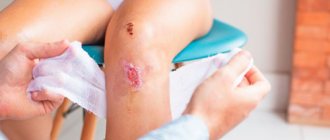
Stomatitis on the lip is an acute inflammation of the oral mucosa. Externally, it can be confused with cheilitis (inflammation of the lips). The causes and treatments for these two diseases differ. Stomatitis often occurs in children, but this problem occurs in adults. The treatment method depends on the cause of its occurrence: herpetic, candida, traumatic, allergic, bacterial, aphthous.
The main signs of stomatitis are similar for most types. For minor stomatitis, treatment with home remedies is acceptable. It is important to know the signs that should prompt you to see a doctor.
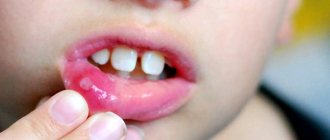
What does stomatitis look like on the upper and lower lips from the inside?
Regardless of the cause of the inflammatory process, the clinical picture is similar:
- areas of redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling, tissue tenderness;
- the formation of round ulcers (a sign of infection with bacterial stomatitis);
- pain, especially when eating or talking;
- increased salivation, then bleeding;
- in severe cases, temperature rise to 39 C or higher;
- general deterioration of health;
- signs of general intoxication of the body.
In children, pain causes the child to refuse food.
Stomatitis on the inside of the lips is a common type, as is stomatitis on the cheeks. Less often it appears on the tongue or under it.
Symptoms
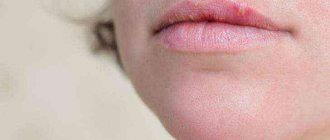
The appearance of stomatitis is difficult to miss. The disease has very specific manifestations in the form of redness and an unpleasant burning sensation in this place. Stomatitis on the upper lip appears as a swelling, the lower lip swells, then white-gray ulcers appear, with a slight reddish outline. The mucous membrane around the spot looks healthy and not affected. Spots can be single or multiple. Touching the stains is unpleasant and painful.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children are practically no different from adults. If you miss the first manifestations of the disease, stomatitis on the child’s lip develops quickly and painfully.
Therefore, it is extremely important to pay attention to the mucous membranes of the child’s lips when the following symptoms appear:
- the child becomes capricious and whiny;
- an increase in temperature is possible as a reaction to the inflammatory process;
- poor appetite or the baby refuses to eat at all;
- Because of the pain, children try not to touch their lips, hence the excessive salivation.
Having discovered the above symptoms and viewed a large number of photos of stomatitis on the lips of a child, presented by a simple request in the browser, do not rush to make a diagnosis, contact a competent specialist for this.
What does stomatitis on the lip look like?
Reasons why it occurs in adults and children
The most common cause is various injuries and damage to the mucous membrane. Through damaged areas, infection enters the body and inflammation occurs. Microtraumas of the thin skin of the lips can be caused by:
- chapping of the skin in winter;
- insufficient oral hygiene (or brushing teeth too intensively);
- thermal, chemical burns;
- pathologies of the endocrine system;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- general intoxication of the body.
Eating too dry or rough foods leads to the development of stomatitis.
With a tendency to allergies, allergic stomatitis occurs.
Prevention of stomatitis
Prevention of stomatitis involves:
- Regular visits to the dentist, timely treatment of caries;
- Maintaining oral hygiene;
- Strengthening the immune system.
At first glance, stomatitis on the lip seems like a minor nuisance, but it can signal serious systemic disorders or a significant decrease in immunity. The consequences of untreated stomatitis can be serious: the addition of a secondary infection, cicatricial changes in the mucous membrane, laryngitis, candidiasis of the skin and genital organs. Stomatitis on the lip should be treated promptly and correctly to avoid possible complications.
Kinds
The treatment regimen for stomatitis depends on the type of disease. Because of this, it is important to visit the dentist to determine the cause of the infection. The type of disease directly depends on this:
- traumatic stomatitis;
- candida;
- aphthous;
- allergic;
- bacterial;
- herpetic. Read more information about the treatment of herpetic stomatitis in this article.
Each type has its own characteristic features and individual treatment regimen.
Without adequate treatment, inflammation simultaneously affects the mucous membrane and skin areas of the lips.
Herpetic
One common type of stomatitis is a herpes infection. Widespread “fever” on the lips causes damage to the mucous membrane. Characteristic features:
- the formation of transparent bubbles filled with liquid;
- with a large number of lesions, painful erosions of the mucous membrane are formed.
Over time, the blisters burst, which is accompanied by severe itching.
At the initial stage, itching, burning sensation, and discomfort occur.
Candida
The candida form is better known as thrush. This is an infectious problem caused by the Candida fungus. This problem is more common in children because it is caused by a weak immune system. This is a natural microflora of the mouth that creates problems when the body weakens. Characteristic symptoms
- whitish “curdled” coating on the mucous membrane;
- the affected mucous membrane under the coating has a bright red tint.
Plaque with herpetic stomatitis increases in volume over time. It is easy to remove. Details about the treatment of candidal stomatitis are in this material.
Herpetic stomatitis can be caused by long-term use of antibiotics.
Aphthous
Aphthous is an atypical form of stomatitis. The main symptom is the formation of aphthae on the mucosa. These are small round ulcers, on the surface of which a white or yellowish coating forms. Most often occurs with severe immunodeficiency, exposure to ionizing radiation and other serious diseases.
In its chronic form, the pathology can last for years. Periods of healing are followed by exacerbations.
In severe cases, the disease develops into an ulcerative-necrotic form. In this case, the lesions do not heal for several weeks.
Allergic
Allergic stomatitis occurs upon contact with sources of allergies. It can be:
- installation of new processes or crowns;
- some medications;
- care products.
The allergic form is not an independent disease, but a sign of pathology. It is characterized by the appearance of swelling, redness and itching of the mucous membrane.
The allergy goes away after taking antihistamines.
Bacterial
Bacterial most often occurs as a result of a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection. This is also a normal microflora, creating problems only when the body is weakened. Infection occurs through microtraumas of the mucous membrane. A bacterial infection causes general intoxication of the body and an increase in temperature.
The basis of treatment for the bacterial form is the use of antibiotics.
Traumatic
In traumatic stomatitis, the root cause is injury to the mucous membrane. This occurs with the following types of damage:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- thermal.
Sometimes the cause is poor-quality dental operations, for example the use of low-quality materials.
In case of trauma, it is necessary to prevent the wounds from becoming infected. This leads to bacterial complications.
Symptoms of pathology
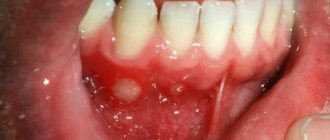
You can notice the symptoms of stomatitis by the appearance of the patient’s lips. These are slight redness on the lips, which are accompanied by a slight burning sensation. After this, a whitish ulcer appears at the site of the discomfort. It has certain distinctive features:
- Oval or round shape;
- Smooth edges and red edging;
- The presence of a film of grayish color.
The main symptom of the disease is ulcers that have a grayish color. When they appear, patients complain of pain. Ulcers can increase in size. In some cases, the size of the ulcers reaches one centimeter in diameter. Patients claim that discomfort and pain are observed during lip movements. If the disease is not treated in a timely manner, two ulcers may merge into one.
Attention ! The tissue around the ulcer looks completely healthy.
When this disease appears, the mucous membrane in most cases is affected from the inner surface of the lip. This makes it difficult to treat the initial stages of the disease.
In adult patients, the acute stage of the disease is observed in fairly rare cases. At the same time, they complain of the appearance of general weakness and fatigue.
Allergic stomatitis is characterized by the presence of distinctive symptoms. After contact with an allergen, rashes in the form of blisters appear on the surface of the lips. They burst in the shortest possible period of time. In their place, the formation of small ulcers is observed. After a certain time, these ulcers merge into large lesions on the lips.
The symptoms of the pathological condition are pronounced, which allows it to be detected almost immediately after its appearance.
Treatment at home
The treatment regimen in each specific case is determined by the doctor based on the results of the examination of the patient. Combination therapy includes: medications, folk remedies. Compliance with nutritional recommendations also contributes to a speedy recovery.
Treatment methods differ for adults and children. First of all, this applies to medications.
Medication
It is recommended to use any pharmaceutical products only as prescribed by the attending physician. For a quick cure, it is important to strictly adhere to the dosage and duration of treatment.
In case of catarrhal form without aphthae, healing is possible in 7–8 days.
Painkillers
If inflammation interferes with eating and speaking, the doctor will prescribe safe anesthetics:
- Anestezin;
- Lidocaine Asept;
- Hexoral tabs;
- Lidohor.
It is recommended to use special dental preparations that act on the mucous membrane.
Antiseptics
Therapy includes local antiseptics and antimicrobials:
- Inhalipt;
- Hexoral;
- Cholisal for stomatitis in adults;
- Kamistad gel;
- Ingafitol (Evkarom);
- Stomatidine (hexetidine);
- Kameton;
- Eucalyptus M.
They are used in the form of rinsing solutions and gels.
Local preparations (sprays, solutions, ointments, gels)
To treat the affected mucosa, topical preparations are used. The most effective forms are:
- solutions for rinsing or application. Read more about how to rinse your mouth for stomatitis here;
- gels;
- spray for irrigation;
- ointment.
Of the thick forms, gels rather than ointments are most effective for treating mucous membranes.
Antiviral
For herpetic stomatitis use:
- Viru-Merz Serol;
- Acyclovir;
- Zovirax;
This is the basis of therapy to help cope with the infection.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are used only for bacterial stomatitis, as prescribed by a doctor:
- Lincomycin;
- Bayoran;
- Claforan.
The recommended duration of treatment should not be exceeded.
Immunostimulants
If the immune system is weak, therapy includes:
- Immunal;
- Polyoxidonium;
- Cycloferon.
It is also important to include foods that help strengthen the immune system in your diet.
Healing
Agents that promote mucosal regeneration:
- Solcoseryl;
- Karotolin;
- Sea buckthorn and rosehip oils;
- Vinilin (Shostakovsky balm);
- Proposol spray.
Used as an aid.
Home Remedies
For non-aphthous stomatitis, herbal immunostimulants are used:
- ginseng;
- St. John's wort;
- seaweed;
- nettle;
- rose hip.
It is enough to include them in the diet for every day.
Features of treatment
Most people believe that there is no need to treat stomatitis, since it goes away on its own. But this is far from true. This disease requires not only correct, but also timely treatment. If a person has the initial stage of the disease, then its treatment can be carried out at home. For this purpose, traditional medicine is used, which are characterized by the presence of bactericidal and soothing properties:
- To eliminate the disease, it is recommended to rinse the mouth . For this purpose, a decoction of oak bark is used. The procedure should be carried out three times a day. If the ulcers are located on the surface of the lips, they must be cauterized with alcohol.
- Stomatitis on the lip can be cured with aloe juice , which is pre-mixed with iodine in a 1:1 ratio. It is recommended to regularly lubricate the ulcers with this medicine.
- It is recommended to prepare decoctions from plants such as string, calendula, and chamomile. To prepare them, you need to take two tablespoons of any herb or a collection of them and pour a glass of boiling water. The medicine is simmered over low heat for 5 minutes, and then infused for 2 hours. Next, the product must be filtered. A cotton pad is soaked in it and applied to the sores. The procedure should be carried out 3 to 5 times a day. To ensure the highest possible effectiveness of disease therapy, it is recommended to add a few drops of boric acid to the infusion.
In order to cure stomatitis on the lips, it is necessary to use ointments that have a healing effect. The most common uses are Oxolinic, Retinol, and Interferon ointments.
Important ! If the cause of the disease is a fungus, the patient is recommended to use an antifungal ointment, which should be prescribed by a doctor.
If the disease is acute, it will be quite difficult to cure it at home. That is why the patient is recommended to seek help from a doctor, who will determine the severity of the disease and also prescribe adequate treatment. In most cases, patients are prescribed:
- Multivitamin complexes;
- Antiviral drugs;
- Immune-strengthening agents;
- Antibiotics.
If stomatitis is allergic in nature, then its therapy is aimed not only at fighting ulcers, but also at eliminating the allergen.
Stomatitis on the lip can be cured using a variety of methods, depending on the characteristics of its course and the cause of its occurrence. To ensure maximum effectiveness of therapy, you must first consult with your doctor.
Prevention of stomatitis
In order to prevent stomatitis from appearing on the lips, it is necessary to take appropriate preventive measures in a timely manner. Since injuries to the lips can lead to disease, they must be avoided. This is why patients are not recommended to bite their lips. If the patient has fillings or chipped teeth, then he needs to seek help from a dentist.
Attention ! A mandatory measure to prevent stomatitis on the lips is proper oral hygiene.
In some cases, stomatitis on the lips appears due to the consumption of certain foods. If a person develops ulcers on his lips while eating certain foods, he is advised to avoid them. In order to prevent the disease, a person is recommended to regularly take multivitamins. To eliminate the possibility of an increase in the bacterial background in the human body, it is recommended to promptly visit the dentist, who, if there are carious cavities, will remove them. This measure is necessary, since in the presence of persistent infections, stomatitis on the lip can occur.
Stomatitis on the lips is a rather unpleasant disease that negatively affects a person’s appearance. That is why, when the first symptoms of a pathological condition appear, the patient needs to seek help from a doctor who can correctly diagnose and prescribe rational treatment.
Chronic and acute form
Acute stomatitis develops when the mucous surface is traumatically damaged by hot food, poor-quality dentures or braces, as well as when affected by the herpes virus. The disease is often diagnosed in people with weakened immune systems during periods of exacerbation of respiratory viral infections and influenza. The acute form is characterized by the appearance of pain, redness and itching in the affected area.
The chronic form is characterized by a long course and periodically recurring periods of exacerbation, which are followed by remission. Most often, the chronic form develops in patients with autoimmune diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and endocrine system. In place of the lesions, new ones appear, which are accompanied by degeneration of the mucous surfaces.
Diagnostics
At the first signs of illness, you should seek advice from a specialist, since it is impossible to independently determine the cause of the formation of ulcers on the lips. Self-medication in this case can only worsen the condition and lead to the development of complications.
The doctor will correctly determine the form of the disease and tell you how to treat the disease. The dentist will make an accurate diagnosis during a visual examination. A conversation with the patient will help determine the time of formation, exact symptoms and possible causes.
To clarify the clinical picture, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed:
- general blood analysis;
- scraping or smear from the source of inflammation to determine the pathogen;
- blood test for hepatitis and HIV;
- determination of immune status;
- examination of the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract).
Causes
The risk of stomatitis occurring after a cold is especially high, since the body’s immune defense is reduced. This creates favorable conditions for activating the growth of pathogenic microflora.
Stomatitis can also develop for the following reasons:
- minor damage to the lips that can occur when eating food (fish bone prick, irritation from excessively salty foods);
- chemical or thermal burns that violate the integrity of the mucous membrane, resulting in a wound that has no protection from bacteria and viruses;
- Chapping occurs due to the habit of licking lips in cold windy weather.