexes
Food should bring maximum benefit to both mother and child, so nutrition should be balanced. To prevent tooth decay during pregnancy, a woman should consume foods rich in calcium (we recommend reading: how to rinse your mouth during pregnancy if you have a bad tooth?). First on this list are:
- cheeses and dairy products;
- eggs;
- sesame;
- greenery;
- cabbage;
- chocolate, etc.
Some substances slow down the absorption of the mineral, so it is better to avoid combining calcium-rich foods with:
- black currant;
- sorrel;
- spinach;
- coffee and tea.
Magnesium also plays an important role - this mineral is good for blood vessels and combines well with calcium. There is a lot of magnesium in milk, potatoes, bananas, nuts and soy. Wheat germ is a real treasure trove of vitamins and minerals.
Also, do not forget about vitamins B, C, E and others, which a woman should receive from food. Many experts believe that taking vitamin complexes can do much more harm than good. Often the fetus is oversaturated with useful elements, and the placenta quickly ages, which leads to premature birth.
However, the period of pregnancy is characterized by significant changes in hormonal levels, in addition, dental diseases often worsen. These and other reasons can lead to teeth crumbling, crumbling or breaking.
Genetic predisposition
If the parents of a pregnant woman have dental problems, then you should not expect that she herself will have perfectly healthy teeth. It has been proven that heredity has a significant influence on dental health - this factor even determines the thickness of the enamel, which protects teeth from damage. The gestation period is characterized by an exacerbation of many pathologies in a woman’s body, so dental problems may also appear.
Hypovitaminosis
Often, pregnant women's teeth break due to a lack of vitamins. The causes of hypovitaminosis can be external (the diet contains foods low in vitamins or containing antivitamin enzymes, the rules for their storage, processing, preparation are violated, the pregnant woman takes medications that interfere with the absorption of vitamins) or internal (a number of pathologies of the digestive system or a low-calorie diet).
Lack of microelements
Insufficient amounts of fluoride, calcium and other microelements necessary to maintain healthy teeth during pregnancy are another common cause of their destruction. Micronutrient deficiency is caused by the same reasons that cause hypovitaminosis - an unbalanced diet, low-quality drinking water, and taking certain medications.
Metabolic disorders
A metabolic disorder that leads to tooth decay can act as a symptom of a serious pathology. Metabolism in a pregnant woman may be disrupted with the development of hypo- or hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, pancreatitis, renal or liver failure and other diseases. In any case, self-treatment is ineffective and even dangerous - you should consult a specialist.
Other reasons
The reasons listed above are considered the most common, but other factors can also cause a pregnant woman’s teeth to begin to crumble or break. Their essence lies in the effect on tooth enamel, the destruction of which makes the tooth defenseless against the pathological influence of the environment:
- dental diseases (for example, caries);
- neglect of oral hygiene;
- stressful situations.
Prevention
The degree of dental caries damage and the presence of soft and calcified dental plaque largely depends on the quality of hygienic care for the oral cavity and teeth. Even the most expensive toothbrush and toothpaste are not a guarantee of high-quality plaque removal.
It is advisable to brush your teeth according to a certain pattern. It starts from the front - outer, cheek side of the chewing teeth on the right and left on the upper jaw and continues to the opposite side, then cleans the chewing surface of the teeth and ends on the palatal surface of the teeth. In the same sequence, brush the teeth on the lower jaw. All surfaces of the teeth of each segment of the jaw must be cleaned with at least 10 paired movements of the brush - from the gums to the cutting edge from the lips or cheeks and from the palate on the upper jaw and from the lingual side on the lower jaw. A total of 400-500 paired movements are performed. On average, brushing your teeth should take at least 7 minutes. You should brush your teeth twice a day: in the morning after breakfast and in the evening before bed. The bristles of the brush should be directed at an acute angle to the surface of the teeth. The brush needs to be placed on the gum, start brushing your teeth more correctly with sweeping movements; on the upper jaw the direction is from top to bottom, on the lower jaw - from bottom to top, from the gum to the cutting edge of the tooth, which allows you to ideally clean the anterior and palatal or lingual surfaces of the teeth. The chewing surfaces of the teeth are cleaned with reciprocating horizontal movements. Finish cleaning with circular movements of the brush along the outer and inner surfaces of the teeth.
Particular attention should be paid to proper nutrition. Breastfeeding depletes calcium reserves in a new mother's body. Therefore, products such as hard cheeses, cottage cheese, bread, potatoes, spinach, cilantro should be included in the menu every day. Perhaps the doctor will prescribe a course of vitamin and mineral prophylaxis, as well as calcium supplements to restore teeth, bones and spine. It should be noted that breast milk is the basis for the future health and resistance of the child’s body to diseases and other harmful environmental influences. A young mother needs to remember that the presence of caries in the mother is a predisposing factor for its development in the child. Close contact leads to the rapid spread of infection in the baby's mouth through airborne droplets. It has been established that microorganisms play an important role in the occurrence of caries. As a result of clinical and experimental studies, it has been determined that without microorganisms, which can be transmitted by airborne droplets, as well as without carbohydrates in contact with the surface of the enamel, caries does not occur. In the meantime, while the baby has no teeth, stomatitis may develop - inflammation of the oral mucosa, in some cases accompanied by the appearance of ulcers, fever, and general malaise. Therefore, a young mother should not forget that, while taking care of the health of her teeth, she is also taking care of her health child.
Yulia Alfimova, dentist, Krasnoarmeysk
Increased tooth sensitivity during pregnancy: causes
Hyperesthesia, increased sensitivity of teeth. Pregnant women turn to dentists with such complaints. This limits their food choices and affects their lifestyle.
Discomfort negatively affects your mood, this becomes a signal that you need to see a doctor. The difficulty of therapy is that during pregnancy the choice of medications and dental treatments is limited.
Causes
When teeth become particularly sensitive, the situation should not be left to chance; the condition may worsen. The first thing you need to understand is what causes hyperesthesia. The reasons may be:
- changes in hormone balance. The restructuring affects the woman’s body, the process is laid down by nature so that the immune system does not reject the baby. An imbalance leads to a weakening of protective systems, which opens up the possibility of the proliferation of bacteria and microbes that provoke periodontitis and caries,
- increased blood circulation. This is a natural process that ensures the delivery of oxygen and nutrition to the fetus. Due to increased blood circulation, the gums swell, become sensitive to food, drinks, especially hot and cold,
- Various dental diseases that were not cured before pregnancy actively develop against the background of a weakened body, causing bleeding gums and complications.
Treatment of hyperesthesia during pregnancy
Treatment difficulties are associated with restrictions on the use of medications and procedures. Dentists and obstetricians provide a number of recommendations on how to treat dental diseases if they provoke increased sensitivity.
The best period of treatment is the 2nd trimester, when the child cannot distinguish sounds and is not afraid of the noise of dental equipment. The placenta has matured to protect the fetus from the drugs that the doctor uses during treatment.
The first trimester limits the range of medical actions. If possible, it is better not to undergo treatment, the active formation of fetal organs occurs, external influences will disrupt the peace and growth process of important organs.
The third trimester, like the first, is not suitable for treatment; it is difficult for a woman to sit in a chair for a long time, and the fetus reacts to the mother’s stress.
Despite the recommendations, if there is a problem with your teeth, it needs to be treated in any trimester. Sensitivity and toothache are stressful for the mother; tolerating such discomfort means increasing stress for the child.
As soon as a pregnant woman is registered with a gynecologist, she will be referred for a consultation with a dentist. This is a scheduled procedure, but if there is cause for concern, you can make an appointment with a doctor at any time. The following procedures do not harm the fetus:
- local anesthesia. Modern anesthetics have a gentle effect on the body and do not enter the bloodstream.
- filling,
- treatment of stomatitis, pulpitis,
- prosthetics.
When there is a need to remove a tooth, it is better to do this after childbirth. The problem comes down to the fact that a wound that takes a long time to heal will be a source of infection; antibiotics are usually prescribed. Antibiotics are not recommended for pregnant women, and extraction is postponed if possible.
Procedures such as bleaching and implantation are not performed on pregnant women, since the process uses chemical compounds that penetrate the blood.
Traditional methods
Based on the fact that many medications are prohibited during pregnancy, the doctor recommends folk remedies that help reduce tooth sensitivity, if there are no diseases:
- tea tree oil. Freshens breath, strengthens gum tissue, reduces dentin sensitivity. Take three drops of oil per 250 ml of water, stir, rinse your mouth 3-4 times a day,
- burdock decoction. Reduces dentin sensitivity, freshens breath. Boil 250 ml of water, add 1 tsp. dry herbs, boil for 5 minutes. Rinse the mouth with the strained product 2-3 times during the day,
- drink warm milk, holding it in the mouth for 20 seconds,
- dilute 1 tsp. salt in 250 ml of water, rinse the mouth vigorously immediately after brushing,
- Massage your gums with your fingers in the morning and evening. Massage will strengthen tissues, improve blood circulation,
- oak bark decoction. Antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agent. One tbsp. crushed bark, pour 200 ml of boiling water, cook for 7 minutes. Strain, cool to room temperature, rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day,
- camomile tea. A well-known antibacterial, analgesic, anti-inflammatory agent. One tbsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water over the flowers and leave for 1 hour. Strain and rinse your mouth 5 times a day.
The listed folk remedies will improve the condition of the gums and teeth, relieve inflammation and reduce tooth sensitivity.
Hygiene rules
There are recommendations that, if followed, will help prevent tooth sensitivity in pregnant women and not only. Proper care will ensure a beautiful and healthy smile.
You need to buy a new brush with thin and soft bristles. It will prevent injury and irritation of inflamed gums. Thin hairs will remove dirt from hidden areas, and soft bristles will gently massage the gums.
The dentist will recommend a toothpaste suitable for sensitive teeth and safe for pregnant women.
It is better to abstain from sweets - they create an environment beneficial for bacteria. Even a few sweets or a piece of cake can give rise to the development of tooth decay. If you consume such products, immediately rinse your mouth or brush your teeth after eating.
The temperature of drinks and food must be controlled. Temporarily you need to give up scalding or ice-cold drinks and dishes.
You should visit the dentist regularly to identify problems in the early stages.
Prevention
As a preventative measure, the doctor will recommend taking a complex of vitamins, paying attention to vitamin C, A, D3. It is necessary to exclude deficiency of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium. There are vitamin and mineral complexes designed for 30 days of taking 1 capsule daily.
Brushing your teeth should be done correctly, without pressing. It was mentioned about choosing a brush and paste; you need to learn how to use the tool correctly - move the brush from the gums to the tips of the teeth, in a circular motion. Horizontal movement harms the gums; they peel off, exposing the neck of the tooth, causing hyperesthesia and serious diseases.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?YesNo
Whitening pastes should not be used during pregnancy; the abrasives they contain thin out the enamel. The cleaning procedure lasts more than 1 minute and is performed in the morning and evening. After each meal, rinse your mouth with warm water, or with a herbal decoction or a special rinse.
For sensitive enamel, applications of toothpaste containing fluoride will help reduce discomfort. After regular cleaning, you need to apply it for 5 minutes, then rinse your mouth well without swallowing the composition. Repeat in the morning, evening, if there are no contraindications. The effect will appear in a couple of days. Further, for prevention, applications are carried out twice a week.
Chewing gum and seeds should be excluded from the diet. This wears out the enamel, leads to microcracks, and increases sensitivity.
The listed measures will help reduce the risk of sensitivity, but if the problem is not solved, a visit to the doctor is required.
Source: //za-rozhdenie.ru/stomatologiya/chuvstvitelnost-zubov-pri-beremennosti
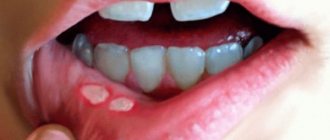
Bad breath
Breastfeeding women often experience bad breath. It causes diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, accumulation of bacteria, and liver dysfunction.
Causes of bad breath:
- improper and irregular care;
- indigestion, gastrointestinal diseases;
- pancreatic diseases;
- colitis, enteritis;
- gingivitis;
- diabetes.
If a symptom such as bad breath is present, treatment is prescribed by a dentist or therapist, depending on the cause. For diagnosis, blood and urine tests, oral x-rays and hygiene assessment are prescribed.
What to do if you have bad breath after childbirth:
- brush your teeth daily morning and evening;
- use natural chewing gum, threads or rinses after each meal;
- take a vitamin-mineral complex;
- review your diet. Eliminate harmful foods, soda;
- start treatment in a timely manner if the odor is caused by a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, liver or thyroid gland;
- use antiseptic mouth rinses. They prevent the proliferation of harmful bacteria.
To eliminate odor, thyme tincture is used. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. To prepare it, 1 tbsp. l. The plants are poured into glasses of boiling water and left for half an hour.
Hygiene rules:
- Dental floss is used to remove food debris. It will clean hard-to-reach places and freshen your breath;
- During the procedure, not only the teeth are treated, but also the tongue;
- After each meal you need to rinse your mouth with clean water;
- You can chew gum for no more than 5 minutes.
Following the recommendations will allow breastfeeding women to maintain oral health and avoid the appearance of unpleasant odors. For better effectiveness of treating problems, take vitamin and mineral complexes rich in phosphorus and calcium.
Immediately after giving birth, you should visit the dentist. An examination will reveal problems with gum health and the presence of caries. During lactation, it is allowed to treat the oral cavity using local anesthetics. It is recommended to exclude whitening and prosthetic procedures.
Dental problems after childbirth are a very common problem. Often young mothers complain of aching pain and destruction of enamel. Carrying and feeding a baby is a serious burden on the body, which is why teeth so often crumble after childbirth.
But the problem cannot be left to chance. The sooner you see a dentist, the better your chances of maintaining a healthy smile.
The main cause of tooth decay is. To build the skeleton and body of a baby, a lot of this mineral is required. If little calcium comes from food, it begins to be washed out by the woman’s body. Skin, hair and nails, blood vessels and teeth suffer. That is why almost all expectant mothers are recommended to take calcium supplements from the very beginning of pregnancy.
Women often wonder why not everyone has dental problems after childbirth, and even regularly taking vitamins with calcium often does not help. The fact is that the likelihood of tooth decay also depends on the quality of the enamel. In some people it is thinner and more easily destroyed.
Don't forget that milk production also requires a lot of energy and calcium. Therefore, you should not stop taking vitamins immediately after childbirth. You just need to choose a new complex that is more suitable for nursing.
Other significant reasons for tooth decay after childbirth include:
- Lack of quality and regular dental care. Sometimes young mothers become so absorbed in their baby that they begin to pay less attention to themselves, brush their teeth quickly, and sometimes forget about it altogether.
- Accompanying illnesses. , arthritis, thyroid disease and diabetes can cause teeth to crumble. Often pregnancy and childbirth stimulate their exacerbation, which negatively affects the strength of tooth enamel.
- Stress. The birth of a child in itself is a difficult moment that affects a woman’s lifestyle and well-being. Sometimes this is accompanied by a lack of milk, poor sleep of the baby and discord in the relationship with the spouse. All this can cause teeth to crumble.
Bad habits have a negative impact on the condition of teeth. Most women stop smoking during pregnancy so as not to harm the fetus. But after childbirth, especially if the child is bottle-fed, many return to the addiction. This is dangerous because cigarette smoke contains substances that cause the body to lose calcium. Considering that a woman’s body has not yet fully recovered from pregnancy and childbirth, this can cause teeth to crumble.
If you were unable to protect your teeth and they began to crumble after childbirth, you should visit a dentist. He will determine the cause of the destruction and will be able to select adequate treatment methods. Modern filling materials and painkillers are absolutely safe even during lactation, so you should not be afraid of visiting a doctor.
If the mother is afraid that the anesthetic will still penetrate into breast milk, it can be treated without anesthesia. Another option is to express the milk in advance and save it until the next feeding. Most drugs are eliminated within 3-6 hours, so the milk will definitely not spoil.
Some young mothers are afraid to take x-rays while breastfeeding. In fact, light irradiation of the jaw does not affect lactation or the quality of milk in any way, so there is no need to worry. Unfounded fears are much more dangerous during this period.
In addition to treating existing problems, ask your doctor to recommend a suitable paste for you. There are a lot of them and choosing the right one can be difficult. You may need a paste with a high calcium or fluoride content, or even a special remineralizing cream. It is also important to choose a suitable calcium-containing bioactive food supplement.