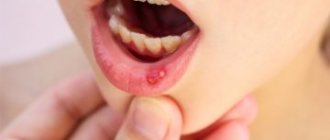
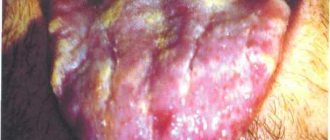
Stomatitis is irritation or damage to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. It appears in the form of ulcers and so-called “pimples” filled with liquid.
It is useful to study medical photographs to know exactly what they look like and contact the hospital in time. Stomatitis can appear in both adults and children, but it is children who are most predisposed to it. The disease equally affects children both at 4-5 months of age and at 4-5 years of age.
Stomatitis in children is explained by the underdevelopment of the mucous membranes, from which they are easily damaged by the slightest influence of any factor. Do not forget that children constantly put dirty hands, toys and various objects into their mouths. The development of bacteria and microorganisms is a powerful impetus for the occurrence of stomatitis. Children also experience frequent disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract, which increase acidity and change the composition of saliva. Such changes lead to problems.
Classification
Depending on the cause of occurrence, there are the following types of stomatitis:
- Allergic – occurs when the body is exposed to an external agent. A common occurrence in young children that is difficult to treat.
- Vesicular – the disease has a viral etiology. A child becomes infected due to contact with an insect carrier or a sick animal.
- Aphthous - is a consequence of advanced stomatitis of herpes etiology.
- Catarrhal – characterized by a blurred clinical picture and a tendency to become chronic.
- Traumatic – occurs after injury to the mucous membrane and is dangerous due to infection. A common occurrence in children aged 3 years, associated with injuries and the lack of a well-developed technique for brushing teeth.
- Herpetic – occurs due to infection with the herpes simplex virus. Often occurs in children 1 year and older.
- Ulcerative - can be either an independent form or a complication of catarrhal stomatitis.
- Viral (infectious) – caused by influenza virus, parainfluenza, chickenpox, measles, adenovirus.
- Candidiasis - occurs as a result of the proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida in the oral cavity. Most often occurs in one-year-old children and in children under 2 years of age.
- Bacterial - the causative agents are staphylococci and streptococci. This type includes gonorrheal and diphtheria stomatitis.
Physiotherapy
Treatment with physical factors for stomatitis is prescribed when the factor that caused this pathology is identified. It is mainly used for chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis. The purpose of physiotherapy in this clinical situation is analgesic and anti-inflammatory, antibacterial/antiseptic, stimulating regenerative processes in affected tissues, as well as reducing the body’s sensitivity to the effects of adverse external factors.
It is preferable to use not local treatment, but the general effect of a physical factor on the body, which helps to increase the immune reactivity of the latter. If chronic stomatitis occurs, occurring with frequent exacerbations, in the period between them, in the remission phase, the patient is prescribed general irradiation of the body with ultraviolet radiation.
If aphthae are visualized in the patient’s oral cavity, the following is performed:
- on the first day or even in the prodromal period - laser therapy (up to 5 minutes on each aphthae; total session duration no more than 10 minutes);
- irradiation of the affected areas with ultraviolet radiation followed by exposure to the collar zone and adrenal gland area; aphthae are irradiated every day; in the first procedure the patient receives 1 biodose, in the next - 2 biodoses, then - 3 and so on; the course of treatment is up to 6 sessions for each aphthae;
- local darsonvalization;
- aeroionotherapy;
- aerosol therapy with novocaine or inhalipt;
- hydrotherapy with mineral waters.
In the developing stage of the disease, as well as in weakened patients at any stage of the pathological process, low-intensity laser radiation therapy is prescribed. Exposure duration is from 0.5 to 5 minutes depending on the clinical situation. When epithelization of the aphthae occurs, therapy is stopped. As a rule, this requires about 10-13 procedures.
In the short term, magnetic therapy will help reduce the activity of the inflammatory process and accelerate the epithelization of mucosal defects. In addition, it enhances the effect of drugs used through applications. The technique is simple: before the procedure, the patient treats the oral cavity with a solution of hydrogen peroxide or another antiseptic solution, then the specialist applies tampons with the drug to the area of aphthae or ulcers and places a pulsating magnetic field inductor over the skin of the cheeks. The duration of the procedure is from 15 to 20 minutes, they are carried out 1 or 2 times a day, the treatment course includes up to 15 effects.
Reasons for the development of stomatitis
Most often, children under 3 years of age are susceptible to the disease, but this does not mean that at another age your child will not be at risk of a dangerous and insidious disease. The immune system of babies is not yet fully functional; the tissues of the oral mucosa are very soft and thin, so putting dirty hands or objects into the mouth in some cases leads to illness.
Many doctors classify childhood stomatitis as any damage (even mechanical) to the oral mucosa or infectious diseases of the oral cavity.
The most common causes of childhood stomatitis may be:
- Entering the oral cavity of the fungus candida (popularly called thrush). A weakened child’s immune system is an ideal condition for the rapid progression and proliferation of a fungal virus. The mouth may become dry and white. Untimely treatment leads to the appearance of cracks, accompanied by unbearable pain while eating.
- The herpes virus can also cause the development of childhood stomatitis. This is a dangerous pathogen that is transmitted through household items, dishes and toys. In 99% of cases, the disease affects children under 3 years of age.
- Bacterial stomatitis occurs due to the child’s habit of not washing his hands after visiting the toilet or after coming in from outside. Children put everything that surrounds them into their mouths, so repetitions and relapses of the disease are possible in the future.
- The causes of aphthous stomatitis have not yet been identified. Doctors argue about who is the causative agent of this form of the disease: bacteria, viruses or herpes. Aphthous stomatitis can easily become chronic.
- Stomatitis is often caused by mechanical damage to the oral cavity and mucous membranes, which a child receives during falls or scratches from a foreign object. Stomatitis may also occur during teething.
Since there are many causes of childhood stomatitis, each child should be observed individually. Even if you look at photos of stomatitis in children’s mouths, they will vary greatly.
Stomatitis happens:
- viral (acute herpetic stomatitis) is transmitted by airborne droplets;
- bacterial - transmitted through household contact, through toys, dishes, etc.;
- fungal (candidal stomatitis) develops against the background of reduced immunity;
- allergic.
The treatment regimen for stomatitis is standard: it includes a specific component (a drug that acts on the cause), antiseptic and regenerating components (keratoplastic drugs).
General symptoms of stomatitis, photos in children
General symptoms that can be observed with any form of stomatitis in children (see photo) include:
- the appearance of ulcers in the mouth, the size, lesions and color of which can vary greatly depending on the type of stomatitis;
- changes in the child’s behavior – tearfulness, irritability, worsening sleep and appetite.
Symptoms of aphthous stomatitis in children:
- A few days before the development of the disease, a characteristic symptom, the so-called geographic tongue, is observed. The tongue becomes covered with small blisters. After a day or two, the next period of illness begins: aphthae on the oral mucosa and an increase in body temperature. The child complains of a burning sensation in the mouth and refuses food and water. Often, in addition to bubbles, a white coating is observed on the tongue. The number of aphthae on the oral mucosa in aphthous stomatitis is much less than in herpetic stomatitis. Usually there are no more than one or two or five or six ulcers. The herpetic form is characterized by a large number of ulcers that cover the child’s entire mouth.
Symptoms of herpetic stomatitis:
- simultaneous appearance of aphthae of almost the same size and configuration on the oral mucosa in several places at once;
- a wave-like course of the disease, manifested in the initial period by a rash of painful ulcers and a sharp increase in body temperature. Then the temperature stabilizes and the child’s general condition improves. After a few days, a relapse develops - new rashes appear, and the temperature begins to rise;
- swelling of the gums;
- bad breath.
Symptoms of candidal stomatitis:
- The development of specific local symptoms of candidal stomatitis in children is preceded by excessive dryness of the mucous membrane, a burning sensation and an unpleasant taste in the mouth, and bad breath. Infants are capricious while eating, refuse the breast or bottle, behave restlessly, and sleep poorly. Soon, small white dots appear on the inside of the cheeks, lips, tongue and gums, which, merging, form a rich white plaque of a cheesy consistency. In severe forms of candidal stomatitis in children, the plaque acquires a dirty gray tint and is difficult to remove from the mucous membrane, revealing a swollen surface that bleeds at the slightest touch. In addition to pseudomembranous candidal stomatitis described above, atrophic candidal stomatitis occurs in children. It usually develops in children wearing orthodontic appliances and occurs with scant symptoms: redness, burning, dryness of the mucous membrane. Plaque is found only in the folds of the cheeks and lips.
Symptoms of bacterial stomatitis:
- When affected by various types of bacteria, the symptoms of the disease in children have characteristic features. Thus, when the oral cavity is affected by the causative agent of diphtheria, the bleeding surface of the gums is covered with a grayish film. The appearance of a white coating on the tongue in the presence of stomatitis indicates that the cause of the disease is scarlet fever. Sometimes a newborn baby becomes infected while passing through the birth canal. For example, if the mother is sick with gonorrhea, then signs of infection of the baby may be the presence of redness and ulcers in the mouth, as well as inflammation of the conjunctiva of the eyes.
Symptoms of viral stomatitis:
- Symptoms of a viral disease of this kind are fever, moody mood, swelling of the submandibular lymph nodes, swelling of the jaws and palate, the appearance of aphthae (painful ulcers), and bad breath. A sick child can infect other children and adult family members.
A common common symptom of any type of stomatitis is enlargement and tenderness of the lymph nodes under the lower jaw.
Childhood stomatitis: symptoms, treatment and prevention
(2 votes, average: 5.00 out of 5) Loading …
Before we start talking about stomatitis in children, I would like to define this concept. This will help in the future to better understand the symptoms and causes of this disease.
Causes of stomatitis
Stomatitis is understood as inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, usually caused by various microorganisms. They can enter the child’s body either from environmental objects, or they can also be in the oral cavity initially, because microbes are constantly there. And only if the baby’s immunity decreases, they begin to actively reproduce, which becomes the cause of the disease.
As for external factors that contribute to the penetration of germs into a child’s mouth, the most common are poorly treated bottles, nipples and pacifiers, as well as various objects and toys that young children constantly try to get into their mouths.
It is absolutely not necessary for this to happen that there should be a layer of dust or dirt on things - microbes cannot be seen with the naked eye. For this you will need a microscope.
For this reason, objects that have fallen on the floor (even for a second) cannot be given back to the pre-treatment baby.
In addition, experts recommend washing your hands thoroughly before holding your infant. After all, on the surface of the hands there is always a huge number of microbes that are dangerous for the baby. According to pediatricians, children of all ages are susceptible to stomatitis, but most often this disease occurs more often in children aged three months to six years, when the child cannot yet understand the full need for hygiene procedures and tries, under any pretext, not to perform them.
Symptoms of stomatitis
Symptoms in children depend to a large extent on the causative agent of the disease. In 80% of cases it becomes the herpes virus. In this case, the infection can be transmitted by airborne droplets or by contact. For example, when an adult with a herpes rash tries to kiss a child, or eats from the same dish with him. However, this is also true for children.
With this type of stomatitis, children begin to develop a fever on days 4-8. At the same time, the baby becomes capricious and lethargic. Then a cough appears, a slight runny nose (although not always), then the gums become swollen and red, and a rash appears in the oral cavity and on the skin around the mouth. The submandibular lymph nodes become painful and enlarged.
With proper and timely treatment, the duration of the disease is approximately a week.
But there is also a more severe form of this disease, in which the child’s body temperature can rise to 40 degrees, its manifestations are more pronounced, and it lasts up to three weeks. Children may have stomatitis of microbial origin. Most often it is caused by streptococci and staphylococci. It can be accompanied by diseases such as pneumonia and tonsillitis.
In this case, a yellow film forms on the child’s lips. They “stick together” and body temperature rises.
Stomatitis can also be caused by different types of fungi. This mainly occurs when using large doses of antibiotics for a long time, although stomatitis can also occur in children when using therapeutic doses of these drugs.
For this reason, before deciding to start treatment for a child, it is advisable to first consult a doctor.
A common problem that parents face is also traumatic stomatitis. It occurs when the mucous membranes of the baby’s mouth are damaged. This can happen when they carelessly try to give the baby a bottle or pacifier, when feeding him with a spoon, when, when the child refuses to eat, they try to force food into his mouth. The baby may be injured when he drags objects that are not intended for him into his mouth (for example, chewing on a pencil). You can also injure the membrane when biting your tongue or lip.
Symptoms that occur in almost all types of stomatitis are:
- increased body temperature in a child;
- presence of rashes;
- redness and swelling of the gums and oral mucosa;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
Their severity may vary depending on the state of the baby’s immune system and the pathogen.
Treatment of stomatitis
Childhood stomatitis must be treated, even if the severity of its manifestations seems mild. It is carried out in several directions at once.
The first is the effect on the causative agent of this disease. There are many medications for this that only a doctor can select.
The second is a reduction in symptoms of the disease, such as pain and swelling.
This is especially important at a younger age, as the pain may cause the child to refuse to eat. Parents must carry out treatment correctly, including isolating the child from other children in the family, and providing separate dishes for his food, which must be processed after each meal.
A sick child should be given good nutrition. After all, due to severe pain, he often refuses food. For this reason, food should be at room temperature, not too salty, and not sour, so as not to further irritate the oral mucosa.
Food, in addition, should have a mushy consistency. Drinking large amounts of liquid promotes a more intense release of toxins from the child's body. If you have severe pain, you can give drinks through a straw. The temperature of the liquid should be room temperature. It is necessary to regularly take all medications prescribed by your doctor and brush your teeth.
As for the alternative treatment of childhood stomatitis, their use must be discussed with a specialist.
The oral mucosa and rashes should never be lubricated with honey - this creates a favorable environment for the development and proliferation of bacteria and other microorganisms.
In addition, it is a mistake to use brilliant green for the treatment of stomatitis. This drug, without a doubt, contributes to the death of microorganisms, but also causes severe burns of the mucous membrane, thereby increasing pain and contributing to the progress of the disease.
The same applies to iodine solution, fucorcin.
If a child has stomatitis not for the first time, then the treatment regimen prescribed in the previous case should not be used without consultation with a pediatrician. The symptoms of this disease are very similar for different types of pathogen, and the use of drugs that previously helped with bacterial stomatitis, if it is of fungal or viral origin, can cause progression of the disease.
Prevention of stomatitis
In terms of preventing the occurrence of stomatitis in children, it will be useful for them to observe the necessary personal hygiene. The simplest of them are brushing your teeth every day, washing your hands before eating and after using the toilet.
A child's toothbrush should be individual. If a baby asks for an adult’s brush, it should not be given under any circumstances (this happens at the age of two or three years).
Parents should explain to the child that biting nails and putting fingers in the mouth is unacceptable.
As for very young children, to prevent stomatitis in them, it is necessary to properly treat bottles, nipples and pacifiers after each use, and also avoid trauma to the oral cavity when feeding.
Thus, many different factors play a role in the occurrence of stomatitis in children, which lead to the entry of various microorganisms into the oral cavity and their development.
Preventive measures are mainly aimed at making it impossible for infectious agents to enter the baby’s mouth and can be carried out by relatives and parents. Older children must be taught how important personal hygiene is.
rusdental.ru
How to treat stomatitis in a child at home
As a reasonable parent, you should contact your doctor (pediatrician) if you find that:
- The child is unable to drink or swallow food.
- The child has a high temperature.
- The child is too fussy and cannot be calmed down.
- The child sleeps restlessly at night, or does not sleep at all.
- Bubbles and a light white coating appeared on the baby's tongue.
Treatment of stomatitis in children directly depends on the causes that caused it. The following treatment strategy is common to all types of stomatitis in children:
- A gentle diet with the exclusion of any solid foods that can “disturb” aphthae in the oral cavity and cause an exacerbation of inflammation. You should also remove spicy and sour foods from your diet, and make sure that the food is not too hot.
- Thorough oral hygiene: gentle brushing of teeth and tongue, as well as daily rinses with antiseptic agents.
- If a child's temperature rises above 38.5°C, he should be given an antipyretic medicine.
If you follow a gentle diet and proper oral hygiene, aphthae (ulcers) completely disappear 10-15 days after their appearance in any type of stomatitis.
To rinse your mouth during the day, you can use solutions of antiseptics - chlorhexidine, furatsilin, etc., as well as herbal decoctions - chamomile, calendula and others. The attending physician will tell you how to properly prepare the solution, and will also prescribe a rinsing regimen (it varies depending on the age of the child and the severity of his illness). In addition, if the ulcers are large and painful to the point that the child is acting too hysterically, the canker sores can be treated with antiseptic sprays from time to time.
However, remember that for stomatitis in children, aerosols should under no circumstances be used on children under one year of age. Pharmacy gels, which are usually used to relieve itching when the first teeth erupt, will help these crumbs relieve pain.
It is also recommended to temporarily “transfer” the child to a toothbrush with the softest bristles, but at the same time he must brush his teeth and gums very carefully.
Pediatric stomatitis can be aggravated by sharp edges of teeth or braces in the mouth - these problems are best addressed in the pediatric dentist's office.
Ulcers with stomatitis
Having discovered ulcerative stomatitis in the mouth, many people panic, since the symptoms of the disease can really be terrifying. The gums turn pale and become covered with blisters, and then may even die if treated incorrectly or untimely. The oral cavity begins to look unsightly, and a putrid stench appears from the mouth. If the ulcers spread to the tongue, it becomes painful to chew and swallow food.
Causes
The source of the disease is bacteria of the Borellia vincentii and Bacillus fusiformis varieties. At the same time, they do not enter the body from the outside, but live within it, but in small quantities and provoke ulcerative stomatitis only when they begin to multiply intensively. The habitat of bacteria is the gingival grooves and periodontal canals, as well as areas of the mouth affected by caries. If the rules of oral hygiene are not followed, bacteria quickly spread from the affected micro-areas to healthy tissues, resulting in plaque, ulcers and, as a result, ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis. The impetus for the proliferation of bacteria can be not only a negligent attitude to hygiene, but also a decrease in immunity, as well as a number of other factors:
- inadequate and monotonous diet;
- avitaminosis;
- constant nervous tension;
- overwork and chronic fatigue syndrome;
- beginning allergic or herpetic stomatitis;
- past acute viral diseases:
Return to contents
Manifestation and symptoms
According to the primary symptoms, ulcerative stomatitis at the initial stage can be easily confused with other types of this disease, since the disease manifests itself with pain and a white-yellow coating, traditional for stomatitis. However, with an increase in the number of pathogenic bacteria, ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis manifests itself fully. Depending on the symptoms, there are 3 types of the disease:
- Vincent's gingevitis. Painful sores appear on the gums.
- Vincent's stomatitis. Ulcers appear on the tongue and oral mucosa.
- Plauta-Vincent's angina. Aphthous-ulcerative formations appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
Return to contents
Diagnostic methods
Diseases can be identified at home.
You can try to determine the disease yourself at home, relying on your own feelings, but it is better to consult a doctor, since only correct diagnosis using bacterioscopic tests will help identify the disease at an early stage, select the necessary medications and quickly cure wounds on the tongue and mouth before how tissue necrosis begins.
Often, to determine the disease, a venous blood test is necessary, because Vincent’s ulcerative-necrotizing stomatitis has similar symptoms to a number of other diseases - mercury poisoning, blood diseases, damage by heavy metals and even syphilis.
Return to contents
Treatment of ulcerative stomatitis in children and adults
Most often, acute ulcerative stomatitis is observed in adults with the following oral problems:
- problematic teeth;
- incorrectly placed dentures, braces;
- fragments of teeth that injure the gum tissue from the side.
In such cases, the therapy is local in nature and gives the first results after just a few procedures. To begin with, the traumatic factor is removed from the mouth, then the ulcers are treated with antiseptic solutions and tampons with painkillers are applied. If therapy is ineffective due to the advanced state of the disease, quartz treatment of the oral cavity in the physiotherapy room and injections of a broad-spectrum antibiotic are prescribed:
- "Erythromycin";
- "Oletetrin."
Return to contents
Anesthesia
Relieving painful symptoms of stomatitis is an important aspect, since pain interferes with normal eating and causes discomfort around the clock. Erosive stomatitis is anesthetized with local applications in the initial stage and injections of anesthetic drugs in the advanced stage. Most often, drugs based on Lidocaine, Trimecaine or Pyromecaine are injected into the gums. The doctor may prescribe menthol-based lozenges with a “freezing” effect if the patient is allergic to anesthetics such as lidocaine.
Return to contents
Treatment
Ulcerative stomatitis most often occurs in adults.
Ulcers with stomatitis are treated in 2 doses. First, the oral cavity should be cleaned of dead tissue, then disinfected. It is better to do cleansing in a clinic, because the appropriate enzymes are only available in dental offices. It is better to treat ulcers there, because the gums and oral cavity must be rinsed with a directed stream of water, but this is problematic to do at home. If purulent blisters go down the throat, only a doctor can effectively treat them, and self-medication can lead to injury.
Return to contents
What can you do at home?
For adults, treating necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis at home is not difficult. Doctors recommend treating the abscess with healing ointments 2-3 times a day, for example, using Metrogyl Denta. The wound is also treated with sea buckthorn oil or rosehip oil. You can treat ulcers on the tongue and gums by rinsing at home using commonly used antiseptics:
- hydrogen peroxide;
- potassium permanganate;
- "Chlorhexidine";
- herbal decoctions of chamomile, eucalyptus, oak bark, St. John's wort.
Return to contents
Treatment of stomatitis in children
Often, stomatitis wounds on the tongue in children appear due to a lack of vitamins, weak immunity, anemia and the infection that develops against this background. Sometimes one large ulcer appears on a child’s tongue, but there are cases when ulcers cover the entire oral cavity, causing discomfort and pain. The child refuses to eat and begins to act up. The doctor will provide first aid by removing dead tissue and cleaning the mouth with disinfectants. This is followed by treatment at home, including a set of drugs presented in the table:
| Drugs | Names of funds |
| Antibacterial | "Furacilin" |
| "Rotokan" | |
| Herbal rinses | |
| Antihistamines and antiallergics | "Suprastin" |
| "Tavegil" | |
| "Fenistil" | |
| Painkillers | "Lidocaine" |
| "Chymopsin" | |
| "Trypsin" | |
| Vitamin complexes | "Alphabet Kids" |
| "Revit" | |
| "Undevit" |
Ulcerative stomatitis of the acute stage, accompanied by a rise in temperature to 38 degrees, requires an antibacterial course of treatment with Penicillin, Lincomycin, Amoxiclav, Ampiox. If the cause of the formation of ulcers was mechanical injuries from braces, they must be temporarily removed and the wounds treated by applying gauze swabs soaked in medicine, anesthetics and disinfecting solutions.
Sometimes the cause of a rash in the mouth in children is caries-affected or improperly grown baby teeth. In this case, the teeth must be removed, otherwise any therapy will be ineffective.
Return to contents
Relapses and their causes
Ulcerative stomatitis may recur.
Even high-quality treatment does not guarantee that ulcerative stomatitis in adults will never recur. Relapse is caused by factors that initially caused the disease:
- not completely removed tartar;
- poorly fitting dentures;
- untreated caries lesions.
Also, a sore on the tongue reoccurs when oral hygiene is not maintained and the tongue is bitten by a sharp, chipped edge of a tooth. If foci of inflammation are detected again, you can first try to cure the ulcers yourself using home methods; if they do not disappear in a couple of days, it is better to consult a doctor.
Return to contents
Preventive actions
Patients who have suffered ulcerative stomatitis should visit their doctor at least once every 2 months throughout the year, because even a small untreated mouth ulcer leads to a relapse. People who experience stomatitis on the tongue due to various traumatic factors, which at the moment cannot be completely excluded, are recommended to rinse their mouth daily with special antibacterial solutions, such as Colgate Plax. A plus would be a preventive course of taking “Imudon” to increase the body’s resistance to harmful microorganisms.
etoherpes.ru
Treatment of aphthous stomatitis in children
Treatment of this stomatitis, due to the uncertainty of the cause, is carried out by several doctors, this may be a dentist, an allergist or a gastroenterologist.
- If the allergic nature of the occurrence of aphthous stomatitis is established, then contact with the allergen is excluded, antihistamines are prescribed - Suprastin, Cetrin in syrup (children over 2 years old), see all allergy medications.
- Solutions of soda, boric acid, herbal decoctions, and Blue are also used to treat canker sores.
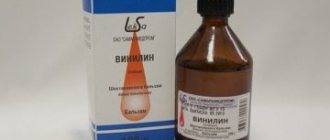
- The selection of antiseptic and antimicrobial agents is often carried out by trial and error, since the course of any inflammatory process is individual, for some people help with Lugol's spray, Hexoral spray, or rinsing with Iodinol, Miramistin, for others Vinilin or methylene blue dye - Blue - helps a lot. Rotokan, an antiseptic with a healing effect (for mouth rinsing), has proven itself well.
- If gastrointestinal disorders are detected, then appropriate treatment of the concomitant disease is carried out.
- Vitamins C, B1, B2, B12 are prescribed.
- Among the antiviral drugs, Bonafton can be prescribed.
- In case of chronic stomatitis, an immunologist can prescribe Decaris and Pyrogenal to correct immunity.
However, in any case, you should not self-medicate; treatment of stomatitis in children should be under the supervision of a qualified doctor.
What vitamins to take for stomatitis in adults?
Stomatitis is a very common disease that affects the oral cavity. To get rid of it, the patient is prescribed a vitamin course that promotes the healing of affected tissues, regeneration of the mucous membrane, and increases immunity at the local level. Vitamins are not used directly for treatment of stomatitis, but they are shown as an effective addition to the main course of treatment.
Causes and symptoms
The main reason why stomatitis appears is a weakened immune system, which is why doctors often include a complex of vitamins in the treatment program.
Stomatitis is caused by a viral pathogen, and feels good in the mouth, where there are excellent conditions for the infection to multiply. The following categories of people are especially at risk:
- Smokers.
- Not maintaining oral hygiene.
- Eating vegetables and fruits unwashed.
- Having incorrectly installed crowns on teeth or dentures.
Symptoms of the disease are usually the following:
- Pain in the oral cavity.
- Feeling of discomfort.
- Mouth ulcers.
Treatment of stomatitis in adults
The method of treatment depends on the type of disease (see table below).
| Type of disease | Type of medications | Medicines |
| Herpes | Immunoenhancing | Levamisole, Immunal |
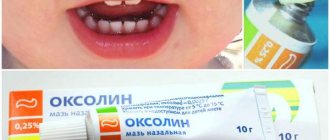
| Antivirus | Zovirax, Acyclovir, oxolinic ointment | |
| Healing | Solcoseryl, Karotolin, Vinylin | |
| Bacterial | Antibacterial | Hexoral, Tantum-Verde, Orasept |
| Aphthous | Antibacterial | Azathioprine, Betamethasone, Prednisolone |
| Healing | Clobetasol, dexamethasone solution | |
| Thrush | Immunoenhancing | Laferobion, Viferon |
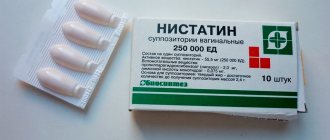
| Antiseptic | Nystatin, Pimafucin, Chlorhexidine |
The course of treatment should be determined by a professional physician after a detailed examination of the patient. The course of treatment should include medications that enhance immunity - these can be vitamins, for example, in the form of lollipops. They have a local effect and fight the cause of stomatitis.
The duration of the course is determined by the stage of the disease, as well as how correctly the patient follows the doctor’s instructions. At your first appointment, you should consult a therapist. If a child is sick, a pediatrician will help.
Why are vitamins prescribed for stomatitis?
The lack of microelements necessary for the body contributes to increased gum looseness and bleeding, and this directly affects the immune system. Almost a quarter of patients suffer from a lack of selenium, B vitamins, iron and other important elements that help destroy infection and regenerate oral tissue.
In addition, taking vitamin complexes can reduce pain and prevent relapses. In other words, they play a significant role in the treatment of stomatitis.
What to take
For stomatitis, the use of vitamin B12 is indicated; its role in the fight against the disease is truly invaluable. It is taken not only internally - it can also be used to treat the oral cavity, including ulcers, from the outside.
It not only has an antibacterial effect, but also strengthens the immune system at the local level, promotes the healing of ulcers and affected areas.
For adults, the doctor will certainly prescribe the following types:
- Vitamins of groups A, B.
- Pantothenic, ascorbic, folic acid.
- Bioflavonoids.
The course also includes minerals in the form of calcium, iron and other elements. It is advisable to add healthy fatty acids (say, Omega-3) to your diet. When using them
duration of stomatitis
decreases noticeably.
The use of vitamins for childhood stomatitis
If a child gets stomatitis, this indicates that the body is lacking a number of microelements.
In this case, the doctor prescribes the same complex as for adults, but supplemented with potassium and vitamins A, PP, C, E. These elements contribute to faster relief from the disease.
“A” is also used for external use; after treatment, the affected areas get rid of the symptoms of the disease much faster.
If you avoid taking vitamins in children, there is a risk of permanent stomatitis. In any case, the course of treatment should be carried out under the close supervision of a specialist. In case of complications, the course may be supplemented with other drugs.
Author of the publication 0
Source: https://vitaminy-vsem.ru/kakie-vitaminy-pit-pri-stomatite-u-vzroslyh.html
How to treat fungal stomatitis
To treat this type of disease, your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Methylene blue, Fucorcin or boric acid. They are applied pointwise to erosions in young children and used as a rinse for older children.
- Nystatin ointment, Clotrimazole, Pimafucin cream. The preparations are applied to the oral mucosa, paying special attention to the cheeks and gums.
- Nystatin - tablets, crushed into powder, applied to erosions and ulcers.
- Candida in the form of a cream, gel or solution.
- Older children and adolescents may be prescribed Diflucan or Fluconazole by mouth.
- Vitamin therapy to improve immunity, Imudon tablets for children from 3 years old.
- Antipyretic drugs (Paracetamol, Panadol, Nurofen) for fever.
Treatment of stomatitis with nystatin in a small child
The instructions for use of the drug directly indicate the permissibility of using the medication for infants. In pharmacies, Nystatin is presented in the form of drops, ointments and tablets.
For babies who have thrush, the best option is to use a tablet solution. It can be obtained independently - the tablet will need to be carefully crushed into small crumbs and diluted in a solution containing vitamin B12, and the latter is best used in oil form.
After this, the finished mixture is brought to a homogeneous state. In this way, you can dilute nystatin and treat a child for stomatitis.
Treatment of affected areas should be done no more than 3 times a day.
In the absence of a vitamin solution, boiled water is also quite suitable; the effect of such a replacement is similar.
In some cases, the doctor prescribes tablets for infants. How, then, should they be used correctly?
- — The dosage should be a quarter of one tablet.
- — It is unacceptable to feed a baby or give him water within a 30-minute period after taking the medicine.
In a situation where it is intended to use Nystatin drops, the dosage is calculated based on 1 ml of solution for each baby’s cheek. To do this, use a sterile bandage - drops are applied to it, then the areas affected by stomatitis are delicately treated.
The duration of treatment is determined by the degree of damage; the course must be prescribed by a doctor. As a rule, the medicine is used for no more than 10 days.
The popular doctor E. Komarovsky advises not to forget that Nystatin is still an antibiotic, therefore, to treat candidiasis-type stomatitis, you must strictly follow the prescribed dosage.
Treatment of herpetic stomatitis
When an acute process develops, which is accompanied by severe symptoms, the child is hospitalized and given symptomatic treatment in the hospital. In cases of mild to moderate severity of the inflammatory process, treatment can be carried out on an outpatient basis. The diet, as with candidal stomatitis, should exclude spicy, salty foods, canned food, and sour foods, especially citrus fruits. For herpes stomatitis in a child, treatment involves local procedures, as well as the use of general therapeutic agents:
- To ensure an anti-inflammatory effect, it is best to treat the affected areas of the mucous membrane in children 3-4 times a day with herbal decoctions - chamomile, sage, Kalanchoe juice; for these purposes, use cotton swabs soaked in the decoction. Pharmacies sell ready-made collections of such herbs (“Evkarom”, “Ingafitol”), which are suitable for rinsing the mouth and treating ulcers in older children.
- As a pain reliever for children over 4 years old, you can use the local antiseptic "Stomatidine", which has a weak analgesic and antimicrobial effect on the oral mucosa, you can also use "Hexoral Tabs" - lozenges with Chlorhexidine and Benzocaine, this drug has a local antimicrobial and analgesic effect.
- Treatment of ulcers with propolis is very effective, for example, “Propolis spray”, has a restorative effect in the presence of any skin lesions, herpes, ulcers.
- Antiherpetic ointments are used for local treatment - Tebrofen ointment, Viru-merz-serol, Oxolinic ointment, Acyclovir, Zovirax.
- Bonafton, an antiviral drug that is used to treat herpetic stomatitis, can be used.
- The healing of wounds is promoted by “Kaotolin” - an oil solution containing sea buckthorn oil, vitamin A and rosehip oil.
- Shostakovsky's balm, also known as "Vinilin", also has an anti-inflammatory effect, accelerates the process of tissue regeneration, epithelization and healing.
- Among the antiseptic agents used are Rotokan, Miramistin, and Lugol.
- In case of frequent relapses, the doctor may prescribe antiviral drugs for oral administration, in tablet form, Acyclovir, Valtrex.
- Vitamin therapy is also indicated in the form of Imudon lozenges, which are taken 6-8 times a day for one week.
Symptoms
Stomatitis in children caused by a fungus of the genus candida is also called oral candidiasis or thrush. It can develop due to infection during the baby’s passage through the mother’s birth canal, or occur as a result of infection of the mother’s nipples by fungus during breastfeeding or failure to comply with hygiene rules.
- with rare exceptions, there is no increase in body temperature in the child;
- the presence of a white, grayish cheesy coating on the oral mucosa;
- easy removal of plaque does not cause concern, in the affected areas under the plaque there is hyperemia (redness), slight bleeding of the mucous membrane is possible;
- lymph nodes correspond to normal sizes and are not painful on palpation;
- the primary localization of inflammation is focal, with subsequent damage to the entire mucosa;
- candidiasis causes significant discomfort to the child: burning, itching, dryness, which is accompanied by decreased appetite, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
If uncomplicated candidal stomatitis is diagnosed in children, local treatment is prescribed. Systemic antifungal drugs (prescription of Diflucan, Clotrimazole, Fluconazole) are indicated for older children or for severe, long-term forms of candidiasis that are not amenable to local therapy.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=he40NuX_PPg
The basis of treatment is changing the acid-base balance of the oral cavity and treatment with antifungal and antiseptic drugs. Candida fungus prefers high acidity, and increasing the alkaline environment in most cases successfully helps the body cope with the infection at the initial stage.
Local therapy methods include:
- treatment of the oral cavity with a solution of sodium carbonate (baking soda): rinsing, wiping with gauze soaked in the solution (1 tablespoon per glass of boiled water) with a frequency of 3 to 6 times a day, after each meal;
- treatment and rinsing with a solution of “Blue”, 2% boric acid, a solution of borax in glycerin;
- the use of local antifungal agents - creams, ointments for the oral cavity (Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Nystatin, Candide). Treatment is carried out in accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions: the drugs are potent, and if the prescription is not followed or the course is interrupted, they can cause both side effects and the formation of resistance of microorganisms to the active substance, which significantly complicates further treatment.
In a healthy child with good immunity and the absence of concomitant factors for the development of candidiasis, treatment is limited to local remedies; most often, treating the oral cavity with a baking soda solution is sufficient. If a breastfed baby has a fungal infection, therapeutic or prophylactic antifungal treatment of the mother's breast areolas is necessary, otherwise the child may be re-infected if candidiasis spreads to the nipple area (or its primary presence).
In addition to prescribing medications for stomatitis in children, maintenance therapy is also recommended, aimed at increasing the body's resistance: vitamins are prescribed, medications can be used to increase local immunity (Imudon for resorption, etc.).
Treatment of oral candidiasis also includes a specific antifungal and anti-traumatic diet: coarse, spicy, salty, hot and cold foods are excluded to reduce inflammation and injury to the oral mucosa, as well as acidic foods (vegetables, fruits, berries, dishes), sweets and high-carbohydrate foods and drinks, as they create a favorable environment for fungal growth.
In patients with stomatitis, areas of hyperemia with plaque or painful ulcers appear on the oral mucosa.
The most common is catarrhal stomatitis. It is characterized by hyperemia (redness) and swelling of some areas of the oral mucosa, pain when touched or while eating. There is also mild general weakness, a slight increase in temperature (usually no more than 37.1-37.
The initial stage of aphthous stomatitis is characterized by general weakness of the patient, malaise, and an increase in body temperature to subfebrile, less often febrile values. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity becomes painful in some places, then round or oval ulcers appear in them, delimited from healthy tissue by a narrow red stripe - aphthae. At the bottom there is a gray or yellow coating. Aphthae heal in 1-4 weeks, leaving behind connective tissue scars.
Ulcerative stomatitis occurs in the absence of timely treatment for the catarrhal form of this disease, or initially as an independent pathology. The patient is worried about an increase in body temperature, general weakness, headache, sharp pain in the area of the affected mucous membrane while eating (for some it is so intense that it becomes easier for a person to refuse food than to endure the pain).
Necrotizing ulcerative stomatitis (Vincent's stomatitis) develops when the mucous membrane is exposed to two bacteria at once - Borrelia vincentii and Bacillus fusiformis - with a pronounced decrease in immune function. It is characterized by deep ulcerative defects (down to the bone) and a sharp disturbance in the general well-being of the patient.
We suggest you read: How to get rid of stomatitis in the mouth quickly
Features of treatment of infants
Infants should be given water or weak chamomile tea frequently.
Feeding is carried out after anesthesia with a special gel, which is applied to the baby’s gums with a finger wrapped in gauze or using a cotton swab. Ointments are applied in the same way. If treatment with acyclovir is prescribed, it is applied in the form of an ointment to the mother's nipple.
To alleviate the condition of stomatitis, doctors sometimes recommend using a solution of soda, infusions of chamomile and calendula to rinse the mouth at home. To prepare them, take 20 g of flowers per 1 glass of boiling water. After cooling, the mixture is filtered. In addition, it is recommended to treat the baby's mouth with carrot juice. Children over 1 year old can lubricate their gums with rosehip, linseed or sea buckthorn oil, which have a good healing effect.
What is the best remedy for stomatitis?
Many parents are interested in the harmless and most effective remedy for children under one year old. A child’s body is not yet strong enough to repel attacks from various microbes, bacteria and fungi; for this reason, the disease often occurs in children. Infants most often develop fungal stomatitis, which is not at all difficult to identify.
Quite often children under 3 years old suffer from a viral type of stomatitis. Treatment of aphthous stomatitis will require the use of painkillers and restorative medications.
Methylene blue remains the most popular and effective substance for the treatment of stomatitis. Nystatin, which has an anti-inflammatory effect and relieves pain, can help with oral thrush. For the treatment of stomatitis, pills are prescribed to children under one year of age very rarely. The complex for the treatment of fungal inflammation includes Fluconazole, Malavit and Nystatin.
Among the effective antiviral agents for children, oxolinic ointment is prescribed.
It is important to know! In order to choose the best method for stomatitis, the patient needs to undergo a complete examination.
First of all, contact your local doctor. Next, the local doctor will redirect you to a pediatric dentist, who will look to see if there are any violations. Only these doctors will diagnose the child’s illness and determine the appropriate treatment method at home without harm to well-being.
Child examination at the dentist
Timely treatment will only have positive results in eliminating the disease. Thanks to the treatment of stomatitis, recovery occurs after a week. When this does not happen, it is necessary to immediately change the prescribed treatment regimen, determine the most effective medications, and expand therapy with proven folk remedies.
Today there are many types of effective remedies for stomatitis that eliminate pain in a child:
- Ibuprofen is prescribed for children at least 3 months old. The dosage of the substance depends on body weight (10 mg per 1 kg).
- Paracetamol eliminates pain and fever. For children under 3 years of age the drug is prescribed in the form of suppositories and syrup, and for older children in tablets.
- Cholisal perfectly removes inflammatory processes and reduces pain, but it is not recommended to take it for up to 12 months.
- Substances with anti-inflammatory results include:
- Inhalipt is made on the basis of streptocide and natural oils.
- Chlorophyllipt is prescribed as a sedative.
- Miramistin is an antiseptic with a wide range of effects. Chlorhexidine can be used by children from 6 months.
- Furacilin is used only for the purpose of irrigating the affected areas of the mucous membrane. Children over 3 years of age are prescribed for rinsing.
- Stomatophyte is a natural substance for rinsing procedures.
- Acyclovir ointments are excellent for treating viral stomatitis. Among them, Virolex, Gerpevir and Viferon stand out.
- Lugol is a solution that promotes wound healing.
- Iodinol based on iodine. Used as a remedy for stomatitis for children from one year old.
Restorative agents are used exclusively after removing the main sign of stomatitis. Medicines in this category are sold in the form of oils, ointments and gels:
- Vinilin has a healing effect and is also used for inflammation in children over the age of one year.
- Sea buckthorn oil is the most famous oil solution for curing stomatitis. The medicine is applied no more than 2 times a day.
Important! Some herbs that do not cause allergic reactions are used as additional therapy.
Regular pharmaceutical chamomile has the quality of promoting an anti-inflammatory and healing effect. In order to prepare the solution, you need to take a tablespoon of the plant and pour 250 ml of boiling water, while stirring the solution. Afterwards you need to wait until the tincture cools down.
As a rule, after half an hour the grass can be filtered. The solution can be used by rinsing or holding in the mouth for several seconds. The procedure can be repeated up to 3 times a day, without harm to well-being.
pharmaceutical camomile
Oak bark is still considered one of the best mild remedies for pain and bacteria in the mouth. Used as a tincture for rinsing the mouth. To do this, take 20 g of the ground plant and pour 250 ml of boiling water. The infusion process is the same as in the case of chamomile.
An infusion of tea rose petals is widely used for application to affected areas of the mouth.
Phytotherapy
To rinse the mouth for stomatitis, decoctions, infusions and solutions prepared from medicinal herbs or herbal preparations are used.
For decoctions use:
- chamomile,
- flax seeds,
- oak bark,
- lingonberry leaves,
- burdock root or elecampane.
Method of preparation: chop the herb, pour boiling water and keep on fire for 10 minutes. Then remove from heat, cool, strain. Store the prepared broth in the refrigerator for three days.
To prepare the infusion, the crushed herb is placed in a container with a tight lid, poured with boiling water and infused. The infusion is used to prepare a solution (water or alcohol). Infusions are prepared from the following medicinal herbs:
- calendula;
- St. John's wort;
- sage;
- anise fruit;
- yarrow.
Rinsing the mouth during stomatitis facilitates the course of the disease, stops the inflammatory process, and prevents the development of possible complications.
Homeopathic treatment
Many parents prefer to treat their children with homeopathy. However, such treatment should only be auxiliary and complement traditional methods.
In pediatric practice, the following drugs can be used:
- Borax,
- Mercuriussublimatuscorrosives,
- Natrum muriaticum,
- Arsenicum.
The group of homeopathic medicines also includes the combination remedy Malavit, which combines homeopathic components, natural herbal extracts and water from artesian springs. For rinsing with stomatitis, a solution is prepared from 5 drops of the drug and 100 ml of water (children under 5 years old need only one drop per year of life). The procedure is carried out 3-5 times a day after meals.
Diet and nutrition
Despite the fact that during stomatitis a child cannot eat many foods, the diet must be balanced. It is important to ensure that your baby’s diet includes carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Dishes should not be hot, but not cold, and in a processed form (without large solid particles).
Sample list of products:
- dairy and fermented milk products without dyes and flavoring additives;
- non-acidic fruits (bananas, melon, watermelon);
- vegetables and juices from them;
- liquid porridge;
- homemade milk ice cream (cold relieves swelling and pain);
- teas and herbal infusions;
- ground lean meat or fish.
It is advisable to cook your child meatballs, steam cutlets, and not chops or steaks. Steam the fish or stew it with vegetables. At first, you should avoid sour fruits, try to salt your dishes less, and do not use spices. Do not buy your baby crackers, bagels, or hard cookies.
Fermented milk products can cause pain while eating, so they can be offered after pain relief.
The baby's nutrition remains unchanged. You just have to try to treat the oral mucosa after feeding and periodically offer him water.
Stomatitis and vitamin deficiency
For the treatment and prevention of stomatitis, an important step is taking vitamin and mineral complexes. It has been proven that the disease occurs against the background of decreased immunity. Therefore, replenishing the body with the missing vitamin, for example B12, for stomatitis in children and adults is necessary as an aid in the fight against the pathogen that caused it, by increasing the protective functions of the body.
Effect
Any inflammation in the body, especially in the oral cavity, develops when natural defenses decrease.
A weakened immune system is not able to resist viruses, bacteria and other pathological agents that cause stomatitis in a child and other inflammations of the oral cavity.
The state of immunity is affected by the concentration of nutrients in the body, such as vitamins and minerals. Due to their insufficiency:
- increased gum looseness;
- bleeding of soft tissues increases;
- the vulnerability of the oral mucosa increases.
Deficiency of group B and microelements such as iron, zinc, folic acid, and selenium has a particularly detrimental effect on local immunity. It is the lack of these beneficial substances that contributes to the development of stomatitis due to:
- reduction of local barrier function;
- increasing the sensitivity and permeability of soft tissues to external pathogens.
Orthomolecular therapy
A new direction in dentistry to provide comprehensive treatment for stomatitis and other problems associated with the oral cavity is called orthomolecular therapy. Its essence lies in the following:
- shock therapy to replenish the required concentration of biologically active substances in the body in order to restore the protective functions of the epithelium with increased regeneration properties;
- therapeutic direction towards the formation of powerful protection against the development of inflammation and allergies by increasing the functional potential of the mucous membrane;
- taking balanced vitamin-mineral complexes with amino acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids for the purpose of general restoration of the body and the performance of the entire immune system;
- treatment with prebiotics, probiotics, and fiber supplements.
What and how to take?
To cure stomatitis, it is not enough for children and adults to take only serious medications, such as powerful antibiotics, antiseptics, anti-inflammatory drugs, etc. It is important to expand the treatment complex with a complex of vitamins, a balanced diet and adequate preventive measures. For this, the child is prescribed the following complexes:
- group B;
- groups C, A, E, RR;
- microelements such as calcium, iron, selenium, magnesium.
Dosages and concentrations are selected individually, depending on the form and stage of stomatitis. The list may also include:
- ascorbic, pantothenic, folic acids;
- bioflavonoids such as quercetin;
- vitamin A, group B1, B3 (niacin), B6.
Of the minerals that are especially useful:
They can reduce gum bleeding. To facilitate the epithelization process, Omega3 PUFAs are always prescribed. Their purpose:
- acceleration of tissue regeneration;
- activation of their nutrition;
- improving the condition of blood vessels by increasing the concentration of lysine, which is responsible for the high protective properties of the mucosa;
- strengthening gums by taking zinc and calcium.
B vitamins
Group B1, B2, B6, B12, B18 should be taken separately so as not to provoke an allergic reaction. Rules for use for stomatitis can be given using the example of taking medicine with B12:
- Open the ampoule.
- Wrap a sterile bandage tightly around tweezers, a pencil or your finger.
- Moisten the winding in liquid.
- Thoroughly treat the entire oral cavity, including aphthae.
- The procedure should be repeated daily three times a day.
Additionally, you can drink vitamin complexes in liquids or pills, the emphasis of which is on group B. More than half of patients with stomatitis during a 14-day vitamin course show a significant improvement in the condition of the mucous membrane, even in severe forms of the pathology.
Vitamin B18 is especially useful for ulcerative inflammation of the mucous membrane. It is found in sufficient quantities in pomegranates and their juice. But it is not advisable to consume these fruits during an exacerbation period. They are prescribed as a preventive measure for people prone to frequent relapses of stomatitis.
Group C, A, E, PP
It is important to take this complex of fat-soluble vitamins together with vegetable oils. Only in this way will they be completely absorbed in the body.
This does not mean that you need to drink oil; it will be enough to increase your daily consumption of fresh salads seasoned with any type of vegetable fat.
Groups C, A, E, PP are absorbed only with food, so they should be taken during a meal or immediately after it.
Microelements
Microelements such as calcium and magnesium are important when curing stomatitis; they are not taken alone due to their poor absorption, but only in combination.
With a lack of selenium and iron, the frequency of relapses of stomatitis increases, so they should also be included in vitamin therapy.
The listed microelements are found in small quantities in food products, so their levels should be corrected with complete vitamin complexes.
Medicines or diet?
Vitamin deficiency and lack of microelements in case of stomatitis can be compensated by following a special fortified diet, enriched with fresh vegetables, fruits, and food products of animal origin. Finding the missing vitamin can begin with choosing the right foods to supplement your diet. Examples are given in the table:
But the content of useful substances in products varies depending on their variety, type, presence of preservatives and flavorings, characteristics of heat treatment and storage. The season also influences fluctuations in their concentration.
But even an optimally nutritious, varied diet with sufficient calories (at least 2500) is on average 25% deficient.
And this leads to a decrease in the rate of regeneration, so the first sign of hypovitaminosis (vitamin imbalance) is stomatitis.
To restore proper biological activity with the initiation of all processes in the body, especially if there is a tendency to decrease immunity, correctly selected pharmaceutical multivitamin complexes should be introduced. The dosage and course are selected depending on the purpose:
- Long courses with daily dosages are used for the purpose of: carrying out replacement therapy for the treatment of hypo- and vitamin deficiency;
- strengthening the body's resistance to pathogens;
- acceleration of metabolism, healing and tissue renewal;
- prevention of stomatitis.
Source: https://TvoyHerpes.ru/stomatitis/tradmed/vitaminy-pri-stomatite.html
Recommendations for parents
With stomatitis, children can only be given soft food with a temperature no higher than 30° (porridge or soup processed in a blender), chicken broth. You should not give sour or sweet juices. If your child has difficulty drinking water or tea, you can give him a straw. The body must not be dehydrated.
The room where the child is during treatment should have moist, cool air so that the child’s mouth does not dry out. Parents need to thoroughly disinfect pacifiers, feeding bottles, and teething aids. You cannot taste the child’s food with the same spoon that will later be used to feed him or lick his pacifier.
Children from a very early age should be taught how to brush their teeth and shown how to rinse their mouth. You can brush your teeth only with children's toothpastes. To prevent caries and timely dental treatment, it is necessary to regularly take children to the dentist.
Instructions for the use of nystatin in older children
Older children are advised to dissolve tablets of the drug. The doctor can also prescribe medication to be taken orally; the daily dose is also selected by the doctor ; it is determined by the degree of damage and the body’s response to the disease.
You should not select the daily dosage by eye. You need to find out which doctor treats stomatitis, go to him and get a consultation.
Usually in these cases you need to take the remedy 3-4 times daily, and this should be done after meals .
You do not need to chew the tablet, but you should take it with plenty of liquid.
The duration of the course is prescribed by the doctor who conducts the treatment.
Usually the doctor prescribes the following dosage:
- - child 1-3 years old: 250,000 units, taken 3-4 times a day;
- - child 3-14 years old: 250,000 or 400,000 units, taken with the same frequency;
- - child over 14 years old: 250,000 / 500,000 units. also 3-4 times a day.
Nystatin in the form of an ointment can be prescribed by a doctor for older children. Application of this (5%) should be carried out a maximum of three times a day. Nystatin for stomatitis completely destroys fungal colonies, as a result of which the patient quickly recovers. The duration of the course is also determined by the depth of the fungal infection.
The drug also has contraindications - in the vast majority of cases it is an allergy to the drug.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of stomatitis in early childhood, simple preventive work can be carried out. Pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky gives useful recommendations for the prevention of stomatitis. In his video lesson, Komarovsky reveals this topic in detail. Main recommendations:
- Personal hygiene. This also applies to the oral cavity and general cleanliness. It is necessary to regularly wash your hands, toys, brush your teeth and rinse your mouth.
- Strengthening the immune system. Adequate intake of vitamins, proper daily routine, walks in the fresh air, physical activity.
- Resistant to bacteria. You should not keep your child in greenhouse conditions. Provided hygiene and normal immunity are maintained, he should play with other children, get dirty and have fun. This makes the child less vulnerable to the environment.
Streptoderma Oral candidiasis Chickenpox in children Seizures in the corners of the mouth: causes and treatment in adults Bad breath: causes and treatment in adults Worms in children: symptoms and treatment at home for worms in a child
So is it worth treating stomatitis with this remedy?
The drug is very effective, reviews of its use are mostly positive. There are also side effects as a result of use, but few have been noted - they are usually limited to diarrhea or nausea. The use of the medicine in the form of an oil (water) solution or ointment practically reduces the side effects to nothing.
Doctor's comments:
- - if “Nystatin” in the form of an ointment or solution was accidentally swallowed by a child, the drug leaves the body in the usual way without causing harm to the baby;
- - it is undesirable to use the medicine without prior consultation with a specialist;
- — the drug in many situations is more effective than similar modern drugs.
However, this drug is an antibiotic, so before using nystatin for stomatitis, you will definitely need to consult a pediatrician.
"Nystatin" belongs to the group of antifungal antibiotics from the polyent category. Nystatin is often prescribed for stomatitis for local treatment of affected areas. The drug works at the cellular level, reducing the cell membranes of fungi and slowing down their growth. The most active against yeast-like fungi is Candida. According to the instructions for use, the medication is approved for use from infancy. Available in several forms: tablets, drops, ointment, suppositories, suspensions for rinsing. Frequency of application: 2 times/day. during the course of treatment - 14 days. A more precise adjustment is made by the doctor based on the severity of the disease and the age category of the patient.
Pediatric candidiasis: about the disease and treatment options
Thrush on a child's tongue
Thrush, which occurs in the mouth, is a disease that is diagnosed in many children in the first year of life. Doctors tend to believe that this form of fungal infection often affects infants, but there are many cases in medical practice when the diagnosis was made to babies after one year. One of the features of this type of thrush is that the disease can progress extremely slowly. Young mothers do not always pay due attention to the first symptoms, attributing this to the characteristics of the fragile organism of newborn children. In order for the treatment of the pathology to be effective and quickly give the desired result, you should remember the characteristic manifestations of thrush localized in the mouth.
The main symptoms characteristic of candidiasis in children
- A cheesy coating gradually appears on the palate, inner sides of the cheeks, on and under the tongue. A thin film may form on the mucous membranes and lips. Often, in children under one year of age, minimal foci of fungal pathology initially appear in the mouth, localized in the area of the tonsils, palate or in the corners of the lips, on the tongue. Gradually they increase in size, the curdled coating itself becomes dense and can change color from white to white-yellow or white-gray.
- When removing the film or characteristic white rashes in newborns, ulcers may open underneath them and bleeding cracks may appear, causing severe pain.
- The surface of the tongue and mucous membranes of the oral cavity looks sharply reddened, painful and swollen.
- Infants sometimes experience temperature changes.
Sick child is naughty - As the fungal pathology develops, the child may become tearful, nervous, and restless. Sometimes sleep is disturbed.
- Due to swelling, pain and itching, babies refuse to eat and drink.
- If treatment is too late, then thrush affects the entire oral cavity, gradually moving to the throat, esophagus and spreading to internal organs and skin.
- Along with the symptoms present in the oral cavity, candidiasis can also affect the child’s genitals at the same time.
In order to try to protect newly born children as much as possible from infection with aggressive fungi of the genus Candida, you need to know about those negative factors, the reasons for which symptoms characteristic of thrush appear.
Why does the disease develop in infants and older children?
- Undeveloped or weak immunity.
- The general microflora in the body is disrupted for any reason. The acidic environment present in the mouths of babies promotes the activation of candida.
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards and sterility both in the maternity hospital or clinic, and in the home environment.
- Lack of vitamins and essential microelements. No hardening process.
Foods containing vitamin B12 - Infection from sick family members. Candidiasis is often observed in children, passed on from the mother during breastfeeding or even before birth.
- The presence of additional painful conditions identified at birth or developed after.
- The need for serious drug therapy with antibiotics. Chemotherapy, radiation.
- Thrush can recur in childhood in situations where no course of treatment was carried out, the mother did not receive medical care along with the child, and there were no preventive measures aimed at other family members. Even in a situation where there are no characteristic signs of thrush, prevention is still worthwhile, since this disease has hidden forms, and some people are candidiasis carriers without even knowing it.
Having identified the disease and gradually eliminating the root cause that gave rise to it, it is necessary to carry out appropriate treatment, based on the recommendations of the children's doctor. Trying to fight off thrush on your own is not recommended.
Without consultation with a pediatrician, the pathology may not only not be cured, but also become chronic or lead to additional negative consequences.
Treatment of childhood candidiasis: main options
- Therapy can be carried out both locally and with the use of drugs orally. Or take an integrated approach.
- During the correction process, the pediatrician prescribes treatment with medications, for example, Nystatin, often in combination with traditional methods, which include herbal medicine (in the absence of allergies) and therapy with soda (if there are no contraindications).
- Along with the general approach, measures that strengthen the immune system should be carried out, appropriate for the child's age.
- Appropriate hygiene, daily routine and nutrition of the baby also play an important role when complex treatment of a fungal disease is carried out.
Nystatin tablets
One of the main and well-proven medications that help overcome oral candidiasis in children is Nystatin, which is recommended to be combined with vitamin B12. Before starting therapy, you should get an idea about this remedy.
Description
"Nystatin" is included in the group of specific and active antibiotics with antifungal properties. The medication destroys colonies of yeast-like fungi Candida at the cellular level, which contributes to the rapid fight against candidal stomatitis in children and adults. Small doses of the product are sufficient to effectively slow down the development of thrush. With systematic treatment, the fungus is completely destroyed.
When applying small doses of the product, the development of thrush slows down. With systematic use of the medicine, complete destruction of the fungus is observed. Benefits of use for stomatitis:
- low price;
- ease of use;
- lack of absorption into the systemic bloodstream;
- Possibility of treating wounds in infants.
The drug is applied pointwise only to the surface of wounds and erosions.
Features of the treatment of stomatitis with Nystatin:
- The drug in the form of an ointment against stomatitis is applied pointwise only to the surface of wounds and erosions.
- For the treatment of infants, an aqueous solution of tablets is used orally or a solution with vitamin B12 for local treatment.
- Drops are used for local sanitation of the oral cavity.
In case of an overdose of an anti-stomatitis drug, the following symptoms are observed:
- burning and itching in the treated area;
- hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane;
- development of a skin allergic reaction.
The maximum course of treatment against candidiasis in the mouth is 14 days when treated 2-3 times a day. The peculiarities of using Nystatin in different age categories are taken into account by the doctor when prescribing the drug.
Return to contents